Deck 16: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at the Α Carbon
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at the Α Carbon
1
Which of the following is the least acidic compound? 
A) II
B) I
C) III
D) IV

A) II
B) I
C) III
D) IV
I
2
Treatment of 2-hexanone with NaOCH2CH3 followed by CH3Br affords compound X (C7H14O) as the major product. X shows a strong absorption in the IR spectrum at 1713 cm?1, and its 1H NMR data is given below. What is the structure of X?
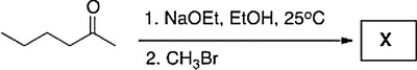
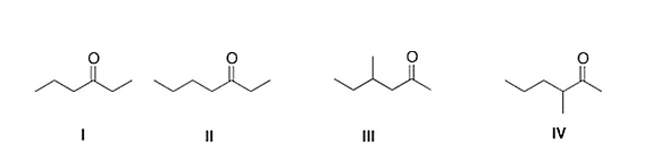
A) IV
B) III
C) II
D) I


A) IV
B) III
C) II
D) I
IV
3
The reaction below is a direct enolate alkylation. It has been found that this reaction only works well with unhindered methyl and 1° alkyl halides. Pick the statement that best explains this observation. 
A) Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN1 reactions.
B) The nucleophilic enolate requires a reaction center that has a positive charge.
C) Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN2 reactions.
D) Methyl and 1° alkyl halides can form carbocations that can readily react with the nucleophilic enolate.

A) Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN1 reactions.
B) The nucleophilic enolate requires a reaction center that has a positive charge.
C) Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN2 reactions.
D) Methyl and 1° alkyl halides can form carbocations that can readily react with the nucleophilic enolate.
Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN2 reactions.
4
Which of the following compound would most likely undergo racemization under basic conditions?
A) (S)-4-Iodo-2-pentanone
B) (R)-5-Iodo-5-bromo-2-pentanone
C) (R)-3-Iodo-2-pentanone
D) (R)-4-Iodo-2-pentanone
A) (S)-4-Iodo-2-pentanone
B) (R)-5-Iodo-5-bromo-2-pentanone
C) (R)-3-Iodo-2-pentanone
D) (R)-4-Iodo-2-pentanone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following molecule is called 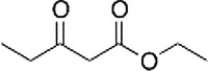
A) an ethyl acetoacetate.
B) a 1,3-diketopentanoate.
C) a b-keto ester.
D) a diethyl malonate.

A) an ethyl acetoacetate.
B) a 1,3-diketopentanoate.
C) a b-keto ester.
D) a diethyl malonate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the product of the following reaction? 
A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II

A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Select the appropriate sequence of reactions to accomplish the following synthesis. ![<strong>Select the appropriate sequence of reactions to accomplish the following synthesis. </strong> A) [1] LDA; [2] BrCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br; [3] NaOEt B) [1] Br<sub>2</sub>, CH<sub>3</sub>CO<sub>2</sub>H; [2] Li<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>, LiBr, DMF; [3] CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br C) [1] Br<sub>2</sub>, CH<sub>3</sub>CO<sub>2</sub>H; [2] Mg, Et<sub>2</sub>O; [3] CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br D) [1] NaOEt; [2] BrCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br; [3] LDA](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMG1035/11ee4665_5cff_24aa_862d_cbbaf637032e_TBMG1035_00.jpg)
A) [1] LDA; [2] BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br; [3] NaOEt
B) [1] Br2, CH3CO2H; [2] Li2CO3, LiBr, DMF; [3] CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
C) [1] Br2, CH3CO2H; [2] Mg, Et2O; [3] CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
D) [1] NaOEt; [2] BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br; [3] LDA
![<strong>Select the appropriate sequence of reactions to accomplish the following synthesis. </strong> A) [1] LDA; [2] BrCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br; [3] NaOEt B) [1] Br<sub>2</sub>, CH<sub>3</sub>CO<sub>2</sub>H; [2] Li<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>, LiBr, DMF; [3] CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br C) [1] Br<sub>2</sub>, CH<sub>3</sub>CO<sub>2</sub>H; [2] Mg, Et<sub>2</sub>O; [3] CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br D) [1] NaOEt; [2] BrCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Br; [3] LDA](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMG1035/11ee4665_5cff_24aa_862d_cbbaf637032e_TBMG1035_00.jpg)
A) [1] LDA; [2] BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br; [3] NaOEt
B) [1] Br2, CH3CO2H; [2] Li2CO3, LiBr, DMF; [3] CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
C) [1] Br2, CH3CO2H; [2] Mg, Et2O; [3] CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
D) [1] NaOEt; [2] BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br; [3] LDA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the product of the following reaction? 
A) II
B) I
C) IV
D) III

A) II
B) I
C) IV
D) III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the major product of the following reaction? 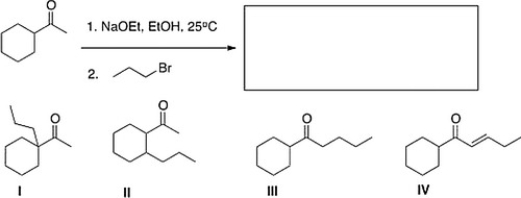
A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II

A) IV
B) I
C) III
D) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the most acidic compound? 
A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) II

A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following organic molecules will undergo decarboxylation to form an amine?
A) Histidine
B) Isoamyl acetate
C) Ethyl acetoacetate
D) Pyridine
A) Histidine
B) Isoamyl acetate
C) Ethyl acetoacetate
D) Pyridine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Starting with cyclohexanone, how could you prepare the diketone below? 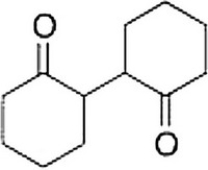
A) Convert cyclohexanone into the a-bromoketone and then react this with the enolate of cyclohexanone.
B) Convert cyclohexanone into an enamine with diethylamine and then react this with more cyclohexanone.
C) Treat cyclohexanone with a base under thermodynamic conditions.
D) Hydrogenate cyclohexanone with Raney nickel.

A) Convert cyclohexanone into the a-bromoketone and then react this with the enolate of cyclohexanone.
B) Convert cyclohexanone into an enamine with diethylamine and then react this with more cyclohexanone.
C) Treat cyclohexanone with a base under thermodynamic conditions.
D) Hydrogenate cyclohexanone with Raney nickel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



