Deck 8: Government and Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Government and Markets
1
Proponents of incentive-based regulations for reducing acid rain maintain that they result in companies with the highest cost of decreasing acid rain being the ones to make relatively large cutbacks.
False
2
Among the sources of market failure are competitive markets, private goods, and economic equality.
False
3
A monopoly results in market failure because it uses too few resources to produce goods at an artificially high price.
True
4
Antitrust policy is the attempt to promote a market environment that results in increased competition and a reduction in anti-competitive behavior that harms consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the Clayton Act, every contract, combination in the form of a trust, or conspiracy in restraint of trade is illegal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Among the business practices outlawed by the Clayton Act are interlocking directorates, price discrimination, mergers, and tying contracts that substantially lessen competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All industries in the United States are subject to the provisions of the Sherman Act and Clayton Act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Social regulation controls the prices, wages, conditions of entry, and standards of service of particular industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During the 1970s, the federal government initiated steps to dismantle economic regulations in industries where they had outlived their usefulness-telecommunications, railroads, energy, airlines, and trucking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The traditional reason for allowing a public utility to operate as a monopoly, subject to regulation of price and output policies, is that the firm is a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the fair-return principle of regulation, a firm can charge a price high enough to allow it to realize an economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Fair-return regulation tends to decrease the motivation for public utilities to reduce costs, because they can attain essentially the same profits irrespective of their cost-reducing efforts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When the production of a good entails spillover benefits, too much of it is produced and there is an over-allocation of resources to its use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the production of a good entails spillover costs, too little of a good is produced and there is an under-allocation of resources to its use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To decrease pollution, the U.S. government relies primarily on command-and-control regulations, rather than incentive-based regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An example of an incentive-based regulation is the imposition of an excise tax on the production of chemicals to encourage chemical firms to reduce pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Whereas social regulation governs the conditions of doing business in a particular industry, economic regulation addresses the conditions under which goods are produced in a variety of industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Environmental Protection Agency, Consumer Production Safety Commission, and Occupational Safety and Health Administration are government agencies that engage in social regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Critics of the North American Free Trade Agreement have maintained that because environmental regulations in the United States are more stringent than those in Mexico, the competitiveness of U.S. firms may suffer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The international environmental policy of the United States and other industrial nations is founded on the polluter-pays principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The market system fails by under-producing public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Because of the free-rider problem, government is looked upon to provide public goods through the use of tax financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Public goods, such as lighthouses and highways, are produced and sold easily in small units and are not subject to the principle of rival consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When sellers or buyers have incomplete or inaccurate information about price and quality, markets will still result in efficient outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To help correct for the problem of economic inequality, government provides people in need with transfer payments such as unemployment compensation, food stamps, and Aid to Families with Dependent Children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Justice Department attempted to break up Microsoft Corp. because it felt the company had used its monopoly power to engage in anticompetitive business practices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis has recommended that cities stop competing for professional sports teams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The power shortages that occurred in California in the mid to late 1990s were caused by the state's complete deregulation of electric utility companies in 1996.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Under a system of peak-load pricing, customers are charged more for using electricity during the off-peak hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If there are spillover benefits associated with individuals receiving their annual flu shots, then the government can improve the free market outcome by subsidizing the cost of flu shots to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Command-and-control regulations impose restrictions on the amount of a polluting activity that is allowed to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Brookings Institution researchers have found that sports stadiums provide a big boost to employment and personal income to residents of local communities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Proponents of government subsidies for the building of sports stadiums argue that the presence of a professional sports team improves the quality of life in the community, even for those who do not attend games.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When someone buys a used car and finds out later that it has defects that were not disclosed, this is a form of market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following are sources of market failure except
A) private goods
B) public goods
C) spillover costs
D) spillover benefits
A) private goods
B) public goods
C) spillover costs
D) spillover benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following are sources of market failure except
A) competitive markets
B) monopoly power
C) inadequate information
D) economic inequality
A) competitive markets
B) monopoly power
C) inadequate information
D) economic inequality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All of the following are sources of market failure except
A) public goods
B) perfect information
C) spillover effects
D) monopoly power
A) public goods
B) perfect information
C) spillover effects
D) monopoly power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given the same costs, a monopolist maximizes profit by selling a ______ output and charging a ______ price than would a competitive market.
A) smaller, higher
B) smaller, lower
C) larger, higher
D) larger, lower
A) smaller, higher
B) smaller, lower
C) larger, higher
D) larger, lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Given the same costs, a competitive market maximizes profit by selling a ______ output and charging a ______ price than would a monopolist.
A) larger, higher
B) larger, lower
C) smaller, higher
D) smaller, lower
A) larger, higher
B) larger, lower
C) smaller, higher
D) smaller, lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
______ is the attempt to foster a market structure that will result in additional competition and less anti-competitive behavior that harms consumers.
A) Social regulation
B) Economic regulation
C) Fair return regulation
D) Antitrust policy
A) Social regulation
B) Economic regulation
C) Fair return regulation
D) Antitrust policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During the late 1800s, large corporations formed ______, a nineteenth century name given to cartels and other business agreements intended to restrain competition.
A) mergers
B) acquisitions
C) consolidations
D) trusts
A) mergers
B) acquisitions
C) consolidations
D) trusts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
According to the ______, every person who shall monopolize, or attempt to monopolize, or combine or conspire with any other person or persons to monopolize any part of the trade or commerce among the several States, or with foreign nations, shall be deemed guilty of a misdemeanor.
A) Clayton Act
B) Walter Act
C) Nixon Act
D) Sherman Act
A) Clayton Act
B) Walter Act
C) Nixon Act
D) Sherman Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The ______ broadened the Sherman Act and outlawed specific business practices that resulted in a substantial lessening of competition-price discrimination, mergers, tying contracts, and interlocking directorates
A) Wilson Act
B) McKinley Act
C) Clayton Act
D) Nelson Act
A) Wilson Act
B) McKinley Act
C) Clayton Act
D) Nelson Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is not a potential violation of the Clayton Act?
A) interlocking directorates
B) price discrimination
C) tying contracts
D) fair-return pricing
A) interlocking directorates
B) price discrimination
C) tying contracts
D) fair-return pricing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
All of the following are potential violations of the Clayton Act except
A) anti-competitive mergers
B) average-cost pricing
C) tying contracts
D) interlocking directorates
A) anti-competitive mergers
B) average-cost pricing
C) tying contracts
D) interlocking directorates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The federal antitrust laws are enforced primarily by the
A) Securities and Exchange Commission
B) Justice Department and the Federal Trade Commission
C) Public Utilities Commission
D) Federal Bureau of Investigation
A) Securities and Exchange Commission
B) Justice Department and the Federal Trade Commission
C) Public Utilities Commission
D) Federal Bureau of Investigation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
To control the wages, prices, conditions of entry, and standards of service in a particular industry, the government has used
A) antitrust regulation
B) social regulation
C) spillover regulation
D) economic regulation
A) antitrust regulation
B) social regulation
C) spillover regulation
D) economic regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the past, economic regulation has been used to control the prices, standards of service, and conditions of entry in all of the following industries except
A) automobiles
B) railroads
C) communications
D) trucking
A) automobiles
B) railroads
C) communications
D) trucking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the past, economic regulation has been used to control the prices, standards of service, and conditions of entry in all of the following industries except
A) energy
B) airlines
C) trucking
D) computers
A) energy
B) airlines
C) trucking
D) computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In response to the problems of economic regulation, the federal government dismantled economic regulations in the 1970s and 1980s in all of the following industries except
A) trucking
B) railroads
C) health care
D) telecommunications
A) trucking
B) railroads
C) health care
D) telecommunications

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The purpose of the deregulation movement of the 1970s and 1980s was to
A) increase competition and provide incentives for firms to introduce new products
B) prevent destructive competition from driving inefficient firms out of industries
C) provide stable markets so firms could realize of economies of scale
D) provide an orderly transition as industries evolve from infancy to maturity
A) increase competition and provide incentives for firms to introduce new products
B) prevent destructive competition from driving inefficient firms out of industries
C) provide stable markets so firms could realize of economies of scale
D) provide an orderly transition as industries evolve from infancy to maturity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The purpose of the deregulation movement of the 1970s and 1980s was to dismantle many ______ that had outlived their usefulness.
A) social regulations
B) economic regulations
C) antitrust laws
D) environmental regulations
A) social regulations
B) economic regulations
C) antitrust laws
D) environmental regulations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
U.S. public policy toward public utilities, such as gas and electric companies, has generally allowed them to operate as
A) private monopolies without government regulation of price and output
B) private monopolies subject to government regulation of price and output
C) firms owned and operated by the federal government
D) firms owned and operated by state governments
A) private monopolies without government regulation of price and output
B) private monopolies subject to government regulation of price and output
C) firms owned and operated by the federal government
D) firms owned and operated by state governments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Concerning public utilities, legislatures have traditionally allowed a regulated firm to receive a price that
A) provides an economic profit of 25 percent of invested capital
B) provides an economic profit of 15 percent of invested capital
C) covers average variable cost, but not average total cost
D) covers average fixed cost plus average variable cost
A) provides an economic profit of 25 percent of invested capital
B) provides an economic profit of 15 percent of invested capital
C) covers average variable cost, but not average total cost
D) covers average fixed cost plus average variable cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the legislature allows a public utility to receive a fair-return price, the firm can charge a price high enough to cover
A) average total cost
B) average variable cost
C) average fixed cost
D) marginal cost
A) average total cost
B) average variable cost
C) average fixed cost
D) marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
______ tends to reduce the incentives for public utilities to contain costs, because the firm realizes essentially the same profits regardless of its efforts.
A) Marginal cost pricing
B) Monopoly pricing
C) Fair-return pricing
D) Cartel pricing
A) Marginal cost pricing
B) Monopoly pricing
C) Fair-return pricing
D) Cartel pricing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Critics of fair-return regulation, as applied to public utilities, maintain that it
A) results in cutthroat competition that drives inefficient producers out of business
B) results in a price that exceeds average total cost
C) does not allow firms to realize economies of large-scale production
D) reduces incentives for public utilities to innovate and to contain costs
A) results in cutthroat competition that drives inefficient producers out of business
B) results in a price that exceeds average total cost
C) does not allow firms to realize economies of large-scale production
D) reduces incentives for public utilities to innovate and to contain costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
During the 1990s, a number of legislatures were deregulating former public utilities such as electricity and cable television companies. Such deregulation was due to an awareness that
A) the regulated firms were not profit-maximizing monopolies
B) the regulated firms were not natural monopolies
C) fair-return regulation could not limit economic profits
D) fair-return regulation only allowed a firm to realize a normal profit
A) the regulated firms were not profit-maximizing monopolies
B) the regulated firms were not natural monopolies
C) fair-return regulation could not limit economic profits
D) fair-return regulation only allowed a firm to realize a normal profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When the production of a good results in spillover costs, the market system fails by producing ______ of it and ______ resources to its use.
A) too little, under-allocating
B) too little, over-allocating
C) too much, over-allocating
D) too much, under-allocating
A) too little, under-allocating
B) too little, over-allocating
C) too much, over-allocating
D) too much, under-allocating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the production of a good results in spillover benefits, the market system fails by producing ______ of it and ______ resources to its use.
A) too little, under-allocating
B) too little, over-allocating
C) too much, over-allocating
D) too much, under-allocating
A) too little, under-allocating
B) too little, over-allocating
C) too much, over-allocating
D) too much, under-allocating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To force the market to decrease its pollution, government imposes command-and-control regulations on producers. Such regulations include all of the following except
A) restrictions on the amount of pollutants that a firm can place into the air
B) excise taxes imposed on the production of chemicals
C) legislation that specifies procedures for the disposal of contaminated soils
D) legislation that specifies dump sites for the disposal of contaminated solvents
A) restrictions on the amount of pollutants that a firm can place into the air
B) excise taxes imposed on the production of chemicals
C) legislation that specifies procedures for the disposal of contaminated soils
D) legislation that specifies dump sites for the disposal of contaminated solvents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Concerning governmental regulation of pollution, command-and-control regulations suffer from all of the following problems except
A) assigning the proper excise tax to discourage pollution
B) being subject to enforcement procedures that are costly for the taxpayer
C) regulators not having detailed knowledge of production facilities and processes
D) regulators not being aware of alternative methods of pollution abatement
A) assigning the proper excise tax to discourage pollution
B) being subject to enforcement procedures that are costly for the taxpayer
C) regulators not having detailed knowledge of production facilities and processes
D) regulators not being aware of alternative methods of pollution abatement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
______ regulation is intended to correct a variety of undesirable side effects in a market economy that relate to the environment, safety, and health.
A) Antitrust
B) Antimonopoly
C) Economic
D) Social
A) Antitrust
B) Antimonopoly
C) Economic
D) Social

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is an example of social regulation in the U.S.?
A) automobiles have seat belts
B) a cat does not eat chocolate
C) books have numbered pages
D) a child wears boots when it rains
A) automobiles have seat belts
B) a cat does not eat chocolate
C) books have numbered pages
D) a child wears boots when it rains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
All of the following statements are true characteristics of private goods except
A) they come in units small enough that they can be purchased by individuals
B) only those who have the ability to pay can purchase the good
C) when one individual consumes a good, another cannot consume the same one
D) they are the same as public goods
A) they come in units small enough that they can be purchased by individuals
B) only those who have the ability to pay can purchase the good
C) when one individual consumes a good, another cannot consume the same one
D) they are the same as public goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Jen puts out holiday decorations in her front yard in December and many passers-by enjoy the display. This is an example of a
A) spillover benefit
B) spillover cost
C) social regulation
D) fair-return price
A) spillover benefit
B) spillover cost
C) social regulation
D) fair-return price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Public goods include all of the following except a(n)
A) Big Mac hamburger
B) lighthouse
C) highway
D) air traffic control system
A) Big Mac hamburger
B) lighthouse
C) highway
D) air traffic control system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The U.S. government has relied primarily on ______ to force firms to decrease their pollution.
A) incentive-based regulations
B) command-and-control regulations
C) free-rider regulations
D) fair-return regulations
A) incentive-based regulations
B) command-and-control regulations
C) free-rider regulations
D) fair-return regulations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the Florida Power Co. is a natural monopoly, government policies that break it up would
A) limit the ability of the firm to realize economies of large-scale production
B) force the firm to realize diseconomies of large-scale production
C) ensure that the firm would realize economic profits
D) prevent the firm from realizing economic profits
A) limit the ability of the firm to realize economies of large-scale production
B) force the firm to realize diseconomies of large-scale production
C) ensure that the firm would realize economic profits
D) prevent the firm from realizing economic profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Market failure occurs when ABC Chemical Co. does not take into account spillover costs. Therefore, the firm produces
A) too little output and charges too low a price
B) too little output and charges too high a price
C) too much output and charges too low a price
D) too much output and charges too nigh a price
A) too little output and charges too low a price
B) too little output and charges too high a price
C) too much output and charges too low a price
D) too much output and charges too nigh a price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
To help clear the skies of acid rain, the U.S. government allows the trading of emission certificates. Such a program is an example of
A) command-and-control regulation
B) incentive-based regulation
C) fair-return regulation
D) social-benefit regulation
A) command-and-control regulation
B) incentive-based regulation
C) fair-return regulation
D) social-benefit regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
To help clear the skies of acid rain, the U.S. government allows the trading of emission certificates. If the price of a certificate is $25,000, then acid rain will be decreased by companies that can do so at a cost of
A) less than $25,000
B) exactly $25,000
C) greater than $25,000
D) any amount
A) less than $25,000
B) exactly $25,000
C) greater than $25,000
D) any amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Proponents of incentive-based regulations for reducing pollution maintain that they result in firms with
A) the lowest cost of decreasing pollution to make relatively large reductions
B) the highest cost of decreasing pollution to make relatively large reductions
C) substantial economic profits making relatively large reductions
D) substantial economic losses making relatively large reductions
A) the lowest cost of decreasing pollution to make relatively large reductions
B) the highest cost of decreasing pollution to make relatively large reductions
C) substantial economic profits making relatively large reductions
D) substantial economic losses making relatively large reductions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Industries have been made subject to economic regulations for all the following reasons except
A) large economies of scale
B) fear of destructive competition
C) extending the scope of service
D) corruption of government officials
A) large economies of scale
B) fear of destructive competition
C) extending the scope of service
D) corruption of government officials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that Rebecca throws her Coke bottle out the car window and it smashes on the road. Jim drives over the broken glass and gets a flat tire. Rebecca's Coke consumption has resulted in a spillover
A) production of Coke
B) benefit
C) cost
D) natural monopoly
A) production of Coke
B) benefit
C) cost
D) natural monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 7.1 Market Failure
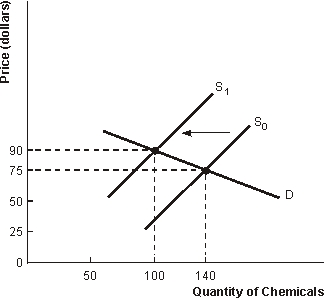
-Refer to Figure 7.1. The market failure depicted is
A) a spillover cost
B) a spillover benefit
C) income inequality
D) a public good

-Refer to Figure 7.1. The market failure depicted is
A) a spillover cost
B) a spillover benefit
C) income inequality
D) a public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 7.1 Market Failure

-Refer to Figure 7.1. Without any government intervention, the free market results in price equal to ______ and quantity equal to ______.
A) $90; 100
B) $75; 140
C) $90; 140
D) $75; 100

-Refer to Figure 7.1. Without any government intervention, the free market results in price equal to ______ and quantity equal to ______.
A) $90; 100
B) $75; 140
C) $90; 140
D) $75; 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 7.1 Market Failure

-Refer to Figure 7.1. The government could make the firm move from S0 to S1 by requiring the firm to
A) take spillover benefits into account
B) sell more output
C) lower its price
D) install pollution-control equipment

-Refer to Figure 7.1. The government could make the firm move from S0 to S1 by requiring the firm to
A) take spillover benefits into account
B) sell more output
C) lower its price
D) install pollution-control equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Education is an activity that is considered to
A) have spillover costs
B) have spillover benefits
C) be a private good
D) be required under the Sherman Act
A) have spillover costs
B) have spillover benefits
C) be a private good
D) be required under the Sherman Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Sources of market failure include all of the following except
A) externalities
B) economic inequality
C) perfect competition
D) inadequate information
A) externalities
B) economic inequality
C) perfect competition
D) inadequate information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



