Deck 35: Government Spending, Taxes, and Fiscal Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/178
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Government Spending, Taxes, and Fiscal Policy
1
Social insurance is provided by:
A)the government.
B)households.
C)foreign investors.
D)businesses.
A)the government.
B)households.
C)foreign investors.
D)businesses.
A
2
Social insurance is:
A)privately purchased car and home insurance.
B)government military spending.
C)government borrowing to ensure that expansionary fiscal policy plans are met.
D)government provided insurance against bad outcomes, such as unemployment and disability.
A)privately purchased car and home insurance.
B)government military spending.
C)government borrowing to ensure that expansionary fiscal policy plans are met.
D)government provided insurance against bad outcomes, such as unemployment and disability.
D
3
The Philippines government provides retirement benefits, unemployment benefits, maternity leave benefits, death and funeral benefits, and other benefits. These are examples of:
A)taxes.
B)social insurance.
C)consumption.
D)items that count toward GDP.
A)taxes.
B)social insurance.
C)consumption.
D)items that count toward GDP.
B
4
Consider this data on the 2017 state budget for Alabama. What were the two largest components of state expenditure in 2017?
A)education and public welfare
B)highways and hospitals
C)insurance trust expenditure and public welfare
D)education and hospitals
A)education and public welfare
B)highways and hospitals
C)insurance trust expenditure and public welfare
D)education and hospitals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In Canada, all the provinces provide health care to all citizens and permanent residents. This is an example of:
A)taxes.
B)crowding out.
C)social insurance.
D)an item that counts toward GDP.
A)taxes.
B)crowding out.
C)social insurance.
D)an item that counts toward GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the United States, the largest components of federal government spending are:
A)social security, unemployment, and labor.
B)state expenditures and housing.
C)military spending and science.
D)Medicare and health.
A)social security, unemployment, and labor.
B)state expenditures and housing.
C)military spending and science.
D)Medicare and health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following services are provided by local government?
A)Medicare
B)military defense
C)bus services
D)Pell grants
A)Medicare
B)military defense
C)bus services
D)Pell grants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following services are provided by the federal government?
A)sewer services
B)military defense
C)bus services
D)trash and recycling
A)sewer services
B)military defense
C)bus services
D)trash and recycling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following services are provided by the local government?
A)Medicaid
B)military defense
C)Medicare
D)trash and recycling
A)Medicaid
B)military defense
C)Medicare
D)trash and recycling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following services are provided by the federal government?
A)Medicare
B)sewer services
C)town firefighters
D)trash and recycling
A)Medicare
B)sewer services
C)town firefighters
D)trash and recycling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The New Deal was created to counter the effects from:
A)hyperinflation.
B)the OPEC oil crisis.
C)the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009.
D)the Great Depression.
A)hyperinflation.
B)the OPEC oil crisis.
C)the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009.
D)the Great Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following did the New Deal create?
A)military defense spending
B)the Securities and Exchange Commission
C)fiscal policy
D)monetary policy
A)military defense spending
B)the Securities and Exchange Commission
C)fiscal policy
D)monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following did the New Deal create?
A)unemployment benefits
B)the stock exchange
C)tariffs
D)quotas
A)unemployment benefits
B)the stock exchange
C)tariffs
D)quotas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following did the New Deal create?
A)monetary policy
B)the stock exchange
C)Social Security
D)fiscal policy
A)monetary policy
B)the stock exchange
C)Social Security
D)fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following graph. Why did government spending rise during the 2007 to 2009 period?

A)It increased due to the use of monetary policy to boost the economy during the Great Recession.
B)It increased due to the introduction of Social Security in the United States.
C)It increased due to the increase in population in the United States.
D)It increased due to the use of expansionary fiscal policy and increased social insurance payments during the Great Recession.

A)It increased due to the use of monetary policy to boost the economy during the Great Recession.
B)It increased due to the introduction of Social Security in the United States.
C)It increased due to the increase in population in the United States.
D)It increased due to the use of expansionary fiscal policy and increased social insurance payments during the Great Recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following graph. One of the reasons that government spending rose during the 2007 to 2009 period was the introduction of:
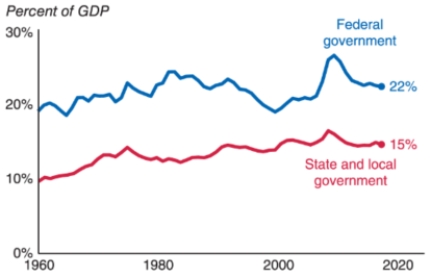
A)the Securities and Exchange Commission.
B)Social Security.
C)Medicaid.
D)the Affordable Care Act.

A)the Securities and Exchange Commission.
B)Social Security.
C)Medicaid.
D)the Affordable Care Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Medicare provides health care to:
A)people who earn $250,000 a year or more.
B)people over the age of 65.
C)foreign visitors to the United States.
D)high-income people who already have health care coverage through their workplaces.
A)people who earn $250,000 a year or more.
B)people over the age of 65.
C)foreign visitors to the United States.
D)high-income people who already have health care coverage through their workplaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mandatory spending is spending that:
A)supports programs that do not get determined annually but instead are set in law.
B)is appropriated by Congress annually.
C)includes all federal government spending.
D)includes all state and local government spending.
A)supports programs that do not get determined annually but instead are set in law.
B)is appropriated by Congress annually.
C)includes all federal government spending.
D)includes all state and local government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Discretionary spending is spending that:
A)supports programs that do not get determined annually but instead are set in law.
B)is appropriated by Congress annually.
C)includes all federal government spending.
D)includes all state and local government spending.
A)supports programs that do not get determined annually but instead are set in law.
B)is appropriated by Congress annually.
C)includes all federal government spending.
D)includes all state and local government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Food stamps are an example of:
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Affordable Care Act is an example of:
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If Congress decides to increase military spending, this is an example of:
A)health care spending.
B)Social Security.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.
A)health care spending.
B)Social Security.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Social Security is an example of:
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.
A)health care spending.
B)military defense spending.
C)mandatory spending.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Social Security is an example of:
A)health care spending.
B)an entitlement program.
C)income tax.
D)discretionary spending.
A)health care spending.
B)an entitlement program.
C)income tax.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In 1913, the sixteenth amendment gave Congress the power to:
A)create Social Security.
B)create the Securities and Exchange Commission.
C)levy an income tax.
D)create the New Deal.
A)create Social Security.
B)create the Securities and Exchange Commission.
C)levy an income tax.
D)create the New Deal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Earned income refers to:
A)all income.
B)wages from an employer or net earnings from self-employment.
C)retirement funds saved over time.
D)gross domestic product.
A)all income.
B)wages from an employer or net earnings from self-employment.
C)retirement funds saved over time.
D)gross domestic product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Income taxes are taxes assessed on:
A)health care contributions.
B)earned income.
C)retirement funds.
D)all income.
A)health care contributions.
B)earned income.
C)retirement funds.
D)all income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Payroll taxes are taxes assessed on:
A)health care contributions.
B)earned income.
C)retirement funds.
D)all income.
A)health care contributions.
B)earned income.
C)retirement funds.
D)all income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. If your employer owes you $1,000, how much will you get after these deductions?
A)$62
B)$29
C)$91
D)$909
A)$62
B)$29
C)$91
D)$909

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Your employer owes you $1,000. How much will your work cost your employer?
A)$91
B)$1,000
C)$1,091
D)$1,009
A)$91
B)$1,000
C)$1,091
D)$1,009

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. If your employer owes you $850, how much will you get after these deductions?
A)$77.35
B)$772.65
C)$52.70
D)$24.65
A)$77.35
B)$772.65
C)$52.70
D)$24.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Your employer owes you $850. How much will your work cost your employer?
A)$927.35
B)$77.35
C)$52.70
D)$24.65
A)$927.35
B)$77.35
C)$52.70
D)$24.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. If your employer owes you $665, approximately how much will you get after these deductions?
A)$19.29
B)$41.23
C)$60.52
D)$604.49
A)$19.29
B)$41.23
C)$60.52
D)$604.49

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Your employer owes you $665. How much will your work cost your employer?
A)$725.52
B)$41.23
C)$60.52
D)$604.48
A)$725.52
B)$41.23
C)$60.52
D)$604.48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
With a progressive tax, those with _____ income tend to pay a _____.
A)more; higher share of their income in taxes
B)more; lower share of their income in taxes
C)less; higher share of their income in taxes
D)more; flat tax rate
A)more; higher share of their income in taxes
B)more; lower share of their income in taxes
C)less; higher share of their income in taxes
D)more; flat tax rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Income taxes are assessed only on earned income.
B)Payroll taxes are assessed on all income earned.
C)Taxable income is less than income earned because of deductions.
D)Taxable income is greater than income earned because of negative taxes.
A)Income taxes are assessed only on earned income.
B)Payroll taxes are assessed on all income earned.
C)Taxable income is less than income earned because of deductions.
D)Taxable income is greater than income earned because of negative taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Taxable income is the:
A)tax on social security.
B)amount of your income that you pay taxes on.
C)amount of tax rebates that you receive at the end of the year.
D)tax rate you pay if you earn another dollar.
A)tax on social security.
B)amount of your income that you pay taxes on.
C)amount of tax rebates that you receive at the end of the year.
D)tax rate you pay if you earn another dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The marginal tax rate is the:
A)tax on social security.
B)amount of your income that you pay taxes on.
C)amount of tax rebates that you receive at the end of the year.
D)tax rate you pay if you earn another dollar.
A)tax on social security.
B)amount of your income that you pay taxes on.
C)amount of tax rebates that you receive at the end of the year.
D)tax rate you pay if you earn another dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The standard deduction is $12,200 for a single person. Suppose you file as a single person, and your current income is $12,200. This means that your taxable income is:
A)$24,400.
B)$5,000.
C)$12,200.
D)$0.
A)$24,400.
B)$5,000.
C)$12,200.
D)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The standard deduction is $12,200 for a single person. Suppose you file as a single person, and your current income is $35,000. This means that your taxable income is:
A)$35,000.
B)$10,000.
C)$22,800.
D)$47,200.
A)$35,000.
B)$10,000.
C)$22,800.
D)$47,200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The standard deduction is $12,200 for a single person. Suppose you file as a single person and your current income is $22,500. This means that your taxable income is:
A)$10,300.
B)$32,800.
C)$22,500.
D)$12,200.
A)$10,300.
B)$32,800.
C)$22,500.
D)$12,200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $22,000, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A)$2,446
B)$982
C)$2,640
D)$970
A)$2,446
B)$982
C)$2,640
D)$970

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $47,000, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A)$4,176
B)$3,012
C)$10,340
D)$3,982
A)$4,176
B)$3,012
C)$10,340
D)$3,982

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $131,000, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A)$9,840
B)$31,440
C)$25,584
D)$22,687
A)$9,840
B)$31,440
C)$25,584
D)$22,687

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $72,000, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A)$22,171
B)$13,156
C)$9,015
D)$15,840
A)$22,171
B)$13,156
C)$9,015
D)$15,840

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $84,200, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A)$11,699
B)$13,156
C)$15,840
D)$18,524
A)$11,699
B)$13,156
C)$15,840
D)$18,524

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In your current job, you earn $55,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $5,000. Given your current taxable income, what is your marginal tax rate?
A)22%
B)12%
C)10%
D)24%
A)22%
B)12%
C)10%
D)24%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In your current job, you earn $55,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $5,000. How much extra will you owe in federal income taxes if you take the new job?
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$500
D)$600
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$500
D)$600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In your current job, you earn $55,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $5,000. Social Security taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. How much extra will you owe in payroll taxes if you take the new job?
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$455
D)$310
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$455
D)$310

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In your current job, you earn $55,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $5,000. Social Security taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Assuming no state and local taxes, when federal income taxes and payroll taxes are deducted, how much of the $5,000 do you get?
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$455
D)$3,445
A)$2,200
B)$1,100
C)$455
D)$3,445

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In your current job, you earn $41,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $6,500. Given your current taxable income, what is your marginal tax rate?
A)22%
B)12%
C)10%
D)24%
A)22%
B)12%
C)10%
D)24%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In your current job, you earn $41,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $6,500. How much extra will you owe in federal income taxes if you take the new job?
A)$780
B)$650
C)$1,430
D)$9,020
A)$780
B)$650
C)$1,430
D)$9,020

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In your current job, you earn $41,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $6,500. Social Security taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. How much extra will you owe in payroll taxes if you take the new job?
A)$403
B)$1,372
C)$592
D)$189
A)$403
B)$1,372
C)$592
D)$189

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In your current job, you earn $41,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $6,500. Social Security taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Assuming no state and local taxes, when federal income taxes and payroll taxes are deducted, about how much of the $6,500 do you get?
A)$403
B)$1,372
C)$592
D)$5,128
A)$403
B)$1,372
C)$592
D)$5,128

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is a reason to worry about government debt?
A)Most of the debt is domestic debt.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)The government never really needs to repay the debt.
D)High and rising debt slows economic growth.
A)Most of the debt is domestic debt.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)The government never really needs to repay the debt.
D)High and rising debt slows economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is a reason to worry about government debt?
A)A debt crisis becomes more likely.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)The government never really needs to repay the debt.
D)Most of the debt is owed by Americans to Americans.
A)A debt crisis becomes more likely.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)The government never really needs to repay the debt.
D)Most of the debt is owed by Americans to Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a reason NOT to worry about government debt?
A)A debt crisis is likely if debt becomes too large relative to GDP.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)Governments never default on sovereign debt.
D)Debt owed to foreign nations can be written off.
A)A debt crisis is likely if debt becomes too large relative to GDP.
B)Future generations can help repay the debt.
C)Governments never default on sovereign debt.
D)Debt owed to foreign nations can be written off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In late 2001, Argentina defaulted on more than $90 billion worth of its external debt. This is an example of:
A)a debt crisis.
B)net capital inflow.
C)crowding out.
D)discretionary spending.
A)a debt crisis.
B)net capital inflow.
C)crowding out.
D)discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
During the economic downturn of the 1970s, lenders to Latin American countries raised interest rates. This caused Latin American debt to balloon, and these countries were unable to pay their debts. This is an example of:
A)the interaction between monetary policy and fiscal policy.
B)an automatic stabilizer.
C)crowding out.
D)a debt crisis.
A)the interaction between monetary policy and fiscal policy.
B)an automatic stabilizer.
C)crowding out.
D)a debt crisis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A debt crisis occurs when:
A)consumers spend too much on credit cards.
B)bond markets weaken.
C)a government cannot repay its loans.
D)interest rates rise.
A)consumers spend too much on credit cards.
B)bond markets weaken.
C)a government cannot repay its loans.
D)interest rates rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How can high government debt lead to slow economic growth in the future?
(i) Stock markets will weaken.
(ii) Governments may find it hard to fund other spending such as infrastructure projects.
(iii) Governments may increase future taxes to pay interest payments on rising debt.
(iv) Governments borrow funds that might otherwise have been used for investment.
A)(i) only
B)(ii), (iii), and (iv)
C)(iii) and (iv)
D)(iv) only
(i) Stock markets will weaken.
(ii) Governments may find it hard to fund other spending such as infrastructure projects.
(iii) Governments may increase future taxes to pay interest payments on rising debt.
(iv) Governments borrow funds that might otherwise have been used for investment.
A)(i) only
B)(ii), (iii), and (iv)
C)(iii) and (iv)
D)(iv) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A sales tax is a tax on:
A)income earned.
B)imports.
C)purchases that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)inputs used in the production of goods and services.
A)income earned.
B)imports.
C)purchases that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)inputs used in the production of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An excise tax is a tax on:
A)luxury goods and services.
B)imports.
C)purchases that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)a specific product.
A)luxury goods and services.
B)imports.
C)purchases that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)a specific product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If an item costs $50 in Connecticut and the sales tax is 6.35%, you will pay a total of $_____ at the register.
A)$53.18
B)$3.18
C)$6.35
D)$46.82
A)$53.18
B)$3.18
C)$6.35
D)$46.82

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If an item costs $95 in California and the sales tax is 7.25%, you will pay a total of $_____ at the register.
A)$101.89
B)$88.11
C)$7.25
D)$6.89
A)$101.89
B)$88.11
C)$7.25
D)$6.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the province of Ontario, consumers pay harmonized sales tax (HST) of 13%. If an item costs $179 in Ontario, you will pay a total of $_____ at the register.
A)$13
B)$202.27
C)$23.27
D)$155.73
A)$13
B)$202.27
C)$23.27
D)$155.73

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Property tax is a tax:
A)on luxury goods and services.
B)on a specific product.
C)that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)on the value of property.
A)on luxury goods and services.
B)on a specific product.
C)that is typically a percentage of the purchase price of goods and services.
D)on the value of property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is a regressive tax?
A)Those with more income tend to pay a higher share of their income in taxes.
B)Those with low incomes pay no taxes.
C)Those with less income tend to pay a higher share of their income in taxes.
D)Those with more income tend to pay a flat tax rate.
A)Those with more income tend to pay a higher share of their income in taxes.
B)Those with low incomes pay no taxes.
C)Those with less income tend to pay a higher share of their income in taxes.
D)Those with more income tend to pay a flat tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Tax expenditures are:
A)purchases made from disposable income.
B)special deductions, credits, or exemptions that lower your tax obligations.
C)consumer expenditures on taxes.
D)payroll taxes.
A)purchases made from disposable income.
B)special deductions, credits, or exemptions that lower your tax obligations.
C)consumer expenditures on taxes.
D)payroll taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The promise to pay Social Security benefits to baby boomers is an example of _____ of the U.S. government.
A)unfunded liabilities
B)unfunded liabilities
C)monetary policy
D)monetary policy
E)automatic stabilizers
F)automatic stabilizers
G)budget surpluses
H)budget surpluses
A)unfunded liabilities
B)unfunded liabilities
C)monetary policy
D)monetary policy
E)automatic stabilizers
F)automatic stabilizers
G)budget surpluses
H)budget surpluses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
On which of the following is there a tax incentive in the United States?
(i) health insurance purchased through employers
(ii) your mortgage
(iii) rental value on owner-occupied housing
(iv) contributions toward your retirement account
A)(i), (iii), and (iv)
B)(iii) and (iv)
C)(iv) only
D)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(i) health insurance purchased through employers
(ii) your mortgage
(iii) rental value on owner-occupied housing
(iv) contributions toward your retirement account
A)(i), (iii), and (iv)
B)(iii) and (iv)
C)(iv) only
D)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose a high-income person, a middle-income person, and a low-income person purchase identical houses that are financed by similar mortgages. Who gets the largest tax benefit?
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all pay the same tax rate.
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all pay the same tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose a high-income person, a middle-income person, and a low-income person purchase identical houses that are financed by similar mortgages. Who gets the lowest tax benefit?
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all pay the same tax rate.
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all pay the same tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose a high-income person, a middle-income person, and a low-income person all purchase identical houses that are financed by similar mortgages. Who spends the most on tax-preferred goods?
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all spend the same on tax-preferred goods.
A)the high-income person
B)the middle-income person
C)the low-income person
D)They all spend the same on tax-preferred goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Why don't most tax expenditures help much if your federal tax bill is zero?
A)Taxes are an automatic stabilizer.
B)Most tax expenditures are specifically for high-income people.
C)You don't qualify for tax breaks if your federal tax bill is zero.
D)Most tax breaks reduce taxable income, but reducing taxable income below zero does not reduce the tax bill.
A)Taxes are an automatic stabilizer.
B)Most tax expenditures are specifically for high-income people.
C)You don't qualify for tax breaks if your federal tax bill is zero.
D)Most tax breaks reduce taxable income, but reducing taxable income below zero does not reduce the tax bill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a government is using fiscal policy, this means that it is using _____ and _____ to attempt to stabilize the economy.
A)spending; interbank loans
B)interest rates; tax policies
C)spending; tax policies
D)bonds; stock markets
A)spending; interbank loans
B)interest rates; tax policies
C)spending; tax policies
D)bonds; stock markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In order to boost output, the federal government engages in _____ fiscal policy, which _____ government spending and _____ taxes.
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; lowers; raises
D)contractionary; raises; lowers
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; lowers; raises
D)contractionary; raises; lowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In order to lower output, the federal government engages in _____ fiscal policy, which _____ government spending and _____ taxes.
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; lowers; raises
D)contractionary; raises; lowers
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; lowers; raises
D)contractionary; raises; lowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In response to an overheating economy, the federal government engages in _____ fiscal policy, which _____ government spending and _____ taxes.
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; raises; lowers
D)contractionary; lowers; raises
A)expansionary; lowers; raises
B)expansionary; raises; lowers
C)contractionary; raises; lowers
D)contractionary; lowers; raises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
_____ income taxes and payroll taxes _____ after-tax incomes, which _____ consumption and therefore raise aggregate expenditure.
A)Lower; raise; increase
B)Lower; lower; increase
C)Higher; raise; increase
D)Higher; lower; increase
A)Lower; raise; increase
B)Lower; lower; increase
C)Higher; raise; increase
D)Higher; lower; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 178 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



