Deck 4: Designing Research
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Designing Research
1
__________ is the ability to tell whether a researcher studied what he or she proposed to study.
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction
Validity
2
__________ is the ability to project the results of a study from a sample to population.
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction
Projectability
3
__________ moves from something known to be true (major premise) toward a supporting idea and then to some conclusion
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Induction
D) Deduction
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Induction
D) Deduction
Deduction
4
__________ makes general conclusions based on individual observations
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Induction
D) Deduction
A) Reliability
B) Validity
C) Induction
D) Deduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
__________starts with a premise based on a sample group and leads to a conclusion involving another individual.
A) Simple Induction
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
__________ goes from a premise based on a sample group and leads to a conclusion about the entire population.
A) Simple Induction
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
__________ is drawing a conclusion about cause-and-effect relationship based on observations of some occurrence and conditions that exist at a given time, which one assumes to be the cause.
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
__________ is going from a generalization to a specific conclusion.
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
__________ goes from similarities between two things to a conclusion about some additional attributes of both things.
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction.
B) Inductive generalization
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The figure below represents __________.
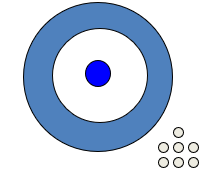
A) Reliabity
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction

A) Reliabity
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Deduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The figure below represents __________.
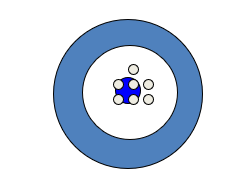
A) Reliabity
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Both (a) and (b)

A) Reliabity
B) Validity
C) Projectability
D) Both (a) and (b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Red cars have higher insurance rates. Sam has a red car. Therefore, Sam has a high auto insurance rate. This is an example of __________ reasoning.
A) Simple Induction
B) Deductive
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy
A) Simple Induction
B) Deductive
C) Causal inference
D) Statistical syllogism
E) Analogy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Method and methodology are one and the same. They can be used interchangeably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The illustration below represents the concept of reliability.
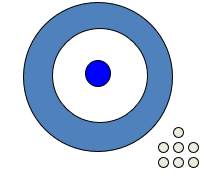


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The illustration below represents validity.
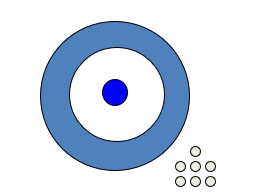


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For an instrument to be valid it also has to be reliable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Prediction involves a conclusion about future from sample in past

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Define any five of the following terms: deduction, induction, projectability, reliability, validity, statistical syllogism, analogy, and causal inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



