Deck 3: Radiologic Evaluation of Fracture
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Radiologic Evaluation of Fracture
1
A trauma survey of radiographs assesses life-threatening injuries in priority order. Usually the first radiographic examination performed is the:
A) Lateral thoracolumbar
B) Anteroposterior abdominal
C) Cross-table lateral of the cervical spine
D) Anteroposterior skull
A) Lateral thoracolumbar
B) Anteroposterior abdominal
C) Cross-table lateral of the cervical spine
D) Anteroposterior skull
Cross-table lateral of the cervical spine
2
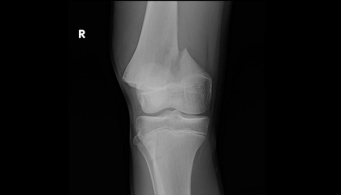
-Refer to the figure. Radiographic assessment of a fractured bone must include:
A) Two views at right angles to each other
B) The routine radiographic exam for the most proximal joint
C) An AP view of the contralateral limb to assess normal values
D) The routine radiographic exam for the most distal joint
Two views at right angles to each other
3
Eponyms are standardized, and the definitive glossary is included in the text for correct use of eponyms in documentation.
False
4
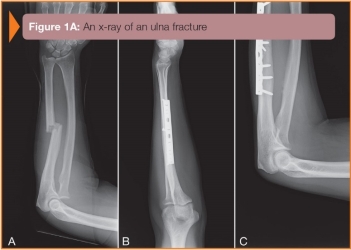
-Refer to the figure. Name the bone and characteristic of the fractures:
A) Midshaft of the ulna, incomplete, displaced
B) Midshaft of the radius, incomplete, displaced
C) Midshaft of the ulna, complete, displaced
D) Midshaft of the radius, complete, displaced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
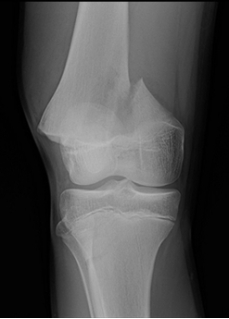
-Refer to the figure. The _______is fractured in the most common epiphyseal injury pattern, a Salter-Harris ________:
A) femur; type 1
B) femur; type 2
C) tibia; type 1
D) tibia; type 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

-Guiding bone fragments toward normal anatomic position via manipulation or traction and followed by stabilization with an external device is known as:
A) Closed reduction
B) Open reduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-"Missed" fractures occur with some frequency because of:
A) Failure to order radiography
B) Failure to recognize fractures on radiographs
C) Subtle fractures that are difficult to see on radiographs
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-A basic principle of fracture management if there is clinical suspicion of fracture but negative radiographs is to:
A) Instruct the patient to use the limb to pain tolerance
B) Immobilize the limb and repeat radiographs in 7 to 10 days
C) Immobilize the limb for the average 4- to 6-week healing phase
D) Initiate physical therapy for sprain management

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

-When all the processes of healing have ceased at an ununited fracture site, the condition is called:
A) Nonunion
B) Malunion
C) Delayed union
D) Avascular necrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
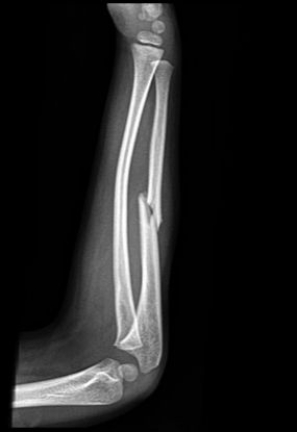
-Refer to the figure. The deformity of the radius is known as:
A) Plastic bowing
B) Greenstick fracture
C) Torus fracture
D) Complete midshaft fracture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



