Deck 14: Market Structure and Market Power
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/216
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Market Structure and Market Power
1
A firm's ability to raise its product price without losing many customers to competing businesses is known as
A)market power.
B)competitive power.
C)marginal revenue.
D)revenue dependability.
A)market power.
B)competitive power.
C)marginal revenue.
D)revenue dependability.
A
2
The market power of a firm is its
A)ranking based on units sold compared to other firms selling the same product.
B)ability to cause other firms in its market to drop out of the market.
C)ability to raise its price without losing many of its customers to competing businesses.
D)market share based on the percentage of total market revenue.
A)ranking based on units sold compared to other firms selling the same product.
B)ability to cause other firms in its market to drop out of the market.
C)ability to raise its price without losing many of its customers to competing businesses.
D)market share based on the percentage of total market revenue.
C
3
What is the relationship between a company's market power and the price that the company's owner can charge for its product?
A)The lower the market power, the lower the price the firm can charge before losing customers.
B)The lower the market power, the higher the price the firm can charge without losing many customers.
C)The greater the market power, the higher the price the firm can charge without losing many customers.
D)The greater the market power, the lower the price the firm must charge to avoid losing many customers.
A)The lower the market power, the lower the price the firm can charge before losing customers.
B)The lower the market power, the higher the price the firm can charge without losing many customers.
C)The greater the market power, the higher the price the firm can charge without losing many customers.
D)The greater the market power, the lower the price the firm must charge to avoid losing many customers.
C
4
What type of relationship exists between the level of a company's market power and the price that its owner is able to charge for its product?
A)circular
B)positive
C)negative
D)opposing
A)circular
B)positive
C)negative
D)opposing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In which of the following situations would Max's Doughnut Shop have the greatest market power?
A)Within three miles, there are five other doughnut shops and three bakeries that sell breakfast pastries.
B)There are two rival doughnut shops within three miles but no other bakeries.
C)The closest doughnut shop is 10 miles away, but there is a bakery with breakfast pastries two miles away.
D)The closest doughnut shop or bakery is 25 miles away from Max's shop.
A)Within three miles, there are five other doughnut shops and three bakeries that sell breakfast pastries.
B)There are two rival doughnut shops within three miles but no other bakeries.
C)The closest doughnut shop is 10 miles away, but there is a bakery with breakfast pastries two miles away.
D)The closest doughnut shop or bakery is 25 miles away from Max's shop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which of the following situations would Maria's Doughnut Shop have the LEAST market power?
A)Within three miles, there are five other doughnut shops and three bakeries that sell breakfast pastries.
B)There are two rival doughnut shops within three miles but no other bakeries.
C)The closest doughnut shop is 10 miles away, but there is a bakery with breakfast pastries two miles away.
D)The closest doughnut shop or bakery is 25 miles away from Maria's shop.
A)Within three miles, there are five other doughnut shops and three bakeries that sell breakfast pastries.
B)There are two rival doughnut shops within three miles but no other bakeries.
C)The closest doughnut shop is 10 miles away, but there is a bakery with breakfast pastries two miles away.
D)The closest doughnut shop or bakery is 25 miles away from Maria's shop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following conditions is NOT present in perfect competition?
A)All companies in the market sell identical goods.
B)All companies in the market sell a small share of the total market output.
C)There are many buyers and sellers in the market.
D)The product price varies across the companies in the market.
A)All companies in the market sell identical goods.
B)All companies in the market sell a small share of the total market output.
C)There are many buyers and sellers in the market.
D)The product price varies across the companies in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following conditions is present for all sellers in a perfectly competitive market?
A)All sellers have an equal and high level of market power.
B)The product price varies across the sellers.
C)The number of sellers is small.
D)All sellers are selling identical products.
A)All sellers have an equal and high level of market power.
B)The product price varies across the sellers.
C)The number of sellers is small.
D)All sellers are selling identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A price-taker is a seller that:
A)keeps taking an increasing share of market sales in its market.
B)sets its price based on the cost of inputs plus an allowance for profit.
C)takes all available information into consideration in deciding how much to charge above or below the current market price.
D)charges the current market price for its product.
A)keeps taking an increasing share of market sales in its market.
B)sets its price based on the cost of inputs plus an allowance for profit.
C)takes all available information into consideration in deciding how much to charge above or below the current market price.
D)charges the current market price for its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What level of market power exists for sellers in a perfectly competitive market?
A)The level of market power varies widely across the sellers in the market.
B)All sellers have an equal and high level of market power.
C)All sellers lack market power.
D)The largest seller in the market holds all market power.
A)The level of market power varies widely across the sellers in the market.
B)All sellers have an equal and high level of market power.
C)All sellers lack market power.
D)The largest seller in the market holds all market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following markets is an example of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Fast-food hamburgers
B)Shares of McDonald's stock
C)Dining chairs
D)Apple computers
A)Fast-food hamburgers
B)Shares of McDonald's stock
C)Dining chairs
D)Apple computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The market structure of _____ is rare because _____ and _____.
A)monopoly; most goods are not identical; most markets have some dominant firms
B)monopoly; most firms advertise; most markets have many firms
C)perfect competition; most goods are not identical; most markets have some dominant firms
D)perfect competition; most firms advertise; most markets have many firms
A)monopoly; most goods are not identical; most markets have some dominant firms
B)monopoly; most firms advertise; most markets have many firms
C)perfect competition; most goods are not identical; most markets have some dominant firms
D)perfect competition; most firms advertise; most markets have many firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Perfectly competitive markets are rare because most
A)firms advertise and most markets have many firms.
B)goods are not identical and most markets have many firms.
C)firms advertise and most markets have many buyers.
D)goods are not identical and most markets have some dominant firms.
A)firms advertise and most markets have many firms.
B)goods are not identical and most markets have many firms.
C)firms advertise and most markets have many buyers.
D)goods are not identical and most markets have some dominant firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A product market has many buyers and many sellers, and its largest company produces 1% of the market output. In addition, all sellers produce identical goods. What market structure is consistent with this description?
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Monopolistic competition
D)Oligopoly
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Monopolistic competition
D)Oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a company has market power, it is _____ in its market.
A)one of many small companies
B)not a price-taker
C)a producer of nondifferentiated products
D)not able to impact the market equilibrium price
A)one of many small companies
B)not a price-taker
C)a producer of nondifferentiated products
D)not able to impact the market equilibrium price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Sellers are price-takers.
B)There are some dominant sellers.
C)There are only a few sellers in the market.
D)The product varies across the sellers.
A)Sellers are price-takers.
B)There are some dominant sellers.
C)There are only a few sellers in the market.
D)The product varies across the sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements about market power is TRUE?
A)All sellers that have market power will have equal market power.
B)Markets can have power, but sellers cannot have market power.
C)The extent of market power held by a seller can vary along a spectrum from none to a high level.
D)There are two types of sellers, those with no market power and those with complete market power.
A)All sellers that have market power will have equal market power.
B)Markets can have power, but sellers cannot have market power.
C)The extent of market power held by a seller can vary along a spectrum from none to a high level.
D)There are two types of sellers, those with no market power and those with complete market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An intense struggle to gain market share is a distinguishing characteristic of what type of market?
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Oligopoly
D)Monopolistic competition
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Oligopoly
D)Monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a characteristic of monopoly that is not present in other market structures?
A)There are many buyers.
B)The product is identical across all sellers.
C)Sellers are price-takers.
D)There is only one seller.
A)There are many buyers.
B)The product is identical across all sellers.
C)Sellers are price-takers.
D)There is only one seller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A product market has only one seller, and that seller has a high level of market power. There are no close substitutes for the product. What type of market is this?
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Oligopoly
D)Monopolistic competition
A)Perfect competition
B)Monopoly
C)Oligopoly
D)Monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A company is the only one producing its type of product. The company's owner is able to set price at the most profitable level. This company is in what type of market?
A)Oligopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Monopoly
D)Perfect competition
A)Oligopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Monopoly
D)Perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When a seller has a high level of market power, the seller
A)produces a product that is identical to the output of other companies in the market.
B)is in a market with growing demand.
C)is one of many sellers selling in its market.
D)can raise its price without losing many customers.
A)produces a product that is identical to the output of other companies in the market.
B)is in a market with growing demand.
C)is one of many sellers selling in its market.
D)can raise its price without losing many customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A characteristic of monopoly that is not present in any other market structure is that
A)no firm in the market has a high level of market power.
B)each firm strives to differentiate its product from others in the market.
C)there is only one seller.
D)the product is identical across the many firms selling in the market.
A)no firm in the market has a high level of market power.
B)each firm strives to differentiate its product from others in the market.
C)there is only one seller.
D)the product is identical across the many firms selling in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A characteristic of oligopoly that is not present in any other market structure is that there
A)is only one seller and that seller has a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers with considerable market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.
A)is only one seller and that seller has a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers with considerable market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A certain city has four hospitals, and there are no other hospitals within 200 miles. Two of the hospitals are more specialized than the other two because one has a large cardiac unit and the other has a specialized cancer-treatment center. The local market for hospital services is what type of market?
A)Monopoly
B)Oligopoly
C)Perfect competition
D)Monopolistic competition
A)Monopoly
B)Oligopoly
C)Perfect competition
D)Monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A characteristic of oligopoly that is not present in other market structures is that there
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces a differentiated version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers and they have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces a differentiated version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers and they have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A characteristic of monopolistic competition that is not present in any other market structure is that there
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers who have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers who have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A characteristic of perfect competition that is not present in any other market structure is that there
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers and at least a few of them have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.
A)is only one seller and that seller holds a high level of market power.
B)are many sellers and each produces its own version of the product.
C)are a small number of sellers and at least a few of them have market power.
D)are many sellers that produce identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In an oligopolistic market, the impact on a seller of the _____ is greater than in other types of market structures.
A)actions of other market sellers
B)total number of buyers in the market
C)fact that all sellers produce identical products
D)lack of rival sellers
A)actions of other market sellers
B)total number of buyers in the market
C)fact that all sellers produce identical products
D)lack of rival sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A market with a large number of sellers and a high level of product differentiation is known as
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In a market, when a company's owner tries to make its product slightly different from the output of other companies so that it is more attractive to buyers, the company is engaged in
A)market fixation.
B)product differentiation.
C)dominant rivalry.
D)rational competition.
A)market fixation.
B)product differentiation.
C)dominant rivalry.
D)rational competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Monopolistic competition is a market characterized by
A)one seller that competes against itself.
B)many sellers that produce identical products.
C)a few sellers that can impact the other sellers through their actions.
D)many sellers that produce different versions of the same product.
A)one seller that competes against itself.
B)many sellers that produce identical products.
C)a few sellers that can impact the other sellers through their actions.
D)many sellers that produce different versions of the same product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Most U.S. grocery stores sell a variety of boxed breakfast cereals. This observation indicates that the boxed breakfast cereal market is
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Walmart has a large aisle that displays many different types of shampoos. This observation indicates that the shampoo market is
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Walmart has a large aisle that displays many different kinds of toothpastes. This observation indicates that the toothpaste market is
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopolistically competitive market.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopoly.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopolistically competitive market.
C)an oligopoly.
D)a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
With a _____ number of sellers in a market, _____ market power tends to exist in the market.
A)smaller; more
B)smaller; less consistent
C)greater; more
D)greater; less consistent
A)smaller; more
B)smaller; less consistent
C)greater; more
D)greater; less consistent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a seller is able to differentiate its product successfully, the seller
A)has a reduction in costs of production.
B)takes its market closer to perfect competition.
C)loses market share.
D)gains market power.
A)has a reduction in costs of production.
B)takes its market closer to perfect competition.
C)loses market share.
D)gains market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements about the prevalence of different types of market structures is TRUE?
A)Monopolistic competition and monopoly are more common than oligopoly and perfect competition.
B)Oligopoly and perfect competition are more common than monopolistic competition and monopoly.
C)Oligopoly and monopolistic competition are more common than monopoly and perfect competition.
D)Monopoly and perfect competition are more common than oligopoly and monopolistic competition.
A)Monopolistic competition and monopoly are more common than oligopoly and perfect competition.
B)Oligopoly and perfect competition are more common than monopolistic competition and monopoly.
C)Oligopoly and monopolistic competition are more common than monopoly and perfect competition.
D)Monopoly and perfect competition are more common than oligopoly and monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following two market structures are LESS common?
A)Monopoly and perfect competition
B)Perfect competition and oligopoly
C)Oligopoly and monopolistic competition
D)Monopolistic competition and monopoly
A)Monopoly and perfect competition
B)Perfect competition and oligopoly
C)Oligopoly and monopolistic competition
D)Monopolistic competition and monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The most common market structures are
A)monopoly and oligopoly.
B)monopoly and monopolistic competition.
C)monopolistic competition and oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition.
A)monopoly and oligopoly.
B)monopoly and monopolistic competition.
C)monopolistic competition and oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Imperfect competition stems from _____ and whether or not the product is _____.
A)the product price; produced by all firms in the market
B)the costs of production; identical across firms
C)market power; a good or a service
D)the number of sellers; differentiated
A)the product price; produced by all firms in the market
B)the costs of production; identical across firms
C)market power; a good or a service
D)the number of sellers; differentiated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT true about imperfect competition?
A)Greater product differentiation decreases market power.
B)A smaller number of sellers in a market increases market power.
C)Imperfect competition among buyers gives them bargaining power.
D)Sellers with market power can use independent pricing strategies.
A)Greater product differentiation decreases market power.
B)A smaller number of sellers in a market increases market power.
C)Imperfect competition among buyers gives them bargaining power.
D)Sellers with market power can use independent pricing strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is an accepted insight into imperfect competition?
A)The higher the number of competitors, the greater the market power of firms.
B)Market power leads to all sellers accepting the market equilibrium price.
C)A seller's best choice depends on the actions that other businesses take.
D)Market power grows when the product is standardized and identical across sellers.
A)The higher the number of competitors, the greater the market power of firms.
B)Market power leads to all sellers accepting the market equilibrium price.
C)A seller's best choice depends on the actions that other businesses take.
D)Market power grows when the product is standardized and identical across sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What "balancing act" do imperfect competitors face as they set their product price?
A)If the price is too high, profit will be large as you sell a large quantity.
B)If the price is too high, profit will be small as you sell a small quantity.
C)If the price is too high, few firms produce and costs rise.
D)If the price is too high, many firms produce and costs rise.
A)If the price is too high, profit will be large as you sell a large quantity.
B)If the price is too high, profit will be small as you sell a small quantity.
C)If the price is too high, few firms produce and costs rise.
D)If the price is too high, many firms produce and costs rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a product market, why would a company owner prefer to face fewer competitors rather than more?
A)Costs of production will be lower when there are fewer companies.
B)With fewer competitors, companies have more market power.
C)With fewer competitors, companies have less market power.
D)Per-unit costs of production rise when the number of companies falls.
A)Costs of production will be lower when there are fewer companies.
B)With fewer competitors, companies have more market power.
C)With fewer competitors, companies have less market power.
D)Per-unit costs of production rise when the number of companies falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When buyers in a market have market power, then the
A)product price is higher.
B)product price is lower.
C)number of sellers rises.
D)number of sellers falls.
A)product price is higher.
B)product price is lower.
C)number of sellers rises.
D)number of sellers falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When interdependence exists between sellers in a market, then
A)each seller relies on another seller in the market to supply its inputs.
B)all sellers produce an identical product.
C)each seller's best choice depends on what the other sellers choose to do.
D)there must be a rising market demand for any seller to increase its sales.
A)each seller relies on another seller in the market to supply its inputs.
B)all sellers produce an identical product.
C)each seller's best choice depends on what the other sellers choose to do.
D)there must be a rising market demand for any seller to increase its sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Market power determines the shape of a firm's
A)market equilibrium.
B)marginal revenue curve.
C)supply curve.
D)demand curve.
A)market equilibrium.
B)marginal revenue curve.
C)supply curve.
D)demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A seller's incentive to increase production is reflected in its
A)marginal revenue curve.
B)demand curve.
C)market equilibrium price.
D)market share.
A)marginal revenue curve.
B)demand curve.
C)market equilibrium price.
D)market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A seller's demand curve summarizes its _____, and its marginal revenue curve measures its _____.
A)incentive to increase production; costs of production
B)market share; market power
C)customer power; costs of production
D)market power; incentive to increase production
A)incentive to increase production; costs of production
B)market share; market power
C)customer power; costs of production
D)market power; incentive to increase production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The degree of a seller's market power has an impact on the
A)market demand curve for the seller's market.
B)seller's demand curve.
C)demand curves for individual customers of the seller.
D)seller's cost curves.
A)market demand curve for the seller's market.
B)seller's demand curve.
C)demand curves for individual customers of the seller.
D)seller's cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What happens to a seller's demand curve as the seller gains market power?
A)The curve becomes horizontal.
B)The curve shifts to the left.
C)The slope of the curve becomes steeper.
D)The slope of the curve becomes less steep.
A)The curve becomes horizontal.
B)The curve shifts to the left.
C)The slope of the curve becomes steeper.
D)The slope of the curve becomes less steep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When a seller has no market power, its demand curve
A)is horizontal.
B)is vertical.
C)has a negative slope.
D)has a positive slope.
A)is horizontal.
B)is vertical.
C)has a negative slope.
D)has a positive slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A seller's demand curve will have a steep negative slope when the seller
A)has a low level of market power.
B)has a high level of market power.
C)is in perfect competition.
D)does not have a differentiated product.
A)has a low level of market power.
B)has a high level of market power.
C)is in perfect competition.
D)does not have a differentiated product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The _____ a seller's market power is, the _____ the price elasticity of its demand curve.
A)more variable; greater
B)greater; lower
C)lower; more variable
D)lower; lower
A)more variable; greater
B)greater; lower
C)lower; more variable
D)lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
(Figure: Market Power) Based on the demand curves for four sellers, which of the following sellers has the most market power?
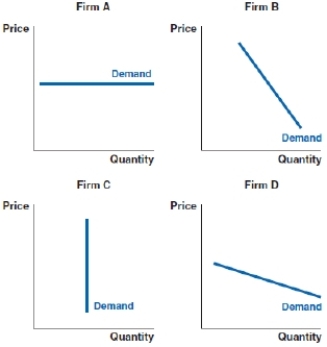
A)Firm A
B)Firm B
C)Firm C
D)Firm D

A)Firm A
B)Firm B
C)Firm C
D)Firm D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
(Figure: Market Power) Based on the demand curves for four sellers, which of the following firms has the least market power?
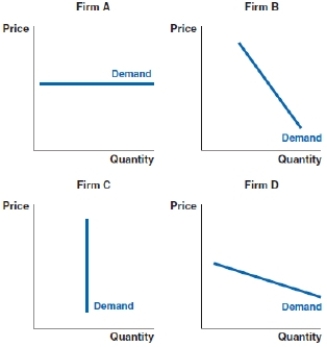
A)Firm A
B)Firm B
C)Firm C
D)Firm D

A)Firm A
B)Firm B
C)Firm C
D)Firm D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How does a business owner discover the business's demand curve?
A)The owner watches its competitors.
B)The owner tries out different versions of a product.
C)The demand curve is found by determining the market equilibrium price.
D)The owner experiments with different prices for its product.
A)The owner watches its competitors.
B)The owner tries out different versions of a product.
C)The demand curve is found by determining the market equilibrium price.
D)The owner experiments with different prices for its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Marginal revenue is the
A)profit a company earns from selling an additional unit of output.
B)change in revenue from selling an additional unit of output.
C)rise in costs when an additional unit of output is produced.
D)revenue obtained from giving discounts to customers to manipulate sales.
A)profit a company earns from selling an additional unit of output.
B)change in revenue from selling an additional unit of output.
C)rise in costs when an additional unit of output is produced.
D)revenue obtained from giving discounts to customers to manipulate sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
(Figure: Marginal Revenue) What is the marginal revenue of the fourth unit in the following example?
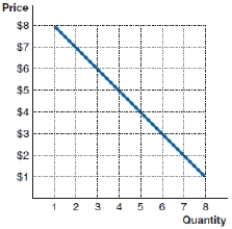
A)$20
B)$5
C)$2
D)$1

A)$20
B)$5
C)$2
D)$1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
(Figure: Marginal Revenue) What is the marginal revenue of the fifth unit in the following example?
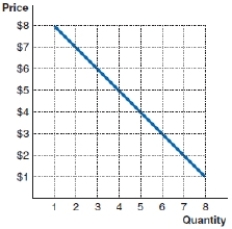
A)$20
B)$5
C)$4
D)$0

A)$20
B)$5
C)$4
D)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Marginal revenue reflects the _____ effect and the _____ effect.
A)cost; revenue
B)output; discount
C)discount; cost
D)revenue; sales
A)cost; revenue
B)output; discount
C)discount; cost
D)revenue; sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Your company sells 19 units at a price of $10 and must change price to $9.90 in order to sell 20 units. What is the marginal revenue of the twentieth unit?
A)-$.10
B)$8.00
C)$9.90
D)$198.00
A)-$.10
B)$8.00
C)$9.90
D)$198.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For a seller with market power, as the number of units sold increases, marginal revenue
A)falls further and further below the price.
B)rises further and further above the price.
C)remains constant and unchanging.
D)remains equal to the price needed to sell the output.
A)falls further and further below the price.
B)rises further and further above the price.
C)remains constant and unchanging.
D)remains equal to the price needed to sell the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How does marginal revenue compare to price for a seller with market power?
A)Marginal revenue is equal to price.
B)Marginal revenue is always higher than price.
C)Beyond the first unit sold, marginal revenue is below price.
D)Beyond the first unit sold, marginal revenue is above price.
A)Marginal revenue is equal to price.
B)Marginal revenue is always higher than price.
C)Beyond the first unit sold, marginal revenue is below price.
D)Beyond the first unit sold, marginal revenue is above price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Marginal revenue is the difference between output effect or price and the _____ effect for a given quantity.
A)output
B)profit
C)sales
D)discount
A)output
B)profit
C)sales
D)discount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As the quantity sold rises, how does marginal revenue compare to price for a company with market power?
A)Marginal revenue falls further and further below price.
B)Marginal revenue rises further and further below price.
C)Marginal revenue remains constant regardless of the price level.
D)Marginal revenue maintains a constant difference from price.
A)Marginal revenue falls further and further below price.
B)Marginal revenue rises further and further below price.
C)Marginal revenue remains constant regardless of the price level.
D)Marginal revenue maintains a constant difference from price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Rational Rule for Sellers is that sellers should choose the quantity _____ and choose the price _____.
A)that is associated with a minimum average total cost; that is on the seller's demand curve for the quantity
B)that is associated with a minimum average total cost; with maximum marginal revenue
C)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; that is on the seller's demand curve for that quantity
D)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; with maximum marginal revenue
A)that is associated with a minimum average total cost; that is on the seller's demand curve for the quantity
B)that is associated with a minimum average total cost; with maximum marginal revenue
C)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; that is on the seller's demand curve for that quantity
D)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; with maximum marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
According to the Rational Rule for Sellers, a seller should choose the output level where _____ and the price level _____.
A)marginal cost equals marginal revenue; that is on the seller's demand curve at that output level
B)maximum revenue is obtained; that is on the seller's demand curve for that output
C)average total cost is minimum; that is associated with maximum revenue
D)sales are maximum; where revenue is maximum
A)marginal cost equals marginal revenue; that is on the seller's demand curve at that output level
B)maximum revenue is obtained; that is on the seller's demand curve for that output
C)average total cost is minimum; that is associated with maximum revenue
D)sales are maximum; where revenue is maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
(Figure: Output Level) According to the rational rule, what output and price should the firm in the following example choose?
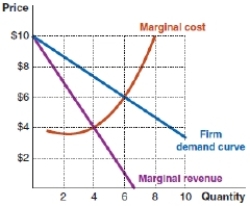
A)quantity = 6; price = $6.00
B)quantity = 4; price = $4.00
C)quantity = 8; price = $9.00
D)quantity = 4; price = $7.00

A)quantity = 6; price = $6.00
B)quantity = 4; price = $4.00
C)quantity = 8; price = $9.00
D)quantity = 4; price = $7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
(Figure: Output Level 2) What price and output should the firm in the following example choose according to the Rational Rule for Sellers if MC = $4?
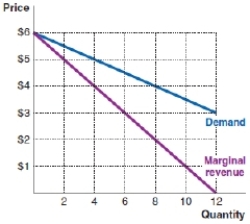
A)output = six; price = $6.00
B)output = five; price = $4.00
C)output = six; price = $4.00
D)output = six; price = $5.00

A)output = six; price = $6.00
B)output = five; price = $4.00
C)output = six; price = $4.00
D)output = six; price = $5.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the Rational Rule for Sellers, this company should produce ____ of output and charge a price of _____.
A)one unit; $300
B)two units; $200
C)three units; $200
D)four units; $150
A)one unit; $300
B)two units; $200
C)three units; $200
D)four units; $150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
According to the Rational Rule for Sellers, the manager of this company should choose to produce _____ of output and charge a price of _____.
A)one unit; $400
B)two units; $450
C)three units; $400
D)four units; $350
A)one unit; $400
B)two units; $450
C)three units; $400
D)four units; $350

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Why would the owner of the following company decide NOT to produce and sell the fourth unit, even though it adds less to costs than the price he could get for it?
A)It would add no additional revenue even though it sells for $150.
B)It has a price that is less than cost per unit of output.
C)It has marginal cost that is less than its marginal revenue.
D)It is associated with an increase in cost per unit.
A)It would add no additional revenue even though it sells for $150.
B)It has a price that is less than cost per unit of output.
C)It has marginal cost that is less than its marginal revenue.
D)It is associated with an increase in cost per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The basic logic behind the Rational Rule for Sellers is that a company owner should increase output as long as the extra output
A)moves the company toward maximum total revenue.
B)leads to a larger gap between price and average total costs.
C)leads the company toward minimum average total costs.
D)adds more to revenue than it adds to costs.
A)moves the company toward maximum total revenue.
B)leads to a larger gap between price and average total costs.
C)leads the company toward minimum average total costs.
D)adds more to revenue than it adds to costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a perfectly competitive market, a company's marginal revenue equals _____. For a company with market power, marginal revenue is _____.
A)price; less than price
B)price; greater than price
C)marginal cost; greater than marginal cost
D)marginal cost; less than marginal cost
A)price; less than price
B)price; greater than price
C)marginal cost; greater than marginal cost
D)marginal cost; less than marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Based on the Rational Rule for Sellers, how does a manager set price and quantity? If the company has no market power, the marginal cost _____ price. If the company has market power, the marginal cost is _____ than price.
A)is less than; greater
B)is greater than; less
C)equals; less
D)equals; greater
A)is less than; greater
B)is greater than; less
C)equals; less
D)equals; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How is the result of the Rational Rule for Sellers different for companies with market power versus companies with no market power?
A)The price is lower for companies with market power.
B)The price is higher for companies with market power.
C)The demand is lower for companies with market power.
D)The demand is higher for companies with market power.
A)The price is lower for companies with market power.
B)The price is higher for companies with market power.
C)The demand is lower for companies with market power.
D)The demand is higher for companies with market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Companies with market power face a trade-off between
A)gaining market share and reducing costs.
B)having a higher marginal cost and a reduction in output.
C)reducing costs and increasing profit.
D)having a higher profit margin and selling a larger quantity.
A)gaining market share and reducing costs.
B)having a higher marginal cost and a reduction in output.
C)reducing costs and increasing profit.
D)having a higher profit margin and selling a larger quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Following the Rational Rule for Sellers, how does output for a seller who has market power compare to output for a seller who does not have market power?
A)Output is the same in both situations.
B)Output is higher with market power than without market power.
C)Output is higher without market power than with market power.
D)The level of market power has no impact on output.
A)Output is the same in both situations.
B)Output is higher with market power than without market power.
C)Output is higher without market power than with market power.
D)The level of market power has no impact on output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 216 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



