Deck 2: The Market Economy: Pure and Simple
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Market Economy: Pure and Simple
1
List and explain the fundamental assumptions about individual and business behaviors that are central to the economic analyses set out by Adam Smith and other defenders of Classical Economics Ideology.
The fundamental assumptions about individual and business behaviors central to the economic analyses set out by Adam Smith and other defenders of Classical Economics Ideology include:
1. Rational self-interest: Individuals and businesses are assumed to act in their own self-interest, seeking to maximize their own utility or profit. This assumption forms the basis for the concept of the invisible hand, where individual pursuit of self-interest leads to overall economic prosperity.
2. Rational decision-making: Individuals and businesses are assumed to make rational decisions based on a careful consideration of costs and benefits. This assumption underpins the idea that markets will naturally reach equilibrium as supply and demand adjust to reflect rational decision-making.
3. Competition: Classical economists assume that markets are characterized by competition, with many buyers and sellers. This assumption leads to the belief that competition will lead to efficient allocation of resources and optimal outcomes for society as a whole.
4. Laissez-faire: Classical economists assume that minimal government intervention in the economy is necessary, as they believe that markets will naturally self-regulate and achieve optimal outcomes. This assumption is based on the idea that individuals and businesses are best equipped to make decisions for themselves without government interference.
These fundamental assumptions about individual and business behaviors form the basis for the economic analyses put forth by Adam Smith and other defenders of Classical Economics Ideology. They provide the theoretical framework for understanding how markets work and how individuals and businesses interact within them.
1. Rational self-interest: Individuals and businesses are assumed to act in their own self-interest, seeking to maximize their own utility or profit. This assumption forms the basis for the concept of the invisible hand, where individual pursuit of self-interest leads to overall economic prosperity.
2. Rational decision-making: Individuals and businesses are assumed to make rational decisions based on a careful consideration of costs and benefits. This assumption underpins the idea that markets will naturally reach equilibrium as supply and demand adjust to reflect rational decision-making.
3. Competition: Classical economists assume that markets are characterized by competition, with many buyers and sellers. This assumption leads to the belief that competition will lead to efficient allocation of resources and optimal outcomes for society as a whole.
4. Laissez-faire: Classical economists assume that minimal government intervention in the economy is necessary, as they believe that markets will naturally self-regulate and achieve optimal outcomes. This assumption is based on the idea that individuals and businesses are best equipped to make decisions for themselves without government interference.
These fundamental assumptions about individual and business behaviors form the basis for the economic analyses put forth by Adam Smith and other defenders of Classical Economics Ideology. They provide the theoretical framework for understanding how markets work and how individuals and businesses interact within them.
2
Consider the various factors that determine the demand for and supply of "normal good" X. How would the price and equilibrium output of that good be affected by the following developments (be sure to explain the reasoning you have used):
a. The economy seems to be entering an inflationary period.
b. Consumer incomes are rising.
c. Labor productivity is increasing.
d. The price of substitute goods is falling.
a. The economy seems to be entering an inflationary period.
b. Consumer incomes are rising.
c. Labor productivity is increasing.
d. The price of substitute goods is falling.
The demand for and supply of a "normal good" X is determined by various factors such as consumer preferences, income levels, prices of related goods, and overall economic conditions.
a. If the economy seems to be entering an inflationary period, the price of "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because inflation typically leads to higher prices for goods and services, causing consumers to have less purchasing power. As a result, the demand for "normal good" X may decrease, leading to a decrease in equilibrium output.
b. If consumer incomes are rising, the demand for "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because consumers have more disposable income to spend on goods and services, leading to an increase in demand for "normal good" X. As a result, the price and equilibrium output of the good may increase.
c. If labor productivity is increasing, the supply of "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because higher productivity leads to lower production costs, allowing producers to supply more of the good at a lower price. As a result, the price of "normal good" X may decrease, leading to an increase in equilibrium output.
d. If the price of substitute goods is falling, the demand for "normal good" X is likely to decrease. This is because consumers may switch to the cheaper substitute goods, leading to a decrease in demand for "normal good" X. As a result, the price and equilibrium output of the good may decrease.
In conclusion, the price and equilibrium output of "normal good" X are affected by various developments such as inflation, changes in consumer incomes, labor productivity, and the price of substitute goods. These factors can lead to changes in demand and supply, ultimately impacting the price and equilibrium output of the good.
a. If the economy seems to be entering an inflationary period, the price of "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because inflation typically leads to higher prices for goods and services, causing consumers to have less purchasing power. As a result, the demand for "normal good" X may decrease, leading to a decrease in equilibrium output.
b. If consumer incomes are rising, the demand for "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because consumers have more disposable income to spend on goods and services, leading to an increase in demand for "normal good" X. As a result, the price and equilibrium output of the good may increase.
c. If labor productivity is increasing, the supply of "normal good" X is likely to increase. This is because higher productivity leads to lower production costs, allowing producers to supply more of the good at a lower price. As a result, the price of "normal good" X may decrease, leading to an increase in equilibrium output.
d. If the price of substitute goods is falling, the demand for "normal good" X is likely to decrease. This is because consumers may switch to the cheaper substitute goods, leading to a decrease in demand for "normal good" X. As a result, the price and equilibrium output of the good may decrease.
In conclusion, the price and equilibrium output of "normal good" X are affected by various developments such as inflation, changes in consumer incomes, labor productivity, and the price of substitute goods. These factors can lead to changes in demand and supply, ultimately impacting the price and equilibrium output of the good.
3
Explain the underlying economic logic of why demand curves are drawn downward sloping to the right while supply curves are represented as upward sloping to the right.
The underlying economic logic behind why demand curves are drawn downward sloping to the right while supply curves are represented as upward sloping to the right is based on the law of demand and the law of supply.
The law of demand states that as the price of a good or service decreases, the quantity demanded by consumers increases, and vice versa. This is because as the price of a good decreases, consumers are more willing and able to purchase larger quantities of the good, leading to a higher quantity demanded. Conversely, as the price of a good increases, consumers are less willing and able to purchase the good, leading to a lower quantity demanded. This relationship between price and quantity demanded is represented by a downward sloping demand curve.
On the other hand, the law of supply states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers also increases, and vice versa. This is because as the price of a good increases, producers are more willing and able to supply larger quantities of the good, leading to a higher quantity supplied. Conversely, as the price of a good decreases, producers are less willing and able to supply the good, leading to a lower quantity supplied. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is represented by an upward sloping supply curve.
Therefore, the downward sloping demand curve and the upward sloping supply curve reflect the fundamental economic principles of how consumers and producers respond to changes in price. This graphical representation helps to illustrate the relationship between price and quantity in the market, and is a fundamental tool in understanding and analyzing the behavior of consumers and producers in the economy.
The law of demand states that as the price of a good or service decreases, the quantity demanded by consumers increases, and vice versa. This is because as the price of a good decreases, consumers are more willing and able to purchase larger quantities of the good, leading to a higher quantity demanded. Conversely, as the price of a good increases, consumers are less willing and able to purchase the good, leading to a lower quantity demanded. This relationship between price and quantity demanded is represented by a downward sloping demand curve.
On the other hand, the law of supply states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied by producers also increases, and vice versa. This is because as the price of a good increases, producers are more willing and able to supply larger quantities of the good, leading to a higher quantity supplied. Conversely, as the price of a good decreases, producers are less willing and able to supply the good, leading to a lower quantity supplied. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is represented by an upward sloping supply curve.
Therefore, the downward sloping demand curve and the upward sloping supply curve reflect the fundamental economic principles of how consumers and producers respond to changes in price. This graphical representation helps to illustrate the relationship between price and quantity in the market, and is a fundamental tool in understanding and analyzing the behavior of consumers and producers in the economy.
4
In what sense can it be argued that a market economy has "a natural tendency" toward equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Explain the concept of "elasticity of demand." Of the following items, which would you expect to have a more elastic demand and which a more inelastic demand? Why?
Salt
Sugar
New Ford Focuses
Restaurant meals
Cigarettes
Shoes
On-demand movies
Mobile phones
Salt
Sugar
New Ford Focuses
Restaurant meals
Cigarettes
Shoes
On-demand movies
Mobile phones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Summarize the logic of those who argue that a market economy will provide better results than those obtained through efforts at intervention in the working of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Discuss some of the "real world" difficulties with markets that indicate that in actual practice conditions arise which do not always produce the "ideal" outcomes of pure market model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Distinguish between and give examples of market imperfections and market failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Markets can be expected to automatically compensate for problems of external
costs or external benefits.
costs or external benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Adam Smith believed that the existence of competition and self-interest might get
out of hand in a free market and therefore advocated the use of "the invisible fist"
of government to control market economies.
out of hand in a free market and therefore advocated the use of "the invisible fist"
of government to control market economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Although opposed to government intervention in the working of markets,
defenders of free market economic theory still believe that government has an
important place in a market society in protecting private property rights and enforcing "the rules of the game" in market transactions.
defenders of free market economic theory still believe that government has an
important place in a market society in protecting private property rights and enforcing "the rules of the game" in market transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to the law of demand we would expect that if the price of a good rises,
the consumer will choose, ceteris paribus, to buy fewer units of the good.
the consumer will choose, ceteris paribus, to buy fewer units of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The substitution effect is explained by the fact that at lower levels of prices we
have more income to buy goods.
have more income to buy goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The law of supply holds that price and quantity supplied are inversely related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The supply curve slopes upward to the right because, at least in the short run,
efforts to raise output involve rising per unit production costs.
efforts to raise output involve rising per unit production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume a free market where a surplus currently exists. Left to itself, we would
expect the market to adjust by seeing prices fall and quantity supplied decline.
expect the market to adjust by seeing prices fall and quantity supplied decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Changes in demand may be accounted for by changes in a number of nonprice
determinants of demand (such as consumer tastes, number of consumers,
expectations, etc.), but changes in quantity demanded are only the result of price changes.
determinants of demand (such as consumer tastes, number of consumers,
expectations, etc.), but changes in quantity demanded are only the result of price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Inferior goods differ from normal goods in that as our income rises we are more
likely to increase inferior goods consumption and lower normal goods consumption.
likely to increase inferior goods consumption and lower normal goods consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ordinarily, the expectation that prices will fall in the future should spur current
consumer spending.
consumer spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A leftward shift in the supply curve of product A indicates a decrease in supply
such as we might expect from the rise in resource prices used in the production of product A.
such as we might expect from the rise in resource prices used in the production of product A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If we know that both the demand and supply of product X has increased, we can be certain that equilibrium output will increase but we do not know if price increases or decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Those goods whose demand tends to be more inelastic over a given price range
are probably goods for which there are few substitutes.
are probably goods for which there are few substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The principal determinant of the elasticity of supply of a particular good is time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the long run the supply of any particular product tends to be increasingly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The reservation price in economics refers to the price of cigarettes at Onondaga Nation Territory stores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Appropriate government policy for dealing with externalities would be to substitute those goods with external costs and to tax those goods with high external benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A good way to raise revenue is to raise the price of goods that have elastic
demand.
demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Market imperfections tend to improve the efficiency of markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Adam Smith maintained that all of the following were essential to a market
Economic system except:
A) private property
B) freedom of choice
C) a large and powerful national government
D) the exercise of rational, maximizing behavior by all market participants
E) competition
Economic system except:
A) private property
B) freedom of choice
C) a large and powerful national government
D) the exercise of rational, maximizing behavior by all market participants
E) competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The law of demand holds that:
A) prices and quantity demanded are directly related
B) price and quantity demanded have no relationship
C) the demand curve is upward sloping to the right
D) quantity demanded will rise if price falls
E) none of the above
A) prices and quantity demanded are directly related
B) price and quantity demanded have no relationship
C) the demand curve is upward sloping to the right
D) quantity demanded will rise if price falls
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Equilibrium in a given product market is obtained:
A) when there are no shortages or surpluses of that product
B) when at a particular price QD = QS
C) at the point on the graph where demand and supply intersect
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) when there are no shortages or surpluses of that product
B) when at a particular price QD = QS
C) at the point on the graph where demand and supply intersect
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A government-imposed price above the equilibrium market price will produce
A) a shortage
B) a decline in demand
C) an increase in supply
D) a surplus
E) a new equilibrium price
A) a shortage
B) a decline in demand
C) an increase in supply
D) a surplus
E) a new equilibrium price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following events could be expected to produce an increase, ceteris
Paribus, in the sales of college economics textbooks?
A) an increase in the number of economic textbook companies
B) a decrease in the price of textbook publication costs
C) an increase in economics majors
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
Paribus, in the sales of college economics textbooks?
A) an increase in the number of economic textbook companies
B) a decrease in the price of textbook publication costs
C) an increase in economics majors
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Tennis balls and tennis racquets are a good example of:
A) inferior goods
B) capital goods
C) substitute goods
D) complementary goods
E) none of the above
A) inferior goods
B) capital goods
C) substitute goods
D) complementary goods
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Holding supply constant and increasing demand for automobiles should, in a free
Market:
A) lead to a higher equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium output
B) lead to lower equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium output
C) lead to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium output
D) lead to a higher equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium output
Market:
A) lead to a higher equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium output
B) lead to lower equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium output
C) lead to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium output
D) lead to a higher equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The development of monopoly power that provides a seller with pricemaking
Power is an example of:
A) a market imperfection
B) a market failure
C) dynamic instability
D) an ethical contradiction
E) none of the above
Power is an example of:
A) a market imperfection
B) a market failure
C) dynamic instability
D) an ethical contradiction
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An example of a Common Property Resource is (are):
A) The Great Lakes
B) The Redwood Forest
C) The electromagnetic spectrum used for communications
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The Great Lakes
B) The Redwood Forest
C) The electromagnetic spectrum used for communications
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An example of an externality is:
A) fire protection
B) national defense
C) industrial pollution
D) monopoly power
E) all of the above
A) fire protection
B) national defense
C) industrial pollution
D) monopoly power
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the supply and demand curves in the following diagram to answer the next five questions.
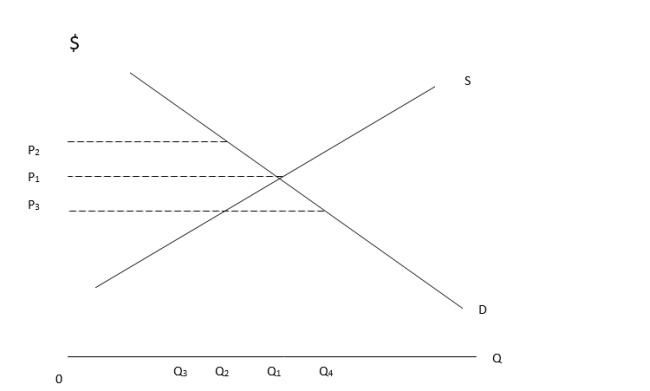
-The equilibrium price and quantity are:
A) P2 and Q2, respectively
B) P1 and Q2, respectively
C) P1 and Q1, respectively
D) P3 and Q4, respectively
E) none of the above

-The equilibrium price and quantity are:
A) P2 and Q2, respectively
B) P1 and Q2, respectively
C) P1 and Q1, respectively
D) P3 and Q4, respectively
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the supply and demand curves in the following diagram to answer the next five questions.

-If price is initially P1 and is reduced to P3, then:
A) quantity supplied will rise to Q4 and quantity demand will fall to Q3
B) quantity supplied will fall to Q3 and quantity demanded will increase to Q4
C) supply will decrease and demand will increase
D) no prediction can be made about the effect of the price change

-If price is initially P1 and is reduced to P3, then:
A) quantity supplied will rise to Q4 and quantity demand will fall to Q3
B) quantity supplied will fall to Q3 and quantity demanded will increase to Q4
C) supply will decrease and demand will increase
D) no prediction can be made about the effect of the price change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the supply and demand curves in the following diagram to answer the next five questions.

-A ceiling price that causes a shortage is best represented by:
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) none of the above

-A ceiling price that causes a shortage is best represented by:
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the supply and demand curves in the following diagram to answer the next five questions.

-Which of the following represents a surplus condition?
A) P3 price
B) P1 price
C) Q2 output
D) P2 price

-Which of the following represents a surplus condition?
A) P3 price
B) P1 price
C) Q2 output
D) P2 price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the supply and demand curves in the following diagram to answer the next five questions.

-In order for the equilibrium price to be P2, which of the following events must
Occur?
A) supply increases
B) demand increases
C) price must fall
D) consumers must stop buying the product
E) a Democrat must be elected president

-In order for the equilibrium price to be P2, which of the following events must
Occur?
A) supply increases
B) demand increases
C) price must fall
D) consumers must stop buying the product
E) a Democrat must be elected president

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The market eliminates shortages through a price increase that increases the
Quantity supplied and decreases the quantity demanded.
B) The market eliminates surpluses by raising price and decreasing quantity supplied.
C) The market eliminates shortages through a price decrease that increases demand.
D) Individual choices concerning collective satisfaction are deliberated behind a wall of ignorance.
A) The market eliminates shortages through a price increase that increases the
Quantity supplied and decreases the quantity demanded.
B) The market eliminates surpluses by raising price and decreasing quantity supplied.
C) The market eliminates shortages through a price decrease that increases demand.
D) Individual choices concerning collective satisfaction are deliberated behind a wall of ignorance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is the correct formula for elasticity of demand?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of the above
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The law of supply states that the relationship between price and quantity supplied
In a given time period is
A) negative
B) inverse
C) direct
D) indeterminate
In a given time period is
A) negative
B) inverse
C) direct
D) indeterminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Mr. McConnell observes that when his publisher raises the price of his textbook
The publisher's revenue goes up and he receives a larger royalty check. He may safely conclude that:
A) the demand for the textbook is falling
B) the demand for the textbook is elastic
C) the demand for the textbook is unit elastic
D) the demand for the textbook is inelastic
The publisher's revenue goes up and he receives a larger royalty check. He may safely conclude that:
A) the demand for the textbook is falling
B) the demand for the textbook is elastic
C) the demand for the textbook is unit elastic
D) the demand for the textbook is inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Diminishing marginal utility means:
A) a consumer realizes less additional satisfaction as additional units are consumed
B) a consumer realizes more satisfaction as additional units are consumed
C) the product becomes less useful when bought in large quantities
D) a market equilibrium may be in doubt
A) a consumer realizes less additional satisfaction as additional units are consumed
B) a consumer realizes more satisfaction as additional units are consumed
C) the product becomes less useful when bought in large quantities
D) a market equilibrium may be in doubt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



