Deck 13: Working With Projects
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Working With Projects
1
A project is a unique, repetitive, and structured work effort to accomplish a specific goal.
False
2
Projects are independent of time because you do not know how long it will take to finish them.
False
3
Commuting to work and maintaining a website are good examples of long-term projects.
False
4
Three key performance dimensions of a project are cost, scope, and time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Project management is the controlling of time and resources to meet and manage stakeholder goals, project risks, and project changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Project managers manage three things: performance, people, and change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The best project manager is the one with only the best technical skills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Very few big budget projects are failures because more money spent means quicker project completion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Seeking improvement in any one dimension of project performance requires acceptance of levels of elevated performance on the others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The four phases of any project are initiation, planning, implementation, and closure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The scope of any project, indicating what will and will not be included as part of the project, is perhaps the most important part of the initiation phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Scope creep in a project is when the project slows to a crawl because of a lack of project details.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the implementation phase, project details are thrashed out and documented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The phase in which we hand over the final deliverables to the client and intimate formal project closure to all stakeholders is called project closure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An important aspect of project closure is that lessons learned are discussed and recorded for future use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A full time equivalent is the number of hours it would take the project team to complete an activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Project teams are organized in a cross-functional or matrix structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Evaluation methods used for projects with predictable cash flows include the payback period, the NPV, the ROI, and the IRR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Evaluation methods used for projects with uncertain cash flows with estimated probabilities include the EMV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Nonfinancial evaluation criteria may include risk tolerances, potential market development options, or political reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Evaluation methods used for projects with cash flows that are too uncertain to estimate probabilities include the minimax, maximax, and the maximin regret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A Gantt chart is a colorful chart showing complex task interdependencies, costs, and activities on a time line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The longest path determines the expected time it will take to finish the project, and this is called the critical path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Critical activities are those activities where no delays can be tolerated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An activity with most slack time is called a critical activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A project can only have exactly one critical path.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The optimistic time estimate is the best time required to perform the activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Reducing project activity expected times or adding more resources (people/tools) to our project is called crashing a project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We crash a project only by reducing critical activity times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Critical paths cannot change when we crash a project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Very few projects are failures because they have well defined goals and their business intent is clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
People are the major reason for project failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Process failures arise when task times are underestimated or utilization of resources is overestimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Having actively engaged executive sponsors is the top driver of project success.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Every project needs a superstar to be successful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Projects with larger and longer deliverables are becoming more popular because of the chance to generate more revenue for the project providers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Portfolio selection and management skills are becoming valuable in overseeing and orchestrating a global portfolio of projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Real options theory from finance is finding use in valuing project growth, deferment, stage, scale, switching, and abandonment options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A project can be recognized by
A) tasks that have specific goals
B) tasks that involve teams with interdependent activities
C) tasks that have linked work steps with a specified time line
D) all of the above
A) tasks that have specific goals
B) tasks that involve teams with interdependent activities
C) tasks that have linked work steps with a specified time line
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not a project?
A) doing a term paper or presentation for your OM class
B) writing a weekly newspaper sports column
C) maintaining your company's website
D) All of the above are projects.
A) doing a term paper or presentation for your OM class
B) writing a weekly newspaper sports column
C) maintaining your company's website
D) All of the above are projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Project management involves managing all of the following except
A) project risks
B) stakeholder quality
C) project changes
D) scenario planning
A) project risks
B) stakeholder quality
C) project changes
D) scenario planning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Project performance can be assessed by measuring all of the following dimensions except
A) quality
B) cost
C) time
D) scope
A) quality
B) cost
C) time
D) scope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is not a phase of a project?
A) scoping
B) implementation
C) closure
D) planning
A) scoping
B) implementation
C) closure
D) planning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An organizational structure where team members are assigned to a project and report directly to the project manager is called
A) a hierarchical structure
B) a matrix structure
C) a mixed project structure
D) a departmental structure
A) a hierarchical structure
B) a matrix structure
C) a mixed project structure
D) a departmental structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The "dual-boss" problem occurs in a
A) matrix organizational structure
B) pure project type structure
C) functional organizational structure
D) multilayered organizational structure
A) matrix organizational structure
B) pure project type structure
C) functional organizational structure
D) multilayered organizational structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Short- to medium-term project selection with predictable cash flows can be done by which of the following methods?
A) simple payback period
B) net present value
C) internal rate of return
D) all of the above
A) simple payback period
B) net present value
C) internal rate of return
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If we cannot estimate probabilities because the project cash flows are uncertain, then we can use all of the following methods except
A) minimax regret
B) maximin
C) maximax
D) EMV
A) minimax regret
B) maximin
C) maximax
D) EMV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is not a method used to evaluate projects with unpredictable cash flows where probabilities cannot be estimated?
A) maximin
B) maximax
C) minimax
D) minimax regret
A) maximin
B) maximax
C) minimax
D) minimax regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Popular techniques to plan for and monitor a project include
A) WBS, Pareto chart, PERT/CPM
B) WBS, Gantt chart, and PERT/CPM
C) LFT, EFT, and EST
D) LFT, EST, and LST
A) WBS, Pareto chart, PERT/CPM
B) WBS, Gantt chart, and PERT/CPM
C) LFT, EFT, and EST
D) LFT, EST, and LST

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Activity times for a project can be estimated by all but which of the following methods?
A) standard normal distribution curve models to improve replications
B) statistical methods based on actual past experiences
C) subcontractors with extensive experience in our project area
D) previous managerial experiences
A) standard normal distribution curve models to improve replications
B) statistical methods based on actual past experiences
C) subcontractors with extensive experience in our project area
D) previous managerial experiences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which one of the following statements best describes the critical path of a project network?
A) It is the sequence of activities between a project's start and finish that has the maximum amount of slack.
B) It is the sequence of activities that has the smallest normal activity cost.
C) It is the set of activities that has the smallest total number of predecessors.
D) It is the sequence of activities between a project's start and finish that takes the longest time to complete.
A) It is the sequence of activities between a project's start and finish that has the maximum amount of slack.
B) It is the sequence of activities that has the smallest normal activity cost.
C) It is the set of activities that has the smallest total number of predecessors.
D) It is the sequence of activities between a project's start and finish that takes the longest time to complete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A project has three possible paths from start to finish. Path A-B-C is 15 hours; path A-C-D is 10 hours, and path A-C-E is 20 hours. Which one of the following statements is true?
A) The expected duration of this project is 10 hours.
B) The expected duration of this project is 15 + 10 + 20 = 45 hours.
C) Path A-C-E is the critical path.
D) Path A-B-C has the most slack.
A) The expected duration of this project is 10 hours.
B) The expected duration of this project is 15 + 10 + 20 = 45 hours.
C) Path A-C-E is the critical path.
D) Path A-B-C has the most slack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given that activity B has the following times, which of the following statements is true about activity B?
Earliest start time = 9 days; latest start time = 17 days; earliest finish time = 15 days; latest finish time = 23 days
A) Activity B has a slack time of 8 days.
B) Activity B is a critical activity.
C) Activity B takes 6 days to complete.
D) Activity B takes 23 days to complete.
Earliest start time = 9 days; latest start time = 17 days; earliest finish time = 15 days; latest finish time = 23 days
A) Activity B has a slack time of 8 days.
B) Activity B is a critical activity.
C) Activity B takes 6 days to complete.
D) Activity B takes 23 days to complete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is the critical path for the project network shown in the following diagram? 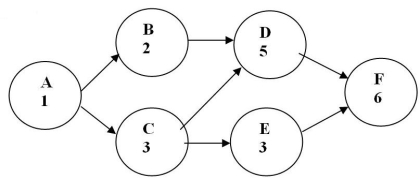
A) ACEF
B) ACDF
C) ABDF
D) ABCDEF

A) ACEF
B) ACDF
C) ABDF
D) ABCDEF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the project duration for the project network shown in the following diagram? 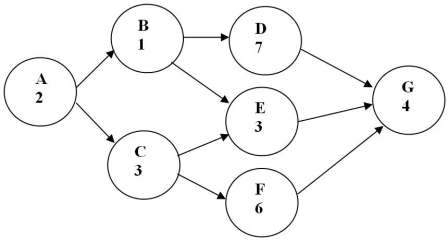
A) 20
B) 13
C) 15
D) 14

A) 20
B) 13
C) 15
D) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Using the information shown in the following table, what is the slack time for activity E?
A) 1
B) 7
C) 6
D) 3
A) 1
B) 7
C) 6
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using the information shown in the previous table, what is the earliest finish time for activity F?
A) 6
B) 0
C) 4
D) 11
A) 6
B) 0
C) 4
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Using the information shown in the previous table, what is the duration time for activity D?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 7
D) 1
A) 3
B) 4
C) 7
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Using the first diagram above, which one of the following paths is the critical path?
A) ACEG
B) ACFG
C) ABEG
D) ABDG
A) ACEG
B) ACFG
C) ABEG
D) ABDG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Using the second diagram above or using the information shown in the previous table, what is the project duration?
A) 15
B) 12
C) 14
D) 10
A) 15
B) 12
C) 14
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Using the information shown in the following table, the expected time for activity B is 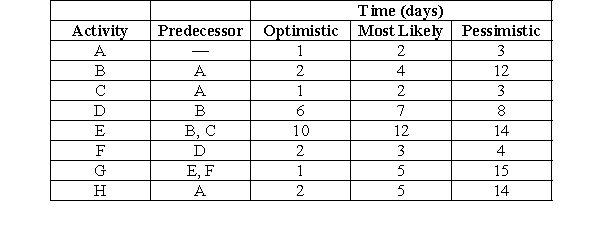
A) more than 12 days
B) 5 days
C) 2 days
D) 4 days

A) more than 12 days
B) 5 days
C) 2 days
D) 4 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Using the information shown in the previous table, what is the variance for activity H?
A) 6
B) 12
C) 4
D) 0.44
A) 6
B) 12
C) 4
D) 0.44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Using the information shown in the previous table, what is the standard deviation for the entire project?
A) 43
B) 1.64
C) 13.11
D) 3.62
A) 43
B) 1.64
C) 13.11
D) 3.62

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the length of the critical path is 25 weeks, what is the probability that the project will be completed on or before 22 weeks?
A) greater than 20 percent but less than 25 percent
B) greater than 25 percent but less than or equal to 35 percent
C) greater than 80 percent but less than or equal to 85 percent
D) greater than 85 percent
A) greater than 20 percent but less than 25 percent
B) greater than 25 percent but less than or equal to 35 percent
C) greater than 80 percent but less than or equal to 85 percent
D) greater than 85 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the length of the critical path is 25 weeks, what is the shortest project due date if the project manager wants at least a 98 percent probability that the project will be completed on or before the due date?
A) less than or equal to 25 weeks
B) greater than 32 weeks but less than 33 weeks
C) greater than 33 weeks but less than or equal to 35 weeks
D) greater than 25 weeks but less than 32 weeks
A) less than or equal to 25 weeks
B) greater than 32 weeks but less than 33 weeks
C) greater than 33 weeks but less than or equal to 35 weeks
D) greater than 25 weeks but less than 32 weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Using the data supplied in the following table, by how many weeks can we crash activity A?
A) 0
B) 6
C) 1
D) 2
A) 0
B) 6
C) 1
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Using the data supplied, what is the crashing cost per week for activity A?
A) $3,000
B) $6,000
C) $2,000
D) cannot be determined
A) $3,000
B) $6,000
C) $2,000
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Using the data supplied, if a decision is made to crash activity C, what is the cost for this one week of crashing?
A) $2,000
B) This activity cannot be crashed.
C) $3,000
D) $2,500
A) $2,000
B) This activity cannot be crashed.
C) $3,000
D) $2,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Using the data supplied, which activity should be crashed first if the critical path is A-B-D-E?
A) B
B) A
C) E
D) D
A) B
B) A
C) E
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If activity E is reduced by 1 week and activity A is reduced by 2 weeks, what is the new total project cost?
A) $69,000
B) $34,000
C) $55,000
D) $76,000
A) $69,000
B) $34,000
C) $55,000
D) $76,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A(n) __________ has specific goals, linked work steps with a specified timeline, a clear start and finish, and is fairly unique and nonrepetitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
__________ is the art of orchestrating time and resources to meet and manage stakeholder goals, project risks, and project changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Managing multiple projects is called __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Project performance has three dimensions: __________, __________, and __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The __________ phase is when project details are thrashed out and documented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Lucy, the project manager, and her team were able to archive important project documents in a safe and accessible place and then celebrate during the __________ phase of the project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Larry was part of a project team due to his technical expertise. However, he was faced with the dilemma of reporting to two bosses: one in his functional area and his project manager. Larry is in a firm that has a(n) __________ organizational structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
__________ and __________ are two methods of evaluating short- to medium-term projects with predictable cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Janet was tasked with assessing competing projects with unpredictable cash flows and where the probabilities could not be estimated. In order for her to perform her analysis, she should use the __________ or __________ techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The __________ is a statement of all work, tasks, and subtasks that have to be completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



