Deck 1: Formal Languages and Automata Theory: Part A
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Formal Languages and Automata Theory: Part A
1
Let L1 = {w ? {0,1}? | w has at least as many occurrences of (110)'s as (011)'s}. Let L2 = { ? {0,1}? | w has at least as many occurrences of (000)'s as (111)'s}. Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) L1 is regular but not L2
B)L2 is regular but not L1
C)Both L1 and L2 are regular
D)Neither L1 nor L2 are regular
A) L1 is regular but not L2
B)L2 is regular but not L1
C)Both L1 and L2 are regular
D)Neither L1 nor L2 are regular
L2 is regular but not L1
2
A spanning tree for a simple graph of order 24 has
A)12 edges
B)6 edges
C)23 edges
D)None of above.
A)12 edges
B)6 edges
C)23 edges
D)None of above.
23 edges
3
If G is a simple connected 3-regular planar graph where every region is bounded by exactly 3 edges, then the edges of G is
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)5
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)5
6
4
If G is a connected planar graph of v vertices e edges and r regions then
A)v-e+r=2
B)e-v+r=2
C)v+e-r=2
D)None of above.
A)v-e+r=2
B)e-v+r=2
C)v+e-r=2
D)None of above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A Hamiltonian cycle in a Hamiltonian graph of order 24 has
A)12 edges.
B)24 edges
C)23 edges
D)None of above.
A)12 edges.
B)24 edges
C)23 edges
D)None of above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If G is a simple connected 3-regular planar graph where every region is bounded by exactly 3 edges, then the edges of G is
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)5
A)3
B)4
C)6
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following grammar
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aSa
S ? aAa
A ? bB
B ? bB
B ? c is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aSa
S ? aAa
A ? bB
B ? bB
B ? c is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following grammar
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B, C, D, E}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aAB
AB ? CD
CD ? CE
C ? aC
C ? b
BE ? bc is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B, C, D, E}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aAB
AB ? CD
CD ? CE
C ? aC
C ? b
BE ? bc is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following grammar
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B, C}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aS
A ? bB
B ? cC
C ? a is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1
G = (N, T, P, S)
N = {S, A, B, C}
T = {a, b, c}
P : S ? aS
A ? bB
B ? cC
C ? a is
A)is type 3
B)is type 2 but not type 3
C)is type 1 but not type 2
D)is type 0 but not type 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
P, Q, R are three languages. If P & R are regular and if PQ=R, then
A)Q has to be regular
B)Q cannot be regular
C)Q need not be regular
D)Q has to be a CFL
A)Q has to be regular
B)Q cannot be regular
C)Q need not be regular
D)Q has to be a CFL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is true with respect to Kleene's theorem?
1 A regular language is accepted by a finite automaton.
2 Every language is accepted by a finite automaton or a turingmachine.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)Both 1 and 2 are true statements
D)None is true
1 A regular language is accepted by a finite automaton.
2 Every language is accepted by a finite automaton or a turingmachine.
A)1 only
B)2 only
C)Both 1 and 2 are true statements
D)None is true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Automaton accepting the regular expression of any number of a ' s is:
A)a*
B)ab*
C)(a/b)*
D)a*b*c
A)a*
B)ab*
C)(a/b)*
D)a*b*c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Grammars that can be translated to DFAs:
A)Left linear grammar
B)Right linear grammar
C)Generic grammar
D)All of these
A)Left linear grammar
B)Right linear grammar
C)Generic grammar
D)All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two strings x and y are indistinguishable if:
A)?*(s, x) = ?* (s, y), i.e. the state reached by a DFA M on input x is the same as the state reached by M on input y
B)if for every string z ? ?* either both xz and yz are in language A on ?* or both xz and yz are not in A
C)Both above statements are true
D)None of the above
A)?*(s, x) = ?* (s, y), i.e. the state reached by a DFA M on input x is the same as the state reached by M on input y
B)if for every string z ? ?* either both xz and yz are in language A on ?* or both xz and yz are not in A
C)Both above statements are true
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Given an arbitrary non-deterministic finite automaton NFA with N states, the maximum number of states in an equivalent minimized DFA is at least:
A)N2
B)2N
C)2N
D)N!
A)N2
B)2N
C)2N
D)N!

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Regular expressions are
A)Type 0 language
B)Type 1 language
C)Type 2 language
D)Type 3 language
A)Type 0 language
B)Type 1 language
C)Type 2 language
D)Type 3 language

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The regular expression 0*(10)* denotes the same set as
A)(1*0)*1*
B)0+(0+10)*
C)(0+1)*10(0+1)*
D)None of the above
A)(1*0)*1*
B)0+(0+10)*
C)(0+1)*10(0+1)*
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the NFA M shown below.
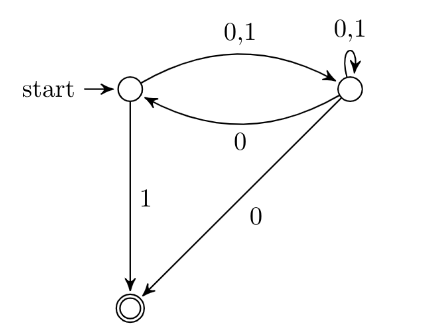 Let the language accepted by M be L. Let L1 be the language accepted by the NFA M1, obtained by changing the accepting state of M to a non-accepting state and by changing the non-accepting state of M to accepting states. Which of the following statements is true?
Let the language accepted by M be L. Let L1 be the language accepted by the NFA M1, obtained by changing the accepting state of M to a non-accepting state and by changing the non-accepting state of M to accepting states. Which of the following statements is true?
A) L1 = {0,1}* ? L
B) L1 = {0,1}*
C) L1 is a subset of L
D) L1 = L
 Let the language accepted by M be L. Let L1 be the language accepted by the NFA M1, obtained by changing the accepting state of M to a non-accepting state and by changing the non-accepting state of M to accepting states. Which of the following statements is true?
Let the language accepted by M be L. Let L1 be the language accepted by the NFA M1, obtained by changing the accepting state of M to a non-accepting state and by changing the non-accepting state of M to accepting states. Which of the following statements is true?A) L1 = {0,1}* ? L
B) L1 = {0,1}*
C) L1 is a subset of L
D) L1 = L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the statements is true:
A)The complement of a regular language is always regular.
B)Homomorphism of a regular language is always regular.
C)Both of the above are true statements
D)None of the above
A)The complement of a regular language is always regular.
B)Homomorphism of a regular language is always regular.
C)Both of the above are true statements
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The regular sets are closed under:
A)Union
B)Concatenation
C)Kleene closure
D)All of the above
A)Union
B)Concatenation
C)Kleene closure
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Any given transition graph has an equivalent:
A)regular
B)DFSM (Deterministic Finite State Machine)
C)NDFSM
D)All of them
A)regular
B)DFSM (Deterministic Finite State Machine)
C)NDFSM
D)All of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A language is regular if and only if
A)Accepted by DFA
B)Accepted by PDA
C)Accepted by LBA
D)Accepted by Turing machine
A)Accepted by DFA
B)Accepted by PDA
C)Accepted by LBA
D)Accepted by Turing machine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a regular expression?
A)[(a+b)*-(aa+bb)]*
B)[(0+1)-(0b+a1)*(a+b)]*
C)(01+11+10)*
D)(1+2+0)*(1+2)*
A)[(a+b)*-(aa+bb)]*
B)[(0+1)-(0b+a1)*(a+b)]*
C)(01+11+10)*
D)(1+2+0)*(1+2)*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the regular language L = (111+111111)*. The minimum number of states inany DFA accepting this language is
A)3
B)5
C)8
D)9
A)3
B)5
C)8
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How many strings of length less than 4 contains the language described by the regular expression (x+y)*y(a+ab)*?
A)7
B)10
C)12
D)11
A)7
B)10
C)12
D)11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is TRUE?
A)Every subset of a regular set is regular
B)Every finite subset of a non-regular set is regular
C)The union of two non-regular sets is not regular
D)Infinite union of finite sets is regular
A)Every subset of a regular set is regular
B)Every finite subset of a non-regular set is regular
C)The union of two non-regular sets is not regular
D)Infinite union of finite sets is regular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The minimum state automaton equivalent to the above FSA has the following number of states
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which one of the following languages over the alphabet {0,1} is described by the regular expression: (0+1)*0(0+1)*0(0+1)*?
A)The set of all strings containing the substring 00.
B)The set of all strings containing at most two 0's.
C)The set of all strings containing at least two 0's.
D)The set of all strings that begin and end with either 0 or 1.
A)The set of all strings containing the substring 00.
B)The set of all strings containing at most two 0's.
C)The set of all strings containing at least two 0's.
D)The set of all strings that begin and end with either 0 or 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Let w be any string of length n is {0,1}*. Let L be the set of all substrings of w. What is the minimum number of states in a non-deterministic finite automaton that accepts L?
A)n-1
B)n
C)n+1
D)2n-1
A)n-1
B)n
C)n+1
D)2n-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following are regular sets?
A)I and IV only
B)I and III only
C)I only
D)IV only
A)I and IV only
B)I and III only
C)I only
D)IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A minimum state deterministic finite automation accepting the language L={W W ? {0,1}*, number of 0s and 1s in are divisible by 3 and 5, respectively} has
A)15 states
B)11 states
C)10 states
D)9 states
A)15 states
B)11 states
C)10 states
D)9 states

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Let P be a regular language and Q be context-free language such that Q ? P. (For example, let P be the language represented by the regular expression p*q* and Q be {pnqn n? N}). Then which of the following is ALWAYS regular?
A)P ? Q
B)P - Q
C)?* - P
D)?* - Q
A)P ? Q
B)P - Q
C)?* - P
D)?* - Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Given a Non-deterministic Finite Automation (NFA) with states p and r as initial and final states respectively and transition table as given below: 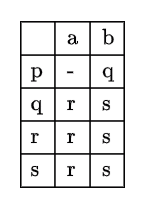 The minimum number of states required in Deterministic Finite Automation(DFA) equivalent to NFA is
The minimum number of states required in Deterministic Finite Automation(DFA) equivalent to NFA is
A)5
B)4
C)3
D)2
 The minimum number of states required in Deterministic Finite Automation(DFA) equivalent to NFA is
The minimum number of states required in Deterministic Finite Automation(DFA) equivalent to NFA isA)5
B)4
C)3
D)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which one of the following statement is true for a regular language L over {a} whose minimal finite state automation has two states?
A)L must be either {an I n is odd} or {an I n is even}
B)L must be {an I n is odd}
C)L must be {an I n is even}
D)L must be {an I n = 0}
A)L must be either {an I n is odd} or {an I n is even}
B)L must be {an I n is odd}
C)L must be {an I n is even}
D)L must be {an I n = 0}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The …………. is said to be ambiguous if there exist at least one word of its language that can be generated by the different production tree .
A)CFL
B)CFG
C)GTG
D)None of the given
A)CFL
B)CFG
C)GTG
D)None of the given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Type-1 Grammar is known as_____________
A)CFG
B)CSG
C)REGULAR
D)All
A)CFG
B)CSG
C)REGULAR
D)All

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If G is "S ? a S/a", then L(G) = ?
A)a*
B)^
C){a}+
D)Both (a) & (c)
A)a*
B)^
C){a}+
D)Both (a) & (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
"S ?a S", what is the type of this production?
A)Type 0
B)Type 1
C)Type 2
D)Type 3
A)Type 0
B)Type 1
C)Type 2
D)Type 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A?abA a type __________productions
A)Type 0
B)Type 1
C)Type 2
D)Type 3
A)Type 0
B)Type 1
C)Type 2
D)Type 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following CFG is in S ? AB**spaceB ? CD**spaceB ? AD**spaceB ? b**spaceD ? AD**spaceD ? d**spaceA ? a**spaceC ? a
A)Chomsky normal form but not strong Chomsky normal form
B)Weak Chomsky normal form but not Chomsky normal form
C)Strong Chomsky normal form
D)Greibach normal form
A)Chomsky normal form but not strong Chomsky normal form
B)Weak Chomsky normal form but not Chomsky normal form
C)Strong Chomsky normal form
D)Greibach normal form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The language accepted by a Push down Automata:
A)Type0
B)Type1
C)Type2
D)Type3
A)Type0
B)Type1
C)Type2
D)Type3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following problems is undecidable?
A)Membership problem for CFGs
B)Ambiguity problem for CFGs
C)Finiteness problem for Finite state automata FSAs
D)Equivalence problem for FSAs
A)Membership problem for CFGs
B)Ambiguity problem for CFGs
C)Finiteness problem for Finite state automata FSAs
D)Equivalence problem for FSAs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which one of the following statement is FALSE?
A)context-free languages are closed under union
B)context-free languages are closed under concatenation
C)context-free languages are closed under intersection
D)context-free languages are closed under Kleene closure
A)context-free languages are closed under union
B)context-free languages are closed under concatenation
C)context-free languages are closed under intersection
D)context-free languages are closed under Kleene closure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statement is wrong?
A)Any regular language can be generated by a context-free grammar
B)Some non-regular languages cannot be generated by any CFG
C)the intersection of a CFL and regular set is a CFL
D)All non-regular languages can be generated by CFGs.
A)Any regular language can be generated by a context-free grammar
B)Some non-regular languages cannot be generated by any CFG
C)the intersection of a CFL and regular set is a CFL
D)All non-regular languages can be generated by CFGs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following strings is not generated by the following grammar? S ? SaSbS ?
A)aabb
B)abab
C)aababb
D)aaabb
A)aabb
B)abab
C)aababb
D)aaabb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following regular expression identity is true?
A)r(*) = r*
B)(r*s*)* = (r + s)*
C)(r + s)* = r* + s*
D)r*s* = r* + s*
A)r(*) = r*
B)(r*s*)* = (r + s)*
C)(r + s)* = r* + s*
D)r*s* = r* + s*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A language L is accepted by a FSA iff it is
A)CFL
B)CSL
C)Recursive
D)Regular
A)CFL
B)CSL
C)Recursive
D)Regular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider the following CFG S ? aB S ? bA**spaceB ? b A ? a**spaceB ? bS A ? aS**spaceB ? aBB A ? bAA**spaceConsider the following derivation**spaceS ?aB**space?aaBB**space?aaBb**space?aabSb**space?aabbAb**space?aabbab**spaceThis derivation is
A)A leftmost derivation
B)A rightmost derivation
C)Both leftmost and rightmost derivation
D)Neither leftmost nor rightmost derivation
A)A leftmost derivation
B)A rightmost derivation
C)Both leftmost and rightmost derivation
D)Neither leftmost nor rightmost derivation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the following language L = {anbncndn n ? 1} L is
A)CFL but not regular
B)CSL but not CFL
C)Regular
D)Type 0 language but not type 1
A)CFL but not regular
B)CSL but not CFL
C)Regular
D)Type 0 language but not type 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A language is represented by a regular expression (a)*(a + ba). Which of the following strings does not belong to the regular set represented by the above expression?
A)aaa
B)aba
C)abab
D)aa
A)aaa
B)aba
C)abab
D)aa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



