Deck 3: Cost Accounting Systems: Job Order Costing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/106
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cost Accounting Systems: Job Order Costing
1
Cost accounting concepts and procedures are only useful in product manufacturing entities.
False
2
In a job order costing system, product costs are recorded and accumulated for specific jobs or products.
True
3
Managers use product costing information in determining budgets and setting prices for products.
True
4
Job order costing is typically employed in companies that use assembly lines for producing identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Predetermined overhead rates are calculated by dividing estimates of total factory overhead cost in the upcoming accounting period (usually a year) by an estimated usage or capacity of some unit of related activity (such as direct labor hours).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Overhead is always allocated on the basis of direct labor hours, so it is relatively simple and accurate to apply these costs to the products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Using a predetermined overhead rate reduces large changes in per-unit product costs that could result from production volume variances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When applying overhead, the total amount incurred for the period is debited to Work in Process Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the journal entries to record the issuance of materials into production, the costs of both direct and indirect materials are credited to the Materials Inventory account and debited directly to Work in Process Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The entry to record direct labor for a job includes a debit to Work in Process Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Time clocks or time records are used to track the amount of time an employee spends on each individual job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If overhead is allocated on the basis of direct labor hours, then overhead must be allocated for the labor hours spent on packaging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a job order costing system, the amount transferred from Work in Process Inventory to Finished Goods Inventory should also equal the amount of Sales Revenue for a given job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If manufacturing overhead is under-applied at the end of the year, the entry to close the account requires a CREDIT to Manufacturing Overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a service firm, the entries to record the completion of a project and billing the client include a CREDIT to Work in Process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Service department costs are considered product costs. They are accumulated in the service departments, and then allocated to the production departments as overhead, where they are then applied to the manufactured goods or provided services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Because service departments do not directly contribute to the production of goods, their costs are generally considered period costs rather than assigned to an individual product, department or activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Service departments are those parts of a business that are not connected with production, such as Sales, Finance, or Customer Service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Service department costs are almost always allocated on the basis of Direct Labor hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The predetermined plant-wide overhead rate is determined by dividing actual overhead costs incurred for the year by the amount of capacity used for the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A departmental overhead rate is determined by dividing the estimated overhead associated with the department by the estimated utilization of the productive capacity of that department.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Accumulating cost information on a per-unit basis is useful for making management decisions in companies such as:
A) Manufacturers
B) Hospitals
C) Insurance companies
D) None of the above
E) A, B, and C
A) Manufacturers
B) Hospitals
C) Insurance companies
D) None of the above
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Using a cost accounting system to track product costs is needed for:
A) Managerial decision making
B) Financial statements
C) Setting product prices
D) All of the above
E) Both A and C
A) Managerial decision making
B) Financial statements
C) Setting product prices
D) All of the above
E) Both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A job order costing system does which of the following?
A) Allocates manufacturing costs to individual jobs to determine unit costs
B) Is used to determine period costs in a service company
C) Is used to determine unit costs when products are manufactured in a continuous flow process
D) Both B and C
E) None of the above
A) Allocates manufacturing costs to individual jobs to determine unit costs
B) Is used to determine period costs in a service company
C) Is used to determine unit costs when products are manufactured in a continuous flow process
D) Both B and C
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following types of production would most likely use job-order costing?
A) Construction of custom homes
B) Farming
C) Manufacturing of heavy-duty machinery
D) Electrical power generation
E) Both A and C.
A) Construction of custom homes
B) Farming
C) Manufacturing of heavy-duty machinery
D) Electrical power generation
E) Both A and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If an actual monthly overhead rate were used to cost products rather than a predetermined rate based on yearly estimates, which of the following would be true?
A) Costs per unit would increase in months where production was greater.
B) Costs per unit would likely be more relevant, because they would reflect actual price fluctuations in the sources of overhead.
C) Costs per unit would probably not fluctuate very much.
D) Costs per unit would increase in months where overhead costs where higher.
E) A and B are both true.
A) Costs per unit would increase in months where production was greater.
B) Costs per unit would likely be more relevant, because they would reflect actual price fluctuations in the sources of overhead.
C) Costs per unit would probably not fluctuate very much.
D) Costs per unit would increase in months where overhead costs where higher.
E) A and B are both true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When calculating the predetermined overhead rate, which of the following is typically used?
A) Daily budgeted overhead
B) Yearly actual overhead incurred
C) Yearly budgeted overhead
D) Monthly actual overhead incurred
E) All of the above
A) Daily budgeted overhead
B) Yearly actual overhead incurred
C) Yearly budgeted overhead
D) Monthly actual overhead incurred
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for a company will generally be:
A) Based on monthly budgets.
B) Based on annual budgets.
C) Higher than actual manufacturing overhead rates.
D) Lower than actual manufacturing overhead rates.
A) Based on monthly budgets.
B) Based on annual budgets.
C) Higher than actual manufacturing overhead rates.
D) Lower than actual manufacturing overhead rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following would not appear on a job order cost sheet?
A) Direct Labor costs incurred
B) Direct Materials requisitioned for the job
C) General administrative expense
D) Total cost of the job
E) All of the above would appear on the job order cost sheet
A) Direct Labor costs incurred
B) Direct Materials requisitioned for the job
C) General administrative expense
D) Total cost of the job
E) All of the above would appear on the job order cost sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following lists the materials necessary to complete a job?
A) Bill of Materials
B) Production order
C) Job order cost sheet
D) Materials requisition
A) Bill of Materials
B) Production order
C) Job order cost sheet
D) Materials requisition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a company uses a perpetual inventory system, what journal entry would correctly record a purchase on account of materials to be used in production?
A) Purchases
Accounts Payable
B) Materials Inventory
Cash
C) Materials Inventory
Accounts Payable
D) Work in Process Inventory
Accounts Payable
E) None of these
A) Purchases
Accounts Payable
B) Materials Inventory
Cash
C) Materials Inventory
Accounts Payable
D) Work in Process Inventory
Accounts Payable
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When recording depreciation on factory equipment, which of the following accounts would be credited?
A) Work in Process Inventory
B) Manufacturing Overhead
C) Equipment
D) Accounts Payable
E) Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment
A) Work in Process Inventory
B) Manufacturing Overhead
C) Equipment
D) Accounts Payable
E) Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When packaging is part of a production process, which of the following accounts will not be affected by the entries to record packing? Assume that all packaging materials are purchased on account and held in materials inventory prior to use.
A) Work in Process Inventory
B) Manufacturing Overhead
C) Wages Payable
D) Materials Inventory
E) Cost of Goods Sold
A) Work in Process Inventory
B) Manufacturing Overhead
C) Wages Payable
D) Materials Inventory
E) Cost of Goods Sold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is correctly included in the entry to record the sale of finished goods?
A) CREDIT to Work in Process Inventory
B) CREDIT to Finished Goods Inventory
C) CREDIT to Cost of Goods Sold
D) DEBIT to Sales Revenue
E) DEBIT to Accounts Payable
A) CREDIT to Work in Process Inventory
B) CREDIT to Finished Goods Inventory
C) CREDIT to Cost of Goods Sold
D) DEBIT to Sales Revenue
E) DEBIT to Accounts Payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following correctly explains what should be done with any under- or over-applied overhead?
A) At the end of a project, any insignificant under- or over-applied overhead should be closed to Work in Process prior to transferring the costs to Finished Goods.
B) Monthly, any significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead should be closed to Cost of Goods Sold.
C) At year end, if there is a significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead, it should be allocated proportionally to Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods sold.
D) At year end, if there is a significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead, it should all be closed to Cost of Goods Sold.
E) It is not normal for a company to have under- or over-applied overhead, because overhead is allocated based on actual costs incurred.
A) At the end of a project, any insignificant under- or over-applied overhead should be closed to Work in Process prior to transferring the costs to Finished Goods.
B) Monthly, any significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead should be closed to Cost of Goods Sold.
C) At year end, if there is a significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead, it should be allocated proportionally to Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods sold.
D) At year end, if there is a significant amount of under- or over-applied overhead, it should all be closed to Cost of Goods Sold.
E) It is not normal for a company to have under- or over-applied overhead, because overhead is allocated based on actual costs incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is most correct?
A) Service firms transfer the costs associated with services completed to a Finished Services account prior to billing the client for work performed.
B) Because they are not engaged in manufacturing work, employees working in service firms do not track the time that they spend on specific jobs or projects.
C) Service firms typically use some driver other than labor to allocate overhead, given that the work is not usually labor intensive.
D) Service firms typically do not use Job-order Costing, because they do not manufacture any products.
E) Service firms typically do not include the cost of any Direct Materials in their Work in Progress Inventory for services that they perform.
A) Service firms transfer the costs associated with services completed to a Finished Services account prior to billing the client for work performed.
B) Because they are not engaged in manufacturing work, employees working in service firms do not track the time that they spend on specific jobs or projects.
C) Service firms typically use some driver other than labor to allocate overhead, given that the work is not usually labor intensive.
D) Service firms typically do not use Job-order Costing, because they do not manufacture any products.
E) Service firms typically do not include the cost of any Direct Materials in their Work in Progress Inventory for services that they perform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following types of costs are not allocated to production departments?
A) Manufacturing overhead costs directly identifiable with the production departments
B) Manufacturing overhead costs requiring allocation to production departments
C) Selling department costs
D) Service department costs
A) Manufacturing overhead costs directly identifiable with the production departments
B) Manufacturing overhead costs requiring allocation to production departments
C) Selling department costs
D) Service department costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a cost incurred by or allocated to service departments?
A) Direct Materials
B) Direct Labor
C) Manufacturing Overhead (allocated based on a predetermined rate)
D) Selling Expenses
E) None of the above are service department costs.
A) Direct Materials
B) Direct Labor
C) Manufacturing Overhead (allocated based on a predetermined rate)
D) Selling Expenses
E) None of the above are service department costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following could be used as a basis to allocate service department costs?
A) Machine Hours
B) Direct Labor Hours
C) Square feet of building used
D) Kilowatts per hour of electricity used
E) All of the above could be used.
A) Machine Hours
B) Direct Labor Hours
C) Square feet of building used
D) Kilowatts per hour of electricity used
E) All of the above could be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would be the most appropriate measure of overhead allocation for a department that is highly automated?
A) Machine hours used
B) Direct Labor hours
C) Direct Materials usage
D) Square feet of floor space
E) Number of employees
A) Machine hours used
B) Direct Labor hours
C) Direct Materials usage
D) Square feet of floor space
E) Number of employees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not a correct reason for using department overhead rates?
A) It provides a more equitable allocation of costs than a plant-wide overhead rate.
B) It is more accurate than activity-based costing when jobs are complex and varied.
C) Different departments may have different production capacities.
D) All of these are reasons to use department overhead rates.
A) It provides a more equitable allocation of costs than a plant-wide overhead rate.
B) It is more accurate than activity-based costing when jobs are complex and varied.
C) Different departments may have different production capacities.
D) All of these are reasons to use department overhead rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Wasatch Company anticipates that they will incur the following costs and expenses during the coming year:
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
A) $6.71
B) $9.14
C) $11.86
D) $14.86
E) None of the above
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?A) $6.71
B) $9.14
C) $11.86
D) $14.86
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Job number 2288 had the following data:
 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2288?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2288?
A) $3,300
B) $3,550
C) $4,620
D) $4,870
E) None of the above
 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2288?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2288?A) $3,300
B) $3,550
C) $4,620
D) $4,870
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Job #2333 incurred the following during production:
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company:
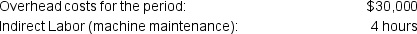 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates:
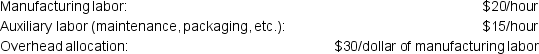 Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
A) $4,500.00
B) $4,600.00
C) $4,607.50
D) $4,610.00
E) $19,607.50
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company: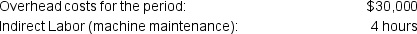 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates: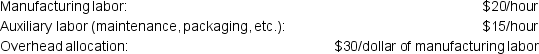 Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?A) $4,500.00
B) $4,600.00
C) $4,607.50
D) $4,610.00
E) $19,607.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is NOT a cost incurred by or allocated to service departments?
A) Direct Materials
B) Direct Labor
C) Manufacturing Overhead (allocated based on a predetermined rate)
D) Selling Expenses
E) None of the above are service department costs
A) Direct Materials
B) Direct Labor
C) Manufacturing Overhead (allocated based on a predetermined rate)
D) Selling Expenses
E) None of the above are service department costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following could be used as a basis to allocate service department costs?
A) Machine Hours
B) Direct Labor Hours
C) Square feet of building used
D) Kilowatts per hour of electricity used
E) All of the above could be used
A) Machine Hours
B) Direct Labor Hours
C) Square feet of building used
D) Kilowatts per hour of electricity used
E) All of the above could be used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Bricks and Mortar Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. BMM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Firing) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space.
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $4,900
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,300
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Firing department?
A) $ 657.14
B) $ 920.00
C) $1,380.00
D) $1,400.00
E) $2,057.14
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $4,900
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,300
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Firing department?
A) $ 657.14
B) $ 920.00
C) $1,380.00
D) $1,400.00
E) $2,057.14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Bricks and Mortar Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. BMM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Firing) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space.
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $4,900
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,300
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
A) $ 657.14
B) $ 920.00
C) $1,380.00
D) $1,400.00
E) $2,780.00
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $4,900
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,300
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
A) $ 657.14
B) $ 920.00
C) $1,380.00
D) $1,400.00
E) $2,780.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Bricks and Mortar Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. BMM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Firing) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. BMM also allocates depreciation on the factory to all departments on the basis of number of employee positions in the department.
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 10 employees
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $4,900 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $2,300, 6 employees
Depreciation on factory: $4,500
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
A) $1,800.00
B) $2,720.00
C) $3,200.00
D) $5,433.71
E) $4,680.00
The following data is available for BMM:
Mixing: 600 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 10 employees
Firing: 400 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $4,900 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $2,300, 6 employees
Depreciation on factory: $4,500
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
A) $1,800.00
B) $2,720.00
C) $3,200.00
D) $5,433.71
E) $4,680.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Job #335 requires work in the following departments:
Machining: 4 hours (all automated)
Sanding: 1 hour (all direct labor)
Painting: 2 hours (including dry time of 1.5 hours)
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $6/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $15/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $3/hour.
How much overhead is allocated to the job?
A) $45
B) $72
C) $67.50
D) $78
E) None of the above
Machining: 4 hours (all automated)
Sanding: 1 hour (all direct labor)
Painting: 2 hours (including dry time of 1.5 hours)
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $6/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $15/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $3/hour.
How much overhead is allocated to the job?
A) $45
B) $72
C) $67.50
D) $78
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Acme Production, Inc. had the following data for their manufacturing process:
 What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
 What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Wasatch Company anticipates that they will incur the following costs and expenses during the coming year:
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Peter Manufacturing, Inc. employs an overhead rate of 150% of direct labor cost. The Job 180 cost sheet shows that $10,000 in direct materials has been used and that $11,000 in direct labor has been incurred.
If 2,000 units of product have been produced on Job 180, what is the unit cost of the product?
If 2,000 units of product have been produced on Job 180, what is the unit cost of the product?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The following costs were recorded by Buddy Co. for the month of January:
 Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $20 per direct labor hour.
Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $20 per direct labor hour.
What is the balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account at the end of January? (Assume that Buddy Co. reports their financial results on a calendar year basis).
 Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $20 per direct labor hour.
Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $20 per direct labor hour.What is the balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account at the end of January? (Assume that Buddy Co. reports their financial results on a calendar year basis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Job number 2873 had the following data:
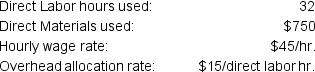 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2873?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2873?
 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2873?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 2873?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Materials purchases for the month were $2,000. The Materials Inventory account had a beginning balance of $250. Direct Materials used were $1,900, and Indirect Materials used were $300.
What is the correct ending balance for the Materials Inventory account?
What is the correct ending balance for the Materials Inventory account?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Job #5632 incurred the following during production:
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company:
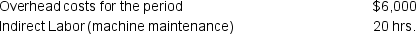 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates:
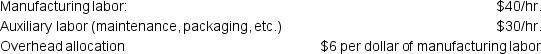 Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company: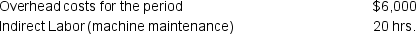 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates: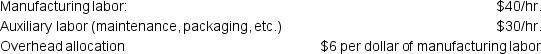 Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is/are the correct journal entry(ies) to record the completion and billing of the following job?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The following information is available for 20X1 for Ocra & Associates Oil Refinery:
Ending Work in Process: $50,000 (including applied overhead of $20,000)
Ending Finished Goods: $130,000 (including applied overhead of $40,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $1,200,000 (including applied overhead of $440,000 from this year)
At year end, the company had an under-applied overhead balance of $38,000. This amount is not considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?
Ending Work in Process: $50,000 (including applied overhead of $20,000)
Ending Finished Goods: $130,000 (including applied overhead of $40,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $1,200,000 (including applied overhead of $440,000 from this year)
At year end, the company had an under-applied overhead balance of $38,000. This amount is not considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following information is available for 20X5 for Ocra & Associates Oil Refinery:
Ending Work in Process: $50,000 (including applied overhead of $20,000)
Ending Finished Goods: $130,000 (including applied overhead of $40,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $1,200,000 (including applied overhead of $440,000 from this year)
At year end, the company had an under-applied overhead balance of $38,000. This amount IS considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?
Ending Work in Process: $50,000 (including applied overhead of $20,000)
Ending Finished Goods: $130,000 (including applied overhead of $40,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $1,200,000 (including applied overhead of $440,000 from this year)
At year end, the company had an under-applied overhead balance of $38,000. This amount IS considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Hardluck Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. HM has two production departments (Mixing and Baking) and two service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space.
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $49,000
Cleaning costs incurred: $23,000
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Baking department?
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $49,000
Cleaning costs incurred: $23,000
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Baking department?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Hardluck Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. HM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Baking) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space.
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $49,000
Cleaning costs incurred: $23,000
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $49,000
Cleaning costs incurred: $23,000
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Hardluck Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. HM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Baking) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. HM also allocates depreciation on the factory to all departments on the basis of number of employee positions in the department.
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 30 employees
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 24 employees
Maintenance: $49,000 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $23,000 incurred, 2 employees
Depreciation on factory: $45,000
What is the total amount that should be allocated to Baking from the Cleaning department?
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 30 employees
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 24 employees
Maintenance: $49,000 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $23,000 incurred, 2 employees
Depreciation on factory: $45,000
What is the total amount that should be allocated to Baking from the Cleaning department?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Hardluck Manufacturing produces building materials for local construction contractors. HM has 2 production departments (Mixing and Baking) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. HM also allocates depreciation on the factory to all departments on the basis of number of employee positions in the department.
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 30 employees
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 24 employees
Maintenance: $49,000 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $23,000, 2 employees
Depreciation on factory: $45,000
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?
The following data is available for HM:
Mixing: 1,100 square feet of floor space, 200 machine hours used, 30 employees
Baking: 900 square feet of floor space, 500 machine hours used, 24 employees
Maintenance: $49,000 incurred, 4 employees
Cleaning: $23,000, 2 employees
Depreciation on factory: $45,000
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Mixing department?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Job #754 requires work in the following departments:
Machining: 9 hours (all automated)
Sanding: 3 hour (all direct labor)
Painting: 15 hours (including dry time of 9 hours)
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $12/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $9/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated strictly on the basis of total time in the department (because dry time is so substantial), and is allocated at a rate of $6/hour.
How much overhead is allocated to the job?
Machining: 9 hours (all automated)
Sanding: 3 hour (all direct labor)
Painting: 15 hours (including dry time of 9 hours)
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $12/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $9/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated strictly on the basis of total time in the department (because dry time is so substantial), and is allocated at a rate of $6/hour.
How much overhead is allocated to the job?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
BorrRedds Mfg. had the following data for their manufacturing process:
 What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
 What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
What was the overhead cost/unit allocated to the units produced in December, if the company's predetermined overhead rate is based on machine hours?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Scraps'N'Co anticipates incurring the following costs and expenses during the coming year:
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
 If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
If manufacturing overhead is assigned on the basis of direct labor hours, what is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Rachael Productions Co. uses an overhead rate of 40% of direct labor cost. The cost sheet for Job 227 shows that $2,000 in direct materials has been used and that $3,000 in direct labor has been incurred.
If 500 units of product have been produced on Job 227, what is the unit cost of the product?
If 500 units of product have been produced on Job 227, what is the unit cost of the product?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The following costs were recorded by Grant Co. for the month of January:
 Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $5 per direct labor hour.
Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $5 per direct labor hour.
What is the balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account at the end of January (assume that Grant Co. reports their financial results on a calendar year basis).
 Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $5 per direct labor hour.
Overhead is allocated based on a predetermined rate of $5 per direct labor hour.What is the balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account at the end of January (assume that Grant Co. reports their financial results on a calendar year basis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Job number 24602 had the following data:
 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 24602?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 24602?
 Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 24602?
Assuming this was the only job completed this month, what was the total cost of Job 24602?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Materials purchases for the month were $26,000. The Materials Inventory account had a beginning balance of $1,250. Direct Materials used were $23,700, and Indirect Materials used were $2,360.
What is the correct ending balance for the Materials Inventory account?
What is the correct ending balance for the Materials Inventory account?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Job #0098 incurred the following during production:
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company:
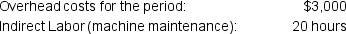 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates:
 Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
 The following data is also available for the company:
The following data is also available for the company: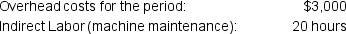 The company incurs costs at the following rates:
The company incurs costs at the following rates: Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Given this information, what was the total cost of the job that was transferred from Work in Process Inventory to the Finished Goods Inventory?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is/are the correct journal entry(ies) to record the completion and billing of the following job?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following information is available for 2019 for Mobile Mfg.:
Ending Work in Process: $7,000 (including applied overhead of $400)
Ending Finished Goods: $12,000 (including applied overhead of $1,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $79,000 (including applied overhead of $3,500 from this year)
At year end, the company had an over-applied overhead balance of $200. This amount is NOT considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?
Ending Work in Process: $7,000 (including applied overhead of $400)
Ending Finished Goods: $12,000 (including applied overhead of $1,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $79,000 (including applied overhead of $3,500 from this year)
At year end, the company had an over-applied overhead balance of $200. This amount is NOT considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The following information is available for 2019 for Mobile Mfg.:
Ending Work in Process: $7,000 (including applied overhead of $400)
Ending Finished Goods: $12,000 (including applied overhead of $1,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $79,000 (including applied overhead of $3,500 from this year)
At year end, the company had an over-applied overhead balance of $200. This amount IS considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end? (Round amounts to the nearest dollar.)
Ending Work in Process: $7,000 (including applied overhead of $400)
Ending Finished Goods: $12,000 (including applied overhead of $1,000)
Cost of Goods Sold for the year: $79,000 (including applied overhead of $3,500 from this year)
At year end, the company had an over-applied overhead balance of $200. This amount IS considered significant.
What is the adjusting entry required with respect to overhead at year end? (Round amounts to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
JKL Mfg. cans food products. JKL has 2 production departments (Canning and Labelling) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. The following data is available for JKL:
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $600
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,000
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Labelling department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $600
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,000
How much of the Cleaning costs should be allocated to the Labelling department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
JKL Mfg. cans food products. JKL has 2 production departments (Canning and Labelling) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. The following data is available for JKL:
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $600
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,000
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Canning department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used
Maintenance costs incurred: $600
Cleaning costs incurred: $2,000
How much total support department costs should be allocated to the Canning department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
JKL Mfg. cans food products. JKL has 2 production departments (Canning and Labelling) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. JKL also allocates depreciation on the factory equipment to all departments on the basis of number of employee positions in the department. The following data is available for JKL:
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used, 10 employees
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $600 incurred, 1 employee
Cleaning: $2,000 incurred, 4 employees
Depreciation on factory equipment: $500
What is the total amount that should be allocated to Canning from the Cleaning department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used, 10 employees
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $600 incurred, 1 employee
Cleaning: $2,000 incurred, 4 employees
Depreciation on factory equipment: $500
What is the total amount that should be allocated to Canning from the Cleaning department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
JKL Mfg. cans food products. JKL has 2 production departments (Canning and Labelling) and 2 service departments (Maintenance and Cleaning). Maintenance costs are allocated based on machine hours used. Cleaning costs are allocated based on square feet of floor space. JKL also allocates depreciation on the factory equipment to all departments on the basis of number of employee positions in the department. The following data is available for JKL:
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used, 10 employees
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $600 incurred, 1 employee
Cleaning: $2,000 incurred, 4 employees
Depreciation on factory equipment: $500
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Labelling department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Canning: 2,000 square feet of floor space, 300 machine hours used, 10 employees
Labelling: 1,000 square feet of floor space, 100 machine hours used, 5 employees
Maintenance: $600 incurred, 1 employee
Cleaning: $2,000 incurred, 4 employees
Depreciation on factory equipment: $500
How much in total costs should be allocated to the Labelling department? (Round to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Job #33 requires work in the following departments:
 The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $8/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $13/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $1/hour.
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $8/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $13/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $1/hour.
How much overhead is allocated to the job?
 The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $8/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $13/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $1/hour.
The company uses departmental overhead rates. Overhead is allocated at the rate of $8/direct labor hour in Sanding, and $13/machine hour in Machining. Painting overhead is allocated on the basis of total time in the department and is allocated at a rate of $1/hour.How much overhead is allocated to the job?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



