Deck 35: Operational Amplifiers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Operational Amplifiers
1
An op amp that uses JFETs in the input differential amp and BJTs for the following stages is called a ______________ op amp.
bi-FET
2
The dc current through the emitter resistor is often called the ______________ current.
tail
3
The signal applied to each differential amplifier input is assumed to have exactly the same phase and amplitude, hence the name ______________-mode input.
common
4
It is most common to specify the CMRR in ______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A(n) ______________ amplifier is a high-gain, direct coupled, differential amplifier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An op amp referred to as the ______________ has become an industry standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The triangular schematic symbol of an op amp shows only the ______________ connections to different points inside the op amp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The ______________ capacitor of the 741 op amp is used to prevent undesirable oscillations within the op amp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
There are two ways to avoid ______________-rate distortion of a sine wave: either use an op amp with a faster slew rate or accept an output waveform with a lower peak voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The ______________ input of an op amp has extremely high input impedance, but its value is not the input impedance of the circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An op amp specification indicating the maximum rate at which the output voltage can change is referred to as the
A) zero crossing rate
B) change rate
C) slew rate
D) input offset rate
A) zero crossing rate
B) change rate
C) slew rate
D) input offset rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Slew-rate distortion of a sine wave produces what type waveform?
A) cosine wave
B) square wave
C) rectangular wave
D) triangular wave
A) cosine wave
B) square wave
C) rectangular wave
D) triangular wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The highest undistorted frequency out of an op amp without slew-rate distortion is called the
A) power bandwidth (fmax)
B) resonant frequency (fr)
C) fundamental frequency
D) harmonic frequency
A) power bandwidth (fmax)
B) resonant frequency (fr)
C) fundamental frequency
D) harmonic frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two identical signals applied to the inputs of an op amp, each with exactly the same phase relationship and voltage values is called a(n)
A) common-mode signal
B) differential input
C) balanced-mode signal
D) identical-mode signal
A) common-mode signal
B) differential input
C) balanced-mode signal
D) identical-mode signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the sampling of a portion of the output signal from an amplifier and feeding it back either to aid or oppose the input signal called?
A) sample rate
B) open loop
C) feedback
D) regulation
A) sample rate
B) open loop
C) feedback
D) regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not an advantage of negative feedback?
A) stabilize voltage gain
B) improve input and output impedances
C) increase amplifier selectivity
D) increase amplifier bandwidth
A) stabilize voltage gain
B) improve input and output impedances
C) increase amplifier selectivity
D) increase amplifier bandwidth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the voltage at the op amp's inverting input is at the same potential as ground, but it can sink no current, this point is considered
A) chassis ground
B) ground loop
C) virtual ground
D) grounded
A) chassis ground
B) ground loop
C) virtual ground
D) grounded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What determines how much of the op amp's output signal is fed back to the input?
A) virtual ground
B) feedback fraction
C) power source
D) input signal
A) virtual ground
B) feedback fraction
C) power source
D) input signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What determines the voltage gain of a noninverting op amp?
A) input signal
B) virtual ground
C) power source
D) RF and Ri
A) input signal
B) virtual ground
C) power source
D) RF and Ri

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not another name for op amp voltage follower?
A) unity gain amplifier
B) instrumentation amplifier
C) buffer amplifier
D) isolation amplifier
A) unity gain amplifier
B) instrumentation amplifier
C) buffer amplifier
D) isolation amplifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Because the stages inside of an op amp are direct coupled,
A) there is no lower cutoff frequency
B) there is no upper cutoff frequency
C) there is no need for a power source
D) the lower cutoff frequency is 100 Hz
A) there is no lower cutoff frequency
B) there is no upper cutoff frequency
C) there is no need for a power source
D) the lower cutoff frequency is 100 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The frequency at which the closed-loop gain decreases to 70.7% of its maximum is called the
A) resonant frequency
B) harmonic frequency
C) closed-loop cutoff frequency
D) open-loop cutoff frequency
A) resonant frequency
B) harmonic frequency
C) closed-loop cutoff frequency
D) open-loop cutoff frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If an op amp's closed-loop voltage gain is decreased
A) the bandwidth will decrease
B) the bandwidth will increase
C) the closed-loop cutoff frequency will be lower
D) the open-loop cutoff frequency will be lower
A) the bandwidth will decrease
B) the bandwidth will increase
C) the closed-loop cutoff frequency will be lower
D) the open-loop cutoff frequency will be lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
With an inverting op amp, the input and output signals are
A) in phase
B) 90° out of phase
C) 180° out of phase
D) 45° out of phase
A) in phase
B) 90° out of phase
C) 180° out of phase
D) 45° out of phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An amplifier whose output voltage equals the negative sum of the input voltages is called a(n)
A) difference amplifier
B) adding amplifier
C) summing amplifier
D) negative sum amplifier
A) difference amplifier
B) adding amplifier
C) summing amplifier
D) negative sum amplifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When each input voltage of a summing amplifier is amplified by a different factor, the circuit is called a
A) factor amplifier
B) sum / difference amplifier
C) scaling amplifier
D) voltage amplifier
A) factor amplifier
B) sum / difference amplifier
C) scaling amplifier
D) voltage amplifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Circuits that can amplify differential input signals but reject or attenuate common-mode input signals is called a(n)
A) attenuation amplifier
B) common-mode amplifier
C) differential amplifier
D) subtracting amplifier
A) attenuation amplifier
B) common-mode amplifier
C) differential amplifier
D) subtracting amplifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
With the instrumentation amplifier shown in Figure 33-19, A1 and A2 are in what op amp configuration? 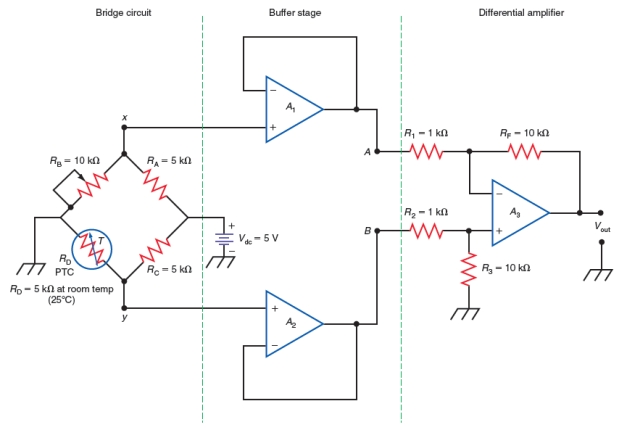
A) inverting
B) noninverting
C) voltage follower
D) differential

A) inverting
B) noninverting
C) voltage follower
D) differential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The differential amplifier shown in Figure has a gain equal to 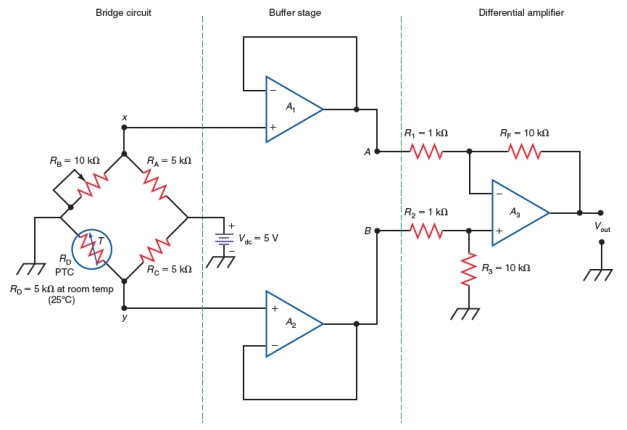
A) -RF/R1
B) RF/R1
C) RF/R2
D) RF/R3

A) -RF/R1
B) RF/R1
C) RF/R2
D) RF/R3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A filter that uses components or devices such as transistors and op amps, which can amplify, is called a(n)
A) active filter
B) passive filter
C) notch filter
D) wavetrap
A) active filter
B) passive filter
C) notch filter
D) wavetrap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The output of a comparator is always
A) inverted
B) noninverted
C) ±Vsat
D) a common-mode signal
A) inverted
B) noninverted
C) ±Vsat
D) a common-mode signal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Because the comparator's output voltage switches when Vin crosses zero, the circuit is sometimes called a
A) zero-crossing detector
B) zero detector
C) zero-switching detector
D) zero comparator
A) zero-crossing detector
B) zero detector
C) zero-switching detector
D) zero comparator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What can be used with diodes to rectify signals with peak values in the millivolt region?
A) bipolar junction transistors
B) MOSFETs
C) JFETs
D) op amps
A) bipolar junction transistors
B) MOSFETs
C) JFETs
D) op amps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The first stage of every operational amplifier is a
A) differential amplifier
B) noninverting amplifier
C) comparator
D) voltage follower
A) differential amplifier
B) noninverting amplifier
C) comparator
D) voltage follower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Operational amplifiers are linear ICs that can be used to amplify signal frequencies that extend from 0 Hz to well above 1 MHz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The first stage of every op amp is an emitter follower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An op amp that uses JFETs in the input differential amp and bipolar transistors for the following stages is called a bi-FET op amp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A differential amp has one input called the inverting input, one input called the noninverting input, and one output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The signal applied to the input of a differential amplifier is assumed to have exactly the same phase and amplitude and is referred to as the common-mode input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The common-mode rejection ratio is usually defined as the ratio of the differential voltage gain to the common-mode voltage gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The lower the value of CMRR, the better the differential amplifier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An op amp is a high-gain, direct coupled, differential amplifier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The 741 op amp, an industry standard is contained in an eight-pin IC and is made by several manufacturers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Bi-FET op amps generally have a wider bandwidth, higher slew rate, larger power output, higher input impedances, and much lower input bias currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Designed into the 741 op amp is a compensating capacitor used to prevent undesirable oscillations within the op amp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The open-loop voltage gain of an op amp is its voltage gain when there is negative feedback.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The open-loop voltage gain of an op amp is the ratio of its output voltage to its differential input voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Input offset current is the difference between the op amp's two input bias currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Open-loop cutoff frequency is the frequency at which the open-loop voltage gain of an op amp is down to 70.7% of its maximum value at dc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



