Deck 20: The Demand for Real Money Balances and Market Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: The Demand for Real Money Balances and Market Equilibrium
1
The __________ suggests that individuals will demand to hold money when interest rates are low (bond prices high) to avoid capital losses when interest rates rise, and to hold bonds when interest rates are high (bond prices low) to capture capital gains when interest rates fall.
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)none of the above
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)none of the above
A
2
The __________ suggests that individuals will demand to hold money in anticipation of unforeseen opportunities or threats.
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory
B
3
The __________ suggests that individuals will demand to hold money in anticipation of the need to make payments.
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory
C
4
The __________ is a theory of the demand for money developed by John Maynard Keynes that results in an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of money and the interest rate.
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transaction motive
D)liquidity preference theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The liquidity preference theory is a theory of the demand for money developed by ____________ that results in an inverse relationship between the quantity of money demanded and the interest rate.
A)John Maynard Keynes
B)Milton Friedman
C)Irving Fisher
D)Paul Samuelson
A)John Maynard Keynes
B)Milton Friedman
C)Irving Fisher
D)Paul Samuelson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Holding extra money in your checking account just in case your car needs to be repaired is an example of which of the following motives for holding money?
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Real Income is best defined as
A)nominal income multiplied by a price index.
B)nominal income divided by a price index.
C)a price index divided by nominal income.
D)income as defined in nominal dollar terms.
A)nominal income multiplied by a price index.
B)nominal income divided by a price index.
C)a price index divided by nominal income.
D)income as defined in nominal dollar terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Nominal Income is best defined as
A)real income multiplied by a price index.
B)nominal income divided by a price index.
C)a price index multiplied by nominal income.
D)income as defined in current dollar terms.
A)real income multiplied by a price index.
B)nominal income divided by a price index.
C)a price index multiplied by nominal income.
D)income as defined in current dollar terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Ceteris paribus, what would happen to real money balances if all prices, including input prices (incomes) and output prices, doubled tomorrow?
A)Nominal money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would double to 2P, and real money balances would approximately double.
B)Real money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would approximately triple to 3P, and nominal money balances would remain the same.
C)Real money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would double to 2P, and the nominal money balances would double.
D)Nominal money balances would remain the same, the overall price level would double to 2P, and real money balances would fall to one-half their previous amount, M/2P.
A)Nominal money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would double to 2P, and real money balances would approximately double.
B)Real money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would approximately triple to 3P, and nominal money balances would remain the same.
C)Real money balances would double to 2M, the nominal price index would double to 2P, and the nominal money balances would double.
D)Nominal money balances would remain the same, the overall price level would double to 2P, and real money balances would fall to one-half their previous amount, M/2P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Household demand for real money balances increases when
A)wealth increases.
B)payment technologies advance.
C)real income decreases.
D)expected inflation increases.
A)wealth increases.
B)payment technologies advance.
C)real income decreases.
D)expected inflation increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Household demand for real money balances decreases when
A)wealth increases.
B)wealth decreases
C)real income increases.
D)expected inflation decreases.
A)wealth increases.
B)wealth decreases
C)real income increases.
D)expected inflation decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Household demand for real money balances decreases when
A)the liquidity of other assets increases.
B)the interest rate decreases.
C)the risk of holding other assets falls.
D)real income increases.
A)the liquidity of other assets increases.
B)the interest rate decreases.
C)the risk of holding other assets falls.
D)real income increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The supply of real money balances increases when
A)the Fed sells securities in the open market.
B)discount loans are paid off at Federal Reserve District Banks.
C)the Fed raises the required reserve ratio.
D)the overall price level falls.
A)the Fed sells securities in the open market.
B)discount loans are paid off at Federal Reserve District Banks.
C)the Fed raises the required reserve ratio.
D)the overall price level falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The supply of real money balances decreases when the Fed
A)increases its discount lending.
B)sells securities in the open market.
C)lowers the required reserve ratio.
D)uses expansionary monetary policy.
A)increases its discount lending.
B)sells securities in the open market.
C)lowers the required reserve ratio.
D)uses expansionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The name given to the theory of interest rate determination based on the demand and supply of money as developed by Keynes is which of the following?
A)transactions theory
B)liquidity preference
C)the loanable funds theory
D)the money market
A)transactions theory
B)liquidity preference
C)the loanable funds theory
D)the money market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Ceteris paribus, according to Keynes, the speculative motive for holding money shows that the
A)demand for money and the interest rate are directly related.
B)quantity demanded of real money balances and the interest rate are inversely related.
C)quantity demanded of money is directly related to income.
D)demand for money is directly related to income.
A)demand for money and the interest rate are directly related.
B)quantity demanded of real money balances and the interest rate are inversely related.
C)quantity demanded of money is directly related to income.
D)demand for money is directly related to income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to monetarism, changes in the money supply are the most important factor in determining changes in which of the following variables?
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)the price level
D)the interest rate
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)the price level
D)the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following can change the supply of real money balances?
A)change in reserves
B)a change in the monetary base
C)price level
D)All of the above are correct.
A)change in reserves
B)a change in the monetary base
C)price level
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The demand for money is inversely related to which of the following?
A)income
B)the riskiness of other financial assets
C)the liquidity of other financial assets
D)wealth
A)income
B)the riskiness of other financial assets
C)the liquidity of other financial assets
D)wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The demand for money is directly related to which of the following?
A)the interest rate
B)the riskiness of other financial assets
C)the liquidity of other financial assets
D)Both a and b are correct.
A)the interest rate
B)the riskiness of other financial assets
C)the liquidity of other financial assets
D)Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What percentage of United States currency is estimated to be held outside the United States?
A)less than10 percent
B)less than 25 percent
C)over 50 percent
D)more than 80 percent
A)less than10 percent
B)less than 25 percent
C)over 50 percent
D)more than 80 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ceteris paribus, if the price level increases by 20 percent,
A)both the nominal demand for money and demand for real balances increases by 20 percent.
B)the nominal demand for money decreases by 20 percent and the demand for real balances decreases.
C)the nominal demand for money increases by 20 percent and the demand for real balances remains the same.
D)both the nominal demand for money and the demand for real balances remains the same.
A)both the nominal demand for money and demand for real balances increases by 20 percent.
B)the nominal demand for money decreases by 20 percent and the demand for real balances decreases.
C)the nominal demand for money increases by 20 percent and the demand for real balances remains the same.
D)both the nominal demand for money and the demand for real balances remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The motive for households holding real money balances as a safeguard measure against unforeseen circumstances is the
A)transactions motive.
B)precautionary motive.
C)liquid asset motive.
D)real balance motive.
A)transactions motive.
B)precautionary motive.
C)liquid asset motive.
D)real balance motive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The relative interest rate differential between nonmonetary and monetary assets is considered which of the following?
A)real income
B)real money balances
C)liquidity preference
D)the opportunity cost of holding money
A)real income
B)real money balances
C)liquidity preference
D)the opportunity cost of holding money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the interest rate decreases, ceteris paribus,
A)the demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)the demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)there is a movement downward along the demand curve for money.
D)there is a movement upward along the demand curve for money.
A)the demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)the demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)there is a movement downward along the demand curve for money.
D)there is a movement upward along the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the immediate response to an increase the growth rate of nominal money supply?
A)a less than a proportional increase in the price level
B)a more than a proportional increase in the price level
C)a proportionate increase in the price level
D)no increase in the price level
A)a less than a proportional increase in the price level
B)a more than a proportional increase in the price level
C)a proportionate increase in the price level
D)no increase in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Ceteris paribus, when real income increases, which of the following happens?
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Ceteris paribus, when wealth increases, which of the following happens?
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Ceteris paribus, when wealth decreases, which of the following happens?
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Ceteris paribus, expectations of higher inflation will
A)shift the demand curve for money to the right.
B)shift the demand curve for money to the left.
C)cause a downward movement on the demand curve for money.
D)cause an upward movement on the demand curve for money.
A)shift the demand curve for money to the right.
B)shift the demand curve for money to the left.
C)cause a downward movement on the demand curve for money.
D)cause an upward movement on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Ceteris paribus, expectations of deflation will
A)shift the demand curve for money to the right.
B)shift the demand curve for money to the left.
C)cause a downward movement on the demand curve for money.
D)cause an upward movement on the demand curve for money.
A)shift the demand curve for money to the right.
B)shift the demand curve for money to the left.
C)cause a downward movement on the demand curve for money.
D)cause an upward movement on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ceteris paribus, when payment technologies become more sophisticated, which of the following happens?
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Ceteris paribus, when payment technologies become disrupted--perhaps as a result of war or a natural disaster--which of the following happens?
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.
A)The demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)The demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)There is a movement downward on the demand curve for money.
D)There is a movement upward on the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
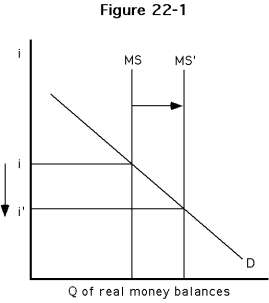
-Which of the following phrases best describes Figure ?
A)The demand for real money balances has increased as the interest rate has fallen.
B)The supply of real money balances has increased and the interest rate has fallen.
C)The supply of real money balances has decreased and the interest rate has fallen.
D)The interest rate has decreased, causing an increase in the supply of real money balances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

-Refer to Figure . Which of the following may have caused the scenario described in the figure?
A)The Fed increased the required reserve ratio.
B)The Fed raised the discount rate.
C)The Fed purchased Treasury securities.
D)The Fed announced a higher target rate for the Fed funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

-Refer to Figure . Which of the following is most likely to occur next?
A)Decreases in the interest rate will cause the demand for real money balances to increase.
B)Increases in the interest rate will cause the demand for real money balances to decrease.
C)Overall prices will fall, leading to a further rightward shift of the money supply curve.
D)Real income will increase, leading to an increase in the demand for real money balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

-Refer to Figure . It would be accurate to say that
A)as the interest rate rose, the demand for real money balances increased.
B)as the interest rate rose, the quantity demanded of real money balances increased.
C)as the interest rate fell, the demand for real money balances increased.
D)as the interest rate fell, the quantity demanded of real money balances increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
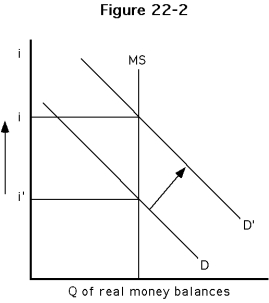
-Which of the phrases below best describes Figure ?
A)The demand for real money balances has increased and the interest rate has increased.
B)The demand for real money balances has decreased and the interest rate has increased.
C)The supply of real money balances has decreased and the interest rate has increased.
D)The demand for real money balances has decreased and the interest rate has decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

-Refer to Figure. Which of the following could cause the phenomena pictured in the diagram?
A)an increase in payments technology
B)an increase in expected inflation
C)an increase in real income
D)an increase in the liquidity of other assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Ceteris paribus, when the Fed decreases the supply of reserves, which of the following happens?
A)There is a movement downward on the supply curve for real money balances.
B)There is a movement upward on the supply curve for real money balances.
C)The supply curve of real money balances shifts to the right.
D)The supply curve of real money balances shifts to the left.
A)There is a movement downward on the supply curve for real money balances.
B)There is a movement upward on the supply curve for real money balances.
C)The supply curve of real money balances shifts to the right.
D)The supply curve of real money balances shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ceteris paribus, which of the following can change the supply curve of real money balances?
A)changes in discount loans
B)changes in the monetary base
C)open market operations
D)All of the above are correct.
A)changes in discount loans
B)changes in the monetary base
C)open market operations
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true regarding the relationship between the demand and supply of real money balances?
A)An increase in the money supply is likely to lead to a decrease in interest rates; a decrease in interest rates is likely to lead to an increase in real income; an increase is real income is likely to lead to an increase in the demand for real money balances.
B)An increase in the demand for real money balances is likely to lead to an increase in the supply of real money balances.
C)Increases in the supply of real money balances are just as likely to lead to a decrease in the demand for real money balances, as they are to lead to an increase in the demand for real money balances.
D)The demand and supply of real money balances are completely independent.
A)An increase in the money supply is likely to lead to a decrease in interest rates; a decrease in interest rates is likely to lead to an increase in real income; an increase is real income is likely to lead to an increase in the demand for real money balances.
B)An increase in the demand for real money balances is likely to lead to an increase in the supply of real money balances.
C)Increases in the supply of real money balances are just as likely to lead to a decrease in the demand for real money balances, as they are to lead to an increase in the demand for real money balances.
D)The demand and supply of real money balances are completely independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following did John Maynard Keynes not prefer when attempting to cure a recession?
A)active fiscal policy
B)changing interest rates
C)changing government spending
D)changing government taxes
A)active fiscal policy
B)changing interest rates
C)changing government spending
D)changing government taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is not an advantage of the check card?
A)It is convenient because it is very much like paying with a credit card.
B)It usually requires additional identification just like checks do.
C)It allows the owner to get cash from a huge network of ATM machines around the world.
D)It is flexible in that it may be used in places that accept credit cards but do not accept checks.
A)It is convenient because it is very much like paying with a credit card.
B)It usually requires additional identification just like checks do.
C)It allows the owner to get cash from a huge network of ATM machines around the world.
D)It is flexible in that it may be used in places that accept credit cards but do not accept checks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The cost of holding real money balances is the foregone interest that holding nonmonetary financial assets would have yielded.
B)The benefits of holding real money balances is the stream of services that holding real money balances yields.
C)The demand for money is a demand for nominal money balances.
D)If the brokerage fee increases, households make fewer calls to the broker.
A)The cost of holding real money balances is the foregone interest that holding nonmonetary financial assets would have yielded.
B)The benefits of holding real money balances is the stream of services that holding real money balances yields.
C)The demand for money is a demand for nominal money balances.
D)If the brokerage fee increases, households make fewer calls to the broker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The _____________________________ occurs when interest rates are abnormally low and virtually everyone believes they will be going up in the future.
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transactions motive
D)liquidity trap
A)speculative demand for money
B)precautionary motive
C)transactions motive
D)liquidity trap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is true?
A)When bond prices rise, interest rates fall, and bondholders make capital losses.
B)The quantity of money demanded is high when interest rates are low because the opportunity cost of holding money is low and people fear a capital loss if they hold bonds.
C)The liquidity preference theory says that people always prefer more liquidity to less.
D)Keynes advocated the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
A)When bond prices rise, interest rates fall, and bondholders make capital losses.
B)The quantity of money demanded is high when interest rates are low because the opportunity cost of holding money is low and people fear a capital loss if they hold bonds.
C)The liquidity preference theory says that people always prefer more liquidity to less.
D)Keynes advocated the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is false?
A)The benefits of additional calls to a broker in a month increase as more calls are made.
B)Calls should be made to a broker as long as the benefits are greater than the costs.
C)The average daily holding of funds is the amount of each withdrawal divided by two.
D)The benefit of an additional call to the broker is the additional interest that is earned on the larger amount of funds held in bonds during the month because of the call.
A)The benefits of additional calls to a broker in a month increase as more calls are made.
B)Calls should be made to a broker as long as the benefits are greater than the costs.
C)The average daily holding of funds is the amount of each withdrawal divided by two.
D)The benefit of an additional call to the broker is the additional interest that is earned on the larger amount of funds held in bonds during the month because of the call.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Ceteris paribus, which of the following will cause the interest rate to increase?
A)the supply of money decreases
B)the demand for money decreases
C)the supply of money increases
D)quantity supplied increases
A)the supply of money decreases
B)the demand for money decreases
C)the supply of money increases
D)quantity supplied increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
ATM machines become more accessible. The demand for money will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
ATM machines become more accessible. The supply of money will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Many near money substitutes are created. The demand for money will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Many near money substitutes are created. The supply of money will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)stay the same.
D)It is impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is false?
A)My real income rises 10 percent; therefore, my demand for real money balances will also rise 10 percent.
B)The nominal money supply and the price level have both risen by 10 percent; therefore, the supply of real money balances is unchanged.
C)The demand for money is really a demand for real money balances, M/P.
D)Ceteris paribus, the quantity demanded of real money balances is inversely related to the interest rate.
A)My real income rises 10 percent; therefore, my demand for real money balances will also rise 10 percent.
B)The nominal money supply and the price level have both risen by 10 percent; therefore, the supply of real money balances is unchanged.
C)The demand for money is really a demand for real money balances, M/P.
D)Ceteris paribus, the quantity demanded of real money balances is inversely related to the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Firms demand real money balances because
A)they need real money balances to consummate transactions.
B)some transactions cannot be perfectly anticipated.
C)inflows and outflows of funds to firms are not perfectly synchronized.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)they need real money balances to consummate transactions.
B)some transactions cannot be perfectly anticipated.
C)inflows and outflows of funds to firms are not perfectly synchronized.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Holding money so you can pay your phone bill next week is an example of which of the following motives for holding money?
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Holding cash because you believe the prices of other financial assets will fall is an example of which of the following motives for holding money?
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Holding cash as a means of payment refers to which of the following motives for holding money?
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.
A)transactions motive
B)precautionary motive
C)speculative motive
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What percentage of currency do some experts estimate is held outside of the United States?
A)30-40 percent
B)40-50 percent
C)50-60 percent
D)60-70 percent
A)30-40 percent
B)40-50 percent
C)50-60 percent
D)60-70 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A real money balance is which of the following?
A)Currency in the hands of the public
B)The money supply divided by the overall price level
C)Currency plus checkable deposits
D)Domestically held deposits rather than foreign-held deposits
A)Currency in the hands of the public
B)The money supply divided by the overall price level
C)Currency plus checkable deposits
D)Domestically held deposits rather than foreign-held deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following will not cause an increase in the demand for real money balances?
A)an increase in income
B)an increase in wealth
C)an improvement in payment technologies
D)a reduction in expected inflation
A)an increase in income
B)an increase in wealth
C)an improvement in payment technologies
D)a reduction in expected inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Ceteris paribus, the relationship between the quantity demanded of real money balances and the interest rate is which of the following?
A)inverse
B)direct
C)positive
D)concurrent
A)inverse
B)direct
C)positive
D)concurrent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following factors would affect the demand for real money balances?
A)payment technologies
B)expected inflation
C)liquidity of other financial assets
D)All of the above are correct.
A)payment technologies
B)expected inflation
C)liquidity of other financial assets
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The demand for money is which of the following?
A)constant and unchanging
B)unable to be met because no one ever has enough money
C)positively (directly) related to income
D)positively (directly) related to interest rates
A)constant and unchanging
B)unable to be met because no one ever has enough money
C)positively (directly) related to income
D)positively (directly) related to interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A real money balance is which of the following?
A)a deposit over $100
B)the money supply divided by the price level
C)the balance in M1
D)the money supply divided by the interest rate
A)a deposit over $100
B)the money supply divided by the price level
C)the balance in M1
D)the money supply divided by the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
According to monetarists, the Fed should use __________ in the conduct of monetary policy to reduce fluctuations in the economy.
A)discretion
B)the prime rate
C)rules
D)the discount rate
A)discretion
B)the prime rate
C)rules
D)the discount rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The amount of currency outstanding per household since 1960 has
A)remained the same.
B)grown.
C)decreased.
D)fluctuated wildly.
A)remained the same.
B)grown.
C)decreased.
D)fluctuated wildly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A real money balance is which of the following?
A)the nominal money supply multiplied by the overall price level
B)the nominal money supply divided by the overall price level
C)the overall price level multiplied by the nominal money supply
D)the overall price level less the nominal money supply
A)the nominal money supply multiplied by the overall price level
B)the nominal money supply divided by the overall price level
C)the overall price level multiplied by the nominal money supply
D)the overall price level less the nominal money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The demand for money is which of the following?
A)a demand for the nominal money supply
B)the overall price level
C)a demand for real money balances
D)a demand for financial liabilities
A)a demand for the nominal money supply
B)the overall price level
C)a demand for real money balances
D)a demand for financial liabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the economy is more prone to inflation, what will generally happen to the demand for real money balances?
A)Demand will remain the same.
B)Demand will increase.
C)Demand will decrease.
D)Demand will fluctuate wildly.
A)Demand will remain the same.
B)Demand will increase.
C)Demand will decrease.
D)Demand will fluctuate wildly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following would not be considered a benefit of holding real money balances?
A)interest income on money balances
B)convenience
C)increasing the transactions costs of exchanges
D)the ability to make payments when due
A)interest income on money balances
B)convenience
C)increasing the transactions costs of exchanges
D)the ability to make payments when due

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is the foregone interest that holding nonmonetary financial assets would have yielded?
A)the costs of holding real money balances
B)benefits of holding real balances
C)transactions motive
D)liquidity preference
A)the costs of holding real money balances
B)benefits of holding real balances
C)transactions motive
D)liquidity preference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In general, interest on business checking accounts is which of the following?
A)more than the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
B)less than the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
C)the same as the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
D)more than the market rate of interest on highly liquid assets
A)more than the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
B)less than the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
C)the same as the market rate of interest on other less liquid assets
D)more than the market rate of interest on highly liquid assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Ceteris paribus, what is the relationship between the interest rate on nonmonetary assets and the quantity demanded of real money balances?
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Ceteris paribus, the relationship between the brokerage fee and the demand for real money balances is which of the following?
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The foregone interest that one gives up when money balances are held is called which of the following?
A)real income
B)real money balances
C)liquidity preference
D)the opportunity cost of holding money
A)real income
B)real money balances
C)liquidity preference
D)the opportunity cost of holding money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Ceteris paribus, the relationship between the quantity demanded of real money balances and the interest rate is which of the following?
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.
A)direct
B)inverse
C)perfectly horizontal
D)There is no relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the interest rate increases, ceteris paribus,
A)the demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)the demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)there is a movement downward along the demand curve for money.
D)there is a movement upward along the demand curve for money.
A)the demand curve for money shifts to the right.
B)the demand curve for money shifts to the left.
C)there is a movement downward along the demand curve for money.
D)there is a movement upward along the demand curve for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Real income is which of the following?
A)nominal income adjusted for changes in prices
B)nominal income multiplied by a price index
C)a price index divided by nominal income
D)a price index multiplied by nominal income
A)nominal income adjusted for changes in prices
B)nominal income multiplied by a price index
C)a price index divided by nominal income
D)a price index multiplied by nominal income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If a price index is 150 and nominal income is $10,000, what is real income?
A)$500,000.00
B)$50,000.00
C)$10,000
D)$6666.67
A)$500,000.00
B)$50,000.00
C)$10,000
D)$6666.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



