Deck 13: Fiscal Policy and the Federal Budget
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Fiscal Policy and the Federal Budget
1
When government spending exceeds tax revenues during a given year, a budget deficit occurs, which the government finances by issuing securities such as Treasury bills, notes, and bonds.
True
2
The multiplier effect that applies to changes in household taxes is larger than the one that applies to changes in government expenditures.
False
3
Discretionary fiscal policy is the deliberate use of changes in government expenditures and taxation to affect aggregate demand and influence the economy's performance in the short run.
True
4
If the federal government's budget is initially balanced, a fiscal policy that combats a recession would cause the budget to move into a surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To combat a recession, fiscal policy would increase government expenditures and/or decrease taxes, thus causing an increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To combat demand-pull inflation, fiscal policy would cut government expenditures and/or raise taxes, which causes the government's budget to move into a deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Automatic stabilizers work by preventing aggregate demand from decreasing as much in bad times and rising as much in good times, thus helping to stabilize the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the concept of automatic stabilizers, tax receipts automatically increase and transfer payments automatically decrease during economic prosperity, thus slowing the growth of aggregate demand and controlling upward pressure on the price level when the economy is expanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Among the problems facing fiscal policy are timing lags, irreversibility, deflationary bias, and the crowding-out effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The crowding-out effect and the foreign-trade effect enhance the ability of fiscal policy to combat recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the crowding-out effect, an increase in government spending will result in inflation, which reduces the purchasing power of the dollar and decreases investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to the foreign-trade effect, an expansionary fiscal policy that boosts interest rates will cause net exports to decrease, partially offsetting the expansionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to supply-side economists, a reduction in marginal tax rates causes take-home pay to increase, which increases consumption spending and the aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Laffer curve shows the relationship between the income tax rate that a government imposes and the total tax revenue that the government collects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Most economists agree that the amount of the U.S. government's debt by itself is the best indicator of the debt's burden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume that the economy's marginal propensity to consume is 0.75 and that the price level is constant. If the government decreases household taxes by $100 billion, real output will increase by $300 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a law is passed that forces the federal government to balance its budget annually, then it will require the government to increase expenditures and/or decrease taxes during a recession, thus making the recession worse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An appropriate fiscal policy for a recession is an increase in government expenditures, an increase in transfer payments, and a decrease in taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, an expansionary fiscal policy will increase real output by less than if the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the U.S., fiscal policy is implemented by the Council of Economic Advisors and the Federal Reserve System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
As national income increases, tax revenues increase and transfer payments decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Food stamps, unemployment compensation benefits, the federal personal income tax, and federal construction expenditures are automatic stabilizers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Critics fear that the U.S. government's debt will have an adverse impact on the nation's saving, investment, and stock of capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Economic theory suggests that a decrease in marginal tax rates will encourage individuals to substitute leisure for work and consumption for saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most of the U.S. government's debt is owned by foreigners who purchase the securities issued by the Treasury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Fiscal policy is a legal mandate of the federal government as a result of the Employment Act of 1946 and the Humphry-Hawkins Act of 1978.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Works Project Administration (WPA) is an example of a federal policy aimed at reducing the national debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A contractionary fiscal policy would most likely be adopted whne the economiy is experiencing high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The most important automatic stabilizer is the tax system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Because of the crowding-out effect, an expansionary fiscal policy will have stronger expects than anticipated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In 2006, 73 percent of the federal debt was owned by foreign investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In 2006, federal debt equaled 38 percent of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Comprehensive Employment and Training Act provided public service jobs for unemployed workers and young people in the
A) 1930's
B) 1950's
C) 1970's
D) 1990's
A) 1930's
B) 1950's
C) 1970's
D) 1990's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
______ is the use of government expenditures and taxes to promote full employment, stable prices, and economic growth.
A) Monetary policy
B) Incomes policy
C) Stabilization policy
D) Fiscal policy
A) Monetary policy
B) Incomes policy
C) Stabilization policy
D) Fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following are major goals of fiscal policy except
A) full employment
B) stable prices
C) economic growth
D) zero net exports
A) full employment
B) stable prices
C) economic growth
D) zero net exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An expansionary fiscal policy tends to increase
A) real output and employment, but not income
B) real output and income, but not employment
C) income and employment, but not real output
D) real output, employment, and income
A) real output and employment, but not income
B) real output and income, but not employment
C) income and employment, but not real output
D) real output, employment, and income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Discretionary fiscal policy affects all the following except
A) consumption
B) investment
C) net exports
D) money supply
A) consumption
B) investment
C) net exports
D) money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
______ is the deliberate use of changes in government expenditures and taxation to affect aggregate demand and influence the economy's performance.
A) Discretionary fiscal policy
B) Nondiscretionary fiscal policy
C) Discretionary monetary policy
D) Nondiscretionary monetary policy
A) Discretionary fiscal policy
B) Nondiscretionary fiscal policy
C) Discretionary monetary policy
D) Nondiscretionary monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
To combat a recession, discretionary policy could result in a(n)
A) increase in taxes, decrease in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
B) decrease in taxes, decrease in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
C) increase in taxes, increase in government expenditures, and cause a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve
D) decrease in taxes, increase in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
A) increase in taxes, decrease in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
B) decrease in taxes, decrease in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
C) increase in taxes, increase in government expenditures, and cause a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve
D) decrease in taxes, increase in government expenditures, and cause a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To combat inflation, discretional fiscal policy could result in a(n)
A) increase in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
B) decrease in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
C) increase in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve
D) decrease in taxes, an increase in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
A) increase in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
B) decrease in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve
C) increase in taxes, a decrease in government expenditures, and a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve
D) decrease in taxes, an increase in government expenditures, and a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To combat a recession, fiscal policy should move toward a budget that is
A) balanced
B) in a deficit
C) in a surplus
D) as low as possible
A) balanced
B) in a deficit
C) in a surplus
D) as low as possible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
To combat inflation, fiscal policy should move toward a
A) balanced budget
B) budget deficit
C) budget surplus
D) budget amendment
A) balanced budget
B) budget deficit
C) budget surplus
D) budget amendment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To combat a recession, the correct fiscal policy would be a
A) cut in taxes, an increase in government spending, and a budget deficit
B) cut in taxes, a decrease in government spending, and a budget surplus
C) hike in taxes, an increase in government spending, and a budget deficit
D) hike in taxes, a decrease in government spending, and a budget surplus
A) cut in taxes, an increase in government spending, and a budget deficit
B) cut in taxes, a decrease in government spending, and a budget surplus
C) hike in taxes, an increase in government spending, and a budget deficit
D) hike in taxes, a decrease in government spending, and a budget surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the federal government implements public-works projects to combat downturns in the economy, this would be an example of
A) discretionary fiscal policy
B) automatic fiscal stabilizers
C) nondiscretionary fiscal policy
D) nonautomatic fiscal stabilizers
A) discretionary fiscal policy
B) automatic fiscal stabilizers
C) nondiscretionary fiscal policy
D) nonautomatic fiscal stabilizers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume that the economy's marginal propensity to consume is 0.9 and the price level is constant. If the U.S. government purchases $10 billion of jet aircraft from American companies, aggregate demand will increase by
A) $50 billion
B) $80 billion
C) $100 billion
D) $120 billion
A) $50 billion
B) $80 billion
C) $100 billion
D) $120 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which combination of fiscal policies would have the greatest expansionary effect on the economy?
A) decrease government expenditures, provide an investment tax credit, and increase personal income taxes
B) provide an investment tax credit, increase government expenditures, and decrease personal income taxes
C) decrease unemployment compensation benefits, increase corporate income taxes, and provide an investment tax credit
D) increase personal income taxes, increase corporate income taxes, and decrease unemployment compensation benefits
A) decrease government expenditures, provide an investment tax credit, and increase personal income taxes
B) provide an investment tax credit, increase government expenditures, and decrease personal income taxes
C) decrease unemployment compensation benefits, increase corporate income taxes, and provide an investment tax credit
D) increase personal income taxes, increase corporate income taxes, and decrease unemployment compensation benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose the economy is in a recession and that the marginal propensity to consume is 0.75. Assuming that the price level is constant, by how much would the government have to increase its expenditures in order to increase real output by $200 billion?
A) $25 billion
B) $50 billion
C) $75 billion
D) $100 billion
A) $25 billion
B) $50 billion
C) $75 billion
D) $100 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose the economy is in a recession and that the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8. Assuming that the price level is constant, by how much would government have to decrease household taxes in order to increase real output by $200 billion?
A) $40 billion
B) $50 billion
C) $60 billion
D) $70 billion
A) $40 billion
B) $50 billion
C) $60 billion
D) $70 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the aggregate supply curve is horizontal, an expansionary fiscal policy will result in increased output, along with
A) higher employment and stable prices
B) lower employment and stable prices
C) higher employment and rising prices
D) lower employment and falling prices
A) higher employment and stable prices
B) lower employment and stable prices
C) higher employment and rising prices
D) lower employment and falling prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping, the cost of using a contractionary fiscal policy to combat inflation will be
A) higher interest rates and lower consumption spending
B) lower taxes for households and business
C) increased rates of inflation
D) decreased real output and employment
A) higher interest rates and lower consumption spending
B) lower taxes for households and business
C) increased rates of inflation
D) decreased real output and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The basic elements of fiscal policy were developed by
A) John Maynard Keynes during the Great Depression
B) Jean Baptiste Say during the Panic of 1907
C) Adam Smith during the Stock Market Crash of the 1890s
D) Ronald Reagan during the recession of the early 1980s
A) John Maynard Keynes during the Great Depression
B) Jean Baptiste Say during the Panic of 1907
C) Adam Smith during the Stock Market Crash of the 1890s
D) Ronald Reagan during the recession of the early 1980s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The automatic fiscal stabilizers include all of the following except
A) corporate income taxes
B) unemployment insurance benefits
C) the prime interest rate
D) food stamps
A) corporate income taxes
B) unemployment insurance benefits
C) the prime interest rate
D) food stamps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Unlike discretionary fiscal policy, automatic stabilizers consist of
A) deliberate changes in government spending to counteract recession and inflation
B) deliberate changes in household taxes to counteract recession and inflation
C) deliberate changes in corporation income taxes to counteract recession and inflation
D) changes in government spending and tax revenues that occur automatically as the economy fluctuates
A) deliberate changes in government spending to counteract recession and inflation
B) deliberate changes in household taxes to counteract recession and inflation
C) deliberate changes in corporation income taxes to counteract recession and inflation
D) changes in government spending and tax revenues that occur automatically as the economy fluctuates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
All of the following are problems of fiscal policy except
A) recognition lags
B) administrative lags
C) crowding-out effect
D) singular-motion effect
A) recognition lags
B) administrative lags
C) crowding-out effect
D) singular-motion effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Fiscal policy is enacted by the
A) Federal Reserve System
B) Council of Economic Advisors
C) Federal Open Market Committee
D) Congress and the president together
A) Federal Reserve System
B) Council of Economic Advisors
C) Federal Open Market Committee
D) Congress and the president together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The lag between the time that a recession is recognized and the time an expansionary fiscal policy is enacted is the
A) instructional lag
B) operation lag
C) administration lag
D) recognition lag
A) instructional lag
B) operation lag
C) administration lag
D) recognition lag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The crowding-out effect occurs when increased government expenditures and the subsequent budget deficits cause
A) the money supply to increase, which curtails loans to consumers
B) interest rates to increase, which reduces investment spending
C) inflation, which erodes the purchasing power of the dollar
D) the imports of goods and services to rise, and exports to decline
A) the money supply to increase, which curtails loans to consumers
B) interest rates to increase, which reduces investment spending
C) inflation, which erodes the purchasing power of the dollar
D) the imports of goods and services to rise, and exports to decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not true for the crowding-out effect?
A) Federal budget deficits increase interest rates, which reduces investment spending.
B) Crowding out reduces the ability of fiscal policy to combat a recession.
C) If the government spends more on education, Bill Nelson may be forced to spend less on a new home.
D) Crowding out occurs especially when the economy is in a deep recession and people are not spending all the available money.
A) Federal budget deficits increase interest rates, which reduces investment spending.
B) Crowding out reduces the ability of fiscal policy to combat a recession.
C) If the government spends more on education, Bill Nelson may be forced to spend less on a new home.
D) Crowding out occurs especially when the economy is in a deep recession and people are not spending all the available money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When there is open international investment, an expansionary fiscal policy in the U.S. will
A) increase deficits in the U.S. which attracts savings from other countries
B) decrease deficits in the U.S. which causes other countries to experience recessions
C) cause more money to be created in the U.S. which creates deficits
D) causes unemployment to rise in the U.S. which causes a recession
A) increase deficits in the U.S. which attracts savings from other countries
B) decrease deficits in the U.S. which causes other countries to experience recessions
C) cause more money to be created in the U.S. which creates deficits
D) causes unemployment to rise in the U.S. which causes a recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The ratio of U.S. federal debt to GDP is
A) rapidly approaching 100 percent
B) the highest of all countries in the world
C) lower in 2006 than it was in 1946
D) not a commonly-used measure
A) rapidly approaching 100 percent
B) the highest of all countries in the world
C) lower in 2006 than it was in 1946
D) not a commonly-used measure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The impact of an expansionary fiscal policy on real output will be greatest when the aggregate supply curve is
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) upward sloping
D) downward sloping
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) upward sloping
D) downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If people are spending all the available money, when the U.S. government borrows to finance a deficit,
A) investment spending increases
B) personal consumption spending increases
C) interest rates increase
D) the exchange value of the dollar declines
A) investment spending increases
B) personal consumption spending increases
C) interest rates increase
D) the exchange value of the dollar declines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to supply-side economists, the U.S. tax system tends to
A) decrease interest rates and loans to businesses
B) intensify the effects of demand-pull inflation
C) dampen incentives to work, save, and invest
D) reduce unemployment and push up the price level
A) decrease interest rates and loans to businesses
B) intensify the effects of demand-pull inflation
C) dampen incentives to work, save, and invest
D) reduce unemployment and push up the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the Laffer Curve, when taxes are increased from 0 percent to a rate consistent with the maximum point on the curve, tax revenues will
A) decrease
B) increase
C) be the same as the tax rate
D) be equal to zero
A) decrease
B) increase
C) be the same as the tax rate
D) be equal to zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to supply-side economists, a policy that ______ will cause productivity to increase, which shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
A) increases interest rates
B) increases expected inflation
C) reduces marginal tax rates
D) reduces the money supply
A) increases interest rates
B) increases expected inflation
C) reduces marginal tax rates
D) reduces the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The ______ shows the relationship between the income tax rate that a government imposes and the total tax revenue that the government collects.
A) fiscal curve
B) automatic stabilizer curve
C) transfer curve
D) Laffer curve
A) fiscal curve
B) automatic stabilizer curve
C) transfer curve
D) Laffer curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
During the 2007-09 recession, the official unemployment rate rose
A) over 9%
B) 11%
C) over 13%
D) over 15%
A) over 9%
B) 11%
C) over 13%
D) over 15%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume that the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping. An expansionary fiscal policy that causes only the aggregate demand curve to increase will
A) increase only output
B) increase only prices
C) decrease output and increase prices
D) increase output and increase prices
A) increase only output
B) increase only prices
C) decrease output and increase prices
D) increase output and increase prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the U.S. government spends $20 billion on unemployment compensation benefits, purchases $75 billion of goods and services, and collects taxes of $100 billion, then there is a budget
A) surplus of $15 billion
B) surplus of $5 billion
C) deficit of $5 billion
D) deficit of $10 billion
A) surplus of $15 billion
B) surplus of $5 billion
C) deficit of $5 billion
D) deficit of $10 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Concerning an annually balanced budget law, if the U.S. government balanced its budget each year, then it would
A) eliminate a recession by increasing expenditures and decreasing taxes during a recession
B) eliminate a recession by decreasing expenditures and increasing taxes during a recession
C) intensify a recession by decreasing expenditures and increasing taxes during a recession
D) intensify a recession by increasing expenditures and decreasing taxes during a recession
A) eliminate a recession by increasing expenditures and decreasing taxes during a recession
B) eliminate a recession by decreasing expenditures and increasing taxes during a recession
C) intensify a recession by decreasing expenditures and increasing taxes during a recession
D) intensify a recession by increasing expenditures and decreasing taxes during a recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When there are automatic stabilizers,
A) the government decreases tax rates as the economy slides into a recession
B) the government increases tax rates as the economy slides into a recession
C) tax receipts increase as the economy slides into a recession
D) tax receipts decrease as the economy slides into a recession
A) the government decreases tax rates as the economy slides into a recession
B) the government increases tax rates as the economy slides into a recession
C) tax receipts increase as the economy slides into a recession
D) tax receipts decrease as the economy slides into a recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A $50 billion increase in taxes on households has a(n)
A) identical impact on aggregate demand as a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures
B) identical impact on aggregate demand as a $50 billion increase in government expenditures
C) stronger impact on aggregate demand than a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures
D) weaker impact on aggregate demand than a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures
A) identical impact on aggregate demand as a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures
B) identical impact on aggregate demand as a $50 billion increase in government expenditures
C) stronger impact on aggregate demand than a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures
D) weaker impact on aggregate demand than a $50 billion decrease in government expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The U.S. government has financed its deficits primarily by borrowing from
A) the U.S. public
B) foreign investors
C) the Federal Reserve
D) the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
A) the U.S. public
B) foreign investors
C) the Federal Reserve
D) the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Critics of a large national debt are concerned that it will do all of the following except:
A) result in the crowding out of investment in the private sector
B) slow down the economy's long-run rate of growth
C) redistribute income from the wealthy to the poor
D) reduce the living standards of future generations
A) result in the crowding out of investment in the private sector
B) slow down the economy's long-run rate of growth
C) redistribute income from the wealthy to the poor
D) reduce the living standards of future generations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 13.1 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
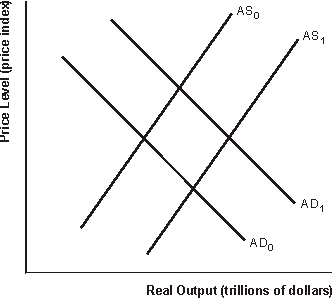
-Refer to Figure 13.1. Increased government spending, as a discretionary fiscal policy, would shift
A) AD0 to AD1
B) AD1 to AD0
C) AS0 to AS1
D) AS1 to AS0

-Refer to Figure 13.1. Increased government spending, as a discretionary fiscal policy, would shift
A) AD0 to AD1
B) AD1 to AD0
C) AS0 to AS1
D) AS1 to AS0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 13.1 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand

-Refer to Figure 13.1 The goal of a supply-side tax cut is to shift
A) AD0 to AD1
B) AD1 to AD0
C) AS0 to AS1
D) AS1 to AS0

-Refer to Figure 13.1 The goal of a supply-side tax cut is to shift
A) AD0 to AD1
B) AD1 to AD0
C) AS0 to AS1
D) AS1 to AS0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 13.1 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand

-Refer to Figure 13.1. A supply-side tax cut will be inflationary if when taxes decrease,
A) AD0 shifts to AD1
B) AD1 shifts to AD0
C) AS0 shifts to AS1
D) AS1 shifts to AS0

-Refer to Figure 13.1. A supply-side tax cut will be inflationary if when taxes decrease,
A) AD0 shifts to AD1
B) AD1 shifts to AD0
C) AS0 shifts to AS1
D) AS1 shifts to AS0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 13.1 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand

-Refer to Figure 13.1. A correct discretionary fiscal policy to enact when the economy is experiencing inflation is to
A) increase government spending, causing AD0 to shift to AD1
B) increase taxes, causing AD0 to shift to AD1
C) decrease government spending, causing AD1 to shift to AD0
D) decrease taxes, causing AD1 to shift to AD0

-Refer to Figure 13.1. A correct discretionary fiscal policy to enact when the economy is experiencing inflation is to
A) increase government spending, causing AD0 to shift to AD1
B) increase taxes, causing AD0 to shift to AD1
C) decrease government spending, causing AD1 to shift to AD0
D) decrease taxes, causing AD1 to shift to AD0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the government spends more on national defense and as a result, Marcy spends less on the construction of a new house, this is an example of
A) crowding out
B) a budget surplus
C) an automatic stabilizer
D) inflationary bias
A) crowding out
B) a budget surplus
C) an automatic stabilizer
D) inflationary bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Advocates of supply-side economics believe that which of the following concepts is of crucial importance?
A) public-works projects
B) discretionary fiscal policy
C) marginal tax rates
D) automatic stabilizers
A) public-works projects
B) discretionary fiscal policy
C) marginal tax rates
D) automatic stabilizers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



