Deck 3: Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Settling the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700
1
In Calvinist thought, the "conversion" was
A) something experienced as a group.
B) earned by a person's good works.
C) a Catholic heresy.
D) an event that freed a person from having to live a holy life.
E) a personal experience when God revealed an individual's heavenly destiny.
A) something experienced as a group.
B) earned by a person's good works.
C) a Catholic heresy.
D) an event that freed a person from having to live a holy life.
E) a personal experience when God revealed an individual's heavenly destiny.
a personal experience when God revealed an individual's heavenly destiny.
2
King James I opposed the Separatists who wanted to break away entirely from the Church of England because he
A) realized that if his subjects could defy him as their spiritual leader, they could defy him as their political leader.
B) strongly believed in the concept of "visible saints."
C) never understood the political implications of their actions.
D) believed that they were turning their backs on the true Calvinist faith.
E) was a strong Catholic and the Separatists' doctrine went counter to the strict interpretation of the Bible.
A) realized that if his subjects could defy him as their spiritual leader, they could defy him as their political leader.
B) strongly believed in the concept of "visible saints."
C) never understood the political implications of their actions.
D) believed that they were turning their backs on the true Calvinist faith.
E) was a strong Catholic and the Separatists' doctrine went counter to the strict interpretation of the Bible.
realized that if his subjects could defy him as their spiritual leader, they could defy him as their political leader.
3
With the franchise in Massachusetts extended to all adult males who belonged to Puritan congregations, the proportion of qualified voters (approximately 2/5)in this colony as compared to England was
A) larger.
B) somewhat smaller.
C) about the same.
D) not known.
E) a great deal smaller.
A) larger.
B) somewhat smaller.
C) about the same.
D) not known.
E) a great deal smaller.
larger.
4
In Puritan doctrine, the "elect" were also referred to as
A) Separatists.
B) "patroons."
C) "visible saints."
D) Pilgrims.
E) Anglicans.
A) Separatists.
B) "patroons."
C) "visible saints."
D) Pilgrims.
E) Anglicans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Colonists in both the North and the South established differences in all of the following areas except
A) patterns of settlement.
B) economies.
C) political systems.
D) values.
E) allegiance to England.
A) patterns of settlement.
B) economies.
C) political systems.
D) values.
E) allegiance to England.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following are true of Martin Luther except
A) he was German.
B) he protested against Catholic doctrines at Wittenberg in 1517.
C) there was little notice of his reforms in Europe.
D) he denounced the authority of priests and popes.
E) he declared that the Bible was the only source of God's word.
A) he was German.
B) he protested against Catholic doctrines at Wittenberg in 1517.
C) there was little notice of his reforms in Europe.
D) he denounced the authority of priests and popes.
E) he declared that the Bible was the only source of God's word.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the Massachusetts "Bible Commonwealth," clergymen
A) could be elected to political office.
B) could not be fired by their congregations.
C) were not allowed to marry.
D) were barred from holding formal political office.
E) could not have children.
A) could be elected to political office.
B) could not be fired by their congregations.
C) were not allowed to marry.
D) were barred from holding formal political office.
E) could not have children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The leader that helped the Pilgrims survive was
A) John Smith.
B) John Winthrop.
C) Roger Williams.
D) William Laud.
E) William Bradford.
A) John Smith.
B) John Winthrop.
C) Roger Williams.
D) William Laud.
E) William Bradford.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the statement that is false.
A) The promise of riches, especially tobacco, drew the first settlers to the southern colonies.
B) Religious devotion primarily shaped the earliest settlements in the New England colonies.
C) Colonists in both the north and south shared a common language and English heritage.
D) Colonists in both the north and south had strong common characteristics that would persist for generations.
E) The colonies in the north and south had different patterns of settlement, different economies, different political systems, and even different sets of values.
A) The promise of riches, especially tobacco, drew the first settlers to the southern colonies.
B) Religious devotion primarily shaped the earliest settlements in the New England colonies.
C) Colonists in both the north and south shared a common language and English heritage.
D) Colonists in both the north and south had strong common characteristics that would persist for generations.
E) The colonies in the north and south had different patterns of settlement, different economies, different political systems, and even different sets of values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
John Calvin profoundly affected the thought of all of the following except
A) Spanish Armenians.
B) New England Puritans.
C) Scottish Presbyterians.
D) French Huguenots.
E) the Dutch Reformed Church.
A) Spanish Armenians.
B) New England Puritans.
C) Scottish Presbyterians.
D) French Huguenots.
E) the Dutch Reformed Church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Separatists migrated from Holland to the New World in order to
A) avoid the coming war with France.
B) gain wealth through all the economic incentives the New World offered.
C) establish a new nation.
D) avoid the Dutchification of their children.
E) escape the jurisdiction of the Virginia Company.
A) avoid the coming war with France.
B) gain wealth through all the economic incentives the New World offered.
C) establish a new nation.
D) avoid the Dutchification of their children.
E) escape the jurisdiction of the Virginia Company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following were true of the Pilgrims except they
A) were also known as Separatists.
B) arrived in the New World on the ship the Mayflower.
C) arrived at their original destination with no casualties.
D) chose Plymouth Bay as their landing site in 1620.
E) were without legal right to the land and specific authority to establish a government.
A) were also known as Separatists.
B) arrived in the New World on the ship the Mayflower.
C) arrived at their original destination with no casualties.
D) chose Plymouth Bay as their landing site in 1620.
E) were without legal right to the land and specific authority to establish a government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The historical significance of the Pilgrims of Plymouth Bay lies in their
A) numerical size.
B) economic power.
C) moral and spiritual qualities.
D) dedication to family life.
E) unwillingness to merge with the Puritans in Massachusetts Bay.
A) numerical size.
B) economic power.
C) moral and spiritual qualities.
D) dedication to family life.
E) unwillingness to merge with the Puritans in Massachusetts Bay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Puritan doctrine included acceptance of
A) antinomianism.
B) the Pope's supremacy.
C) the idea of a covenant with God.
D) the doctrine of good works.
E) the King as the final religious authority.
A) antinomianism.
B) the Pope's supremacy.
C) the idea of a covenant with God.
D) the doctrine of good works.
E) the King as the final religious authority.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Unlike Separatists, the Puritans
A) advocated strict separation of church and state.
B) practiced passive resistance to oppression.
C) remained members of the Church of England.
D) were Calvinists.
E) rejected belief in witchcraft.
A) advocated strict separation of church and state.
B) practiced passive resistance to oppression.
C) remained members of the Church of England.
D) were Calvinists.
E) rejected belief in witchcraft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Among the Puritans, it was understood that
A) they would establish democratic government in America.
B) clergymen would hold the most powerful political office.
C) the purpose of government was to enforce God's laws.
D) all adult white male landowners could vote for political leaders.
E) women could become religious leaders.
A) they would establish democratic government in America.
B) clergymen would hold the most powerful political office.
C) the purpose of government was to enforce God's laws.
D) all adult white male landowners could vote for political leaders.
E) women could become religious leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Henry VIII aided the entrance of Protestant beliefs into England when he
A) allowed Martin Luther to journey to England.
B) broke England's ties with the Roman Catholic Church.
C) removed himself as the head of the Church of England.
D) ordered John Calvin to go to Switzerland.
E) supported the Puritans.
A) allowed Martin Luther to journey to England.
B) broke England's ties with the Roman Catholic Church.
C) removed himself as the head of the Church of England.
D) ordered John Calvin to go to Switzerland.
E) supported the Puritans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Puritan religious beliefs allowed all of the following except
A) drinking alcohol.
B) eating plentifully.
C) challenging religious authority.
D) making love discreetly.
E) singing songs.
A) drinking alcohol.
B) eating plentifully.
C) challenging religious authority.
D) making love discreetly.
E) singing songs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Mayflower Compact can be best described as a(n)
A) agreement to follow the dictates of Parliament.
B) document that allowed women limited participation in government.
C) constitution that established a working government.
D) complex agreement to form an oligarchy.
E) promising step toward genuine self-government.
A) agreement to follow the dictates of Parliament.
B) document that allowed women limited participation in government.
C) constitution that established a working government.
D) complex agreement to form an oligarchy.
E) promising step toward genuine self-government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Initially, the Massachusetts Bay Colony enjoyed all of the following advantages except that of
A) being a well-equipped expedition.
B) starting off on a larger scale than any other English colony.
C) receiving many fairly prosperous and educated immigrants.
D) receiving a majority of the Puritans coming to the New World.
E) a shared purpose among the first settlers.
A) being a well-equipped expedition.
B) starting off on a larger scale than any other English colony.
C) receiving many fairly prosperous and educated immigrants.
D) receiving a majority of the Puritans coming to the New World.
E) a shared purpose among the first settlers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All of the following were true of Roger Williams except
A) he was a personable and popular Salem minister.
B) he was not a Separatist and advocated reconciliation with the Church of England.
C) aided by Indians, he fled the Puritan community and established Rhode Island in 1636.
D) he challenged the legality of the Bay Colony's charter.
E) he denied the authority of the civil government to regulate religious behavior.
A) he was a personable and popular Salem minister.
B) he was not a Separatist and advocated reconciliation with the Church of England.
C) aided by Indians, he fled the Puritan community and established Rhode Island in 1636.
D) he challenged the legality of the Bay Colony's charter.
E) he denied the authority of the civil government to regulate religious behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As the head of Dominion of New England, Sir Edmund Andros was all of the following except
A) an able military man.
B) conscientious.
C) a Puritan.
D) tactless.
E) a leader who restricted the press.
A) an able military man.
B) conscientious.
C) a Puritan.
D) tactless.
E) a leader who restricted the press.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
People who flouted the authority of the Puritan clergy in Massachusetts Bay were subject to which of the following punishments?
A) Fines
B) Floggings
C) Banishment
D) Death
E) All of these
A) Fines
B) Floggings
C) Banishment
D) Death
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One of the traits that made Quakers unpopular in England was
A) their refusal to do military service.
B) the high pay given their clergy.
C) their support of slavery.
D) their violent treatment of their enemies.
E) their refusal to hold public office.
A) their refusal to do military service.
B) the high pay given their clergy.
C) their support of slavery.
D) their violent treatment of their enemies.
E) their refusal to hold public office.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these is NOT a true statement about the fate of Anne Hutchinson?
A) She was banished from the Massachusetts Bay Colony for her beliefs.
B) She was pregnant when she headed with her family for Rhode Island.
C) She and most of her family members were killed by Indians in New York.
D) John Winthrop saw "God's hand" in her fate.
E) She preached to fellow residents of Salem.
A) She was banished from the Massachusetts Bay Colony for her beliefs.
B) She was pregnant when she headed with her family for Rhode Island.
C) She and most of her family members were killed by Indians in New York.
D) John Winthrop saw "God's hand" in her fate.
E) She preached to fellow residents of Salem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
As a result of England's Glorious Revolution
A) the Dominion of the New World collapsed.
B) Sir Edmund Andros gained control over Massachusetts.
C) Massachusetts regained its original charter.
D) opposition to English rule in the colonies subsided.
E) James II regained his legitimate right to the crown.
A) the Dominion of the New World collapsed.
B) Sir Edmund Andros gained control over Massachusetts.
C) Massachusetts regained its original charter.
D) opposition to English rule in the colonies subsided.
E) James II regained his legitimate right to the crown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the English gained control over New Netherland
A) the autocratic spirit survived.
B) democracy replaced the old autocratic system.
C) the colony grew quickly.
D) new leaders distributed land grants in a more democratic fashion.
E) they did so with great bloodshed.
A) the autocratic spirit survived.
B) democracy replaced the old autocratic system.
C) the colony grew quickly.
D) new leaders distributed land grants in a more democratic fashion.
E) they did so with great bloodshed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to Anne Hutchinson, a dissenter in Massachusetts Bay
A) predestination was not a valid idea.
B) the truly saved need not bother to obey the laws of God or man.
C) antinomianism was heresy.
D) direct revelation from God was impossible.
E) a person needs only to obey the law of God.
A) predestination was not a valid idea.
B) the truly saved need not bother to obey the laws of God or man.
C) antinomianism was heresy.
D) direct revelation from God was impossible.
E) a person needs only to obey the law of God.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During the early years of colonization in the New World, England
A) closely controlled its colonies.
B) maintained an excellent relationship with the Indians.
C) paid little attention to its colonies.
D) made sure all the colonies had royal charters.
E) began the importation of African slaves in large numbers.
A) closely controlled its colonies.
B) maintained an excellent relationship with the Indians.
C) paid little attention to its colonies.
D) made sure all the colonies had royal charters.
E) began the importation of African slaves in large numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Roger Williams' beliefs included all of the following except
A) breaking away from the Church of England.
B) denying Catholics and Jews complete religious freedom in Rhode Island.
C) condemning the taking of Indian land without fair compensation.
D) denying the authority of the civil government to regulate religious matters.
E) challenging the legality of Massachusetts Bay's charter.
A) breaking away from the Church of England.
B) denying Catholics and Jews complete religious freedom in Rhode Island.
C) condemning the taking of Indian land without fair compensation.
D) denying the authority of the civil government to regulate religious matters.
E) challenging the legality of Massachusetts Bay's charter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Dutch colony of New Netherland (later New York)
A) allowed only Dutch immigrants to settle there.
B) was established for its quick profit of fur trading.
C) tolerated Quakers from nearby Pennsylvania.
D) supported free speech and other democratic practices.
E) All of these
A) allowed only Dutch immigrants to settle there.
B) was established for its quick profit of fur trading.
C) tolerated Quakers from nearby Pennsylvania.
D) supported free speech and other democratic practices.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The physical growth of English New York was slowed because
A) of the Indian threat.
B) of an unhealthy climate.
C) the Dutch engaged in guerrilla warfare.
D) of the monopolistic land policies of the aristocrats.
E) of the French threat.
A) of the Indian threat.
B) of an unhealthy climate.
C) the Dutch engaged in guerrilla warfare.
D) of the monopolistic land policies of the aristocrats.
E) of the French threat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Puritans who founded the city of New Haven had a goal of
A) establishing it in tribute to Charles II.
B) creating a haven for Quakers and other religious refugees.
C) maintaining a democratic government controlled by its citizens.
D) becoming self-supporting and prosperous in the fishing and fur trades.
E) setting up an even closer church-state alliance than in Massachusetts.
A) establishing it in tribute to Charles II.
B) creating a haven for Quakers and other religious refugees.
C) maintaining a democratic government controlled by its citizens.
D) becoming self-supporting and prosperous in the fishing and fur trades.
E) setting up an even closer church-state alliance than in Massachusetts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The New England Confederation
A) included all the New England colonies.
B) was designed to bolster colonial defense.
C) led the American colonies to seek independence from England.
D) was created by the English government to streamline its administration of the colonies.
E) was an economic and trade alliance.
A) included all the New England colonies.
B) was designed to bolster colonial defense.
C) led the American colonies to seek independence from England.
D) was created by the English government to streamline its administration of the colonies.
E) was an economic and trade alliance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
King Philip's War resulted in all of the following except
A) the lasting defeat of New England's Indians.
B) the immediate westward march of English settlement in New England.
C) the death of hundreds of colonists and many more Indians.
D) the destruction of 12 Puritan towns.
E) the beheading of Wampanoag Chief Metacom and the sale of his wife and son into slavery
A) the lasting defeat of New England's Indians.
B) the immediate westward march of English settlement in New England.
C) the death of hundreds of colonists and many more Indians.
D) the destruction of 12 Puritan towns.
E) the beheading of Wampanoag Chief Metacom and the sale of his wife and son into slavery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The New England Indians' only hope for resisting English encroachment lay in
A) acquiring English muskets.
B) enlisting the aid of the French.
C) intertribal unity against the English.
D) building fortifications.
E) allying themselves with the Dutch.
A) acquiring English muskets.
B) enlisting the aid of the French.
C) intertribal unity against the English.
D) building fortifications.
E) allying themselves with the Dutch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
After the Pequot War, Puritan efforts to convert Indians to Christianity can best be described as
A) vigorous but unsuccessful.
B) more zealous than those made by Catholics, but still unsuccessful.
C) filling "praying towns" with hundreds of Indians.
D) feeble, not equaling that of the Spanish or the French.
E) very successful.
A) vigorous but unsuccessful.
B) more zealous than those made by Catholics, but still unsuccessful.
C) filling "praying towns" with hundreds of Indians.
D) feeble, not equaling that of the Spanish or the French.
E) very successful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As a colony, Rhode Island became known for
A) its poor treatment of Indians.
B) unified religious beliefs.
C) support of special privilege.
D) never having secured a charter from Parliament.
E) individualistic and independent attitudes.
A) its poor treatment of Indians.
B) unified religious beliefs.
C) support of special privilege.
D) never having secured a charter from Parliament.
E) individualistic and independent attitudes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
All of the following were characteristics of New Netherland except
A) New England immigrants made up half its population of 10,000 in 1664.
B) its development was not a priority of the Dutch.
C) it took on an aristocratic tint, including feudal estates known as patroonships.
D) its main seaport city was the cosmopolitan New Amsterdam,
E) it was established by the Dutch East India Company.
A) New England immigrants made up half its population of 10,000 in 1664.
B) its development was not a priority of the Dutch.
C) it took on an aristocratic tint, including feudal estates known as patroonships.
D) its main seaport city was the cosmopolitan New Amsterdam,
E) it was established by the Dutch East India Company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
As a result of Sir Edmund Andros's rule
A) the power of town meetings was curbed.
B) officials tried to enforce the Navigation Laws.
C) taxes were levied without the consent of elected representatives.
D) smuggling was suppressed.
E) All of these
A) the power of town meetings was curbed.
B) officials tried to enforce the Navigation Laws.
C) taxes were levied without the consent of elected representatives.
D) smuggling was suppressed.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Recently, historians have increasingly viewed the colonial period as one
A) in which the Puritans had been overlooked.
B) of contact and adaptation between European and native populations.
C) in which the settlement of the Caribbean has been stressed too much.
D) in which economic ambition was the main reason all colonists came.
E) All of these
A) in which the Puritans had been overlooked.
B) of contact and adaptation between European and native populations.
C) in which the settlement of the Caribbean has been stressed too much.
D) in which economic ambition was the main reason all colonists came.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700
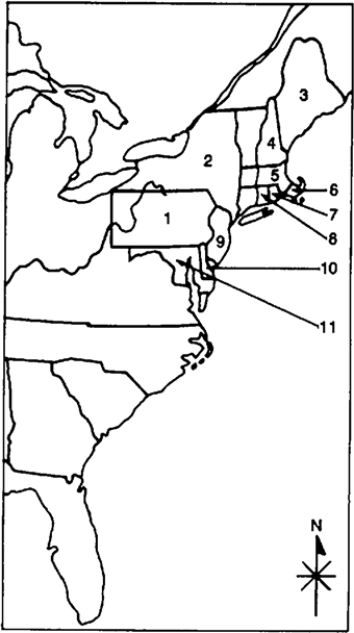
____ Massachusetts Bay
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Massachusetts Bay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Arrange the following in chronological order: the founding of (A)New York, (B)Massachusetts Bay, (C)Pennsylvania, and (D)Plymouth.
A) C, B, A, D
B) B, D, C, A
C) A, C, D, B
D) D, B, A, C
E) A, C, B, D
A) C, B, A, D
B) B, D, C, A
C) A, C, D, B
D) D, B, A, C
E) A, C, B, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Factors leading to the first major European migration include
A) a population explosion.
B) economic depression.
C) better quality oceangoing vessels.
D) religious repression.
E) the use of African slaves.
A) a population explosion.
B) economic depression.
C) better quality oceangoing vessels.
D) religious repression.
E) the use of African slaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Pennsylvania
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Pennsylvania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Pequot War of 1637 resulted in
A) the abolition of Indian "praying towns."
B) the virtual annihilation of the Pequots.
C) four decades of uneasy peace between the Puritans and the Indians.
D) praise for the colonists from people in England for having dealt effectively with the Indians.
E) better relations with the remaining Indians.
A) the abolition of Indian "praying towns."
B) the virtual annihilation of the Pequots.
C) four decades of uneasy peace between the Puritans and the Indians.
D) praise for the colonists from people in England for having dealt effectively with the Indians.
E) better relations with the remaining Indians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Puritans
A) were Calvinists.
B) thought that the Church of England should be open to all comers.
C) especially attracted England's economically depressed.
D) thought that the Protestant Reformation was bringing too much change too quickly.
E) supported the Separatists.
A) were Calvinists.
B) thought that the Church of England should be open to all comers.
C) especially attracted England's economically depressed.
D) thought that the Protestant Reformation was bringing too much change too quickly.
E) supported the Separatists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Indian policy in early Pennsylvania can be best described as
A) extremely harsh.
B) bad at first but improving later.
C) influenced mainly by the state-supported church.
D) fair.
E) None of these
A) extremely harsh.
B) bad at first but improving later.
C) influenced mainly by the state-supported church.
D) fair.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Pennsylvania
A) introduced an unusually liberal land policy that attracted a heavy flow of immigrants.
B) had fertile soil that produced surplus grain for export.
C) was first settled by small colonies of Swedes.
D) was founded with the intention of making a profit.
E) was named after William Penn.
A) introduced an unusually liberal land policy that attracted a heavy flow of immigrants.
B) had fertile soil that produced surplus grain for export.
C) was first settled by small colonies of Swedes.
D) was founded with the intention of making a profit.
E) was named after William Penn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Delaware
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Delaware

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Pennsylvania was the
A) best advertised.
B) most lied about.
C) slowest to attract settlers.
D) only settlement with royal colony status.
E) All of these
A) best advertised.
B) most lied about.
C) slowest to attract settlers.
D) only settlement with royal colony status.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Separatists
A) were radical Puritans.
B) were also known as Pilgrims.
C) authored the Mayflower Compact.
D) sought to reform the Church of England from within.
E) were led by John Winthrop.
A) were radical Puritans.
B) were also known as Pilgrims.
C) authored the Mayflower Compact.
D) sought to reform the Church of England from within.
E) were led by John Winthrop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New Hampshire
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New Hampshire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Economically, the colony of Pennsylvania
A) got off to a very slow start.
B) never prospered.
C) received much help from New York.
D) became profitable very quickly.
E) had extensive plantations.
A) got off to a very slow start.
B) never prospered.
C) received much help from New York.
D) became profitable very quickly.
E) had extensive plantations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New York
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New York

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All of the following are true statements about Quakers except
A) they were shrewd businessmen.
B) they built simple meetinghouses and believed they were all children in the sight of God.
C) they advocated passive resistance and turning the other cheek against their enemies.
D) they swore solemn oaths of faith and devotion.
E) they trusted Indians in Pennsylvania as babysitters.
A) they were shrewd businessmen.
B) they built simple meetinghouses and believed they were all children in the sight of God.
C) they advocated passive resistance and turning the other cheek against their enemies.
D) they swore solemn oaths of faith and devotion.
E) they trusted Indians in Pennsylvania as babysitters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Rhode Island
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Rhode Island

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Plymouth
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Plymouth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New Jersey
The Settlement of the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New Jersey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The middle colonies were notable for their
A) lack of good river transportation.
B) unusual degree of democratic control.
C) lack of industry.
D) status as the least "American" of the colonies.
E) established churches.
A) lack of good river transportation.
B) unusual degree of democratic control.
C) lack of industry.
D) status as the least "American" of the colonies.
E) established churches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700
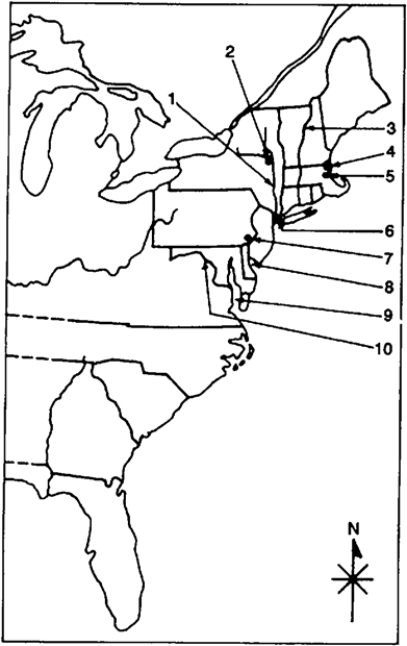
____ Delaware Bay
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Delaware Bay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Albany
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Albany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
John Cotton
John Cotton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Roger Williams
Roger Williams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New York City
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ New York City

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Thomas Hooker
Thomas Hooker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
William Penn
William Penn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
William Bradford
William Bradford

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
John Calvin
John Calvin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
King Philip (Metacom)
King Philip (Metacom)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Philadelphia
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Philadelphia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
John Winthrop
John Winthrop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Connecticut River
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Connecticut River

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Sir Edmund Andros
Sir Edmund Andros

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Hudson River
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Hudson River

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Salem
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Salem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Boston
Key Locales of Political, Economic, and Religious Ferment and Development in the Northern Colonies, 1619-1700

____ Boston

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



