Deck 14: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
1
What is the correct IUPAC name of the following compound? 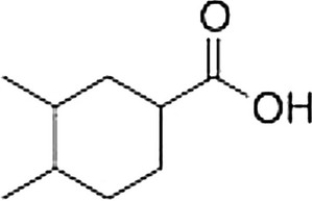
A) 4,5-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
B) 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
C) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanoic acid
D) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid

A) 4,5-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
B) 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
C) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanoic acid
D) 3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
3,4-Dimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
2
What two strong absorptions are characteristic of the IR spectrum of carboxylic acids?
A) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
B) A C=O absorption at 1600 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3000 cm-1.
C) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and a C-H absorption at 3000 cm-1.
D) A C-O absorption at 1500 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
A) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
B) A C=O absorption at 1600 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3000 cm-1.
C) A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and a C-H absorption at 3000 cm-1.
D) A C-O absorption at 1500 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
A C=O absorption at 1710 cm-1 and an O-H absorption at 2500-3500 cm-1.
3
What physical property and reaction type are used by extraction as useful techniques to separate and purify mixtures of compounds?
A) Physical property = density; reaction type = oxidation-reduction
B) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = acid-base reaction
C) Physical property = boiling point; reaction type = acid-base reaction
D) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = oxidation-reduction
A) Physical property = density; reaction type = oxidation-reduction
B) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = acid-base reaction
C) Physical property = boiling point; reaction type = acid-base reaction
D) Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = oxidation-reduction
Physical property = solubility differences; reaction type = acid-base reaction
4
What would happen if a mixture of benzoic acid and cyclohexanol dissolved in CH2Cl2 is treated with aqueous NaOH solution?
A) The salt of benzoic acid would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer while cyclohexanol would dissolve in the aqueous layer.
B) Benzoic acid would dissolve in the aqueous layer while cyclohexanol would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer.
C) The salt of benzoic acid would dissolve in the aqueous layer while cyclohexanol would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer.
D) Benzoic acid would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer, and cyclohexanol would dissolve in the aqueous layer.
A) The salt of benzoic acid would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer while cyclohexanol would dissolve in the aqueous layer.
B) Benzoic acid would dissolve in the aqueous layer while cyclohexanol would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer.
C) The salt of benzoic acid would dissolve in the aqueous layer while cyclohexanol would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer.
D) Benzoic acid would remain in the CH2Cl2 layer, and cyclohexanol would dissolve in the aqueous layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What would happen if a mixture of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) and NaCl is added to a separatory funnel containing H2O and CH2Cl2?
A) The benzoic acid would dissolve in the organic layer and the NaCl would dissolve in the water layer.
B) Both benzoic acid and NaCl would dissolve in the organic layer.
C) Both benzoic acid and NaCl would dissolve in the water layer.
D) The benzoic acid would dissolve in the water layer and the NaCl would dissolve in the organic layer.
A) The benzoic acid would dissolve in the organic layer and the NaCl would dissolve in the water layer.
B) Both benzoic acid and NaCl would dissolve in the organic layer.
C) Both benzoic acid and NaCl would dissolve in the water layer.
D) The benzoic acid would dissolve in the water layer and the NaCl would dissolve in the organic layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Where do the two noteworthy peaks of carboxylic acids appear in1HNMR spectra?
A) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
B) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
C) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
D) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
A) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
B) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 1-1.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
C) Between 10 and 12 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.
D) Between 6 and 9 ppm for the OH proton and 2-2.5 ppm for the protons on the a carbon to the carboxy group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why is the C-O single bond of a carboxylic acid shorter than the C-O single bond of an alcohol?
A) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp3 hybridized and has a lower percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
B) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
C) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
D) The carbon in the alcohol issp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that lengthens the C-O bond in the alcohol.
A) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp3 hybridized and has a lower percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
B) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
C) The carbon in the carboxylic acid issp hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that shortens the C-O bond in the carboxylic acid.
D) The carbon in the alcohol issp2 hybridized and has a higher percent s-character that lengthens the C-O bond in the alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the presence of strong acids, which of the oxygen atoms on the carboxyl group is preferentially protonated and why?
A) Protonation occurs at the hydroxyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate acid is stabilized by resonance.
B) Protonation occurs at the carbonyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate acid is stabilized by resonance.
C) Protonation occurs at the carbonyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate base is stabilized by the inductive effect.
D) Protonation occurs at the hydroxyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate base is stabilized by the inductive effect.
A) Protonation occurs at the hydroxyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate acid is stabilized by resonance.
B) Protonation occurs at the carbonyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate acid is stabilized by resonance.
C) Protonation occurs at the carbonyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate base is stabilized by the inductive effect.
D) Protonation occurs at the hydroxyl oxygen because the resulting conjugate base is stabilized by the inductive effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the correct IUPAC name of the following compound? 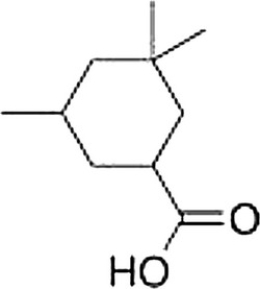
A) 3,5,5-Trimethylcyclohexanoic acid
B) 3,5,5-Trimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
C) 3,3,5-Trimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
D) 3,3,5-Trimethylcyclohexanoic acid

A) 3,5,5-Trimethylcyclohexanoic acid
B) 3,5,5-Trimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
C) 3,3,5-Trimethylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
D) 3,3,5-Trimethylcyclohexanoic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following reagents can accomplish the transformation below? ![<strong>Which of the following reagents can accomplish the transformation below? </strong> A) [1] LiAlH<sub>4</sub>, THF; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O B) PCC, CH<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> C) [1] O<sub>3</sub>; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O D) K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>O](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMG1035/11ee4665_5d00_3630_862d_b73de682c6aa_TBMG1035_00.jpg)
A) [1] LiAlH4, THF; [2] H2O
B) PCC, CH2Cl2
C) [1] O3; [2] H2O
D) K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reagents can accomplish the transformation below? </strong> A) [1] LiAlH<sub>4</sub>, THF; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O B) PCC, CH<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> C) [1] O<sub>3</sub>; [2] H<sub>2</sub>O D) K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>, H<sub>2</sub>O](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMG1035/11ee4665_5d00_3630_862d_b73de682c6aa_TBMG1035_00.jpg)
A) [1] LiAlH4, THF; [2] H2O
B) PCC, CH2Cl2
C) [1] O3; [2] H2O
D) K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the correct IUPAC name of the following compound? 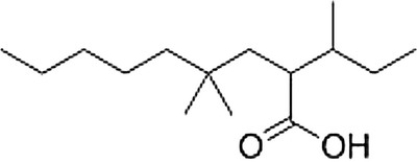
A) 4,4-Dimethyl-2-isobutylnonanoic acid
B) 2-sec-Butyl-4,4-dimethylnonanoic acid
C) 2-Isobutyl-4,4-dimethylnonanoic acid
D) 4,4-Dimethyl-2-sec-butylnonanoic acid

A) 4,4-Dimethyl-2-isobutylnonanoic acid
B) 2-sec-Butyl-4,4-dimethylnonanoic acid
C) 2-Isobutyl-4,4-dimethylnonanoic acid
D) 4,4-Dimethyl-2-sec-butylnonanoic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



