Deck 3: Supply: Thinking Like a Seller
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/168
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Supply: Thinking Like a Seller
1
An individual supply curve is
A)a graph with quantities of a product that a seller is willing to supply at different price points.
B)a graph that plots how much a seller produces at different points in time.
C)a graph that plots the quantities of an item that a buyer plans to buy at different prices.
D)the quantity a seller is willing to supply at one particular price.
A)a graph with quantities of a product that a seller is willing to supply at different price points.
B)a graph that plots how much a seller produces at different points in time.
C)a graph that plots the quantities of an item that a buyer plans to buy at different prices.
D)the quantity a seller is willing to supply at one particular price.
A
2
What is quantity supplied?
A)It is a graph that plots the quantities of an item that a seller plans to sell at different prices.
B)It is the amount of an item that a buyer is willing to buy at a particular price.
C)It is the amount of an item that a seller is willing to sell at a particular price.
D)It is a graph that plots how much a seller produces at different points in time.
A)It is a graph that plots the quantities of an item that a seller plans to sell at different prices.
B)It is the amount of an item that a buyer is willing to buy at a particular price.
C)It is the amount of an item that a seller is willing to sell at a particular price.
D)It is a graph that plots how much a seller produces at different points in time.
C
3
(Figure: Spice King Burgers' Supply Curve) Take a look at Spice King Burgers' supply curve for burgers. How many burgers will they supply at a market price of $1.50 per burger? 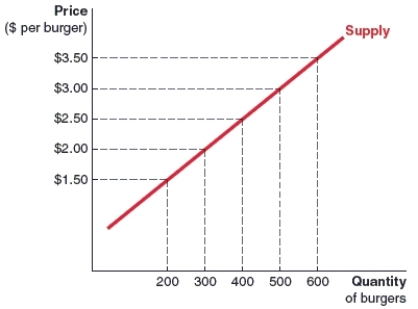
A)200 units
B)300 units
C)400 units
D)500 units

A)200 units
B)300 units
C)400 units
D)500 units
A
4
(Figure: Spice King Burgers' Supply Curve) Take a look at Spice King Burgers' supply curve for burgers. How many burgers is Spice King Burgers willing to supply at a market price of $3.50 per burger? 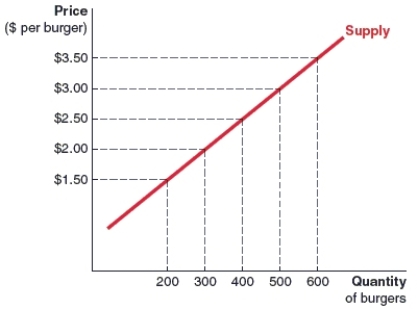
A)200 units
B)300 units
C)500 units
D)600 units

A)200 units
B)300 units
C)500 units
D)600 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why are supply curves typically upward-sloping?
A)They slope upward because sellers prefer to sell more when prices are lower.
B)They slope upward because higher prices lead individual businesses to supply a larger quantity and more businesses are willing to supply goods and services.
C)They slope upward because sellers demand more when prices are lower.
D)They slope upward due to the law of demand.
A)They slope upward because sellers prefer to sell more when prices are lower.
B)They slope upward because higher prices lead individual businesses to supply a larger quantity and more businesses are willing to supply goods and services.
C)They slope upward because sellers demand more when prices are lower.
D)They slope upward due to the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An upward-sloping supply curve shows that
A)there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity supplied.
B)there is a positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
C)there is no relationship between price and quantity supplied.
D)sellers are willing to sell less when the prices are higher in the market.
A)there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity supplied.
B)there is a positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
C)there is no relationship between price and quantity supplied.
D)sellers are willing to sell less when the prices are higher in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following scenarios describes a business that is NOT following the law of supply?
A)The higher the price of custom-made cakes in the market, the more Manfred is willing to bake and sell cakes.
B)Delilah is less willing to chauffeur people to the airport when the price of airport rides falls.
C)Automobiles fall in price, and Maria's Autorama Ltd. is now willing to sell more vehicles.
D)When the price of car detailing rises, Ermo's Auto Garage hires more workers to do car detailing.
A)The higher the price of custom-made cakes in the market, the more Manfred is willing to bake and sell cakes.
B)Delilah is less willing to chauffeur people to the airport when the price of airport rides falls.
C)Automobiles fall in price, and Maria's Autorama Ltd. is now willing to sell more vehicles.
D)When the price of car detailing rises, Ermo's Auto Garage hires more workers to do car detailing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The accompanying table provides data for five different oatmeal cookie sellers. Out of the sellers listed, who all are following the law of supply? 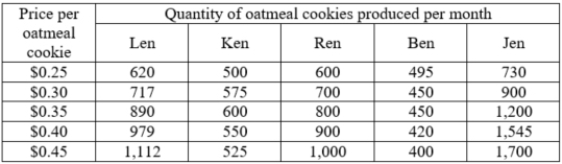
A)Ren only
B)Ken and Ben
C)Len, Ken, Ren, and Ben
D)Len, Ren, and Jen

A)Ren only
B)Ken and Ben
C)Len, Ken, Ren, and Ben
D)Len, Ren, and Jen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Look at the chart which shows data for five different oatmeal cookie producers. Which sellers are NOT following the law of supply? 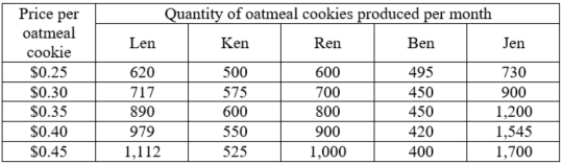
A)Ren only
B)Ken and Ben
C)Len, Ken, Ren, and Ben
D)Len, Ren, and Jen

A)Ren only
B)Ken and Ben
C)Len, Ken, Ren, and Ben
D)Len, Ren, and Jen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When plotting a supply curve
A)the quantity supplied goes on the vertical axis.
B)the price goes on the horizontal axis.
C)the quantity supplied goes on the horizontal axis.
D)the quantity demanded goes on the vertical axis.
A)the quantity supplied goes on the vertical axis.
B)the price goes on the horizontal axis.
C)the quantity supplied goes on the horizontal axis.
D)the quantity demanded goes on the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The supply curve is upward-sloping because
A)sellers can make more profit per unit if the market prices rise.
B)the government determines the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
C)it follows the law of demand.
D)the number of sellers rises as prices rise.
A)sellers can make more profit per unit if the market prices rise.
B)the government determines the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
C)it follows the law of demand.
D)the number of sellers rises as prices rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Rational Rule for Sellers involves applying
A)only the cost-benefit principle.
B)only the marginal principle.
C)the marginal principle, the cost-benefit principle, and the opportunity cost principle.
D)only the opportunity cost principle.
A)only the cost-benefit principle.
B)only the marginal principle.
C)the marginal principle, the cost-benefit principle, and the opportunity cost principle.
D)only the opportunity cost principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Rational Rule for Sellers says that a seller should sell one more unit of an item if the price is:
A)less than the marginal cost.
B)greater than or equal to the marginal cost.
C)less than the marginal benefit.
D)greater than or equal to the marginal benefit.
A)less than the marginal cost.
B)greater than or equal to the marginal cost.
C)less than the marginal benefit.
D)greater than or equal to the marginal benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When you calculate marginal costs, they should include:
A)only fixed costs.
B)only variable costs.
C)both the variable and fixed costs.
D)the market price of the product.
A)only fixed costs.
B)only variable costs.
C)both the variable and fixed costs.
D)the market price of the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following scenarios does NOT depict a rational seller?
A)The Flowery Bower calculates the marginal cost of a bouquet of red roses as $10 and sells it at $45.
B)United Airlines determines the marginal cost of an extra passenger to be $55 and sells a discount seat for $150.
C)An auto-rickshaw driver in New Delhi, India, calculates a trip to have a marginal cost of 350 rupees and accepts a ride request for 500 rupees.
D)Main Street Bakery calculates the marginal cost of a multilayer red velvet cake sd $9 and sells it for $8.
A)The Flowery Bower calculates the marginal cost of a bouquet of red roses as $10 and sells it at $45.
B)United Airlines determines the marginal cost of an extra passenger to be $55 and sells a discount seat for $150.
C)An auto-rickshaw driver in New Delhi, India, calculates a trip to have a marginal cost of 350 rupees and accepts a ride request for 500 rupees.
D)Main Street Bakery calculates the marginal cost of a multilayer red velvet cake sd $9 and sells it for $8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following scenarios depicts a seller who is following the Rational Rule for Sellers?
A)American Airlines determines the marginal cost of an extra passenger to be $75 and sells a discount seat for $250.
B)Andy's Diner finds that the marginal cost of a fish and chips meal is $7 and lists the item for sale at $6.50.
C)An auto-rickshaw driver in New Delhi, India, calculates a trip to have a marginal cost of 350 rupees and accepts a ride request for 315 rupees.
D)Mindy sets up a lemonade stand and calculates the cost of an additional cup of lemonade at 50 cents, and sells it for 25 cents.
A)American Airlines determines the marginal cost of an extra passenger to be $75 and sells a discount seat for $250.
B)Andy's Diner finds that the marginal cost of a fish and chips meal is $7 and lists the item for sale at $6.50.
C)An auto-rickshaw driver in New Delhi, India, calculates a trip to have a marginal cost of 350 rupees and accepts a ride request for 315 rupees.
D)Mindy sets up a lemonade stand and calculates the cost of an additional cup of lemonade at 50 cents, and sells it for 25 cents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Rising marginal costs imply
A)falling variable costs.
B)rising fixed costs.
C)a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)an upward-sloping supply curve.
A)falling variable costs.
B)rising fixed costs.
C)a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)an upward-sloping supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A supply curve
(i) plots the quantities a seller is willing to sell at different prices.
(ii) shows the total cost to the seller.
(iii) shows rising marginal costs.
(iv) shows rising fixed costs.
A)only (i)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)
(i) plots the quantities a seller is willing to sell at different prices.
(ii) shows the total cost to the seller.
(iii) shows rising marginal costs.
(iv) shows rising fixed costs.
A)only (i)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
D)(i), (ii), and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the data in the table. The price of gasoline is $3.99 per gallon at the gas station. If Rexhall Fuel Supplies is a rational seller, how many gallons of gasoline should this seller be willing to sell? 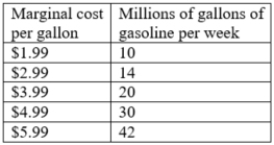
A)14 million gallons per week
B)30 million gallons per week
C)20 million gallons per week
D)42 million gallons per week

A)14 million gallons per week
B)30 million gallons per week
C)20 million gallons per week
D)42 million gallons per week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The market supply curve is upward-sloping because a higher price implies that
(i) individual sellers can increase the output supplied.
(ii) more sellers can supply to the market.
(iii) the government supplies goods and services to the market.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)only (iii)
D)(ii) and (iii)
(i) individual sellers can increase the output supplied.
(ii) more sellers can supply to the market.
(iii) the government supplies goods and services to the market.
A)(i) and (ii)
B)(i) and (iii)
C)only (iii)
D)(ii) and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A bakery hires a baker who can make 15 cakes per day. The bakery then decides to hire a second baker who will use the kitchen at the same time as the first baker. The bakery finds that the second baker can produce only an additional nine cakes per day. What concept does this scenario illustrate?
A)The cost-benefit principle
B)The marginal principle
C)The opportunity cost principle
D)Diminishing marginal product
A)The cost-benefit principle
B)The marginal principle
C)The opportunity cost principle
D)Diminishing marginal product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The market supply is
A)a graph that plots the total quantity of an item supplied by the entire market at each price.
B)a graph that plots the quantity supplied at each price by one seller.
C)a graph that plots the total quantity demanded of an item by the entire market at each price.
D)the total cost of production of the item for the entire market.
A)a graph that plots the total quantity of an item supplied by the entire market at each price.
B)a graph that plots the quantity supplied at each price by one seller.
C)a graph that plots the total quantity demanded of an item by the entire market at each price.
D)the total cost of production of the item for the entire market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The market supply is the
A)sum of all prices that sellers charge for a particular quantity.
B)quantity supplied at each price by one seller.
C)total quantity produced by all sellers in the market at each price.
D)total cost of production of an item for the entire market.
A)sum of all prices that sellers charge for a particular quantity.
B)quantity supplied at each price by one seller.
C)total quantity produced by all sellers in the market at each price.
D)total cost of production of an item for the entire market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A market consists of ten similar suppliers that are making the same supply decisions. To find the market supply of these ten suppliers, you:
A)find the average quantity produced by the ten suppliers.
B)multiply the individual supply of one of the suppliers by ten.
C)take the individual supply of one supplier.
D)take one-tenth of the individual supply of each supplier and add it up.
A)find the average quantity produced by the ten suppliers.
B)multiply the individual supply of one of the suppliers by ten.
C)take the individual supply of one supplier.
D)take one-tenth of the individual supply of each supplier and add it up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following are correct about fixed costs?
(i) They do not change with the level of production in the short run.
(ii) They include variable costs.
(iii) They are present even when the firm is producing zero units.
(iv) They are irrelevant to marginal cost.
A)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
B)(i), (ii), and (iii)
C)(ii) and (iv)
D)(i), (iii), and (iv)
(i) They do not change with the level of production in the short run.
(ii) They include variable costs.
(iii) They are present even when the firm is producing zero units.
(iv) They are irrelevant to marginal cost.
A)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
B)(i), (ii), and (iii)
C)(ii) and (iv)
D)(i), (iii), and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Variable costs are the costs that
A)are incurred to build factories and assembly plants.
B)are independent of the amount of output produced.
C)stay fixed with the quantity of output produced.
D)vary with the quantity of output produced.
A)are incurred to build factories and assembly plants.
B)are independent of the amount of output produced.
C)stay fixed with the quantity of output produced.
D)vary with the quantity of output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Amul Food Factory in India makes ice cream and produces processed and condensed milk. In the factory, the firm's employees use raw milk and sugar. The firm runs on electricity and purchases raw milk every day. Large robotic assembly lines fill and package the ice cream containers. Large industrial freezers store the ice cream. Based on this scenario, can you identify the fixed costs for Amul Food Factory?
A)The cost of the raw milk purchased from the farmers.
B)The cost of building the factory, purchasing the robotic assembly lines and industrial freezers.
C)The cost of the employees hired and the number of packages purchased.
D)The cost of purchasing electricity, raw milk, and sugar.
A)The cost of the raw milk purchased from the farmers.
B)The cost of building the factory, purchasing the robotic assembly lines and industrial freezers.
C)The cost of the employees hired and the number of packages purchased.
D)The cost of purchasing electricity, raw milk, and sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Amul Food Factory in India makes ice cream and produces processed and condensed milk. In the factory, the firm's employees use milk and sugar. The firm runs on electricity and purchases raw milk every day. Large robotic assembly lines fill and package the ice cream containers. Large industrial freezers store the ice cream. Which of the following are variable costs for Amul Food Factory?
(i) The cost of the raw milk purchased from farmers.
(ii) The cost of buying the robotic assembly lines.
(iii) The cost of buying electricity.
(iv) The cost of buying industrial freezers.
(v) The cost of sugar.
A)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
B)(iii) and (v)
C)(i), (iii), and (v)
D)(ii) and (iv)
(i) The cost of the raw milk purchased from farmers.
(ii) The cost of buying the robotic assembly lines.
(iii) The cost of buying electricity.
(iv) The cost of buying industrial freezers.
(v) The cost of sugar.
A)(i), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
B)(iii) and (v)
C)(i), (iii), and (v)
D)(ii) and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A beach resort in Bali builds 24 villas with private pools. They also establish two restaurants using state-of-the-art equipment (such as multipurpose ovens, freezers, and food processors). Meals are prepared using organic, locally sourced vegetables and meat. The hotel also uses water from the town supplier. Based on this scenario, what are the variable costs for the beach resort?
A)Organic vegetables and water.
B)Multipurpose ovens and freezers.
C)Food processors.
D)The construction of the villas.
A)Organic vegetables and water.
B)Multipurpose ovens and freezers.
C)Food processors.
D)The construction of the villas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A beach resort in Bali builds 24 villas with private pools. They also establish two restaurants using state-of-the-art equipment (such as multipurpose ovens, freezers, and food processors). Meals are prepared using organic, locally sourced vegetables and meat. The hotel also uses water from the town supplier. Based on this scenario, what are the fixed costs for the beach resort?
A)The construction of the villas.
B)Organic vegetables.
C)Organic meat products.
D)Water from the town supplier.
A)The construction of the villas.
B)Organic vegetables.
C)Organic meat products.
D)Water from the town supplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A seller in a perfectly competitive market
A)sells the same product that other sellers sell.
B)is a single producer in the market.
C)sets the market price of the product.
D)can increase its profitability by charging a higher price than other sellers.
A)sells the same product that other sellers sell.
B)is a single producer in the market.
C)sets the market price of the product.
D)can increase its profitability by charging a higher price than other sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A seller in a perfectly competitive market cannot
A)raise the market price of a product.
B)increase the amount he supplies.
C)decrease its marginal cost.
D)leave the industry.
A)raise the market price of a product.
B)increase the amount he supplies.
C)decrease its marginal cost.
D)leave the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Daisy is a milk farmer in a perfectly competitive market where there are many milk farmers. The market price of milk is $0.15 per gallon, which is also the marginal cost per gallon of milk. If Daisy charges $0.25 per gallon, she will
A)not sell any milk.
B)sell more milk than the other farmers.
C)sell the same amount of milk as she did when she charged $0.15 per gallon.
D)increase her profitability by $0.10 per gallon.
A)not sell any milk.
B)sell more milk than the other farmers.
C)sell the same amount of milk as she did when she charged $0.15 per gallon.
D)increase her profitability by $0.10 per gallon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Frank is a barley farmer in a perfectly competitive market. The market price of barley is $250 per ton. If Frank charges $245 per ton, he will
A)not sell any barley.
B)raise his profitability by $5 per ton.
C)sell less barley than other farmers.
D)lower his profitability by $5 per ton.
A)not sell any barley.
B)raise his profitability by $5 per ton.
C)sell less barley than other farmers.
D)lower his profitability by $5 per ton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Price takers
A)set their market prices.
B)charge the prevailing prices and do not have any effect on the market price.
C)can control the market prices of the products they sell.
D)produce only agricultural items in the market.
A)set their market prices.
B)charge the prevailing prices and do not have any effect on the market price.
C)can control the market prices of the products they sell.
D)produce only agricultural items in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The table shows the monthly individual supply schedules for four firms in the packed-meals market. What is the market supply at $5.75 per meal?
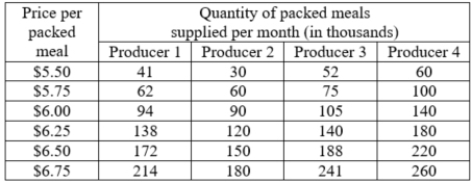
A)183,000 meals
B)895,000 meals
C)297,000 meals
D)730,000 meals

A)183,000 meals
B)895,000 meals
C)297,000 meals
D)730,000 meals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The table shows the monthly individual supply schedules for the four firms in the packed-meals market. What is the market supply at $6.75 per meal?
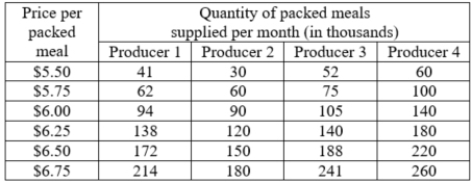
A)183,000 meals
B)895,000 meals
C)297,000 meals
D)730,000 meals

A)183,000 meals
B)895,000 meals
C)297,000 meals
D)730,000 meals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
There are four suppliers in the packed meals market. The quantity of packed meals that each one is willing to supply per week at various prices is provided in the accompanying table. What is the change in the market supply for packed meals when the price rises from $6.25 per meal to $6.50 per meal?
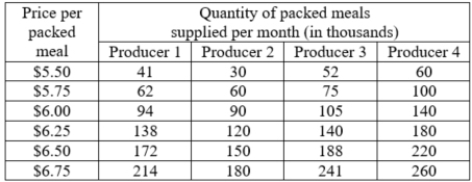
A)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 152,000.
B)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 132,000.
C)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 165,000.
D)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 132,000.

A)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 152,000.
B)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 132,000.
C)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 165,000.
D)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 132,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
There are four suppliers in the packed meals market. The quantity of packed meals that each one is willing to supply per week at various prices is provided in the accompanying table. What is the change in the market supply for packed meals when the price falls from $6.25 per meal to $6.00 per meal? 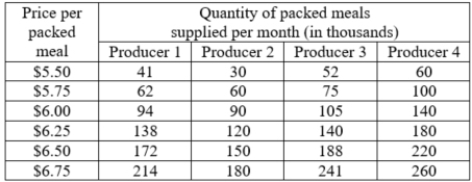
A)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 152,000.
B)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 149,000.
C)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 165,000.
D)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 149,000.

A)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 152,000.
B)The quantity supplied in the market rises by 149,000.
C)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 165,000.
D)The quantity supplied in the market falls by 149,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
As a part of a market research project, you survey six food trucks across the city to gather data on how many meals they would plan to sale at various prices. The data you collect is in the accompanying table. What is the total supply of meals in your survey at $8 per meal?
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)835 meals
B)980 meals
C)1,485 meals
D)1,135 meals
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)835 meals
B)980 meals
C)1,485 meals
D)1,135 meals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
As a part of a market research project, you survey six food trucks across the city to gather data on how many meals they would plan to sale at various prices. The data you collect is in the accompanying table. What is the total supply of meals in your survey at $10 per meal?
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
?
A)835 meals
B)980 meals
C)1,485 meals
D)1,135 meals
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
?
A)835 meals
B)980 meals
C)1,485 meals
D)1,135 meals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As a part of a market research project, you survey six food trucks across the city to gather data on how many meals they would plan to sale at various prices. The data you collect is in the accompanying table. What is the change in the total supply of meals in your survey when the price increases from $8 per meal to $9 per meal?
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)The quantity supplied rises by 165.
B)The quantity supplied falls by 155.
C)The quantity supplied rises by 155.
D)The quantity supplied falls by 185.
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)The quantity supplied rises by 165.
B)The quantity supplied falls by 155.
C)The quantity supplied rises by 155.
D)The quantity supplied falls by 185.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As a part of a market research project, you survey six food trucks across the city to gather data on how many meals they would plan to sale at various prices. The data you collect is in the accompanying table. What is the change in the total supply of meals in your survey when the price falls from $7 per meal to $6 per meal?
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)The quantity supplied rises by 165.
B)The quantity supplied falls by 155.
C)The quantity supplied rises by 155.
D)The quantity supplied falls by 145.
?
Quantity of Meals Supplied Per Week
A)The quantity supplied rises by 165.
B)The quantity supplied falls by 155.
C)The quantity supplied rises by 155.
D)The quantity supplied falls by 145.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point E to point F represents 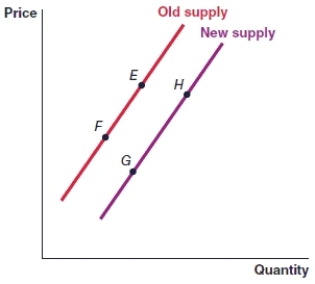
A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point H to point G represents 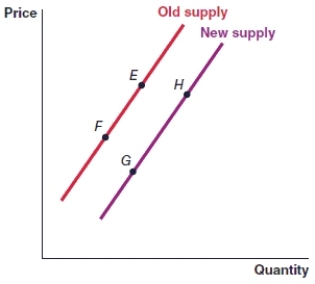
A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point H to point L represents 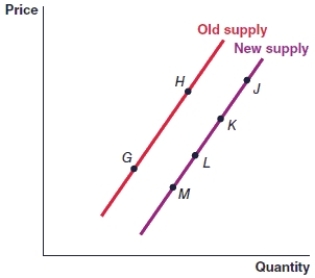
A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point M to point G represents 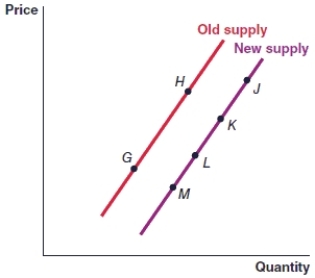
A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

A)a decrease in supply.
B)a decrease in quantity supplied.
C)an increase in quantity supplied.
D)an increase in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point J to point K must have been caused by: 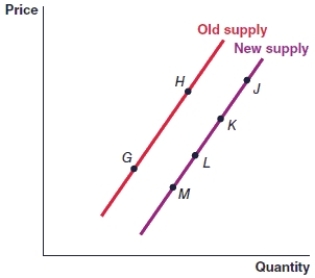
A)a rise in the price of the item.
B)a fall in the price of the item.
C)a decrease in the total supply of the item.
D)an increase in the total supply of the item.

A)a rise in the price of the item.
B)a fall in the price of the item.
C)a decrease in the total supply of the item.
D)an increase in the total supply of the item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, the movement from point L to point K is caused by 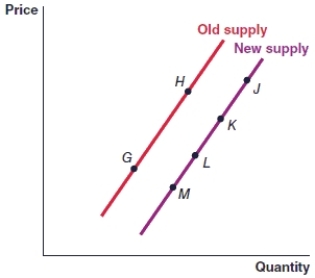
A)an increase in the price of the item.
B)a decrease in the price of the item.
C)a decrease in the supply of the item.
D)an increase in the supply of the item.

A)an increase in the price of the item.
B)a decrease in the price of the item.
C)a decrease in the supply of the item.
D)an increase in the supply of the item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, an increase in the price of the item will cause the movement from 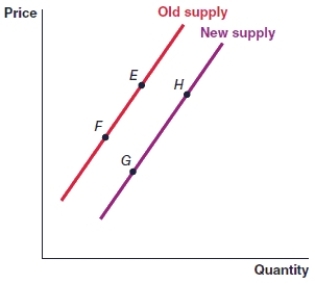


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
(Figure: Graph) In the graph, a decrease in the price of the item will cause the movement from 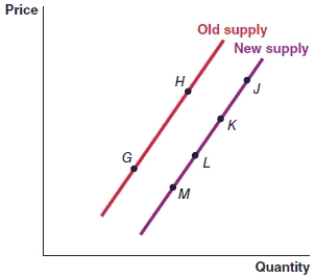
A)point G to point L.
B)point H to point
C)point M to point J.
D)point L to point K.

A)point G to point L.
B)point H to point
C)point M to point J.
D)point L to point K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(Figure: Market for Coffee) A coffee shop opens next to an existing coffee shop. Which of the following graphs shows the effect of this new coffee shop on the market supply curve for coffee in this area?
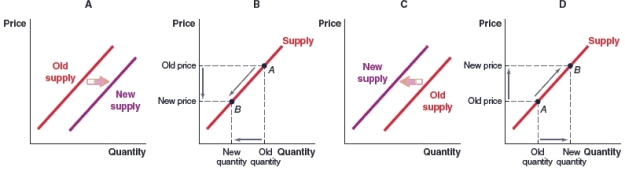
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
(Figure: Change in Supply) There are four gas stations in your town. Which graph shows the effect on the local supply curve for gasoline if one of them shuts down?
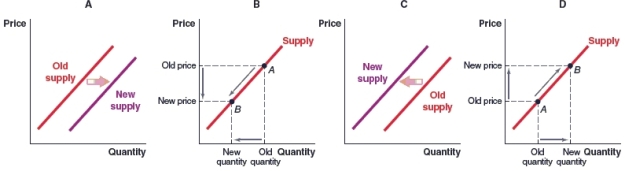
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is NOT a factor that can shift supply?
A)The expected future price of a product.
B)The price of a substitute-in-production.
C)The market price of a product.
D)The price of a complement-in-production.
A)The expected future price of a product.
B)The price of a substitute-in-production.
C)The market price of a product.
D)The price of a complement-in-production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is NOT a factor that can shift supply?
A)The price of the product.
B)The cost of raw materials used in the production process.
C)The state of technology used for production.
D)The change in the price of a complement-in-production.
A)The price of the product.
B)The cost of raw materials used in the production process.
C)The state of technology used for production.
D)The change in the price of a complement-in-production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
(Figure: Market for Leather Wallets) Producers of hand-made leather wallets have made manufacturing changes that have improved quality but reduced efficiency. Which graph shows this change in the market?
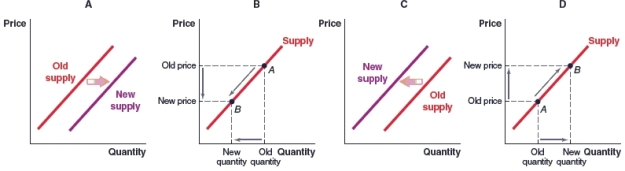
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
(Figure: Market for Drones) If companies frequently start using drones to deliver products, which graph shows the effect this will have on the market for drones.
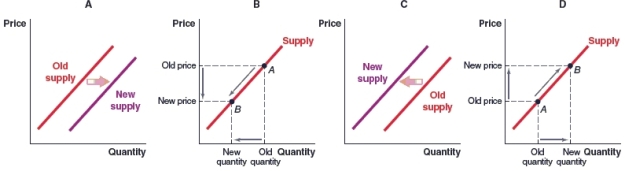
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
(Figure: Market for Tropicana Juices) Tropicana produces both orange juice and lemonade. What will happen to the supply of Tropicana orange juice when the price of lemonade rises in the market and the price of orange juice stays the same?
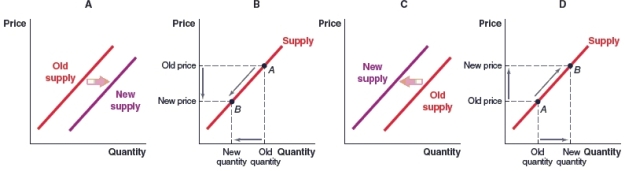
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
(Figure: Market for Tropicana Juices) Tropicana produces both orange juice and tropical juice blends. What will happen to the supply of Tropicana orange juice when the opportunity cost of producing tropical juice blends rises, and the opportunity cost of producing orange juice stays the same? (Hint: Opportunity costs are part of a producer's marginal cost.)
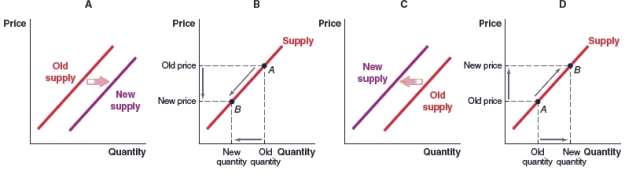
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
(Figure: Market for Steel Bars) Which graph illustrates what will happen in the market for processed, industrial steel bars when the price of raw steel falls?
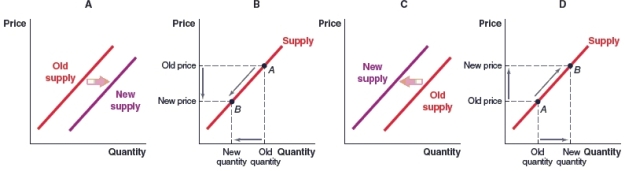
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
(Figure: Market for Luxury SUVs) Which of the following graphs shows what will happen to the supply curve for luxury SUVs, if economists predict an increase in demand for these vehicles?
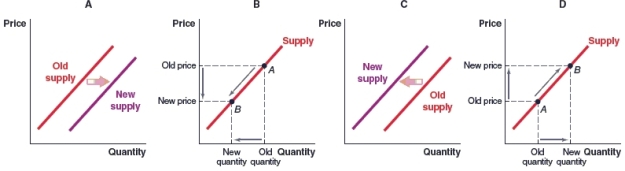
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Figure: Market for New Housing in Dubai) Which graph shows the effect on the supply curve for new housing in Dubai, if economists predict a decrease in demand for new housing?
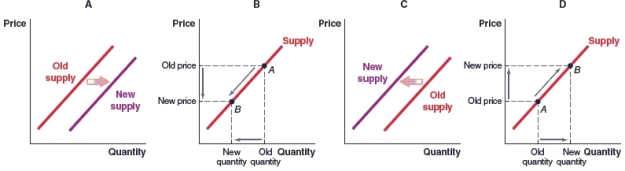
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A large amount of harvested grain used to make flour grows mold due to flooding. How will this affect the supply of flour in the market?
A)The supply of flour will increase in the market.
B)The supply of flour will decrease in the market.
C)The supply of flour will remain unchanged in the market.
D)Suppliers of flour will switch to supplying grain.
A)The supply of flour will increase in the market.
B)The supply of flour will decrease in the market.
C)The supply of flour will remain unchanged in the market.
D)Suppliers of flour will switch to supplying grain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
(Figure: Market for Furniture) Which graph shows what will happen in the market for furniture if an excess supply of timber drives down wood prices?
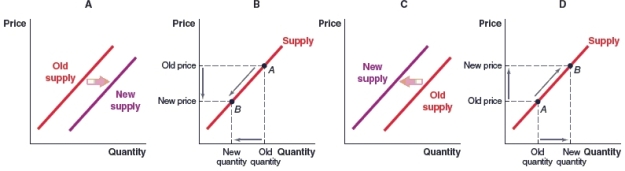
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
(Figure: Market for Automobiles) Which graph shows what will happen in the market for automobiles if there is an advancement in production technology?
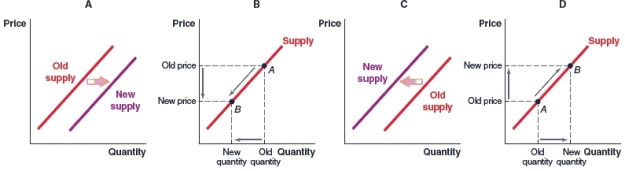
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How will the supply of clothing change if the forecast is that clothing prices will rise in the next few months?
A)The supply of clothing will increase in the market today.
B)The supply of clothing will remain unchanged today.
C)The supply of clothing will decrease in the market today.
D)Suppliers will stop producing clothing and switch to an alternate item.
A)The supply of clothing will increase in the market today.
B)The supply of clothing will remain unchanged today.
C)The supply of clothing will decrease in the market today.
D)Suppliers will stop producing clothing and switch to an alternate item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How will the supply of clothing change if the forecast is that clothing prices will fall in the next few months?
A)The supply of clothing will increase in the market today.
B)The supply of clothing will remain unchanged today.
C)The supply of clothing will decrease in the market today.
D)Suppliers will stop producing clothing and switch to an alternate item.
A)The supply of clothing will increase in the market today.
B)The supply of clothing will remain unchanged today.
C)The supply of clothing will decrease in the market today.
D)Suppliers will stop producing clothing and switch to an alternate item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(Figure: Market for Printing Paper) Which of the following graphs shows what will happen in the market for printing paper if the price of printing paper rises?
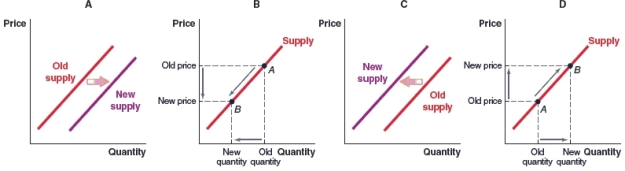
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
(Figure: Market for Roses) Which graph shows what will happen to the supply of roses if the price of roses falls?
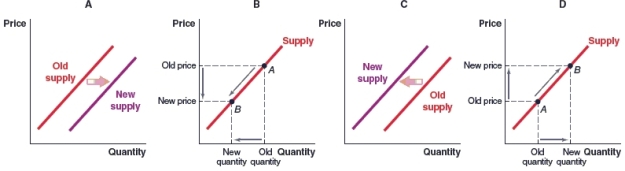
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Peanut butter and peanut oil are complements-in-production. When the price of peanut butter rises, the
A)quantity supplied of peanut butter will fall.
B)supply of peanut oil will rise.
C)supply of peanut oil will fall.
D)quantity supplied of peanut butter will remain unchanged.
A)quantity supplied of peanut butter will fall.
B)supply of peanut oil will rise.
C)supply of peanut oil will fall.
D)quantity supplied of peanut butter will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Due to a decline in demand and popularity, Ford Motor Company is planning to phase out traditional sedans such as 'Fusion' and 'Taurus' to focus on SUVs and trucks. Ford's sedans and trucks/SUVs are
A)complements-in-production.
B)substitutes-in-production.
C)inputs in production.
D)products that do not follow the law of supply.
A)complements-in-production.
B)substitutes-in-production.
C)inputs in production.
D)products that do not follow the law of supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
(Figure: Market for Stevia) Stevia is a natural sweetener that is used as a substitute for sugar. Which of the following graphs shows the effect on the supply of bakery desserts made with stevia when the price of stevia rises?
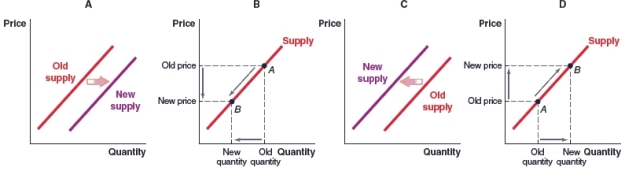
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
(Figure: Market for Bread) Which of the following graphs shows what will happen in the market for bread if the price of organic wheat used in bread production rises?
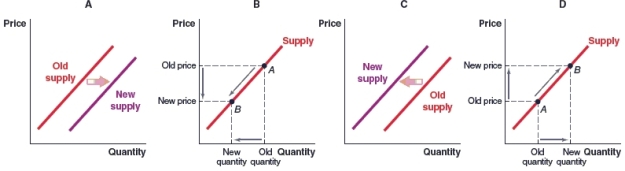
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
(Figure: Market for Lenovo Desktops) Lenovo produces laptops and desktop computers. Which graph shows what will happen in the market for Lenovo desktops if the demand for laptops increases?
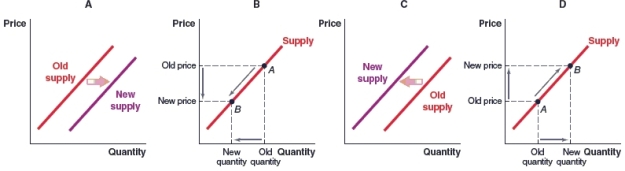
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following lists only the factors that would cause a decrease in the supply of an item?
A)A fall in input prices; an increase in productivity; a fall in the price of a substitute-in-production.
B)A rise in the price of a substitute-in-production; a rise in the price of a complement-in-production; an expectation that the price of the item will rise in the future.
C)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a fall in the price of a complement-in-production; an increase in productivity.
D)A rise in input prices; a decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a rise in the price of a substitute-in-production.
A)A fall in input prices; an increase in productivity; a fall in the price of a substitute-in-production.
B)A rise in the price of a substitute-in-production; a rise in the price of a complement-in-production; an expectation that the price of the item will rise in the future.
C)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a fall in the price of a complement-in-production; an increase in productivity.
D)A rise in input prices; a decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a rise in the price of a substitute-in-production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following lists only factors that would cause an increase in the supply of an item?
A)A decrease in input prices; a technological innovation; a fall in the price of a substitute-in-production.
B)A rise in the price of a substitute-in-production; an increase in the price of a complement-in-production; an expectation that the price of the item will increase in the future.
C)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a fall in the price of a complement-in-production; a technological setback.
D)An increase in input prices; a decrease in the number of sellers in the market; an increase in the price of a substitute-in-production.
A)A decrease in input prices; a technological innovation; a fall in the price of a substitute-in-production.
B)A rise in the price of a substitute-in-production; an increase in the price of a complement-in-production; an expectation that the price of the item will increase in the future.
C)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market; a fall in the price of a complement-in-production; a technological setback.
D)An increase in input prices; a decrease in the number of sellers in the market; an increase in the price of a substitute-in-production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Figure: Market for Lenovo Tablets) Lenovo produces laptops and tablets. What will happen to the supply of Lenovo tablets, if laptops lose popularity and their demand falls?
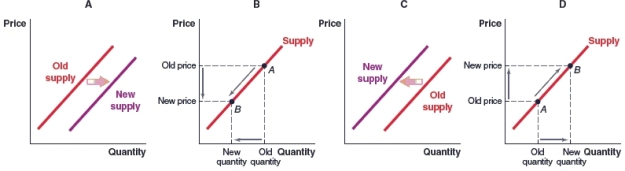
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Figure: Market for Video Games) Microsoft's Project Scarlett Xbox release date is 2020. Which graph shows what will happen to the development and supply of new compatible video games once the Xbox launches in the market?
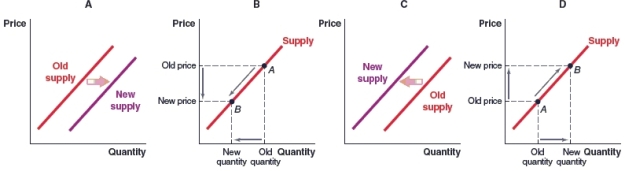
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If expected future profits in an industry fall,
A)the number of sellers in the market does not change.
B)supply is not affected.
C)supply will shift left.
D)supply will shift right.
A)the number of sellers in the market does not change.
B)supply is not affected.
C)supply will shift left.
D)supply will shift right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If expected future profits in an industry rise
A)the number of sellers in the market does not change.
B)supply will shift right.
C)supply will shift left.
D)supply is not affected.
A)the number of sellers in the market does not change.
B)supply will shift right.
C)supply will shift left.
D)supply is not affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 168 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



