Deck 42: Consumer Spending and Labor Income
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 42: Consumer Spending and Labor Income
1
Whats defention of terms:
-average propensity to consume
-average propensity to consume
the proportion of income spent for consumption
2
Whats defention of terms:
-average propensity to save
-average propensity to save
the proportion of savings to income
3
Whats defention of terms:
-consumption function
-consumption function
Keynesian schedule of aggregate consumer spending at different income levels; as income increases consumption increases by some fraction
4
Whats defention of terms:
-dis-saving
-dis-saving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Whats defention of terms:
-marginal propensity to consume
-marginal propensity to consume

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Whats defention of terms:
-marginal propensity to save
-marginal propensity to save

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Whats defention of terms:
-savings
-savings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explain how consumption has grown over the long run.
-Even though labor income stagnated after 1970, consumer spending rose. Explain.
-Even though labor income stagnated after 1970, consumer spending rose. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Explain how consumption has grown over the long run.
-How does wealth and debt affect spending?
-How does wealth and debt affect spending?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe how consumption behaves over the business cycle.
-Define average propensity to consume, average propensity to save, marginal propensity to consume, marginal propensity to save.
-Define average propensity to consume, average propensity to save, marginal propensity to consume, marginal propensity to save.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Describe how consumption behaves over the business cycle.
-Why does a decline in the labor share cause a decline in the propensity to consume for the average of all consumers?
-Why does a decline in the labor share cause a decline in the propensity to consume for the average of all consumers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Describe how consumption behaves over the business cycle.
-Why does the labor share decline as economic expansion continues?
-Why does the labor share decline as economic expansion continues?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Describe how consumption behaves over the business cycle.
-Why does the ratio of consumer debt to income rise during the average expansion?
-Why does the ratio of consumer debt to income rise during the average expansion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Compare and discuss determinants of aggregate consumption.
-Why do people purchase less if they have less wealth, even if their income remains constant?
-Why do people purchase less if they have less wealth, even if their income remains constant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Compare and discuss determinants of aggregate consumption.
-How does aggregate consumption behave over the business cycle?
-How does aggregate consumption behave over the business cycle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Keynes believed that consumer demand in the aggregate is determined primarily by
A) the interest rate.
B) the rate of inflation.
C) national income.
D) government spending.
A) the interest rate.
B) the rate of inflation.
C) national income.
D) government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
At very low levels of income, consumer spending is likely to
A) be less than income
B) be greater than income
C) be the same as income
D) be the same as savings.
A) be less than income
B) be greater than income
C) be the same as income
D) be the same as savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The term, "dis-saving" means
A) having no respect for savings.
B) drawing money out of savings.
C) putting money into savings.
D) not saving at all.
A) having no respect for savings.
B) drawing money out of savings.
C) putting money into savings.
D) not saving at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Those who currently have no savings and have no income
A) are unable to consume.
B) will go into debt in order to consume.
C) have a zero marginal propensity to consume.
D) will increase their level of savings.
A) are unable to consume.
B) will go into debt in order to consume.
C) have a zero marginal propensity to consume.
D) will increase their level of savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The wealthy tend to have
A) higher average propensities to consume
B) higher average propensities to save.
C) lower average propensities to save.
D) the same average propensity to consume as less wealth persons.
A) higher average propensities to consume
B) higher average propensities to save.
C) lower average propensities to save.
D) the same average propensity to consume as less wealth persons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A shift in income distribution from wealthy individuals to poor individuals is likely to
A) increase consumer debt.
B) increase the national propensity to consume.
C) leave the national propensity to consume unchanged.
D) decrease the national propensity to consume.
A) increase consumer debt.
B) increase the national propensity to consume.
C) leave the national propensity to consume unchanged.
D) decrease the national propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In an economic expansion, the average ratio of consumption to income (APC)
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) could either increase or decrease.
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) could either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the definition of the term, "labor share?"
A) it is the share of labor costs in a firm's total costs.
B) it is the share of labor income in national income.
C) it is the share of federal taxes paid by employees rather than by capitalists.
D) It is the share in total business revenues that employees receive.
A) it is the share of labor costs in a firm's total costs.
B) it is the share of labor income in national income.
C) it is the share of federal taxes paid by employees rather than by capitalists.
D) It is the share in total business revenues that employees receive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consumer debt as a percentage of national income in the cycle 1991 to 2001 was approximately
A) 22%
B) 52%
C) 72%
D) 92%
A) 22%
B) 52%
C) 72%
D) 92%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the wealth effect?
A) the tendency for many individuals to copy the consumption patterns of the wealthy.
B) the tendency for increases in wealth to lead to increases in savings.
C) the tendency for increases in wealth to lead to increases in consumption.
D) the tendency for the wealthy to willingly share their good fortune with the less well off.
A) the tendency for many individuals to copy the consumption patterns of the wealthy.
B) the tendency for increases in wealth to lead to increases in savings.
C) the tendency for increases in wealth to lead to increases in consumption.
D) the tendency for the wealthy to willingly share their good fortune with the less well off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Assume that Sam has $2000 in savings and a car worth about $10,000. He owes $9,000 on his car and $3000 on his credit card. What is Sam's wealth?
A) $2,000
B) $12,000
C) 0
D) -$1,000
A) $2,000
B) $12,000
C) 0
D) -$1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Brad and Angie own a nice house worth $400,000. They have 2 cars worth $20,000 each, and $5,000 in the bank. They recently borrowed $100,000 on their house in order to send their daughter, Jennifer, to college. They also gave Jennifer a credit card for her expenses, and the balance is now $10,000. How much wealth do Brad and Angie have?
A) $330,000
B) $445,000
C) $110,000
D) $525,000
A) $330,000
B) $445,000
C) $110,000
D) $525,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why consumers tend to purchase less if they have less wealth (or more debt), even if their income remains constant?
A) consumers are irrational.
B) consumers may feel richer, so they increase their savings in order to emulate the wealthy.
C) consumers may feel poorer, so they want to increase their savings.
D) consumers may already have bought all they want.
A) consumers are irrational.
B) consumers may feel richer, so they increase their savings in order to emulate the wealthy.
C) consumers may feel poorer, so they want to increase their savings.
D) consumers may already have bought all they want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Diagram 42a
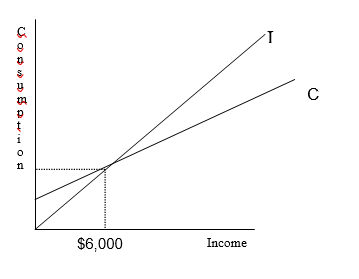
-Diagram 42a indicates that
A) consumption increases faster than income.
B) income is always less than consumption.
C) consumption is always less than income.
D) income increases faster than consumption.

-Diagram 42a indicates that
A) consumption increases faster than income.
B) income is always less than consumption.
C) consumption is always less than income.
D) income increases faster than consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Diagram 42a

-Diagram 42a indicates that
A) consumption is unrelated to income.
B) consumption is positively related to income.
C) consumption is inversely related to income.
D) consumption is constant.

-Diagram 42a indicates that
A) consumption is unrelated to income.
B) consumption is positively related to income.
C) consumption is inversely related to income.
D) consumption is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Diagram 42a

-Diagram 42a indicates that when income is greater than $6,000
A) consumers are spending more than income.
B) consumers are not spending.
C) consumers are spending less than income.
D) consumers are spending exactly all of their income.

-Diagram 42a indicates that when income is greater than $6,000
A) consumers are spending more than income.
B) consumers are not spending.
C) consumers are spending less than income.
D) consumers are spending exactly all of their income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



