Deck 16: America in the World: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: America in the World: International Trade
1
Explain the arguments in favor of protecting domestic industries.
There are several arguments in favor of protecting domestic industries.
Firstly, protecting domestic industries can help to preserve jobs and prevent unemployment. By imposing tariffs or other trade barriers, the government can make it more expensive for foreign companies to compete with domestic industries, thus ensuring that local businesses can continue to operate and provide employment opportunities for the local workforce.
Secondly, protecting domestic industries can also help to maintain national security. By ensuring that essential industries such as defense, energy, and food production remain within the country, the government can reduce its reliance on foreign suppliers and safeguard against potential disruptions in the global supply chain.
Additionally, protecting domestic industries can also promote economic development and innovation. By providing a level playing field for local businesses to compete, the government can encourage investment in research and development, leading to the creation of new technologies and products that can drive economic growth and enhance the country's competitiveness in the global market.
Furthermore, protecting domestic industries can also help to address environmental and labor standards. By imposing trade barriers on goods produced in countries with lower environmental and labor regulations, the government can prevent the outsourcing of production to countries with lax standards, thus promoting sustainable and ethical business practices within the country.
In conclusion, protecting domestic industries can have several benefits, including preserving jobs, maintaining national security, promoting economic development and innovation, and upholding environmental and labor standards. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential drawbacks and unintended consequences of protectionist policies, such as higher consumer prices and retaliation from trading partners.
Firstly, protecting domestic industries can help to preserve jobs and prevent unemployment. By imposing tariffs or other trade barriers, the government can make it more expensive for foreign companies to compete with domestic industries, thus ensuring that local businesses can continue to operate and provide employment opportunities for the local workforce.
Secondly, protecting domestic industries can also help to maintain national security. By ensuring that essential industries such as defense, energy, and food production remain within the country, the government can reduce its reliance on foreign suppliers and safeguard against potential disruptions in the global supply chain.
Additionally, protecting domestic industries can also promote economic development and innovation. By providing a level playing field for local businesses to compete, the government can encourage investment in research and development, leading to the creation of new technologies and products that can drive economic growth and enhance the country's competitiveness in the global market.
Furthermore, protecting domestic industries can also help to address environmental and labor standards. By imposing trade barriers on goods produced in countries with lower environmental and labor regulations, the government can prevent the outsourcing of production to countries with lax standards, thus promoting sustainable and ethical business practices within the country.
In conclusion, protecting domestic industries can have several benefits, including preserving jobs, maintaining national security, promoting economic development and innovation, and upholding environmental and labor standards. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential drawbacks and unintended consequences of protectionist policies, such as higher consumer prices and retaliation from trading partners.
2
Develop the rationale behind the theory of comparative advantage. How does this serve as a basis for free trade policies?
The theory of comparative advantage was first introduced by economist David Ricardo in the early 19th century. The rationale behind this theory is that countries should specialize in producing goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, meaning they can produce at a lower opportunity cost than other countries. This allows for more efficient allocation of resources and leads to increased overall production and economic welfare.
The theory of comparative advantage serves as a basis for free trade policies because it demonstrates the benefits of allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. By doing so, countries can trade with one another, exchanging the goods and services they produce most efficiently for those produced more efficiently by other countries. This leads to increased global efficiency and overall economic welfare.
Free trade policies are based on the idea that by removing barriers to trade, such as tariffs and quotas, countries can take advantage of their comparative advantages and benefit from the increased efficiency and productivity that comes from specialization and trade. This can lead to lower prices for consumers, increased competition, and a more efficient allocation of resources on a global scale.
In summary, the theory of comparative advantage provides a rationale for free trade policies by demonstrating the benefits of allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. This leads to increased efficiency, productivity, and economic welfare on a global scale.
The theory of comparative advantage serves as a basis for free trade policies because it demonstrates the benefits of allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. By doing so, countries can trade with one another, exchanging the goods and services they produce most efficiently for those produced more efficiently by other countries. This leads to increased global efficiency and overall economic welfare.
Free trade policies are based on the idea that by removing barriers to trade, such as tariffs and quotas, countries can take advantage of their comparative advantages and benefit from the increased efficiency and productivity that comes from specialization and trade. This can lead to lower prices for consumers, increased competition, and a more efficient allocation of resources on a global scale.
In summary, the theory of comparative advantage provides a rationale for free trade policies by demonstrating the benefits of allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. This leads to increased efficiency, productivity, and economic welfare on a global scale.
3
Discuss multilateral efforts to reduce trade barriers. How do trading blocs reduce some trade barriers while erecting others?
Multilateral efforts to reduce trade barriers involve negotiations and agreements between multiple countries to lower tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions on international trade. One example of this is the World Trade Organization (WTO), which aims to promote free and fair trade by facilitating negotiations and resolving disputes among its member countries.
Trading blocs, such as the European Union and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), also work to reduce trade barriers among their member countries. These blocs often eliminate tariffs and quotas on goods traded within the bloc, making it easier and cheaper for member countries to trade with each other. However, trading blocs can also erect trade barriers for non-member countries, such as imposing tariffs or quotas on imports from outside the bloc. This can create challenges for countries that are not part of the bloc and may lead to trade disputes.
Overall, while multilateral efforts and trading blocs aim to reduce trade barriers and promote economic integration, they can also create new barriers for non-member countries. It is important for countries to carefully consider the potential impacts of joining or not joining trading blocs in order to effectively navigate the complex landscape of international trade.
Trading blocs, such as the European Union and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), also work to reduce trade barriers among their member countries. These blocs often eliminate tariffs and quotas on goods traded within the bloc, making it easier and cheaper for member countries to trade with each other. However, trading blocs can also erect trade barriers for non-member countries, such as imposing tariffs or quotas on imports from outside the bloc. This can create challenges for countries that are not part of the bloc and may lead to trade disputes.
Overall, while multilateral efforts and trading blocs aim to reduce trade barriers and promote economic integration, they can also create new barriers for non-member countries. It is important for countries to carefully consider the potential impacts of joining or not joining trading blocs in order to effectively navigate the complex landscape of international trade.
4
Graph the following production possibilities data for the United States and India. Identify their respective comparative advantages. Graph the trading-possibilities curve of each country if the terms of trade are 1 oil can be exchanged for 1¼ steel.
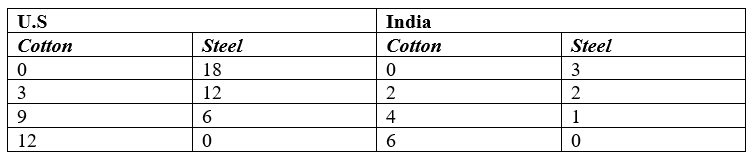


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An import quota restricts the physical number of units of a product that can be imported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Mercantilist policies argue for specialization and free trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The purpose of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade is to erect trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a country can produce a product at lower opportunity cost than another nation the country possesses a comparative advantage in the production of that product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Answer the next three questions using the following diagrams.
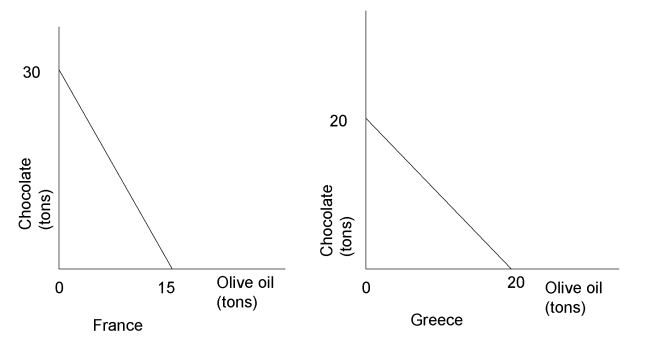
-If the actual terms of trade between the two countries were that one ton of olive oil is exchanged for one and one-half tons of chocolate, which of the following statements is correct with respect to complete specialization and trade?
A) France's trading possibilities curve will be anchored at 45 tons of olive oil.
B) Greece's trading possibilities curve will be anchored at 45 tons of olive oil.
C) Greece's trading possibilities curve will located at 30 tons of chocolate.
D) People in France will have to use a lot less olive oil.

-If the actual terms of trade between the two countries were that one ton of olive oil is exchanged for one and one-half tons of chocolate, which of the following statements is correct with respect to complete specialization and trade?
A) France's trading possibilities curve will be anchored at 45 tons of olive oil.
B) Greece's trading possibilities curve will be anchored at 45 tons of olive oil.
C) Greece's trading possibilities curve will located at 30 tons of chocolate.
D) People in France will have to use a lot less olive oil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Autarky means opening the economy to international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The trading possibilities curve shows the outputs that can be obtained without trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Trade restrictions raise the prices of imported goods, but the prices of domestic goods are not affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Higher domestic income levels generally cause imports to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Protectionism is the practice of shielding domestic industries from international competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade was designed to promote bilateral trade agreements rather than multilateral reductions in trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One good thing about U.S. restrictions on imports is that they have really saved U.S. jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A comparative advantage exists when a country can produce a product at a lower absolute cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A comparative advantage exists when a country can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Industrial policy would seek a comprehensive government-business strategy to improve export growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The role of GATT was subsumed by the creation of the World Trade Organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Technical trade barriers are associated with unnecessarily cumbersome regulations and licensing arrangements that restrict trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Empirical research conclusively states that successful completion of the Doha Round of trade negotiations will generate no economic gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Bilateral trade agreements involve agreements between just two countries while multilateral trade agreements involve many nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The national defense argument argues that trade restrictions are necessary for national security reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The infant industries argument favors trade protection for industries such as manufacturers of diapers, strollers, cribs, babyfood, baby rattles, toys, diaper rash medications and other products for very young children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the U.S. opportunity cost of producing apples is lower than that of Canada:
A) the United States has a disadvantage in apple production
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in apple production
C) Canada has a comparative advantage in apple production
D) neither country can be discerned to possess a comparative advantage in apple production
E) somebody better erect tariffs fast
A) the United States has a disadvantage in apple production
B) the United States has a comparative advantage in apple production
C) Canada has a comparative advantage in apple production
D) neither country can be discerned to possess a comparative advantage in apple production
E) somebody better erect tariffs fast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A tariff is:
A) an excise tax on a domestically produced good
B) an excise tax on an imported product
C) a restriction upon the physical number of units of a product that can be imported
D) a license to import a foreign-produced product
E) a brush used to apply tar to waterproof certain goods for export
A) an excise tax on a domestically produced good
B) an excise tax on an imported product
C) a restriction upon the physical number of units of a product that can be imported
D) a license to import a foreign-produced product
E) a brush used to apply tar to waterproof certain goods for export

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The members of the European Union:
A) have largely achieved full economic integration among the member countries
B) adopted a uniform external tariff policy of no tariffs, but charge tariffs among themselves
C) plan to move away from economic integration in order to maintain national autonomy
D) none of the above
A) have largely achieved full economic integration among the member countries
B) adopted a uniform external tariff policy of no tariffs, but charge tariffs among themselves
C) plan to move away from economic integration in order to maintain national autonomy
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Protectionists argue that:
A) imports reduce domestic employment
B) other countries dump products on the domestic markets
C) industries that are of strategic importance to national defense require protection from foreign competition
D) all of the above
A) imports reduce domestic employment
B) other countries dump products on the domestic markets
C) industries that are of strategic importance to national defense require protection from foreign competition
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The "breathing room" argument maintains that:
A) industries of importance to national security need protection from foreign competition
B) industries that are in their infancy require trade protection
C) temporary protectionist measures can help revive ailing domestic industries that have been smothered by foreign competition
D) too many people breathing in a room results in carbon dioxide poisoning. Some people must hang their heads out the window to suck in some air.
E) trade agreement negotiators must have a break room where they can breathe away from the smoke-filled negotiating room
A) industries of importance to national security need protection from foreign competition
B) industries that are in their infancy require trade protection
C) temporary protectionist measures can help revive ailing domestic industries that have been smothered by foreign competition
D) too many people breathing in a room results in carbon dioxide poisoning. Some people must hang their heads out the window to suck in some air.
E) trade agreement negotiators must have a break room where they can breathe away from the smoke-filled negotiating room

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:
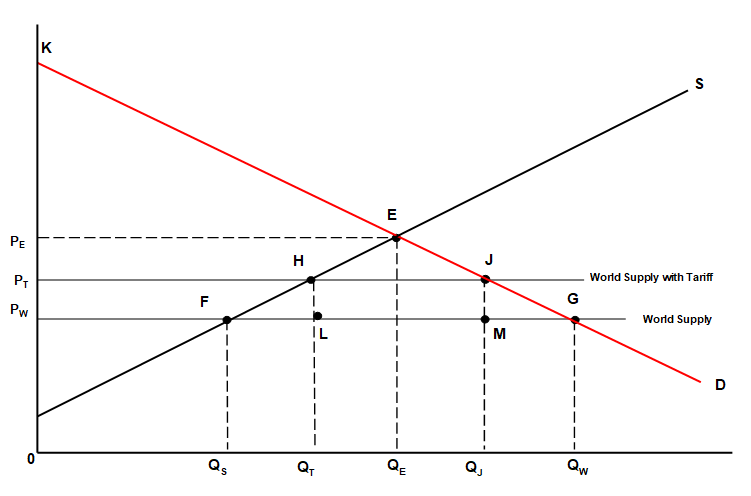
-In a tariff-free environment and a world supply of the product as shown:
A) domestic producers would supply 0QE and QEQW will be supplied by the rest of the world
B) domestic producers would supply 0QS and QSQW will be supplied by the rest of the world
C) domestic producers would supply QSQW and 0QS will be supplied by the rest of the world
D) 0QE will be supplied, divided equally between domestic and foreigner suppliers in order to be fair

-In a tariff-free environment and a world supply of the product as shown:
A) domestic producers would supply 0QE and QEQW will be supplied by the rest of the world
B) domestic producers would supply 0QS and QSQW will be supplied by the rest of the world
C) domestic producers would supply QSQW and 0QS will be supplied by the rest of the world
D) 0QE will be supplied, divided equally between domestic and foreigner suppliers in order to be fair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:

-If a tariff is imposed as shown:
A) domestic suppliers gain PWPTHF
B) domestic suppliers gain FHL
C) domestic suppliers lose JMG
D) domestic consumers gain QJQWGJ
E) domestic consumers gain QJQWGM

-If a tariff is imposed as shown:
A) domestic suppliers gain PWPTHF
B) domestic suppliers gain FHL
C) domestic suppliers lose JMG
D) domestic consumers gain QJQWGJ
E) domestic consumers gain QJQWGM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:

-If a tariff is imposed as shown:
A) the revenue going to the government is FHJM
B) the revenue going to the government is LHJM
C) the revenue going to the government is QTQJJH
D) no revenue is raised by the tariff

-If a tariff is imposed as shown:
A) the revenue going to the government is FHJM
B) the revenue going to the government is LHJM
C) the revenue going to the government is QTQJJH
D) no revenue is raised by the tariff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:

-Moving from autarky to free trade:
A) is bad economic policy
B) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQT
C) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQE
D) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQW
E) enlarges consumer surplus by FHL

-Moving from autarky to free trade:
A) is bad economic policy
B) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQT
C) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQE
D) causes domestic suppliers to contract output by QSQW
E) enlarges consumer surplus by FHL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:

-Moving from autarky to free trade:
A) leaves consumer surplus unaffected
B) ought to go slow by imposing a tariff of PT first
C) results in a loss of consumer surplus
D) enlarges consumer surplus by PWPEEG

-Moving from autarky to free trade:
A) leaves consumer surplus unaffected
B) ought to go slow by imposing a tariff of PT first
C) results in a loss of consumer surplus
D) enlarges consumer surplus by PWPEEG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Answer the next six questions using the following diagram:

-If the government resorts to a quota of QTQJ:
A) the effect is identical to that of the tariff shown in the diagram
B) society will be safer by buying fewer foreign-made goods
C) technical barriers to trade are definitely involved
D) the government forgoes revenue of LHJM, which is realized as a gain by foreign sellers

-If the government resorts to a quota of QTQJ:
A) the effect is identical to that of the tariff shown in the diagram
B) society will be safer by buying fewer foreign-made goods
C) technical barriers to trade are definitely involved
D) the government forgoes revenue of LHJM, which is realized as a gain by foreign sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following alternatives is the best for reestablishing higher levels of U.S. exports:
A) slap tariffs on everything in which the United States. lacks a comparative advantage
B) treat all U.S. industry as infants
C) become more competitive and produce better products
D) regard more industries as essential to national defense and security
A) slap tariffs on everything in which the United States. lacks a comparative advantage
B) treat all U.S. industry as infants
C) become more competitive and produce better products
D) regard more industries as essential to national defense and security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Answer the next three questions using the following diagrams.

-Which country has the comparative advantage in the production of chocolate?
A) France
B) Greece
C) Neither possesses a comparative advantage in chocolate production.
D) Both posses a comparative advantage in chocolate production.

-Which country has the comparative advantage in the production of chocolate?
A) France
B) Greece
C) Neither possesses a comparative advantage in chocolate production.
D) Both posses a comparative advantage in chocolate production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Answer the next three questions using the following diagrams.

-According to information provided:
A) Greece should specialize in and import olive oil.
B) France should specialize in and export olive oil.
C) Greece should specialize in and export olive oil.
D) Greece will be better off without trade.

-According to information provided:
A) Greece should specialize in and import olive oil.
B) France should specialize in and export olive oil.
C) Greece should specialize in and export olive oil.
D) Greece will be better off without trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



