Deck 10: The Economics of Biodiversity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Economics of Biodiversity
1
According to the Malthusian perspective, technology is the solution to resource
scarcity.
scarcity.
False
2
Ricardo concluded that growth would be hampered in the long run by explosive growth of human population.
False
3
If the quality of land overtime declines, then there will be a steady decrease in
land rent.
land rent.
False
4
Malthus believed that coal would ultimately determine the future economic prosperity or decline of a nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Jevons paradox states that the advantages gained by technological will offset the rate of increase in consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Malthus' theory considers the role of technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Human population that stood at 4 billion in 1930.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Humans have been able to increase their population by 1 billion in just 30
years.
years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Neo-Malthusians are very critical of economic growth at any cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Paul Ehrlich predicted a future of resource shortage and famine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Paul Ehrlich, like Malthus, asserts that human population-growth is the main reason for continued resource depletion and environmental degradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Using the simple mathematical model, I = P x F, one can interpret F as the ecological footprint of the average person.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Neo-Malthusians policy implications for protecting the environment
necessarily favor the inclusion of private markets for the allocation of resources.
necessarily favor the inclusion of private markets for the allocation of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The ecological economics perspective is almost identical to that of the neo-
Malthusians: natural resources are understood to be a limiting factor to economic growth in the long-run.
Malthusians: natural resources are understood to be a limiting factor to economic growth in the long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Arguments based on the laws of thermodynamics and ecological principles for the existence of biophysical limits forms the basis of the ecological economics
school of thought.
school of thought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Malthus 's theory is usually associated with the view that
A) Efficient use of improved technology can overcome the problems of population growth.
B) Social and political crises will result from uncontrolled growth in the population.
C) Colonisation, if implemented properly, would lead to reduced resource use.
D) Ecological footprints understate the effects of overpopulation.
E) All of the above.
A) Efficient use of improved technology can overcome the problems of population growth.
B) Social and political crises will result from uncontrolled growth in the population.
C) Colonisation, if implemented properly, would lead to reduced resource use.
D) Ecological footprints understate the effects of overpopulation.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The growth rate of world population peaked in ___ at an annual rate of ___ percent.
A) 1770; 5.50
B) 1885; 2.10
C) 1972; 2.06
D) 1982; 1.02
E) 1995; 2.09
A) 1770; 5.50
B) 1885; 2.10
C) 1972; 2.06
D) 1982; 1.02
E) 1995; 2.09

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the ecological economics perspective,
A) scarcity of energy is a more prominent factor for sustainably than the Neo-
Malthusian view.
B) scarcity of natural capital is a more prominent factor for sustainably than
The Neo-Malthusian view.
C) Ecological resilience is a more prominent factor for sustainably than the
Neo-Malthusian view.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) scarcity of energy is a more prominent factor for sustainably than the Neo-
Malthusian view.
B) scarcity of natural capital is a more prominent factor for sustainably than
The Neo-Malthusian view.
C) Ecological resilience is a more prominent factor for sustainably than the
Neo-Malthusian view.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The British economist Thomas Malthus predicted which of the following?
A) Efficiency gains in technology will improve living standards over time.
B) Given that population growth is exponential, the Earth will eventually see a population in excess of 25 billion people.
C) Resource constraints will pressure the global population to enter a demographic transition
resulting in lower birth and death rates.
D) Famines and low living standards will always be the results because food supplies will
eventually become insufficient to meet demand.
E) All of the above.
A) Efficiency gains in technology will improve living standards over time.
B) Given that population growth is exponential, the Earth will eventually see a population in excess of 25 billion people.
C) Resource constraints will pressure the global population to enter a demographic transition
resulting in lower birth and death rates.
D) Famines and low living standards will always be the results because food supplies will
eventually become insufficient to meet demand.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Commoner's view of modern technology implies which of the following?
A) Modern technology is ill-conceived because it does not consider its effects
On the environment.
B) Modern technology is poorly designed it purposely harms the natural
Environment.
C) Technical efficiency is not based on input and output decisions.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) Modern technology is ill-conceived because it does not consider its effects
On the environment.
B) Modern technology is poorly designed it purposely harms the natural
Environment.
C) Technical efficiency is not based on input and output decisions.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why do some consider an aspect of Commoner's IPAT model controversial?
A) Commoner is the first person to suggest that the most significant portion
Of total environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises
From population increases.
B) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in the mix of inputs and outputs.
C) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in ecological resilience.
D) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in human capital.
E) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in the stock of non-renewal resources.
A) Commoner is the first person to suggest that the most significant portion
Of total environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises
From population increases.
B) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in the mix of inputs and outputs.
C) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in ecological resilience.
D) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in human capital.
E) Commoner suggested that the most significant portion of total
Environmental damage in contemporary industrial nations arises from changes in the stock of non-renewal resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The environmental impact equation by Commoner defines environmental impacts as a function of which variables?
A) Energy and population.
B) Energy, population, and natural resources.
C) Technology, natural capital, human capital, and physical capital.
D) Affluence, energy, and technology.
E) Technology, affluence, and population.
A) Energy and population.
B) Energy, population, and natural resources.
C) Technology, natural capital, human capital, and physical capital.
D) Affluence, energy, and technology.
E) Technology, affluence, and population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In what way was classical economist John Stuart Mill's population and human material progress perspective different from Malthus' perspective?
A) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that unlimited
Economic growth would lead to the destruction of the environment and a
Lower quality of life.
B) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that unlimited
Population growth would lead to the destruction of the environment and a lower quality of life.
C) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that low prices
For non-renewal resources would lead to the destruction of the
Environment.
D) Material progress would lead to too great a population growth rate, which,
In turn, would lead to the destruction of the environment.
E) All of the above.
A) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that unlimited
Economic growth would lead to the destruction of the environment and a
Lower quality of life.
B) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that unlimited
Population growth would lead to the destruction of the environment and a lower quality of life.
C) Mill's book The Principles of Political Economy argued that low prices
For non-renewal resources would lead to the destruction of the
Environment.
D) Material progress would lead to too great a population growth rate, which,
In turn, would lead to the destruction of the environment.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure A
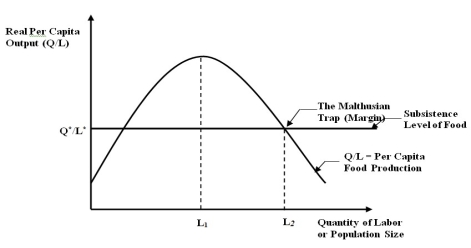
-Refer to Figure A. Assume a society initially is at a level below Q*/L*. Which of the following is correct concerning the evolution of this society?
A) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches the subsistence
level of food.
B) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches L1.
C) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches L2.
D) Population rises only if per capita food output continues to rise.
E) The Malthusian trap does not apply if a society initially is at a level below
Q*/L*.

-Refer to Figure A. Assume a society initially is at a level below Q*/L*. Which of the following is correct concerning the evolution of this society?
A) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches the subsistence
level of food.
B) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches L1.
C) Per capita food output continues to rise until it reaches L2.
D) Population rises only if per capita food output continues to rise.
E) The Malthusian trap does not apply if a society initially is at a level below
Q*/L*.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Assume that you are endowed with a large piece of good farm land. You decide to have 10 children to work on the land. Your crop yield is very good. As such, you decide to have 10 more children in the belief that you will double your crop yield. Which of the following statements best describes what may happen with 10 more children?
A) The next set of children will starve.
B) You are correct - you will double output.
C) Output will remain the same.
D) Unsure - your family will grow as long as the yield per child food is more
than your family's subsistence level, which is not provided.
E) None of the statements above are possible outcomes.
A) The next set of children will starve.
B) You are correct - you will double output.
C) Output will remain the same.
D) Unsure - your family will grow as long as the yield per child food is more
than your family's subsistence level, which is not provided.
E) None of the statements above are possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



