Deck 19: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
1
What is the major product of the following reaction? 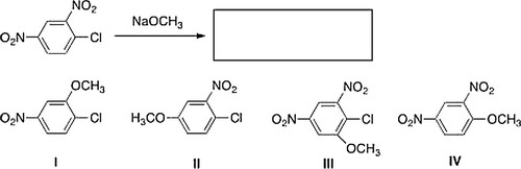
A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II

A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II
IV
2
How can polyalkylation be minimized in Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
A) Use an alkyl halide without a Lewis acid catalyst.
B) Use a large excess of the Lewis acid catalyst.
C) Use a large excess of alkyl halide relative to the aromatic compound.
D) Use a large excess of benzene relative to the alkyl halide.
A) Use an alkyl halide without a Lewis acid catalyst.
B) Use a large excess of the Lewis acid catalyst.
C) Use a large excess of alkyl halide relative to the aromatic compound.
D) Use a large excess of benzene relative to the alkyl halide.
Use a large excess of benzene relative to the alkyl halide.
3
Which of the following statements about nucleophilic aromatic substitution isnot true?
A) Electron-withdrawing groups stabilize the intermediate carbanion, and lower the energy of the transition state.
B) When a nitro group is located meta to the halogen, the negative charge of the intermediate carbanion can be delocalized onto the NO2 group, thus stabilizing it.
C) Increasing the number of electron-withdrawing groups increases the reactivity of the aryl halide.
D) Increasing the electronegativity of the halogen increases the reactivity of the aryl halide.
A) Electron-withdrawing groups stabilize the intermediate carbanion, and lower the energy of the transition state.
B) When a nitro group is located meta to the halogen, the negative charge of the intermediate carbanion can be delocalized onto the NO2 group, thus stabilizing it.
C) Increasing the number of electron-withdrawing groups increases the reactivity of the aryl halide.
D) Increasing the electronegativity of the halogen increases the reactivity of the aryl halide.
When a nitro group is located meta to the halogen, the negative charge of the intermediate carbanion can be delocalized onto the NO2 group, thus stabilizing it.
4
What is the product of the following reaction? 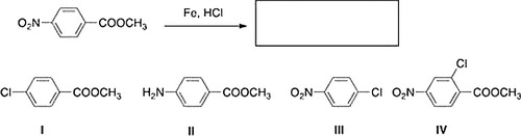
A) II
B) I
C) III
D) IV

A) II
B) I
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the major product of the following reaction? 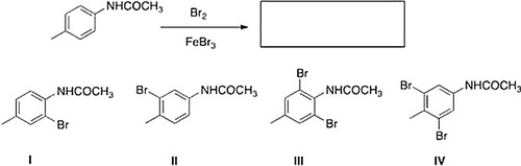
A) IV
B) II
C) I
D) III

A) IV
B) II
C) I
D) III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the product of the following reaction? 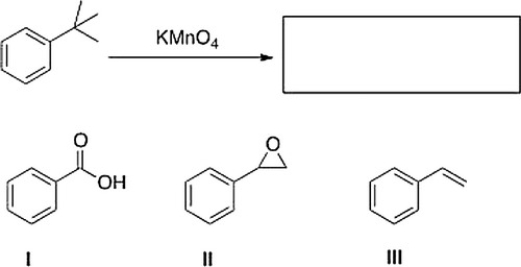
A) I
B) None of these
C) III
D) II

A) I
B) None of these
C) III
D) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why is the nitro group ameta director?
A) Because it is sterically very large
B) Because it removes more electron density from theortho andpara positions than themeta position, thus deactivating themeta position less
C) Because it adds electron density to themeta position, thus activating it
D) Because it stabilizes the intermediate cation
A) Because it is sterically very large
B) Because it removes more electron density from theortho andpara positions than themeta position, thus deactivating themeta position less
C) Because it adds electron density to themeta position, thus activating it
D) Because it stabilizes the intermediate cation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What reagents would be necessary to produce the following product from benzene? 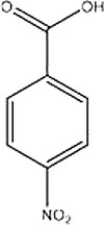
A) KMnO4 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3.CH3Cl, AlCl3
B) CH3Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. KMnO4
C) HNO3, H2SO4 2. CH3Cl, AlCl3 3. KMnO4
D) KMnO4 2. CH3Cl, AlCl3 3. HNO3, H2SO4

A) KMnO4 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3.CH3Cl, AlCl3
B) CH3Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. KMnO4
C) HNO3, H2SO4 2. CH3Cl, AlCl3 3. KMnO4
D) KMnO4 2. CH3Cl, AlCl3 3. HNO3, H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is a major problem with Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
A) The products coordinate with the aluminum chloride.
B) The starting material is frequently over-alkylated.
C) It requires high temperatures.
D) The conditions are too acidic.
A) The products coordinate with the aluminum chloride.
B) The starting material is frequently over-alkylated.
C) It requires high temperatures.
D) The conditions are too acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What reagents would be necessary to produce the following product from benzene? 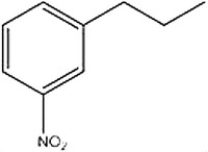
A) Zn(Hg), HCl 2. CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 3. HNO3, H2SO4
B) CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. Zn(Hg), HCl 3. HNO3, H2SO4
C) CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. Zn(Hg), HCl
D) HNO3, H2SO4 2. CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 3. Zn(Hg), HCl

A) Zn(Hg), HCl 2. CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 3. HNO3, H2SO4
B) CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. Zn(Hg), HCl 3. HNO3, H2SO4
C) CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. Zn(Hg), HCl
D) HNO3, H2SO4 2. CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 3. Zn(Hg), HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about nucleophilic aromatic substitution is true?
A) For the elimination-addition pathway, the nucleophile becomes attached only at the site bearing the leaving group.
B) For the addition-elimination pathway, the nucleophile may become attached either at the site bearing the leaving group or at the site bearing the ortho hydrogen atom.
C) The elimination-addition mechanism is not as common as the addition-elimination mechanism.
D) In the addition-elimination mechanism, the aromatic ring first accepts a pair of electrons from a nucleophile to form a cationic intermediate.
A) For the elimination-addition pathway, the nucleophile becomes attached only at the site bearing the leaving group.
B) For the addition-elimination pathway, the nucleophile may become attached either at the site bearing the leaving group or at the site bearing the ortho hydrogen atom.
C) The elimination-addition mechanism is not as common as the addition-elimination mechanism.
D) In the addition-elimination mechanism, the aromatic ring first accepts a pair of electrons from a nucleophile to form a cationic intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the product of the following reaction? 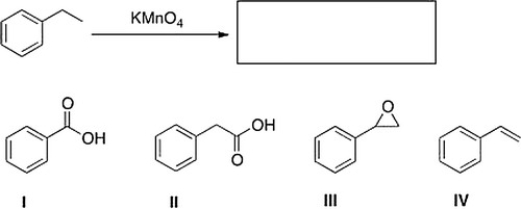
A) IV
B) III
C) II
D) I

A) IV
B) III
C) II
D) I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



