Deck 10: Oligopoly and Firm Architecture
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Oligopoly and Firm Architecture
1
A market is composed of five firms, and their market shares are 30 percent, 25 percent, 20 percent, 15 percent, and 10 percent. What is the Herfindahl index for the industry?
A) 100
B) 2,250
C) 6,116
D) 10,000
A) 100
B) 2,250
C) 6,116
D) 10,000
2,250
2
Which of the following is an oligopoly model where firms assume that their rivals will hold their rates of production constant?
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
The kinked demand curve model
3
Which of the following is an oligopoly model where firms assume that their rivals will hold their rate prices constant?
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
The Bertrand model
4
Which of the following is an oligopoly model where firms assume that their rivals will match price cuts but not price increases?
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an oligopoly model where firms respond to the behavior of a dominant firm?
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model
A) The kinked demand curve model
B) The Cournot model
C) The Bertrand model
D) The price leadership model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following to answer questions below : 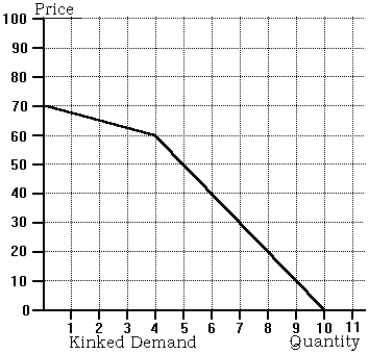
-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $60 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) produce 2 units of output.
B) produce 3 units of output.
C) produce 4 units of output.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $60 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) produce 2 units of output.
B) produce 3 units of output.
C) produce 4 units of output.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions below : 
-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $60 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) charge $60.00 per unit.
B) charge $62.50 per unit.
C) charge $65.00 per unit.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $60 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) charge $60.00 per unit.
B) charge $62.50 per unit.
C) charge $65.00 per unit.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer questions below : 
-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $40 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) produce 2 units of output.
B) produce 4 units of output.
C) produce 6 units of output.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $40 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) produce 2 units of output.
B) produce 4 units of output.
C) produce 6 units of output.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following to answer questions below : 
-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $40 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) charge $40.00 per unit.
B) charge $50.00 per unit.
C) charge $60.00 per unit.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the kinked demand graph. If an oligopolistic firm with constant unit cost equal to $40 faces this demand curve, then the firm will
A) charge $40.00 per unit.
B) charge $50.00 per unit.
C) charge $60.00 per unit.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the following to answer questions below : 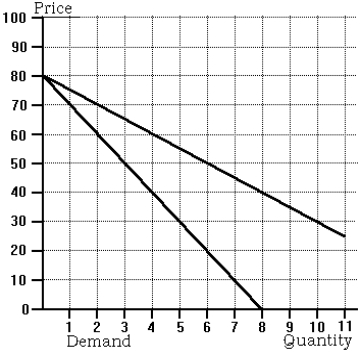
-Refer to the graph of market demand and marginal revenue. Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are given below:
MC1 = 5Q1 and MC2 = 10Q2
In order to maximize profit, the firms should produce
A) Q1 = 4, Q2 = 2, and charge P = 50.
B) Q1 = 8, Q2 = 0, and charge P = 40.
C) Q1 = 3, Q2 = 1, and charge P = 60.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the graph of market demand and marginal revenue. Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are given below:
MC1 = 5Q1 and MC2 = 10Q2
In order to maximize profit, the firms should produce
A) Q1 = 4, Q2 = 2, and charge P = 50.
B) Q1 = 8, Q2 = 0, and charge P = 40.
C) Q1 = 3, Q2 = 1, and charge P = 60.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer questions below : 
-Refer to the graph of market demand and marginal revenue. Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are given below:
MC1 = 10Q1 and MC2 = 30Q2
In order to maximize profit, the firms should produce
A) Q1 = 4, Q2 = 2, and charge P = 50.
B) Q1 = 8, Q2 = 0, and charge P = 40.
C) Q1 = 3, Q2 = 1, and charge P = 60.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the graph of market demand and marginal revenue. Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are given below:
MC1 = 10Q1 and MC2 = 30Q2
In order to maximize profit, the firms should produce
A) Q1 = 4, Q2 = 2, and charge P = 50.
B) Q1 = 8, Q2 = 0, and charge P = 40.
C) Q1 = 3, Q2 = 1, and charge P = 60.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the following to answer questions below: 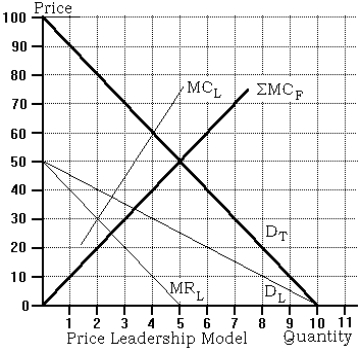
-Refer to the price leadership graph. The equilibrium price is
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $60.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the price leadership graph. The equilibrium price is
A) $40.
B) $50.
C) $60.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following to answer questions below: 
-Refer to the price leadership graph. The total quantity traded on the market at equilibrium is
A) 3 units.
B) 5 units.
C) 6 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the price leadership graph. The total quantity traded on the market at equilibrium is
A) 3 units.
B) 5 units.
C) 6 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the following to answer questions below: 
-Refer to the price leadership graph. The quantity supplied by the barometric firm is
A) 2 units.
B) 3 units.
C) 4 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the price leadership graph. The quantity supplied by the barometric firm is
A) 2 units.
B) 3 units.
C) 4 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following to answer questions below: 
-Refer to the price leadership graph. The quantity supplied by the follower firms is
A) 2 units.
B) 3 units.
C) 4 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

-Refer to the price leadership graph. The quantity supplied by the follower firms is
A) 2 units.
B) 3 units.
C) 4 units.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If an oligopolist is attempting to maximize revenue, it should produce a quantity of output where marginal revenue is
A) greater than marginal cost.
B) equal to zero.
C) equal to marginal cost.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) greater than marginal cost.
B) equal to zero.
C) equal to marginal cost.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning profits in the short run, then in the long run the behavior of competing firms
A) will cause the firm's supply curve to shift to the left.
B) will cause the firm's supply curve to shift to the right.
C) will cause the firm's demand curve to shift to the left.
D) will cause the firm's demand curve to shift to the right.
A) will cause the firm's supply curve to shift to the left.
B) will cause the firm's supply curve to shift to the right.
C) will cause the firm's demand curve to shift to the left.
D) will cause the firm's demand curve to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Two firms that comprise an industry have decided to engage in collusion. They intend to maximize their total collective profit, that is, to behave as a single monopolist. How should they behave?
A) Both firms should increase their levels of output.
B) The firm with the higher marginal cost should reduce output and the firm with the lower marginal cost should increase output.
C) The firm with the lower marginal cost should reduce output and the firm with the higher marginal cost should increase output.
D) Both firms should reduce their levels of output.
A) Both firms should increase their levels of output.
B) The firm with the higher marginal cost should reduce output and the firm with the lower marginal cost should increase output.
C) The firm with the lower marginal cost should reduce output and the firm with the higher marginal cost should increase output.
D) Both firms should reduce their levels of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Oligopolist A is considering a price reduction. The payoff from this strategy depends on the behavior of Oligopolist B. If Oligopolist B also reduces price, then Oligopolist A will earn a profit of $50,000. If Oligopolist B does not reduce price, then Oligopolist A will earn a profit of $100,000. The situation is symmetrical; that is, if Oligopolist B reduces price and Oligopolist A doesn't, then Oligopolist B will earn a profit of $100,000, and if both oligopolists reduce their prices, then Oligopolist B will earn a profit of $50,000. If neither oligopolist reduces price, then both will continue to earn profits of $75,000. What can Oligopolist A and Oligopolist B be expected to do in the absence of collusion?
A) Both will refrain from reducing price.
B) Both will reduce price.
C) Oligopolist A will reduce price, but Oligopolist B won't.
D) Oligopolist B will reduce price, but Oligopolist A won't.
A) Both will refrain from reducing price.
B) Both will reduce price.
C) Oligopolist A will reduce price, but Oligopolist B won't.
D) Oligopolist B will reduce price, but Oligopolist A won't.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Some economists have suggested that oligopolists tend to maintain stable prices when there are changes in the demand for their products or in their costs of production. Which of the following models provides an explanation for this type of behavior?
A) Price leadership
B) Centralized cartel
C) Prisoners' dilemma
D) Kinked demand curve
A) Price leadership
B) Centralized cartel
C) Prisoners' dilemma
D) Kinked demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The market for automobiles is an example of
A) monopolistic competition.
B) duopoly.
C) differentiated oligopoly.
D) pure oligopoly.
A) monopolistic competition.
B) duopoly.
C) differentiated oligopoly.
D) pure oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If an industry is composed of four firms and their market shares are 40 percent, 30 percent, 20 percent, and 10 percent, then the Herfindahl index for the industry is
A) 100.
B) 200.
C) 3,000.
D) 10,000.
A) 100.
B) 200.
C) 3,000.
D) 10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Herfindahl index will be largest for an industry that is
A) a monopoly.
B) perfectly competitive.
C) a duopoly.
D) monopolistically competitive.
A) a monopoly.
B) perfectly competitive.
C) a duopoly.
D) monopolistically competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Herfindahl index will be smallest for an industry that is
A) a monopoly.
B) perfectly competitive.
C) a duopoly.
D) a differentiated oligopoly.
A) a monopoly.
B) perfectly competitive.
C) a duopoly.
D) a differentiated oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to the Cournot model, a firm will
A) assume that rival firms will keep their production constant.
B) produce the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) respond to changes in production by rival firms by adjusting its production.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) assume that rival firms will keep their production constant.
B) produce the quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) respond to changes in production by rival firms by adjusting its production.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to the Bertrand model, a firm will assume that rival firms will
A) keep their rates of production constant.
B) keep their prices constant.
C) match price cuts but not price increases.
D) match price increases but not price cuts.
A) keep their rates of production constant.
B) keep their prices constant.
C) match price cuts but not price increases.
D) match price increases but not price cuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the kinked demand curve model, a firm will assume that rival firms will
A) keep their rates of production constant.
B) keep their prices constant.
C) match price cuts but not price increases.
D) match price increases but not price cuts.
A) keep their rates of production constant.
B) keep their prices constant.
C) match price cuts but not price increases.
D) match price increases but not price cuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The refrigerator industry is an example of
A) monopolistic competition.
B) monopoly.
C) oligopoly.
D) perfect competition.
A) monopolistic competition.
B) monopoly.
C) oligopoly.
D) perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The petroleum industry is an example of
A) monopolistic competition.
B) pure oligopoly.
C) duopoly.
D) differentiated oligopoly.
A) monopolistic competition.
B) pure oligopoly.
C) duopoly.
D) differentiated oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The kinked demand curve model assumes that
A) firms match price increases, but not price cuts.
B) demand is more elastic for price cuts than for price increases.
C) changes in marginal cost can never lead to changes in market price.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) firms match price increases, but not price cuts.
B) demand is more elastic for price cuts than for price increases.
C) changes in marginal cost can never lead to changes in market price.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not a form of nonprice competition?
A) Advertising
B) Quality of service
C) Product quality
D) All of the above are forms of nonprice competition.
A) Advertising
B) Quality of service
C) Product quality
D) All of the above are forms of nonprice competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A cartel that gives each member the exclusive right to operate in a particular geographic area is a
A) market-sharing cartel.
B) centralized cartel.
C) price leadership cartel.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) market-sharing cartel.
B) centralized cartel.
C) price leadership cartel.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A cartel that operates like a multiplant monopolist is a
A) market-sharing cartel.
B) centralized cartel.
C) price leadership cartel.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) market-sharing cartel.
B) centralized cartel.
C) price leadership cartel.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under the dominant-firm price leadership model,
A) all firms but the dominant firm are price takers.
B) the dominant firm acts as the residual monopolistic supplier.
C) the demand curve faced by the dominant firm is flatter than the market demand curve.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) all firms but the dominant firm are price takers.
B) the dominant firm acts as the residual monopolistic supplier.
C) the demand curve faced by the dominant firm is flatter than the market demand curve.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Oligopolistic firms can earn positive economic profits
A) in the short run, but not in the long run.
B) in the short run and in the long run.
C) in the long run, but not in the short run.
D) in neither the short run nor the long run.
A) in the short run, but not in the long run.
B) in the short run and in the long run.
C) in the long run, but not in the short run.
D) in neither the short run nor the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following forms of market organization assumes that entry and exit of firms is costless?
A) Differentiated oligopoly
B) Duopoly
C) Monopolistic competition
D) Pure oligopoly
A) Differentiated oligopoly
B) Duopoly
C) Monopolistic competition
D) Pure oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The harmful effects of oligopoly include all of the following except:
A) economies of scale result in a small number of large firms that spend more on research and development.
B) price is greater than long-run marginal and average cost.
C) production does not generally take place at the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve.
D) All of the above are harmful effects of oligopoly.
A) economies of scale result in a small number of large firms that spend more on research and development.
B) price is greater than long-run marginal and average cost.
C) production does not generally take place at the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve.
D) All of the above are harmful effects of oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The sales maximization model assumes that imperfectly competitive firms will produce a level of output where
A) marginal revenue is equal to zero.
B) marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue is equal to zero if profit is satisfactory.
D) they will break even.
A) marginal revenue is equal to zero.
B) marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue is equal to zero if profit is satisfactory.
D) they will break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One reason that most economists do not support government industrial and trade policies is that the outcomes of these policies cannot
A) have a positive effect on a country's industries.
B) be accurately predicted.
C) help a country to overcome a comparative disadvantage.
D) prevent a country from losing a comparative advantage.
A) have a positive effect on a country's industries.
B) be accurately predicted.
C) help a country to overcome a comparative disadvantage.
D) prevent a country from losing a comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The growth of global oligopolists has been encouraged by
A) the development of new transportation and telecommunications technologies.
B) the globalization of tastes.
C) reductions in barriers to international trade and investment.
D) All of the above have encouraged the growth of global oligopolists.
A) the development of new transportation and telecommunications technologies.
B) the globalization of tastes.
C) reductions in barriers to international trade and investment.
D) All of the above have encouraged the growth of global oligopolists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In which of the sectors listed below has the growth in concentration been most pronounced during the past decade?
A) Agriculture
B) Mining
C) Banking
D) Home construction
A) Agriculture
B) Mining
C) Banking
D) Home construction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Firms in which of the following industries have used mergers and acquisitions to grow and globalize?
A) Telecommunications
B) Entertainment and communications media
C) Consumer products
D) All of the above are correct.
A) Telecommunications
B) Entertainment and communications media
C) Consumer products
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Compared to relationship enterprises, virtual corporations are more likely to be
A) lasting and stable.
B) short term and temporary.
C) global in scope.
D) oligopolistic.
A) lasting and stable.
B) short term and temporary.
C) global in scope.
D) oligopolistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When several independent firms form a temporary network to take advantage of a short-term business opportunity, the result is called a
A) collaborative firm.
B) relationship enterprise.
C) virtual corporation.
D) cartelized partnership.
A) collaborative firm.
B) relationship enterprise.
C) virtual corporation.
D) cartelized partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The ideal firm architecture includes all of the following except
A) a focus on core competencies.
B) the integration of physical and virtual systems.
C) a hierarchical, top-down management structure.
D) smaller, more flexible production facilities.
A) a focus on core competencies.
B) the integration of physical and virtual systems.
C) a hierarchical, top-down management structure.
D) smaller, more flexible production facilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Porter's strategic framework identifies forces that influence an industry's
A) intensity of competition and profitability.
B) rate of growth.
C) popularity among consumers.
D) potential as an exporter within the global economy.
A) intensity of competition and profitability.
B) rate of growth.
C) popularity among consumers.
D) potential as an exporter within the global economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not a force identified by Porter's strategic framework?
A) Threat of entry
B) Intensity of rivalry
C) Government tax policy
D) Bargaining power of buyers
A) Threat of entry
B) Intensity of rivalry
C) Government tax policy
D) Bargaining power of buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The knowledge economy is characterized by a reliance on
A) innovation and creativity.
B) a customer-centric approach.
C) efficiency in production.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) innovation and creativity.
B) a customer-centric approach.
C) efficiency in production.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An emphasis on design innovation is typical of
A) the knowledge economy.
B) the virtual corporation.
C) relationship enterprises.
D) the creative firm.
A) the knowledge economy.
B) the virtual corporation.
C) relationship enterprises.
D) the creative firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
CENCOR is an acronym for a design strategy that consists of the following parts:
A) collaborate, evaluate, celebrate, occlude, and rationalize
B) calibrate, explore, create, organize, and realize
C) create, evoke, circumvent, officiate, and redeem
D) calculate, erect, consign, offer, and return
A) collaborate, evaluate, celebrate, occlude, and rationalize
B) calibrate, explore, create, organize, and realize
C) create, evoke, circumvent, officiate, and redeem
D) calculate, erect, consign, offer, and return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Assume that the industry consists of 10 firms with 10% of the market share each. If three of these firms are allowed to merge and form a new firm with a 30% market share, while the remaining seven firms will remain with 10% each, what would the change in the Herfindahl index be due to this merger?
A) 1000
B) 600
C) 300
D) 100
A) 1000
B) 600
C) 300
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A market is composed of 2 firms, and the bigger firm takes up 60 percent of the market. What is the Herfindahl index for the industry?
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A market is composed of three firms. If the bigger two firms' market shares are 45 and 30 percent, what is the Herfindahl index for the industry?
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A market is composed of 4 firms. The three bigger firms take up 40, 30 and 20 percent of the market share. What is the Herfindahl index for the industry?
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250
A) 3,000
B) 3,550
C) 5,200
D) 6,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Assume that the industry consists of 5 firms each with 20 percent of the market share. If two of them merge, by how much does the Herfindahl index increase?
A) 800
B) 2,000
C) 2,500
D) 2,800
A) 800
B) 2,000
C) 2,500
D) 2,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Assume that the industry consists of 2 firms each with 50 percent of the market share. If each of them is split into 2 smaller companies, by how much does the Herfindahl index decrease?
A) 800
B) 2,000
C) 2,500
D) 2,800
A) 800
B) 2,000
C) 2,500
D) 2,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are: MC1 = 2Q1 and MC2 = 3Q2. If the marginal revenue curve of the market is MR = 100-0.8Q, what quantity should the profit maximizing cartel produce?
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are: MCA = 2QA and MCB = 3QB. If the marginal revenue curve of the market is MR = 100-0.8Q, what quantity should Firm A produce?
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are: MCA = 2QA and MCB = 3QB. If the marginal revenue curve of the market is MR = 100-0.8Q, what quantity should Firm B produce?
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50
A) Q=20
B) Q=30
C) Q=40
D) Q=50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Two firms have formed a centralized cartel in order to maximize profit on the market. Their marginal cost curves are: MCA = 2QA and MCB = 3QB. If the marginal revenue curve of the market is MR = 100-0.8Q, what price should the cartel charge?
A) P=40
B) P=60
C) P=80
D) P=90
A) P=40
B) P=60
C) P=80
D) P=90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following U.S. corporations had the highest sales in 2015?
A) Walmart
B) CVS
C) Ford Motor
D) AT&T
A) Walmart
B) CVS
C) Ford Motor
D) AT&T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following automobile manufacturers produced the most vehicles in 2016?
A) Volkswagen Group
B) Renault/Nissan
C) Honda
D) Fiat/Chrysler
A) Volkswagen Group
B) Renault/Nissan
C) Honda
D) Fiat/Chrysler

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The most innovative firms are mostly from
A) Germany
B) Japan
C) China
D) Untied States
A) Germany
B) Japan
C) China
D) Untied States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A duopoly is an oligopoly in which several firms duel for consumer demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Oligopoly is the prevalent form of market organization in the manufacturing sectors of industrial nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Oligopolistic markets are characterized by rivalries between firms that arise because the actions of each firm in an industry have an effect on the other firms in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Limit pricing refers to the oligopolistic practice of charging a price so low that new firms are discouraged from entering the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The sources of oligopoly are generally the same as for monopoly, that is, barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Concentration ratios measure the total number of firms required to supply the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the concentration ratio for an industry is small, then the Herfindahl index is likely to be large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An oligopolistic industry is likely to have a large concentration ratio and a large Herfindahl index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The Cournot model focuses on interdependence among firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The kinked demand curve model describes a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The kinked demand curve model provides an explanation of price rigidity in the face of changes in costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Oligopolists prefer to avoid engaging in nonprice competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A cartel is an organization of colluding oligopolists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cartels tend to self-destruct because each member has an incentive to cheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Price leadership is an example of formal collusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The sector in which the size of the largest firms has grown most is retail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If a firm with marginal cost equal to $2 faces a demand curve defined as QD = 10 - 2P, then revenue is at a maximum when price is $6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



