Deck 8: Muscle Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Muscle Physiology
1
Within a muscle fiber the contractile elements may constitute as much as ______ of the cell volume.
A) 50%
B) 60%
C) 70%
D) 80%
E) 90%
A) 50%
B) 60%
C) 70%
D) 80%
E) 90%
90%
2
The sarcomere lies within the boundaries of which of these structures?
A) A bands
B) H bands
C) I bands
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum
E) Z lines
A) A bands
B) H bands
C) I bands
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum
E) Z lines
Z lines
3
The principal role of calcium in skeletal muscle contraction is to
A) participate in the propagation of an action potential along the surface of the muscle fiber.
B) bind troponin, which in turn permits tropomyosin to uncover the cross-bridge binding site on the thin filament.
C) bind tropomyosin, which in turn permits troponin to uncover the cross-bridge binding site on the thin filament.
D) activate a calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, which in turn phosphorylates and activates myosin.
A) participate in the propagation of an action potential along the surface of the muscle fiber.
B) bind troponin, which in turn permits tropomyosin to uncover the cross-bridge binding site on the thin filament.
C) bind tropomyosin, which in turn permits troponin to uncover the cross-bridge binding site on the thin filament.
D) activate a calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, which in turn phosphorylates and activates myosin.
bind troponin, which in turn permits tropomyosin to uncover the cross-bridge binding site on the thin filament.
4
Which of the following observations confirms the sliding filament mechanism for muscle contraction?
A) As the sarcomere shortens, the H zone becomes smaller.
B) As the sarcomere shortens, the width of the A band remains the same.
C) As the sarcomere shortens, the I band becomes smaller.
D) Two of these.
E) All of these.
A) As the sarcomere shortens, the H zone becomes smaller.
B) As the sarcomere shortens, the width of the A band remains the same.
C) As the sarcomere shortens, the I band becomes smaller.
D) Two of these.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In skeletal muscle depolarization of the T tubule membrane causes
A) activation of Ca2+ ATPase pumps which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels
B) dihydropyridine to bind calcium channel receptors which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
C) activation of stretch-activated Ca2+ channels which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
D) activation of dihydroxypyridine receptors in membrane of the T tubule which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
E) ryanodine to bind calcium channel receptors which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
A) activation of Ca2+ ATPase pumps which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels
B) dihydropyridine to bind calcium channel receptors which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
C) activation of stretch-activated Ca2+ channels which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
D) activation of dihydroxypyridine receptors in membrane of the T tubule which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.
E) ryanodine to bind calcium channel receptors which triggers a rise in intracellular calcium levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following choices most accurately represents the sequence of steps occurring in the contraction cycle? The events numbered 1 through 6 may be used more than once.
1) Mysoin binds ATP
2) Mysoin hydrolyzes ATP and goes into cocked position
3) Myosin releases ADP and inorganic phosphate
4) Myosin binds actin filament
5) Power stroke
6) Myosin releases actin filament
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1
B) 1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
C) 1, 6, 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
D) 1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1
E) None of these.
1) Mysoin binds ATP
2) Mysoin hydrolyzes ATP and goes into cocked position
3) Myosin releases ADP and inorganic phosphate
4) Myosin binds actin filament
5) Power stroke
6) Myosin releases actin filament
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1
B) 1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
C) 1, 6, 2, 4, 3, 5, 1, 6
D) 1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One way one can purify myosin from other skeletal muscle proteins is to immobilize actin on a column, pour a mix of the muscle proteins through, wash first to get out the nonspecific proteins and then do a second to wash to obtain myosin. Based on the contraction cycle, your first wash should
A) include ATP, but the second wash should not.
B) not include ATP, but the second wash should.
C) include ATP, as should the second wash.
D) not include ATP, and neither should the second.
E) should include calcium, but the second one should not.
A) include ATP, but the second wash should not.
B) not include ATP, but the second wash should.
C) include ATP, as should the second wash.
D) not include ATP, and neither should the second.
E) should include calcium, but the second one should not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) Rigor mortis occurs as a result of a rise in intracellular calcium concentrations.
B) In skeletal muscle a single action potential lasts about 5-10 msec.
C) In skeletal muscle the relaxation time lasts slightly longer than the contractile time.
D) In skeletal muscle the contractile response ceases when the lateral sacs take up Ca2+.
E) A spring can move much faster than a muscle can contract.
A) Rigor mortis occurs as a result of a rise in intracellular calcium concentrations.
B) In skeletal muscle a single action potential lasts about 5-10 msec.
C) In skeletal muscle the relaxation time lasts slightly longer than the contractile time.
D) In skeletal muscle the contractile response ceases when the lateral sacs take up Ca2+.
E) A spring can move much faster than a muscle can contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following does NOT affect the tension that can be developed by a muscle fiber?
A) the number of motor units recruited
B) the frequency of action potentials conducted by the motor neuron
C) the length of the fiber at the onset of contraction
D) diameter of the muscle fiber
E) All of these affect tension development by a muscle fiber.
A) the number of motor units recruited
B) the frequency of action potentials conducted by the motor neuron
C) the length of the fiber at the onset of contraction
D) diameter of the muscle fiber
E) All of these affect tension development by a muscle fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Arthropod muscle differs from vertebrate muscle in that
A) a single muscle fiber may be innervated by multiple motor neurons.
B) a single motor neuron forms multiple synapses (multiterminal innervation) with a single muscle fiber.
C) development of muscle tension is modulated by inhibitory presynaptic inputs.
D) muscle fibers are innervated by both excitatory and inhibitory neurons.
E) All of these.
A) a single muscle fiber may be innervated by multiple motor neurons.
B) a single motor neuron forms multiple synapses (multiterminal innervation) with a single muscle fiber.
C) development of muscle tension is modulated by inhibitory presynaptic inputs.
D) muscle fibers are innervated by both excitatory and inhibitory neurons.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the length-tension curve shown, why does force decrease at sarcomere lengths less than lo? 
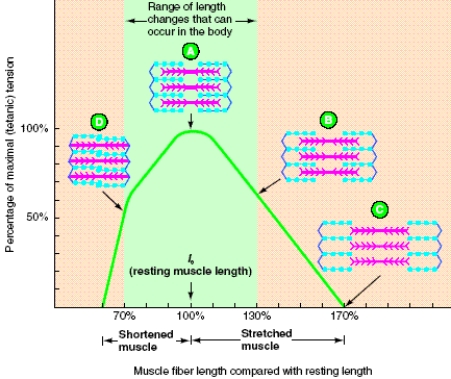
A) Not as much Ca2+ is released in a sarcomere with a length less than lo..
B) Interference between actin filaments originating from opposite ends of the sarcomere prevents maximal or optimal cross-bridge formation.
C) The muscle fiber runs out of ATP.
D) In this situation, Ca2+ availability and the position of the actin filaments are responsible for the decrease in muscle shortening because ATP will still be available.
E) All of these contribute to reduced muscle shortening in a sarcomere with a length less than lo.


A) Not as much Ca2+ is released in a sarcomere with a length less than lo..
B) Interference between actin filaments originating from opposite ends of the sarcomere prevents maximal or optimal cross-bridge formation.
C) The muscle fiber runs out of ATP.
D) In this situation, Ca2+ availability and the position of the actin filaments are responsible for the decrease in muscle shortening because ATP will still be available.
E) All of these contribute to reduced muscle shortening in a sarcomere with a length less than lo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is NOT true?
A) Muscle tension is produced internally within the sarcomeres.
B) Muscle tension is transmitted to the skeleton by tightening of the series-elastic component within the sarcomere.
C) It is possible for a skeletal muscle to produce movement without the muscle being attached to bone at both ends.
D) With respect to skeletal muscle, the load and velocity for shortening are inversely related for concentric contractions.
E) Actually, all of these are true statements.
A) Muscle tension is produced internally within the sarcomeres.
B) Muscle tension is transmitted to the skeleton by tightening of the series-elastic component within the sarcomere.
C) It is possible for a skeletal muscle to produce movement without the muscle being attached to bone at both ends.
D) With respect to skeletal muscle, the load and velocity for shortening are inversely related for concentric contractions.
E) Actually, all of these are true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An isometric contraction is a contraction in which
A) tension (or force) increases, but length stays the same.
B) tension (or force) stays the same, but length increases.
C) tension (or force) stays the same, and length stays the same.
D) tension (or force) stays the same, but length decreases.
E) tension (or force) decreases, and length decreases.
A) tension (or force) increases, but length stays the same.
B) tension (or force) stays the same, but length increases.
C) tension (or force) stays the same, and length stays the same.
D) tension (or force) stays the same, but length decreases.
E) tension (or force) decreases, and length decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In an isotonic, concentric contraction,
A) circular muscles (like those in the iris of the eye) contract, making a smaller aperture.
B) muscle length shortens while tension remains constant.
C) muscle lengths shorten, drawing objects closer to the body midline.
D) None of these.
A) circular muscles (like those in the iris of the eye) contract, making a smaller aperture.
B) muscle length shortens while tension remains constant.
C) muscle lengths shorten, drawing objects closer to the body midline.
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following ATP-dependent steps of the contraction-relaxation cycle could be accomplished with a non-hydrolyzable form of ATP such as ATP- -S for example?
A) cocking of the cross-bridge in anticipation of the power-stroke
B) release of actin by myosin
C) sequestration of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
D) All of these could be accomplished with ATP- -S.
E) None of these could be accomplished with ATP- -S.
A) cocking of the cross-bridge in anticipation of the power-stroke
B) release of actin by myosin
C) sequestration of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
D) All of these could be accomplished with ATP- -S.
E) None of these could be accomplished with ATP- -S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Creatine is an important metabolite in muscle physiology. Based on your understanding of its role in muscle energetics, which of the following statements is true?
A) The concentration of creatine rises as the concentration of ATP rises.
B) The concentration of creatine falls as the concentration of ATP rises.
C) The concentration of creatine is independent of the concentration of ATP.
D) The concentration of creatine rises as the concentration of ADP rises.
A) The concentration of creatine rises as the concentration of ATP rises.
B) The concentration of creatine falls as the concentration of ATP rises.
C) The concentration of creatine is independent of the concentration of ATP.
D) The concentration of creatine rises as the concentration of ADP rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How much of the energy available in ATP is lost as heat energy during an isotonic contraction by skeletal muscle?
A) 15%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 60%
E) 75%
A) 15%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 60%
E) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Fast muscle fibers differ from slow muscle fibers in that fast muscle fibers
A) are able to take up oxygen more quickly from the blood.
B) are equipped with a myosin-ATPase with more rapid kinetics.
C) are able to generate ATP more rapidly.
D) conduction action potentials more rapidly.
E) are recruited by the nervous system more rapidly.
A) are able to take up oxygen more quickly from the blood.
B) are equipped with a myosin-ATPase with more rapid kinetics.
C) are able to generate ATP more rapidly.
D) conduction action potentials more rapidly.
E) are recruited by the nervous system more rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An advantage of the large fiber diameter of fast glycolytic muscle is
A) it's correlated with its large volume, which in turn means it can hold more oxygen, and generate ATP aerobically.
B) it implies more cross-sectional area and the fiber can therefore hold more mitochondria, which means it can generate more ATP to power contraction.
C) it has less surface area relative to its volume, so it depolarizes more rapidly, since current has less distance to spread.
D) it has more myofibrils per unit length, which means it can form more
Cross-bridges, and generate more power (force).
E) none of these.
A) it's correlated with its large volume, which in turn means it can hold more oxygen, and generate ATP aerobically.
B) it implies more cross-sectional area and the fiber can therefore hold more mitochondria, which means it can generate more ATP to power contraction.
C) it has less surface area relative to its volume, so it depolarizes more rapidly, since current has less distance to spread.
D) it has more myofibrils per unit length, which means it can form more
Cross-bridges, and generate more power (force).
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which fibers will have a rich blood supply and a high myoglobin content?
A) slow oxidative fibers (Type I)
B) fast oxidative fibers (Type IIa)
C) fast glycolytic fibers (Type IIx)
D) fast and slow glycolytic fibers
E) fast and slow oxidative fibers
A) slow oxidative fibers (Type I)
B) fast oxidative fibers (Type IIa)
C) fast glycolytic fibers (Type IIx)
D) fast and slow glycolytic fibers
E) fast and slow oxidative fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In spinal reflex pathways, motor neurons receive inputs from
A) sensory afferents and/or internurons.
B) cortical neurons whose cell bodies reside in the primary motor cortex.
C) cortical neurons whose cell bodies reside in the somatosensory cortex.
D) cerebellar neurons.
E) brain stem neurons.
A) sensory afferents and/or internurons.
B) cortical neurons whose cell bodies reside in the primary motor cortex.
C) cortical neurons whose cell bodies reside in the somatosensory cortex.
D) cerebellar neurons.
E) brain stem neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Regarding the proprioceptors concerned with muscles, the ________ gives information about muscle length, whereas the ________ gives information about muscle tension.
A) muscle spindle; Golgi tendon organ
B) Golgi tendon organ; muscle spindle
C) muscle spindle; Golgi apparatus
D) Golgi apparatus; muscle spindle
E) None of these.
A) muscle spindle; Golgi tendon organ
B) Golgi tendon organ; muscle spindle
C) muscle spindle; Golgi apparatus
D) Golgi apparatus; muscle spindle
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Golgi tendon organs are
A) regulated by the activity of motor neurons.
B) activated by sensory input from the muscle spindle.
C) activated by changes in muscle tension.
D) activated by changes in muscle length.
E) activated by input from the muscle receptor organ.
A) regulated by the activity of motor neurons.
B) activated by sensory input from the muscle spindle.
C) activated by changes in muscle tension.
D) activated by changes in muscle length.
E) activated by input from the muscle receptor organ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Gamma motor neuron activity is too weak to affect whole muscle tension.
B) Golgi tendon organs lie within the belly of the muscle.
C) A muscle spindle is a collection of extrafusal fibers.
D) The primary purpose of the stretch reflex is to counteract the unintended contraction of the quadriceps.
E) Each muscle spindle has one efferent and two afferent neurons which are used for reciprocal innvervation.
A) Gamma motor neuron activity is too weak to affect whole muscle tension.
B) Golgi tendon organs lie within the belly of the muscle.
C) A muscle spindle is a collection of extrafusal fibers.
D) The primary purpose of the stretch reflex is to counteract the unintended contraction of the quadriceps.
E) Each muscle spindle has one efferent and two afferent neurons which are used for reciprocal innvervation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following characteristics do skeletal muscle and smooth muscle have in common?
A) Calcium is bound by the protein calmodulin prior to formation of cross-bridges.
B) Tropomyosin is removed from the myosin-binding site on actin, permitting formation of cross-bridges
C) Sliding of thick and thin filaments relative to one another depends on a rise in cytosolic calcium.
D) Sliding of thick and thin filaments relative to one another results in shortening of the sarcomeres.
E) All of these.
A) Calcium is bound by the protein calmodulin prior to formation of cross-bridges.
B) Tropomyosin is removed from the myosin-binding site on actin, permitting formation of cross-bridges
C) Sliding of thick and thin filaments relative to one another depends on a rise in cytosolic calcium.
D) Sliding of thick and thin filaments relative to one another results in shortening of the sarcomeres.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Multiunit smooth muscle is considered neurogenic, which means
A) contraction occurs following a spontaneous depolarization event.
B) contraction is regulated by pacemaker cells lying within the muscle.
C) the muscle is stimulated to contract through direct nervous input.
D) contraction is proportional to the generator potential of the nerve.
E) more than one of these.
A) contraction occurs following a spontaneous depolarization event.
B) contraction is regulated by pacemaker cells lying within the muscle.
C) the muscle is stimulated to contract through direct nervous input.
D) contraction is proportional to the generator potential of the nerve.
E) more than one of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The stress relaxation response enables hollow organs, like the stomach, to accommodate increases in the volume of its contents. Typically, an upper limit is placed on the volume, however, by
A) reflex contraction initiated in response to stretch.
B) tension due to stretching of the intermediate filaments within the smooth muscle.
C) inelastic connective tissue associated with the smooth muscle of the organ.
D) the number of cross-bridge sites present on the myosin filaments.
A) reflex contraction initiated in response to stretch.
B) tension due to stretching of the intermediate filaments within the smooth muscle.
C) inelastic connective tissue associated with the smooth muscle of the organ.
D) the number of cross-bridge sites present on the myosin filaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following features distinguishes cardiac muscle from skeletal muscle?
A) Cardiac muscle contraction is modified by hormones.
B) Cardiac cells lack T tubules.
C) Only cardiac muscle has slow myosin ATPase activity.
D) In skeletal muscle Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
E) Skeletal muscle has thick myosin and thin actin filaments
A) Cardiac muscle contraction is modified by hormones.
B) Cardiac cells lack T tubules.
C) Only cardiac muscle has slow myosin ATPase activity.
D) In skeletal muscle Ca2+ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
E) Skeletal muscle has thick myosin and thin actin filaments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) Smooth muscle can be classified according to the timing and means of increasing cytosolic Ca2+.
B) In smooth muscle, C-type Ca2+ channels regulate the influx of extracellular Ca2+.
C) Smooth muscle tone exists because the muscle has a relatively low resting potential.
D) In smooth muscle, Ca2+ binds directly to myosin light chain kinase as opposed to troponin as it does in skeletal muscle.
E) Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle differ in the energy source used for contraction.
A) Smooth muscle can be classified according to the timing and means of increasing cytosolic Ca2+.
B) In smooth muscle, C-type Ca2+ channels regulate the influx of extracellular Ca2+.
C) Smooth muscle tone exists because the muscle has a relatively low resting potential.
D) In smooth muscle, Ca2+ binds directly to myosin light chain kinase as opposed to troponin as it does in skeletal muscle.
E) Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle differ in the energy source used for contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following features distinguishes skeletal muscle from smooth muscle?
A) Only smooth muscle contraction is modified by hormones.
B) Only smooth muscle takes up Ca2+ from the extracellular fluid.
C) Only skeletal muscle is neurogenic.
D) Only skeletal muscle has a moderately developed sacroplasmic reticulum.
E) Two of these.
A) Only smooth muscle contraction is modified by hormones.
B) Only smooth muscle takes up Ca2+ from the extracellular fluid.
C) Only skeletal muscle is neurogenic.
D) Only skeletal muscle has a moderately developed sacroplasmic reticulum.
E) Two of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Varicosities
A) are bulges at the end of certain types of nerve terminal branches
B) can be found on the postganglionic autonomic fibers associated with certain smooth muscle cells
C) contain neurotransmitter
D) all of these
E) none of these.
A) are bulges at the end of certain types of nerve terminal branches
B) can be found on the postganglionic autonomic fibers associated with certain smooth muscle cells
C) contain neurotransmitter
D) all of these
E) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In single unit smooth muscle, tension is increased by
A) increasing the number of individual cells recruited by neurons to contract.
B) increasing the levels of cytoplasmic calcium available to permit cross-bridge formation.
C) increasing the synthesis of contractile units so that more power is attained.
D) doing all of these.
E) doing none of these.
A) increasing the number of individual cells recruited by neurons to contract.
B) increasing the levels of cytoplasmic calcium available to permit cross-bridge formation.
C) increasing the synthesis of contractile units so that more power is attained.
D) doing all of these.
E) doing none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following muscle types has tone in the absence of an external stimulus?
A) skeletal
B) multiunit smooth muscle
C) single-unit smooth muscle
D) cardiac muscle
E) all of these
A) skeletal
B) multiunit smooth muscle
C) single-unit smooth muscle
D) cardiac muscle
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The myosin filaments of a sarcomere are attached to the Z line by an elastic protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The largest known protein in any organism is called connectin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The cross-bridges aligned with given thin filaments stroke in unison during a
contraction.
contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A single action potential in a skeletal muscle lasts only about 3-5 msec.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In skeletal muscle, a single contractile response may last up to 100 times longer than the
action potential that produced it.
action potential that produced it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Arthropod muscles attach to internal ridges of the exoskeleton called apodemes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A tectonic contraction is a summation of individual twitches and therefore has the same
strength.
strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In vivo, muscles are usually positioned at a relaxed length that is approximately 80% of
their optimal length which maximizes contraction strength.
their optimal length which maximizes contraction strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Load and velocity are directly related for eccentric contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
It is known that interconversion of muscle fiber types is possible. Thus, depending on
usage, fast-glycolytic fibers can be converted to slow-glycolytic fibers.
usage, fast-glycolytic fibers can be converted to slow-glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Dihydropyridine receptor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Dihydropyridine receptor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Ryanodine receptor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Ryanodine receptor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Cardiac muscle
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Cardiac muscle
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Slow-oxidative
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Slow-oxidative
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Fast-oxidative
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Fast-oxidative
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Fast-glycolytic
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Fast-glycolytic
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Rigor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Rigor
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-Cross bridges
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-Cross bridges
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match each sentence with the most appropriate choice:
-H-zone
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails
-H-zone
A) T tubule
B) Lateral sacs
C) Motor endplate
D) Heart
E) Type I
F) Type IIa
G) Type IIx
H) ATP depletion
I) Myosin heads
J) Myosin tails

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Compare and contrast 8 major characteristics of multiunit and single-unit smooth muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Compare and contrast the source and involvement of Ca2+ in smooth muscle and skeletal
muscle contraction. In addition, why is it that T tubules are absent in smooth muscle but present in skeletal muscle cells?.
muscle contraction. In addition, why is it that T tubules are absent in smooth muscle but present in skeletal muscle cells?.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Discuss the importance of creatine phosphate in muscle contraction. Where does creatine phosphate come from?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Compare and contrast excitation and contraction in neurogenic multiunit smooth muscle cells and myogenic single-unit smooth muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain why muscles evolved for speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



