Deck 15: Radiologic Evaluation of the Shoulder
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Radiologic Evaluation of the Shoulder
1
A patient fell off her bike onto her shoulder and subsequently went to emergency department. Initial radiographs were negative for fracture, and she was referred to physical therapy with shoulder pain. On evaluation you suspect an acromioclavicular strain. What radiographic projection would help confirm this diagnosis?
A) Anteroposterior of the shoulder
B) Lateral view of the scapula
C) Acromioclavicular bilateral view with and without weights
D) Axillary view of glenohumeral joint
A) Anteroposterior of the shoulder
B) Lateral view of the scapula
C) Acromioclavicular bilateral view with and without weights
D) Axillary view of glenohumeral joint
Acromioclavicular bilateral view with and without weights
2
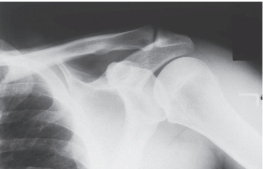
-Refer to the figure. Name the radiographic projection.
A) Anteroposterior external rotation
B) Lateral view of the scapula
C) Anteroposterior internal rotation
D) Axillary view of glenohumeral joint
Anteroposterior internal rotation
3
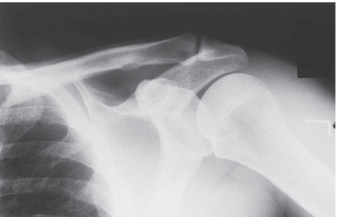
-Refer to the figure. You have chosen the correct answer because you recognized what region of anatomy seen in profile?
A) Greater tuberosity
B) Acromioclavicular joint
C) Lesser tuberosity
D) Coracoid process
Lesser tuberosity
4

-What view helps determine the relationship of the humeral head to the glenoid fossa, in the setting of a suspected glenohumeral joint dislocation?
A) Anteroposterior of the shoulder
B) Lateral view of the scapula
C) Acromioclavicular bilateral view with and without weights
D) Axillary view of glenohumeral joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
-Refer to the figure. Name the imaging modality.
A) MRI
B) Radiograph
C) Arthrogram
D) 3D CT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
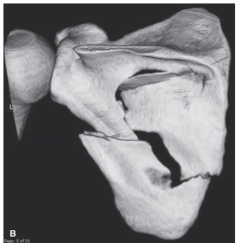
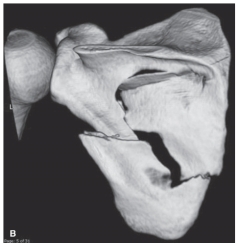
-Refer to the figure. Describe the pathological condition.
A) Osteolytic destruction
B) Degenerative joint disease
C) Fracture of the scapula
D) Dislocation of the glenohumeral joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-Refer to the figure. Identify the imaging modality and plane.
A) Oblique coronal MRI
B) Coronal MRI
C) Oblique coronal CT
D) Coronal CT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
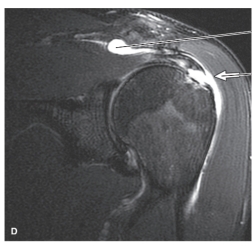
-Refer to the figure. Contrast has been added to the ______________joint. This procedure is called _________________.
A) glenohumeral; myelography
B) acromioclavicular; arthrography
C) coracoclavicular; arthrography
D) glenohumeral; arthrography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
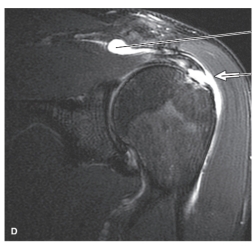
-Refer to the figure. The most common reason this image is made is to identify:
A) Occult or stress fractures
B) Osteochondritis dissecans
C) Labral or ligamentous tears
D) Glenohumeral dislocations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The most common rotator cuff tear involves the hypovascular critical zone of the _______________, 1 cm proximal to its insertion on the _______________________.
A) infraspinatus; lesser tuberosity
B) teres minor; surgical neck
C) supraspinatus; greater tuberosity
D) subscapularis; greater tuberosity
A) infraspinatus; lesser tuberosity
B) teres minor; surgical neck
C) supraspinatus; greater tuberosity
D) subscapularis; greater tuberosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



