Deck 7: Series and Parallel Networks
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/9
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Series and Parallel Networks
1
Resistance's of 5 , 7 , and 8 are connected in series. If a 10 V supply voltage is connected across the arrangement determine the current flowing through and the p.d. across the 7 resistor. Calculate also the power dissipated in the 8 resistor.
The circuit is shown in Figure 1.
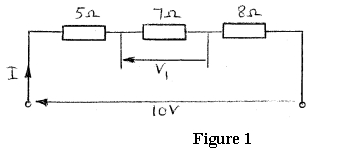
Current
Hence, current in resistor
P.d. across resistor,
Power dissipated in resistor

Current
Hence, current in resistor
P.d. across resistor,
Power dissipated in resistor
2
For the series-parallel network shown in Figure RT2.1, find (a) the supply current, (b) the current flowing through each resistor, (c) the p.d. across each resistor, (d) the total power dissipated in the circuit, (e) the cost of energy if the circuit is connected for 80 hours. Assume electrical energy costs 14 p per unit.
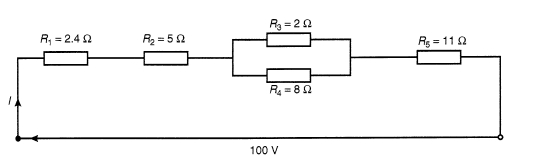 Figure RT2.1
Figure RT2.1
 Figure RT2.1
Figure RT2.1
3
The charge on the plates of a capacitor is 8 mC when the potential between them is 4 kV. Determine the capacitance of the capacitor.
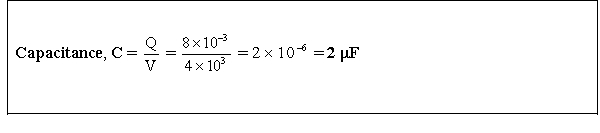
4
Two parallel rectangular plates measuring 80 mm by 120 mm are separated by 4 mm of mica and carry an electric charge of 0.48 C. The voltage between the plates is 500 V. Calculate
(a) the electric flux density (b) the electric field strength, and (c) the capacitance of the capacitor, in picofarads, if the relative permittivity of mica is 5.
(a) the electric flux density (b) the electric field strength, and (c) the capacitance of the capacitor, in picofarads, if the relative permittivity of mica is 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 4 F capacitor is connected in parallel with a 6 F capacitor. This arrangement is then connected in series with a 10 F capacitor. A supply p.d. of 250 V is connected across the circuit. Find (a) the equivalent capacitance of the circuit, (b) the voltage across the 10 F capacitor, and (c) the charge on each capacitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A coil of 600 turns is wound uniformly on a ring of non-magnetic material. The ring has a uniform cross-sectional area of 200 mm2 and a mean circumference of 500 mm. If the current in the coil is 4 A, determine (a) the magnetic field strength, (b) the flux density, and (c) the total magnetic flux in the ring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A mild steel ring of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 has a radial air-gap of 3 mm cut into it. If the mean length of the mild steel path is 300 mm, calculate the magnetomotive force to produce a flux of 0.48 mWb. (Use the B-H curve on page 146).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the circuit shown in Figure RT2.2, the slider S is at the half-way point.
Figure RT2.2
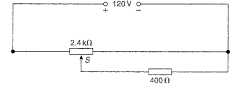 (a) Calculate the p.d. across and the current flowing in the 400 load resistor.
(a) Calculate the p.d. across and the current flowing in the 400 load resistor.
(b) Is the circuit a potentiometer or a rheostat?
Figure RT2.2
 (a) Calculate the p.d. across and the current flowing in the 400 load resistor.
(a) Calculate the p.d. across and the current flowing in the 400 load resistor.(b) Is the circuit a potentiometer or a rheostat?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
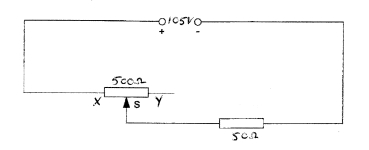
9
For the circuit shown in Figure RT2.3, calculate the current flowing in the 50 load and
the voltage drop across the load when (a) XS is 3/5 of XY
(b) point S coincides with point Y
Figure RT2.3
the voltage drop across the load when (a) XS is 3/5 of XY
(b) point S coincides with point Y
Figure RT2.3


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



