Deck 1: The Natural Environment and the Human Economy: the Neoclassical Perspective
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Natural Environment and the Human Economy: the Neoclassical Perspective
1
Neoclassical economics is the dominant approach to economic analyses.
True
2
Neoclassical economists are fully aware of the critical significance of ecosystem services
to humans.
to humans.
True
3
Only environmental resources, unlike economic resources, such as capital and labor, are
considered to be scarce resources.
considered to be scarce resources.
False
4
The provision of ecosystem services is essential for supporting and sustaining life, and by
extension, is also necessary for the human economy to function.
extension, is also necessary for the human economy to function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In many respects, there is little trade-off between economic goods and services and the
preservation of the quality of the natural environment.
preservation of the quality of the natural environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A renewable resource is one that is, by definition, priced at zero dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Market price is an indicator of absolute scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Market prices are market-clearing prices because they fully account for all the costs of
either extracting or using resources.
either extracting or using resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Factor substitution suggests that basic resources do not need to be used in combinations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
It is possible to substitute natural capital with human-made capital and vice-versa to
produce a desired level of output.
produce a desired level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Environmental resources can always be substituted by other factors of production at a
decreasing opportunity cost.
decreasing opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Technological advance implies a possibility of producing a given level of
output with less of any resources, with the exception of the environment.
output with less of any resources, with the exception of the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Technological advancement is the ability to produce a given amount of output by using
less of all inputs.
less of all inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The anthropocentric economic view implies that environmental services have no intrinsic
value.
value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The primary goal of a market-oriented economy is maximizing consumers' wellbeing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Economics approach is called anthropocentric because
A) Environmental resources are deemed to have no intrinsic value.
B) Environmental resources are evaluated based on their uses to all living beings, human or
non-human.
C) Environmental degradation is considered unacceptable, even if benefits to humans are
accrued.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) Environmental resources are deemed to have no intrinsic value.
B) Environmental resources are evaluated based on their uses to all living beings, human or
non-human.
C) Environmental degradation is considered unacceptable, even if benefits to humans are
accrued.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The provision of ecosystem services
A) Are essential for supporting and sustaining life.
B) Are not fully accounted for by the market-clearing price.
C) Have been overlooked by neoclassical economists.
D) None of the above.
E) All of the above.
A) Are essential for supporting and sustaining life.
B) Are not fully accounted for by the market-clearing price.
C) Have been overlooked by neoclassical economists.
D) None of the above.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The natural environment is assumed to depend on which of the following?
A) Extraction of non-renewable resources.
B) Extraction of renewable resources.
C) Sunlight.
D) Humans.
E) All of the above.
A) Extraction of non-renewable resources.
B) Extraction of renewable resources.
C) Sunlight.
D) Humans.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The opportunity cost of a particular activity
A) Is always unknown with certainty.
B) Is a concept applicable to ecological economics, but not to the neoclassical approach.
C) Usually decreases as more of that activity is pursued.
D) Increases when more environmental resources need to used to substitute for the same
amount of other factors of production.
E) None of the above.
A) Is always unknown with certainty.
B) Is a concept applicable to ecological economics, but not to the neoclassical approach.
C) Usually decreases as more of that activity is pursued.
D) Increases when more environmental resources need to used to substitute for the same
amount of other factors of production.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An ecosystem service, such as bee pollination, is dramatically increase because of reduction in pesticide use. How would this influence the opportunity cost for an apple orchard that relies on bees for pollination of their apple trees?
A) It would not affect the opportunity cost
B) It would increase the opportunity
C) It would decrease the opportunity cost
D) From an economic standpoint, opportunity cost should not be an issue
E) None of the above
A) It would not affect the opportunity cost
B) It would increase the opportunity
C) It would decrease the opportunity cost
D) From an economic standpoint, opportunity cost should not be an issue
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the following substitution possibility graph. Assume that the output level (i.e. Economic production) is the same for each line (Q0 = Q1 = Q2). Which of the following statements is correct?
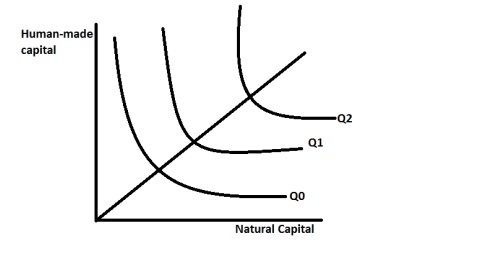
A) With Q1, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
is lower relative to Q0.
B) With Q2, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
is lowest relative to Q0 and Q1.
C) With Q0, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
Is highest relative to Q1 and Q2.
D) Only b) and c) are correct
E) A), b), and c) are correct

A) With Q1, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
is lower relative to Q0.
B) With Q2, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
is lowest relative to Q0 and Q1.
C) With Q0, technological improvements are such that resource conservation
Is highest relative to Q1 and Q2.
D) Only b) and c) are correct
E) A), b), and c) are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the following substitution possibility graph. Assume that the output level (i.e. Economic production) is the same for each line (Q0 = Q1 = Q2). Which of the following statements is correct?
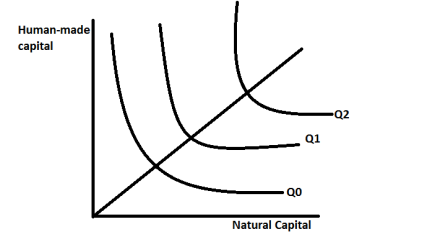
A) Any point along Q2 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more natural capital relative to any point along Q1 or Q2.
B) Any point along Q2 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more human-made capital relative to any point along Q0 or Q1.
C) Any point along Q0 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more human-made capital relative to any point along Q1 or Q2.
D) Both a and b
E) None of the above

A) Any point along Q2 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more natural capital relative to any point along Q1 or Q2.
B) Any point along Q2 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more human-made capital relative to any point along Q0 or Q1.
C) Any point along Q0 represents a combination of resource outputs that
requires more human-made capital relative to any point along Q1 or Q2.
D) Both a and b
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A free market system
A) Allows for the determination of absolute scarcity by constructing a ratio of
two market-clearing prices
B) Provides information about the scarcity values of non-renewable resources
only
C) Exhibits a shortage when the supply of a resources exceeds the demand of
a resource
D) None of the above
E) All of the above
A) Allows for the determination of absolute scarcity by constructing a ratio of
two market-clearing prices
B) Provides information about the scarcity values of non-renewable resources
only
C) Exhibits a shortage when the supply of a resources exceeds the demand of
a resource
D) None of the above
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Correcting for possible market price distortions
A) Is required because prices deliver perfect information on absolute scarcity
B) Is challenging because most ecosystem services are easily traded through
normal market mechanisms
C) Is easily done because it is known that that ecosystem services are
valuable
D) Allows one to estimate the value ecosystem services
E) All of the above
A) Is required because prices deliver perfect information on absolute scarcity
B) Is challenging because most ecosystem services are easily traded through
normal market mechanisms
C) Is easily done because it is known that that ecosystem services are
valuable
D) Allows one to estimate the value ecosystem services
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the factor market,
A) Supply provides information about households as resource owners
B) Firms are the suppliers of capital and natural resources
C) Households provide services for the product market
D) None of the above
E) All of the above
A) Supply provides information about households as resource owners
B) Firms are the suppliers of capital and natural resources
C) Households provide services for the product market
D) None of the above
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



