Deck 5: Interest Rates and Bond Prices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Interest Rates and Bond Prices
1
The interest rate is the
A)cost to borrowers of obtaining money.
B)return or yield to money for lenders.
C)time value of money.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)cost to borrowers of obtaining money.
B)return or yield to money for lenders.
C)time value of money.
D)All of the above are correct.
D
2
__________ represents the value today of funds to be received or lent on a future date.
A)Compounding
B)The money illusion
C)The present value
D)The principal
A)Compounding
B)The money illusion
C)The present value
D)The principal
C
3
If Erik lends Dan $5,000 and Dan agrees to repay Erik $6,000 in 1 year's time, the $5,000 is the
A)interest rate.
B)compounding amount.
C)principal.
D)real return.
A)interest rate.
B)compounding amount.
C)principal.
D)real return.
C
4
Discounting answers which of these questions?
A)What is the present value of money to be paid in the future?
B)What is the future value of money to be paid in the future?
C)What is the future value of money to be paid in the present?
D)None of the above
A)What is the present value of money to be paid in the future?
B)What is the future value of money to be paid in the future?
C)What is the future value of money to be paid in the present?
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The periodic payment made to bondholders is called the
A)dividend.
B)coupon payment.
C)consol.
D)principal.
A)dividend.
B)coupon payment.
C)consol.
D)principal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Coupon payments are equal to the
A)coupon rate on a bond multiplied by the face value of the bond.
B)par value on a bond divided by the face value of the bond.
C)par value on a bond minus the face value of the bond.
D)coupon rate on a bond minus the face value of the bond.
A)coupon rate on a bond multiplied by the face value of the bond.
B)par value on a bond divided by the face value of the bond.
C)par value on a bond minus the face value of the bond.
D)coupon rate on a bond minus the face value of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Bonds generally share the following characteristics:
A)a maturity greater than ten years
B)a par or face value
C)equal periodic interest payments
D)All of the above
A)a maturity greater than ten years
B)a par or face value
C)equal periodic interest payments
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A bond sells at __________ because interest rates have increased since the bond was originally issued.
A)an inflation premium
B)par value
C)a premium above par
D)a discount from par
A)an inflation premium
B)par value
C)a premium above par
D)a discount from par

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If a bond is sold at a discount from par, this
A)lowers the yield on the bond.
B)does not change the yield on the bond.
C)raises the yield on the bond.
D)None of the above
A)lowers the yield on the bond.
B)does not change the yield on the bond.
C)raises the yield on the bond.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In general, if bond prices are rising, then interest rates are
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In general, if interest rates are falling, then bond prices are
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If interest rates have risen since a bond was originally issued, then the bond's price will fall until the yield to maturity of the bond becomes
A)less than the current interest rate.
B)more than the current interest rate.
C)equal to the current interest rate.
D)less than comparable stock options.
A)less than the current interest rate.
B)more than the current interest rate.
C)equal to the current interest rate.
D)less than comparable stock options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As market interest rates fall, what happens to the prices of existing bonds?
A)Prices of existing bonds fall.
B)Prices of existing bonds increase.
C)Prices of existing bonds remain the same.
D)Prices of existing bonds increase and then decrease.
A)Prices of existing bonds fall.
B)Prices of existing bonds increase.
C)Prices of existing bonds remain the same.
D)Prices of existing bonds increase and then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
As market interest rates rise, what happens to the prices of previously-issued bonds?
A)Prices of existing bonds fall.
B)Prices of existing bonds increase.
C)Prices of existing bonds remain the same.
D)Prices of existing bonds increase and then decrease.
A)Prices of existing bonds fall.
B)Prices of existing bonds increase.
C)Prices of existing bonds remain the same.
D)Prices of existing bonds increase and then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A/An__________ relationship exists between the price of outstanding bonds in the secondary market and the prevailing level of market interest rates.
A)inverse
B)direct
C)uncertain
D)positive
A)inverse
B)direct
C)uncertain
D)positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand for loanable funds comes from
A)household, business, government, and foreign net borrowers who spend more than their income.
B)household, business, government, and foreign net borrowers who spend less than their income.
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves in the conduct of monetary policy.
D)Both b and c are correct.
A)household, business, government, and foreign net borrowers who spend more than their income.
B)household, business, government, and foreign net borrowers who spend less than their income.
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves in the conduct of monetary policy.
D)Both b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The supply of loanable funds originates from
A)an excess demand for loanable funds.
B)household, business, government and foreign net lenders who are prepared to lend because they are spending less than their current incomes.
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves that lead to increases in the growth rate of money.
D)Both b and c are correct.
A)an excess demand for loanable funds.
B)household, business, government and foreign net lenders who are prepared to lend because they are spending less than their current incomes.
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves that lead to increases in the growth rate of money.
D)Both b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is generally true when Gross Domestic Product (GDP) rises?
A)the demand for loanable funds increases
B)people are more willing and able to borrow more
C)the demand for loanable funds decreases
D)Both a and b are correct.
A)the demand for loanable funds increases
B)people are more willing and able to borrow more
C)the demand for loanable funds decreases
D)Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When GDP rises, ceteris paribus, firms and households become
A)less willing to borrow.
B)more willing and able to borrow.
C)indifferent with regard to borrowing.
D)less able to borrow.
A)less willing to borrow.
B)more willing and able to borrow.
C)indifferent with regard to borrowing.
D)less able to borrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In general, when income falls, the willingness and ability to borrow and spend will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
D)be impossible to determine.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
D)be impossible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In general, when income rises, the willingness and ability to borrow and spend will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
D)be impossible to determine.
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)remain the same.
D)be impossible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What happens when the quantity of funds demanded exceeds the quantity supplied?
A)interest rates fall
B)interest rates and bond prices rise
C)bond prices rise
D)interest rates rise and bond prices fall
A)interest rates fall
B)interest rates and bond prices rise
C)bond prices rise
D)interest rates rise and bond prices fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What happens when the quantity of funds demanded is less than the quantity supplied?
A)interest rates rise
B)interest rates rise and bond prices fall
C)bond prices fall
D)interest rates fall and bond prices rise
A)interest rates rise
B)interest rates rise and bond prices fall
C)bond prices fall
D)interest rates fall and bond prices rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Ceteris paribus, the interest rate is a _______ function of income or GDP, and a ________ function of the money supply.
A)positive, negative
B)negative, positive
C)negative, negative
D)positive, positive
A)positive, negative
B)negative, positive
C)negative, negative
D)positive, positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the anticipated productivity of capital investment increases, the demand for loanable funds
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)reaches equilibrium.
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)reaches equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the anticipated productivity of capital investment decreases, the demand for loanable funds
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)reaches equilibrium.
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)reaches equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The __________ is the interest rate corrected for changes in the purchasing power of money.
A)nominal interest rate
B)nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation
C)real interest rate
D)Both b and c
A)nominal interest rate
B)nominal interest rate minus the expected rate of inflation
C)real interest rate
D)Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Reacting to nominal changes caused by changes in prices when real variables, such as interest rates, have not changed is called
A)compounding.
B)money illusion.
C)discounting.
D)principal.
A)compounding.
B)money illusion.
C)discounting.
D)principal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the amount of nominal interest that will compensate a lender for the expected loss of purchasing power accompanying any inflation?
A)the risk premium
B)the inflation premium
C)the discount rate
D)the federal funds rate
A)the risk premium
B)the inflation premium
C)the discount rate
D)the federal funds rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One of the first economists to statistically analyze the relationship between inflation and nominal interest rates was
A)Adam Smith
B)Irving Fisher
C)Irving Forbesh
D)Alan Greenspan
A)Adam Smith
B)Irving Fisher
C)Irving Forbesh
D)Alan Greenspan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Ceteris paribus, a rise in expectations of inflation will lead to a ________ in nominal interest rates.
A)rise
B)fall
C)equilibrium value
D)both b and c
A)rise
B)fall
C)equilibrium value
D)both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ceteris paribus, a fall in expectations of inflation will lead to a ________ in nominal interest rates.
A)rise
B)fall
C)equilibrium value
D)both b and c
A)rise
B)fall
C)equilibrium value
D)both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A consol is
A)a special type of bond that matures in 100 years.
B)a perpetual bond with no maturity date.
C)a bond whose price is directly related to changes in the interest rate.
D)a sum resulting from compounding. as opposed to discounting.
A)a special type of bond that matures in 100 years.
B)a perpetual bond with no maturity date.
C)a bond whose price is directly related to changes in the interest rate.
D)a sum resulting from compounding. as opposed to discounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assuming an interest rate of 5%, what would the present value be of $4 million to be received in 4 years?
A)$2,468,107.42
B)$2,887,753.24
C)$3,290,809.89
D)$3,469,145.89
A)$2,468,107.42
B)$2,887,753.24
C)$3,290,809.89
D)$3,469,145.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In general, the direction of the change in interest rates will
A)follow the direction of the change in inflationary expectations.
B)not be affected by the direction of the change in inflationary expectations.
C)go the opposite direction of the change in inflationary expectation.
D)either go in the opposite direction of the change in inflationary expectations or remain the same.
A)follow the direction of the change in inflationary expectations.
B)not be affected by the direction of the change in inflationary expectations.
C)go the opposite direction of the change in inflationary expectation.
D)either go in the opposite direction of the change in inflationary expectations or remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given an interest rate of 5%, which has a higher present value: A payment of $80 at the present time, or $100 in 2 years?
A)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher present value because of a positive time preference.
B)The future amount ($100 in 2 years ) has a higher present value, give an interest rate of 5%.
C)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher present value, given an interest rate of 5 %.
D)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher compounded value.
A)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher present value because of a positive time preference.
B)The future amount ($100 in 2 years ) has a higher present value, give an interest rate of 5%.
C)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher present value, given an interest rate of 5 %.
D)The present amount ($80 now) has a higher compounded value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under what conditions will a bond sell at a premium above its initial selling price?
A)When interest rates have increased since the bond was issued.
B)When interest rates have fallen since the bond was issued.
C)When a broker in secondary market is charging a commission.
D)A bond will never sell above its initial selling price.
A)When interest rates have increased since the bond was issued.
B)When interest rates have fallen since the bond was issued.
C)When a broker in secondary market is charging a commission.
D)A bond will never sell above its initial selling price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The interest rate is __________ related to changes in income, __________ related to changes in money supply, and __________ related to changes in expected inflation.
A)positively, positively, positively
B)negatively, negatively, negatively
C)positively, negatively, negatively
D)positively, negatively, positively
A)positively, positively, positively
B)negatively, negatively, negatively
C)positively, negatively, negatively
D)positively, negatively, positively

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
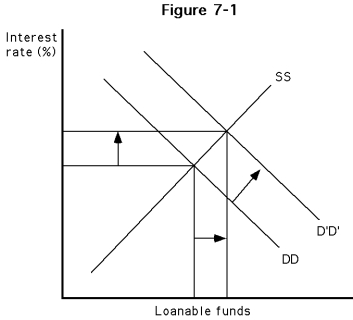
-Which of the following best describes the diagram of Figure ?
A)The demand for loanable funds increased. This, in turn, increased the interest rate and the supply of loanable funds.
B)The demand for loanable funds increased. This, in turn, increased the interest rate and the quantity supplied of loanable funds.
C)The supply of loanable fund increased. In turn, interest rates increased.
D)Interest rates increased, causing the demand of loanable funds to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-Which of the following occurrences could have generated the phenomena diagrammed in Figure ?
A)a decrease in income
B)an increase in income
C)an increase in money supply
D)a decrease in money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

-In which phase of the business cycle would the diagrammed phenomena of the Figure most likely have occurred?
A)recession
B)expansion
C)trough
D)depression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
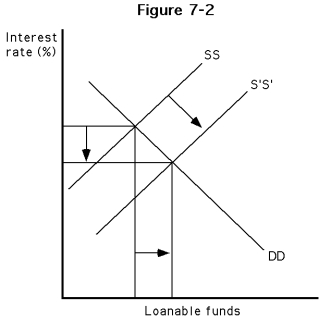
-Which of the following best describes the diagram of Figure ?
A)The demand for loanable funds decreased. This in turn decreased the interest rate and increased the quantity supplied of loanable funds.
B)The supply of loanable funds increased. This in turn increased the interest rate.
C)The supply of loanable funds increased. In turn, interest rates decreased and the quantity demanded of loanable funds increased.
D)The interest rate fell, causing an increase in the supply of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

-Which of the following occurrences could have generated the phenomena diagrammed in Figure?
A)A decrease in income
B)A tighter monetary policy by the Federal Reserve
C)An easier monetary policy by the Federal Reserve
D)An increase in income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44

-In which phase of the business cycle would the diagrammed phenomena of Figure most likely have occurred?
A)recession
B)expansion
C)trough
D)depression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the nominal interest rate is 7% and the real interest rate is 3%, then the expected rate of inflation must be
A)6%.
B)4%.
C)- 4%.
D)5%.
A)6%.
B)4%.
C)- 4%.
D)5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the nominal interest rate is 9% and expected inflation is 11%, then the real interest rate is
A)-2%.
B)2%.
C)20%.
D)unknown.
A)-2%.
B)2%.
C)20%.
D)unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the real interest rate is 3% and expected inflation is 5%, then the nominal interest rate is
A)2%.
B)-2%.
C)8%.
D)unknown.
A)2%.
B)-2%.
C)8%.
D)unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A consol with a coupon payment of $100 is purchased for $1,000. When the consol is sold, the interest rate is 20%. What has happened to the price of the consol?
A)The consol's price remains at $1,000.
B)The consol's price will have increased to $2,000.
C)The consol's price will have decreased to $500.
D)It is impossible to determined from the information given what the price of the consol will be.
A)The consol's price remains at $1,000.
B)The consol's price will have increased to $2,000.
C)The consol's price will have decreased to $500.
D)It is impossible to determined from the information given what the price of the consol will be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is false?
A)A price index measures the growth of the average price level over time.
B)The producer price index (PPI) measures changes in the costs of goods and services purchased by the typical producer.
C)The inflation rate is the rate of change (growth rate) of the average level of prices paid.
D)The consumer price index (CPI) measures changes in the cost of every item that every consumer purchases.
A)A price index measures the growth of the average price level over time.
B)The producer price index (PPI) measures changes in the costs of goods and services purchased by the typical producer.
C)The inflation rate is the rate of change (growth rate) of the average level of prices paid.
D)The consumer price index (CPI) measures changes in the cost of every item that every consumer purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is false?
A)Flows are measured at a point in time whereas stocks are measured overtime.
B)Keynes developed the liquidity preference theory that hypothesizes that the interest is determined by the demand and supply of money.
C)The loanable funds theory says that the interest rate is determined by the demand and supply of loanable funds.
D)Flows over time add to stocks measured at successive points in time.
A)Flows are measured at a point in time whereas stocks are measured overtime.
B)Keynes developed the liquidity preference theory that hypothesizes that the interest is determined by the demand and supply of money.
C)The loanable funds theory says that the interest rate is determined by the demand and supply of loanable funds.
D)Flows over time add to stocks measured at successive points in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A bond sells at __________ because interest rates have fallen since the bond was originally issued.
A)an inflation premium
B)par value
C)a premium above par
D)a discount from par
A)an inflation premium
B)par value
C)a premium above par
D)a discount from par

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The amount of nominal interest added to the real interest rate to compensate the lender for the expected loss in purchasing power that will accompany any inflation is called
A)an inflation premium.
B)par value.
C)a premium above par.
D)a discount from par.
A)an inflation premium.
B)par value.
C)a premium above par.
D)a discount from par.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The __________ is the market interest rate.
A)nominal interest rate
B)inflation-adjusted interest rate
C)real interest rate
D)Both b and c
A)nominal interest rate
B)inflation-adjusted interest rate
C)real interest rate
D)Both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
__________ is the method used to determine the future value of a sum lent today.
A)Discounting
B)Compounding
C)Present value
D)A consol
A)Discounting
B)Compounding
C)Present value
D)A consol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
__________ is the method used to determine the present value of a sum to be received in the future.
A)Discounting
B)Compounding
C)Present value
D)The time value of money
A)Discounting
B)Compounding
C)Present value
D)The time value of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The original amount of funds lent is called the
A)dividend.
B)coupon payment.
C)consol.
D)principal.
A)dividend.
B)coupon payment.
C)consol.
D)principal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The loanable funds theory and the liquidity preference theory can be reconciled by recognizing that
A)a flow over time results in a change in a stock.
B)stock and flow variables are really the same thing.
C)summing stock variables results in the total flow variable.
D)the two theories can not be reconciled.
A)a flow over time results in a change in a stock.
B)stock and flow variables are really the same thing.
C)summing stock variables results in the total flow variable.
D)the two theories can not be reconciled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The supply of loanable funds comes from
A)net borrowers
B)net lenders
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves in the conduct of monetary policy.
D)Both b and c are correct.
A)net borrowers
B)net lenders
C)the Fed in its provision of reserves in the conduct of monetary policy.
D)Both b and c are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The relationship between the willingness to postpone purchases into the future and the reward is which of the following?
A)Direct
B)Inverse
C)Negative
D)Inverse with falling diminishing returns
A)Direct
B)Inverse
C)Negative
D)Inverse with falling diminishing returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Lending in the present enables which of the following?
A)Spending the sum of what is lent minus the interest earned in the future
B)Spending the sum of what is lent plus the interest earned in the present
C)Spending the sum of what is lent plus the interest earned in the future
D)Spending the sum of what is lent minus the interest earned in the future
A)Spending the sum of what is lent minus the interest earned in the future
B)Spending the sum of what is lent plus the interest earned in the present
C)Spending the sum of what is lent plus the interest earned in the future
D)Spending the sum of what is lent minus the interest earned in the future

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Borrowing involves which of he following?
A)Spending today and paying back with interest tomorrow
B)Spending today and paying back without interest tomorrow
C)Spending today and paying back with interest today
D)None of the above
A)Spending today and paying back with interest tomorrow
B)Spending today and paying back without interest tomorrow
C)Spending today and paying back with interest today
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The interest rate is a major influence of
A)consumption in the future.
B)consumption in the present.
C)saving in the present.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)consumption in the future.
B)consumption in the present.
C)saving in the present.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The time value of money is represented by the
A)demand for loanable funds.
B)inflation rate.
C)interest rate.
D)terms of trade.
A)demand for loanable funds.
B)inflation rate.
C)interest rate.
D)terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Ceteris paribus, the phenomenon of a dollar today being worth more than a dollar tomorrow is called which of these terms?
A)time value of money
B)future value
C)present value
D)compounding
A)time value of money
B)future value
C)present value
D)compounding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When trying to determine the future value of money lent today, which method is used?
A)the present-value borrowing formula
B)the present-value lending formula
C)compounding
D)discounting
A)the present-value borrowing formula
B)the present-value lending formula
C)compounding
D)discounting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If you have $10,000 today, which of the following methods should you use to determine what it will be worth in the future, assuming a 10% interest rate?
A)time value of money
B)compounding
C)discounting
D)guessing
A)time value of money
B)compounding
C)discounting
D)guessing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following equations represents the method used to determine present value of a sum of money to be received n years from now in the future?
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + F / (1+i)n
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + F / (1+i)n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following equations represents the method used to determine the future value in n years of a sum that you have today?
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)PB = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + F / (1+i)n
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)PB = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + F / (1+i)n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following equations represents the method used to determine the present value of a bond?
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + $F / (1+i)n
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)I = C/P
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + $F / (1+i)n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following equations represents the method used to determine the present value of a consol?
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)P = C/i
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + $F / (1+i)n
A)V1 = V0 x (1 + i) n
B)P = C/i
C)V0 = Vn / (1 + i)n
D)P = C1 /(1+i)1 + C2/(1+i)2 + . . . Cn / (1+i)n + $F / (1+i)n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If a bank will pay 15% interest compounded annually on a $1,000 deposit today, the depositor will receive how much at the end of 2 years?
A)$1,150.00
B)$1,300.00
C)$1,322.50
D)$1,645.00
A)$1,150.00
B)$1,300.00
C)$1,322.50
D)$1,645.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a bank will pay 7% interest compounded annually on $2,500 deposited today, the depositor will receive how much at the end of 8 years?
A)$3,900.00
B)$3,950.45
C)$4,267.63
D)$4,295.47
A)$3,900.00
B)$3,950.45
C)$4,267.63
D)$4,295.47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Corporate bonds and government bonds share all of the following characteristics except that
A)They both have a face value.
B)They are both issued for a certain number of years.
C)The issuer agrees to make coupon payments.
D)They both pay dividends.
A)They both have a face value.
B)They are both issued for a certain number of years.
C)The issuer agrees to make coupon payments.
D)They both pay dividends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Periodic interest payments over the term to maturity of bonds are called
A)par values.
B)present values.
C)coupon payments.
D)discountings.
A)par values.
B)present values.
C)coupon payments.
D)discountings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following best describes the relationship between bond prices and the interest rate?
A)When the interest rate decreases, the price of the bond decreases.
B)When the interest rate increases, the price of the bond increases.
C)When the interest rate increases, the price of the bond decreases.
D)Both a and b
A)When the interest rate decreases, the price of the bond decreases.
B)When the interest rate increases, the price of the bond increases.
C)When the interest rate increases, the price of the bond decreases.
D)Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In general, if bond prices are rising, then interest rates are
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In general, if interest rates are rising, then bond prices are
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.
A)rising.
B)falling.
C)unchanging.
D)rising slightly, then stabilizing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The relationship between GDP and the demand for funds is
A)negative.
B)direct.
C)indifferent.
D)inverse.
A)negative.
B)direct.
C)indifferent.
D)inverse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Typically the quantity demanded of loanable funds and the interest rate are __________related.
A)directly
B)inversely
C)positively
D)unrelated
A)directly
B)inversely
C)positively
D)unrelated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The interest rate corrected for changes in the purchasing power of money is called the
A)nominal interest rate.
B)real interest rate.
C)discount rate.
D)prime lending rate.
A)nominal interest rate.
B)real interest rate.
C)discount rate.
D)prime lending rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



