Deck 10: The Chest Radiograph and Cardiopulmonary Imaging
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Chest Radiograph and Cardiopulmonary Imaging
1
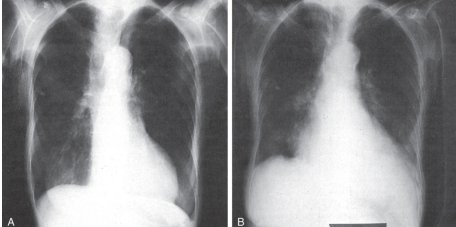
-Refer to the figure. Both radiographs of the chest are normal. Which patient was radiographed in a PA (posteroanterior) projection?
A) Patient A
B) Patient B
Patient A
2
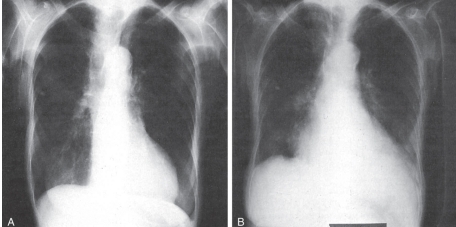
-Refer to the figure. You know which chest radiograph was made in an AP (anteroposterior) projection because of what factor?
A) A reversal of the mediastinum
B) An appearance of an enlarged heart in the cardiothoracic ratio
C) Sharpening of the edges of the anatomic structures
D) Less lung inflation
An appearance of an enlarged heart in the cardiothoracic ratio
3

-The chest radiograph is useful to determine:
A) The cause of a consolidation.
B) If the pathological condition is cardiac or pulmonary in nature
C) Subtle fractures in the thoracic spine
D) Spinous process fractures at the cervicothoracic junction
If the pathological condition is cardiac or pulmonary in nature
4

-The value of the silhouette sign, which is a loss of a radiographic interface between air and soft tissue, is that it can localize a lesion:
A) To one lobe of the lung
B) To one chamber of the heart
C) To one branch of the bronchial tree
D) In the bony thorax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

-Atelectasis is:
A) A common postoperative complication caused by poor inspiratory effort
B) Revealed as a lung field that is abnormally white because it is no longer filled with air
C) A condition that responds well to physical therapy
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

-The lateral chest radiograph is often made as a second-level decision, based on findings obtained from the PA view, because the lateral view:
A) Incurs more radiation exposure and less useful clinical information
B) Demonstrates the same location of lesions as the PA view
C) Demonstrates anatomic structures already seen on the lateral view of the thoracic spine
D) Incurs less radiation and less resolution than the PA view

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-Radiographically, the primary finding of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is hyperinflation of both lungs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is the current standard of care in the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism because of high accuracy, wide availability, and rapid turnaround time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

-In this study, contrast is delivered into the left side of the heart to evaluate the coronary arteries. This study is included under a group of cardiac catheterization procedures that include both diagnostic evaluation and interventional treatment (e.g., balloon angioplasty,stent placement).
A) Echocardiogram
B) Coronary angiogram
C) Pulmonary angiogram
D) Magnetic resonance angiogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

-A patient with chest pain and shortness of breath is evaluated with a chest radiograph, which shows blunting of the costophrenic angles. This finding is called:
A) Myocardial infarction
B) Pneumonia
C) Pleural effusion
D) Aortic dissection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



