Deck 18: The International Financial System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: The International Financial System
1
Which of the following is true?
A)The international financial system enables international payments to be made.
B)The international financial system enables funds to flow across borders.
C)The international financial system has been dramatically affected by technological changes.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)The international financial system enables international payments to be made.
B)The international financial system enables funds to flow across borders.
C)The international financial system has been dramatically affected by technological changes.
D)All of the above are correct.
D
2
When financial markets are more efficient
A)resources are allocated more efficiently.
B)living standards around the world should rise.
C)interest rates are lower.
D)Both a and b are correct.
A)resources are allocated more efficiently.
B)living standards around the world should rise.
C)interest rates are lower.
D)Both a and b are correct.
D
3
The Asian financial crisis of 1997-98 is a good example of
A)an efficient allocation of resources.
B)the IMF's attempt to contain a crisis and prevent it from spreading to the global economy.
C)the Bretton Woods Accord.
D)prompt corrective action.
A)an efficient allocation of resources.
B)the IMF's attempt to contain a crisis and prevent it from spreading to the global economy.
C)the Bretton Woods Accord.
D)prompt corrective action.
B
4
The international money market trades
A)short-term claims.
B)capital market instruments.
C)long-term claims.
D)stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and mortgages.
A)short-term claims.
B)capital market instruments.
C)long-term claims.
D)stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and mortgages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following affects the trading of all international financial instruments?
A)the exchange rate
B)the federal funds rate
C)the discount rate
D)the prime rate
A)the exchange rate
B)the federal funds rate
C)the discount rate
D)the prime rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under the Bretton Woods Accord,
A)gold served as the official reserve currency.
B)the British pound served as the official reserve currency.
C)there was no need for an official reserve currency because the accord was based on flexible exchange rates.
D)the U.S. dollar served as the official reserve currency.
A)gold served as the official reserve currency.
B)the British pound served as the official reserve currency.
C)there was no need for an official reserve currency because the accord was based on flexible exchange rates.
D)the U.S. dollar served as the official reserve currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Under the Bretton Woods agreement, if a country other than the United States ran a trade deficit, downward pressure was exerted on the currency's exchange rate. In order to maintain the agreed-upon exchange rate, what must this foreign central bank do?
A)It must purchase the excess supply of dollars with its own currency.
B)It must purchase the excess supply of its own currency with dollars.
C)It must supply its own currency and demand dollars to create a surplus in the official reserve account that just equals its deficit on current and capital accounts.
D)Both b and c
A)It must purchase the excess supply of dollars with its own currency.
B)It must purchase the excess supply of its own currency with dollars.
C)It must supply its own currency and demand dollars to create a surplus in the official reserve account that just equals its deficit on current and capital accounts.
D)Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements concerning the Bretton Woods Accord is false?
A)The accord was signed in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire in 1944.
B)The accord established fixed exchange rates among the major industrialized nations.
C)The accord created the Bank for International Settlements.
D)Under the accord, the U.S. dollar served as the official reserve currency and was fully convertible to gold.
A)The accord was signed in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire in 1944.
B)The accord established fixed exchange rates among the major industrialized nations.
C)The accord created the Bank for International Settlements.
D)Under the accord, the U.S. dollar served as the official reserve currency and was fully convertible to gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Devaluation occurs when the monetary authorities
A)reduce the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate system
B)increase the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate system
C)reduce the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate system
D)increase the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate system
A)reduce the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate system
B)increase the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate system
C)reduce the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate system
D)increase the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under the Bretton Woods Accord, official government transactions ________ brought the balance of payments into balance at the fixed exchange rate.
A)always
B)once upon a time
C)never
D)occasionally
A)always
B)once upon a time
C)never
D)occasionally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Revaluation occurs when monetary authorities
A)increase the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate
B)decrease the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate
C)increase the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate
D)decrease the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate
A)increase the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate
B)decrease the value of a country's currency under a fixed exchange rate
C)increase the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate
D)decrease the value of a country's currency under a flexible exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Revaluation can
A)affect a country's economy.
B)reduce net exports.
C)have a negative impact on employment.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)affect a country's economy.
B)reduce net exports.
C)have a negative impact on employment.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The breakdown of the Bretton Woods Accord in 1971 resulted in which of these?
A)continuation of the international conversion of dollars to gold
B)the Vietnam War
C)the Great Society's War on Poverty
D)the suspension of the international conversion of dollars to gold
A)continuation of the international conversion of dollars to gold
B)the Vietnam War
C)the Great Society's War on Poverty
D)the suspension of the international conversion of dollars to gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the Bretton Wood Accord broke down,
A)the United States was unable to respond to requests of other countries to back the dollar with gold at the agreed-upon rate.
B)the United States became flooded with gold.
C)central banks outside of the United States had accumulated too little gold.
D)European countries all returned to a gold standard.
A)the United States was unable to respond to requests of other countries to back the dollar with gold at the agreed-upon rate.
B)the United States became flooded with gold.
C)central banks outside of the United States had accumulated too little gold.
D)European countries all returned to a gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements best describes the implications of a currency devaluation?
A)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments less expensive in domestic currency terms.
B)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments more expensive in domestic currency terms.
C)The country devaluing would be expected to reduce its net exports, which is likely to have a negative impact on domestic employment.
D)Both b and c are correct.
A)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments less expensive in domestic currency terms.
B)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments more expensive in domestic currency terms.
C)The country devaluing would be expected to reduce its net exports, which is likely to have a negative impact on domestic employment.
D)Both b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements best describes the economic implications of a currency revaluation?
A)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments cheaper in domestic currency terms.
B)Other countries would now find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments more expensive in domestic currency terms.
C)The country revaluing would be likely to experience decreased net exports and employment.
D)Both b and c are correct.
A)Other countries would find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments cheaper in domestic currency terms.
B)Other countries would now find the country's goods, services, and financial instruments more expensive in domestic currency terms.
C)The country revaluing would be likely to experience decreased net exports and employment.
D)Both b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following situations is a positive for a country?
A)increase in the trade deficit
B)increase in net capital outflow
C)increase in net exports
D)increase in net imports
A)increase in the trade deficit
B)increase in net capital outflow
C)increase in net exports
D)increase in net imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An exchange rate system where currency values are determined by the forces of supply and demand and where currency values fluctuate in response to changes in supply and demand is called a(n)
A)fixed exchange rate system.
B)floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)managed float exchange rate system.
D)international financial system.
A)fixed exchange rate system.
B)floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)managed float exchange rate system.
D)international financial system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ceteris paribus, the quantity demanded is what kind of function of the exchange rate?
A)negative
B)positive
C)neutral
D)zero
A)negative
B)positive
C)neutral
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Currency values under a flexible exchange rate system are determined by the forces of supply and demand. Other things equal, if U.S. incomes, U.S. inflation, or foreign interest rates increase
A)there will be a decreased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will appreciate.
B)there will be an increased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will appreciate.
C)there will be an increased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will depreciate.
D)there will be a decreased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will depreciate.
A)there will be a decreased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will appreciate.
B)there will be an increased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will appreciate.
C)there will be an increased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will depreciate.
D)there will be a decreased demand for foreign goods, services and securities, an increase in the supply of dollars, and the dollar will depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exchange rates are affected by
A)market forces.
B)central banks.
C)commercial bank gold reserves.
D)Both a and b are correct.
A)market forces.
B)central banks.
C)commercial bank gold reserves.
D)Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A system where currency values fluctuate with changes in supply and demand, but where central banks may intervene if currency values are thought to be over- or under-valued is called a(n)
A)fixed exchange rate system.
B)floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)managed float exchange rate system.
D)international financial system.
A)fixed exchange rate system.
B)floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)managed float exchange rate system.
D)international financial system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Under the flexible exchange rate system, markets are exposed to
A)substantial exchange rate risk.
B)no exchange rate risk.
C)unpredictable exchange rate risk.
D)Both a and c are correct.
A)substantial exchange rate risk.
B)no exchange rate risk.
C)unpredictable exchange rate risk.
D)Both a and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Derivatives can be used
A)to hedge exchange rate risk.
B)to reduce exchange rate risk.
C)to increase overall risk.
D)Both a and b are correct.
A)to hedge exchange rate risk.
B)to reduce exchange rate risk.
C)to increase overall risk.
D)Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The dollar acts as a store of value because of
A)U.S. political stability.
B)the dollar's acceptance over time.
C)vast gold and oil reserves.
D)All of the above are correct.
E)Both a and b are correct.
A)U.S. political stability.
B)the dollar's acceptance over time.
C)vast gold and oil reserves.
D)All of the above are correct.
E)Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The __________ is an organization of 185 countries created in 1944 to oversee the monetary and exchange rate policies of its members; member countries pay quotas that are then used to assist countries with temporary imbalances in their balance of payments.
A)International Finance Corporation
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Monetary Fund (IMF)
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
A)International Finance Corporation
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Monetary Fund (IMF)
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following did the International Monetary Fund (IMF) recommend for the countries of Southeast Asia while providing short-term loans and technical assistance to them in 1997-1998?
A)revaluations of currencies
B)decreases in interest rates
C)contractionary fiscal policies, improved bank regulation and oversight, as well as less dependence on short-term financing (especially from abroad)
D)All of the above are correct.
A)revaluations of currencies
B)decreases in interest rates
C)contractionary fiscal policies, improved bank regulation and oversight, as well as less dependence on short-term financing (especially from abroad)
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Member countries of the IMF
A)pay a quota based on economic importance and the amount of international trade.
B)are carefully scrutinized and regulated by the IMF.
C)agree to exchange their currencies with other foreign countries.
D)are controlled by the U.S.
E)Both a and c are correct.
A)pay a quota based on economic importance and the amount of international trade.
B)are carefully scrutinized and regulated by the IMF.
C)agree to exchange their currencies with other foreign countries.
D)are controlled by the U.S.
E)Both a and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
International assets created by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to supplement other international reserves are called
A)international drawing rights.
B)IMFs.
C)special drawing rights (SDRs).
D)Eurobonds.
A)international drawing rights.
B)IMFs.
C)special drawing rights (SDRs).
D)Eurobonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The __________ is an association that makes interest-free loans with a 35-to 40-year maturity to the world's poorest countries; it is affiliated with the World Bank.
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The __________ is an organization that mobilizes funding for private enterprise projects in poor countries; it is legally separate from but works closely with the World Bank.
A)International Finance Corporation
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements
A)International Finance Corporation
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following best describes the main role(s) of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
A)Promoting economic development by raising funds and making economic development loans
B)Using member quotas to make short-term loans to members experiencing temporary balance of payment deficits
C)Acting as a bank for central banks
D)All of the above
A)Promoting economic development by raising funds and making economic development loans
B)Using member quotas to make short-term loans to members experiencing temporary balance of payment deficits
C)Acting as a bank for central banks
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The original purpose of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) was
A)to promote the cooperation of central banks
B)to provide additional facilities for international financial operations
C)to make loans to Third World countries
D)All of the above
E)Both a and b
A)to promote the cooperation of central banks
B)to provide additional facilities for international financial operations
C)to make loans to Third World countries
D)All of the above
E)Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In order to have an account with the BIS,
A)a country must be a member
B)a country does not have to be a member
C)a country must pay a quota
D)must be a member of the G-7 or G-10
A)a country must be a member
B)a country does not have to be a member
C)a country must pay a quota
D)must be a member of the G-7 or G-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Financial Stability Forum (FSF) was created
A)to promote international financial stability
B)to foster cooperation in financial supervision and surveillance
C)by the G-7 nations
D)All of the above
A)to promote international financial stability
B)to foster cooperation in financial supervision and surveillance
C)by the G-7 nations
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In order to participate in the Financial Stability Forum (FSF), a country
A)must have sound economic policies
B)must establish banking systems that encourage appropriate risk taking
C)must standardize the reporting of qualitative and quantitative information
D)All of the above
A)must have sound economic policies
B)must establish banking systems that encourage appropriate risk taking
C)must standardize the reporting of qualitative and quantitative information
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
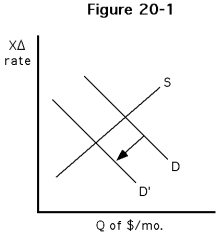
-Which of the following would best explain the decrease in demand for dollars illustrated in Figure ?
A)A decrease in U.S. prices, ceteris paribus
B)A decrease in U.S. interest rates, ceteris paribus
C)An increase in foreign incomes, ceteris paribus
D)A decrease in foreign interest rates, ceteris paribus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
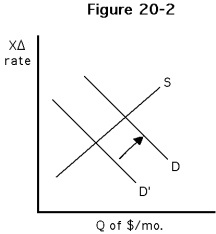
-Which of the following would best explain the increase in demand for dollars illustrated in Figure ?
A)An increase in U.S. prices, ceteris paribus
B)A decrease in U.S. interest rates, ceteris paribus
C)An increase in foreign incomes, ceteris paribus
D)An increase in foreign interest rates, ceteris paribus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
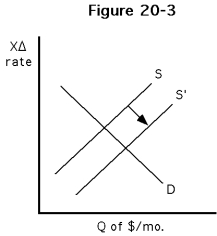
-Which of the following would best explain the increase in the supply of dollars illustrated in Figure ?
A)A decrease in U.S. prices, ceteris paribus
B)An increase in U.S. interest rates, ceteris paribus
C)An increase in U.S. incomes, ceteris paribus
D)An increase in foreign incomes, ceteris paribus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
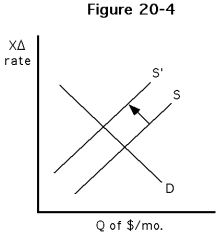
-Which of the following would best explain the decrease in the supply of dollars illustrated in Figure ?
A)An increase in U.S. prices, ceteris paribus
B)An increase in U.S. interest rates, ceteris paribus
C)An increase in U.S. incomes, ceteris paribus
D)An increase in foreign incomes, ceteris paribus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Under a fixed exchange rate system such as the gold standard, __________ is when a country increases the units of currency equal to one ounce of gold.
A)devaluation
B)appreciation
C)depreciation
D)revaluation
A)devaluation
B)appreciation
C)depreciation
D)revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the United States and its major trading partners were on a gold standard. Which of the following statements about the gold standard is false?
A)The gold standard was a fixed exchange-rate system.
B)The gold standard stabilized international trade and eliminated financial crises.
C)A devaluation was an increase in the number of dollars that had to be presented to the Treasury to receive an ounce of gold.
D)The gold standard could become strained when countries experienced different growth rates.
A)The gold standard was a fixed exchange-rate system.
B)The gold standard stabilized international trade and eliminated financial crises.
C)A devaluation was an increase in the number of dollars that had to be presented to the Treasury to receive an ounce of gold.
D)The gold standard could become strained when countries experienced different growth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the Fed wanted to increase the value of the Yen, what would it do?
A)Buy dollars and sell yen
B)Buy both dollars and yen
C)Buy yen and sell dollars
D)Sell both yen and dollars
A)Buy dollars and sell yen
B)Buy both dollars and yen
C)Buy yen and sell dollars
D)Sell both yen and dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the Fed wanted to reduce the value of the Yen, what would it do?
A)Buy dollars and sell yen
B)Buy both dollars and yen
C)Buy yen and sell dollars
D)Sell both yen and dollars
A)Buy dollars and sell yen
B)Buy both dollars and yen
C)Buy yen and sell dollars
D)Sell both yen and dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The __________ is an international financial organization located in Basle Switzerland created in 1930 that promotes international cooperation among central banks and provides facilities for international financial operations.
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The __________ is an agreement reached in 1944 among major industrialized countries that established fixed exchange rates with the U.S. dollar serving as the official reserve currency.
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)Bank for International Settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The __________ makes 12-to 15-year loans to poor countries, but not the poorest, charging an interest rate just above the rate at which the bank borrowed; it is affiliated with the World Bank...
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
A)Bretton Woods Accord
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The __________ is an investment bank created in 1944 that issues bonds to make low interest rate or interest-free, long-term loans to poor countries for economic development projects.
A)International Monetary Fund
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
A)International Monetary Fund
B)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
C)International Development Association
D)International Bank for Reconstruction and Development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Since World War II, the international financial system has been coordinated
A)by a fixed exchange rate system only.
B)by a flexible exchange rate system only.
C)first by a fixed exchange rate system and then by a flexible exchange rate system.
D)first by a flexible exchange rate system and then by a fixed exchange rate system.
A)by a fixed exchange rate system only.
B)by a flexible exchange rate system only.
C)first by a fixed exchange rate system and then by a flexible exchange rate system.
D)first by a flexible exchange rate system and then by a fixed exchange rate system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The numerous rules, customs, instruments, facilities, markets, and organizations through which international payments are made and through which funds flow across borders is called
A)a fixed exchange rate system.
B)a floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)a managed float exchange rate system.
D)the international financial system.
A)a fixed exchange rate system.
B)a floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
C)a managed float exchange rate system.
D)the international financial system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The U.S. dollar served as the __________ under the Bretton Woods accord.
A)official reserve account
B)fixed exchange rate system
C)official reserve currency
D)Both b and c
A)official reserve account
B)fixed exchange rate system
C)official reserve currency
D)Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
__________ is when a currency has increased in value relative to another currency under a flexible exchange rate system.
A)Depreciation
B)Appreciation
C)Devaluation
D)Revaluation
A)Depreciation
B)Appreciation
C)Devaluation
D)Revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
__________ is when a currency has decreased in value relative to another currency under a flexible exchange rate system.
A)Depreciation
B)Appreciation
C)Devaluation
D)Revaluation
A)Depreciation
B)Appreciation
C)Devaluation
D)Revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
__________ is when a country increases the units of its currency equal to one unit of the official reserve asset under a fixed exchange rate system.
A)Devaluation
B)Appreciation
C)Depreciation
D)Revaluation
A)Devaluation
B)Appreciation
C)Depreciation
D)Revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
__________ is when a country decreases the units of its currency equal to one ounce of the official reserve asset under a fixed exchange rate system.
A)Devaluation
B)Appreciation
C)Depreciation
D)Revaluation
A)Devaluation
B)Appreciation
C)Depreciation
D)Revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
During recent years, financial markets have
A)stabilized since the advent of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
B)developed rigidity to protect against the globalized environment.
C)been driven by technological improvements in telecommunications and increased globalization.
D)experienced little change.
A)stabilized since the advent of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
B)developed rigidity to protect against the globalized environment.
C)been driven by technological improvements in telecommunications and increased globalization.
D)experienced little change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose the dollar and the euro had an agreed-upon exchange of $1 = 1 euro and supply and demand factors caused the market value of the two currencies to move to $3 = 1 euro; in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate, the European Central Bank would
A)buy dollars with euros.
B)buy euros with dollars.
C)ask the United States to buy more euros.
D)restrict the exports of the European Union.
A)buy dollars with euros.
B)buy euros with dollars.
C)ask the United States to buy more euros.
D)restrict the exports of the European Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose the dollar and the euro had an agreed-upon exchange of $1 = 1 euro and supply and demand factors caused the market value of the two currencies to move to $1 = 3 euros; in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate, the European Central Bank would
A)increase the number of euros in the market.
B)buy euros with dollars.
C)ask the United States to buy more dollars.
D)restrict the exports of the European Union.
A)increase the number of euros in the market.
B)buy euros with dollars.
C)ask the United States to buy more dollars.
D)restrict the exports of the European Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is a major change since the Bretton Woods Accord broke down?
A)A retreat to isolationism reduced trade and capital flows.
B)Nations of the world have grown more interdependent because of the growth of world trade.
C)Nations of the world have become more independent as a result of increased trade.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)A retreat to isolationism reduced trade and capital flows.
B)Nations of the world have grown more interdependent because of the growth of world trade.
C)Nations of the world have become more independent as a result of increased trade.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements about fixed exchange rates is true?
A)To devalue a currency means to increase its value relative to the dollar.
B)Fixed exchange rate systems do not require international coordination.
C)Exchange rate risk is higher under fixed exchange rate systems than under flexible exchange rate systems.
D)To revalue a currency means to increase its value relative to the official reserve asset.
A)To devalue a currency means to increase its value relative to the dollar.
B)Fixed exchange rate systems do not require international coordination.
C)Exchange rate risk is higher under fixed exchange rate systems than under flexible exchange rate systems.
D)To revalue a currency means to increase its value relative to the official reserve asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The International Monetary Fund was
A)started in 1917 at the end of World War I.
B)created at the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944.
C)originally part of the World Bank.
D)developed as one of the arms of the United Nations.
A)started in 1917 at the end of World War I.
B)created at the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944.
C)originally part of the World Bank.
D)developed as one of the arms of the United Nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is true?
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established a system of flexible exchange rates, with the U.S. dollar (backed by gold) functioning as the official reserve currency.
B)Under the Bretton Woods Accord, if the trade deficit of a country other than the United States. increased, ceteris paribus, there was upward pressure on that country's exchange rate.
C)Revaluation is likely to reduce net exports and have a negative impact on employment.
D)Other things equal, if U.S. incomes rise, there will likely be an increase in U.S. demand for foreign goods, services, and securities, and thus an increase in the demand for dollars.
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established a system of flexible exchange rates, with the U.S. dollar (backed by gold) functioning as the official reserve currency.
B)Under the Bretton Woods Accord, if the trade deficit of a country other than the United States. increased, ceteris paribus, there was upward pressure on that country's exchange rate.
C)Revaluation is likely to reduce net exports and have a negative impact on employment.
D)Other things equal, if U.S. incomes rise, there will likely be an increase in U.S. demand for foreign goods, services, and securities, and thus an increase in the demand for dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is true?
A)The present international monetary system can be correctly called a floating (flexible) exchange rate system because market forces are the only factor affecting exchange rates.
B)The fixed exchanged rate system established by the Bretton Woods Accord broke down in the early 1970s and resulted in the establishment of a managed floating exchange rate system.
C)Since the creation of the managed float system, smaller countries no longer fix the value of their currencies to the value of other major currencies.
D)All of the above are true.
A)The present international monetary system can be correctly called a floating (flexible) exchange rate system because market forces are the only factor affecting exchange rates.
B)The fixed exchanged rate system established by the Bretton Woods Accord broke down in the early 1970s and resulted in the establishment of a managed floating exchange rate system.
C)Since the creation of the managed float system, smaller countries no longer fix the value of their currencies to the value of other major currencies.
D)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is false?
A)The dollar and the euro are demanded in international financial markets because of their perceived stability.
B)Roughly 50 to 60 percent of all U.S. currency and over 70 percent of all $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and the Bank for International Settlements were created in 1944 at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire.
D)The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development makes 12- to 15-year loans to poor countries.
A)The dollar and the euro are demanded in international financial markets because of their perceived stability.
B)Roughly 50 to 60 percent of all U.S. currency and over 70 percent of all $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and the Bank for International Settlements were created in 1944 at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire.
D)The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development makes 12- to 15-year loans to poor countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An exchange rate system in which the value of a currency is determined by supply and demand is called which of these?
A)a flexible rate system
B)a fixed rate system
C)a managed system
D)None of the above is correct.
A)a flexible rate system
B)a fixed rate system
C)a managed system
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established the flexible exchange rate system in 1971.
B)Over half of U.S. currency and over 70 percent of $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The price of oil from the Middle East is quoted, bought, and sold in dollars.
D)The euro is now used as international reserves.
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established the flexible exchange rate system in 1971.
B)Over half of U.S. currency and over 70 percent of $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The price of oil from the Middle East is quoted, bought, and sold in dollars.
D)The euro is now used as international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An exchange rate system in which the value of a currency is determined by supply and demand and where central banks on occasion intervene in the market is called which of these?
A)a flexible (floating) rate system
B)a fixed rate system
C)a managed floating exchange rate system
D)None of the above is correct
A)a flexible (floating) rate system
B)a fixed rate system
C)a managed floating exchange rate system
D)None of the above is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following statements is false?
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established a fixed exchange rate system among the major industrialized countries in 1944.
B)Over half of U.S. currency and over 70 percent of $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The price of oil from the Middle East is quoted, bought, and sold in euros. This was a blow to the U.S. dollar which used to be the currency in which oil was quoted, bought, and sold.
D)The euro is now used as international reserves.
A)The Bretton Woods Accord established a fixed exchange rate system among the major industrialized countries in 1944.
B)Over half of U.S. currency and over 70 percent of $100 bills are held abroad.
C)The price of oil from the Middle East is quoted, bought, and sold in euros. This was a blow to the U.S. dollar which used to be the currency in which oil was quoted, bought, and sold.
D)The euro is now used as international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is true?
A)The present international monetary system can be correctly called a managed floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
B)The fixed exchanged rate system established by the Bretton Woods Accord broke down in the early 1944 and resulted in the establishment of a managed floating exchange rate system.
C)Since the creation of the flexible exchange rate system, the values of all currencies in the world are determined independently by the forces of supply and demand.
D)All of the above are true.
A)The present international monetary system can be correctly called a managed floating (flexible) exchange rate system.
B)The fixed exchanged rate system established by the Bretton Woods Accord broke down in the early 1944 and resulted in the establishment of a managed floating exchange rate system.
C)Since the creation of the flexible exchange rate system, the values of all currencies in the world are determined independently by the forces of supply and demand.
D)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



