Deck 22: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
Below is a proposed method for resolving a racemic mixture of (R)- and (S)-phenylalanine. Upon separation of the products, will this method produce (R)- or (S)-phenylalanine? 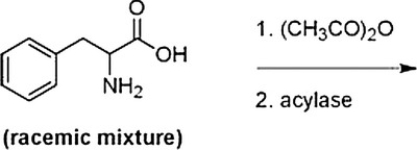
A) (S)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of D-amino acids.
B) (R)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of D-amino acids.
C) (S)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of L-amino acids.
D) (R)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of L-amino acids.

A) (S)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of D-amino acids.
B) (R)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of D-amino acids.
C) (S)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of L-amino acids.
D) (R)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of L-amino acids.
(S)-Phenylalanine is produced since the acylase only hydrolyzes the amides of L-amino acids.
2
What is the appropriate sequence of reaction conditions used to synthesize valine from acetamidomalonic ester? 
A) (1) NaOCH2CH3; (2) (CH3)2CH2CHBr; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
B) (1) NaOCH2CH3; (2) (CH3)2CHBr; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
C) (1) NaOH; (2) (CH3)2CHBr; (3) Cl2, H2O, heat
D) (1) NaOH; (2) CH3CH2CH2Br; (3) HCl, H2O, heat

A) (1) NaOCH2CH3; (2) (CH3)2CH2CHBr; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
B) (1) NaOCH2CH3; (2) (CH3)2CHBr; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
C) (1) NaOH; (2) (CH3)2CHBr; (3) Cl2, H2O, heat
D) (1) NaOH; (2) CH3CH2CH2Br; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
(1) NaOCH2CH3; (2) (CH3)2CHBr; (3) HCl, H2O, heat
3
Which of the following correctly describes the Merrifield synthesis?
A) It uses BOC (tert-butoxycarbonyl) as a protecting group for peptide synthesis.
B) It uses a solid phase technique for the synthesis of peptides.
C) It uses aqueous phase techniques for the synthesis of large polypeptides.
D) It uses DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) to form the amide bond in a peptide synthesis.
A) It uses BOC (tert-butoxycarbonyl) as a protecting group for peptide synthesis.
B) It uses a solid phase technique for the synthesis of peptides.
C) It uses aqueous phase techniques for the synthesis of large polypeptides.
D) It uses DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) to form the amide bond in a peptide synthesis.
It uses BOC (tert-butoxycarbonyl) as a protecting group for peptide synthesis.
4
Reaction of a polypeptide, composed of 12 amino acids, with carboxypeptidase A releases Met (C-terminal amino acid). The polypeptide undergoes partial hydrolysis to give 12 groups of peptides. Use the groups of overlapping amino acids to determine the proper sequence of this polypeptide.Note: Since these lists of peptides are separated by commas, they are not necessarily in the proper sequence.Ser, Lys, Trp-5. Met, Ala, Gly- 9. Lys, Ser
Gly, His, Ala-6. Ser, Lys, Val -10. Glu, His, Val
Glu, Val, Ser-7. Glu, His-11. Trp, Leu, Glu
Leu, Glu, Ser-8. Leu, Lys, Trp-12. Ala, Met
A) Met-Ala-Gly-Glu-His-Ser-Val-Lys-Trp-Leu-Glu-Ser
B) Met-Ala-Gly-His-Glu-Val-Ser-Lys-Trp-Leu-Glu-Ser
C) Ser-Lys-Leu-Trp-Lys-Ser-Val-His-Glu-Gly-Ala-Met
D) Ser-Glu-Leu-Trp-Lys-Ser-Val-Glu-His-Gly-Ala-Met
Gly, His, Ala-6. Ser, Lys, Val -10. Glu, His, Val
Glu, Val, Ser-7. Glu, His-11. Trp, Leu, Glu
Leu, Glu, Ser-8. Leu, Lys, Trp-12. Ala, Met
A) Met-Ala-Gly-Glu-His-Ser-Val-Lys-Trp-Leu-Glu-Ser
B) Met-Ala-Gly-His-Glu-Val-Ser-Lys-Trp-Leu-Glu-Ser
C) Ser-Lys-Leu-Trp-Lys-Ser-Val-His-Glu-Gly-Ala-Met
D) Ser-Glu-Leu-Trp-Lys-Ser-Val-Glu-His-Gly-Ala-Met

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Iosmerase performs the following function:
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
C) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
D) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
C) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
D) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Amino acid synthesis is possible by allexcept one of the pathways listed. Which isnot a synthetic pathway for amino acids?
A) SN2 reaction using an a-halo carboxylic acid with ammonia as the nucleophile
B) Reaction of NH4Cl and NaCN with an aldehyde followed by an acidic work-up
C) Nucleophilic addition of NH3 to an aldehyde followed by addition of cyanide to the imine, and, finally, hydrolysis
D) Amination of malonic ester followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation
A) SN2 reaction using an a-halo carboxylic acid with ammonia as the nucleophile
B) Reaction of NH4Cl and NaCN with an aldehyde followed by an acidic work-up
C) Nucleophilic addition of NH3 to an aldehyde followed by addition of cyanide to the imine, and, finally, hydrolysis
D) Amination of malonic ester followed by hydrolysis and decarboxylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Transferase performs the following function:
A) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
B) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
A) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
B) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Oxidoreductase performs the following function:
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Below is a 2D chromatogram that shows the separation of five amino acids. In this technique, the amino acid mixture is first separated by chromatography using a polar solvent system. Then the plate is rotated 90°, and the amino acids are further separated by electrophoresis. Identify the spots obtained from a mixture of Trp, Glu, Lys, Ile and Thr. A table with isoelectric points is included to aid in solving this problem.
Amino acid-pI value
Trp-5.9
Glu-3.2
Lys-9.7
Ile-6.0
Thr-5.6
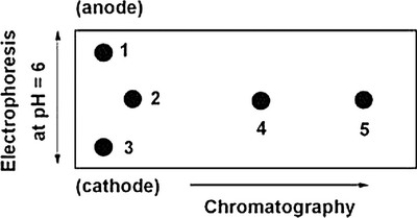
A) 1=Glu, 2=Ile, 3=Lys, 4=Trp, 5=Thr
B) 1=Lys, 2=Thr, 3=Glu, 4=Trp, 5=Ile
C) 1=Glu, 2=Thr, 3=Lys, 4=Trp, 5=Ile
D) 1=Lys, 2=Ile, 3=Glu, 4=Trp, 5=Thr
Amino acid-pI value
Trp-5.9
Glu-3.2
Lys-9.7
Ile-6.0
Thr-5.6

A) 1=Glu, 2=Ile, 3=Lys, 4=Trp, 5=Thr
B) 1=Lys, 2=Thr, 3=Glu, 4=Trp, 5=Ile
C) 1=Glu, 2=Thr, 3=Lys, 4=Trp, 5=Ile
D) 1=Lys, 2=Ile, 3=Glu, 4=Trp, 5=Thr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Hydrolase performs the following function:
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
A) Catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters, amides, and other functional groups that are cleaved when they react with water
B) Catalyzes the transfer of a group from one molecule to another
C) Catalyzes the conversion of one isomer to another
D) Catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following compounds is not an amino acid? 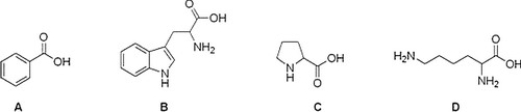
A) A
B) B
C) D
D) C

A) A
B) B
C) D
D) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



