Deck 7: The Common Catabolic Pathway
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: The Common Catabolic Pathway
1
In the citric acid cycle, what reduced cofactors are derived from the oxidation of one molecule of acetyl-CoA to two molecules of CO2?
A) 2 NADH and 1 FADH2
B) 3 NADH and 1 FADH2
C) 2 NADH and 2 FADH2
D) 3 NADH and 2 FADH2
E) 4 NADH and 2 FADH2
A) 2 NADH and 1 FADH2
B) 3 NADH and 1 FADH2
C) 2 NADH and 2 FADH2
D) 3 NADH and 2 FADH2
E) 4 NADH and 2 FADH2
3 NADH and 1 FADH2
2
If acetyl-CoA labeled with 14C, as shown in the figure to the right, were used as the substrate for the citric acid cycle, which of the following intermediates would be produced during the first round of the cycle? 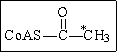
A)
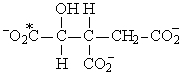
B)
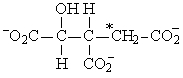
C)
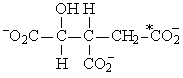
D)
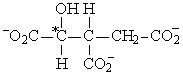
E)
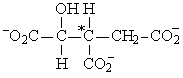

A)
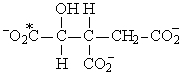
B)
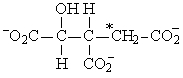
C)
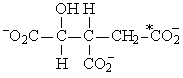
D)
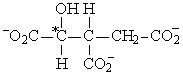
E)
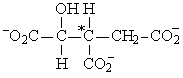
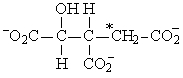
3
Which of the following condenses with oxaloacetate to form citrate?
A) acetyl-CoA
B) cis-aconitate
C) carboxybiotin
D) oxalosuccinate
E) succinyl-phosphate
A) acetyl-CoA
B) cis-aconitate
C) carboxybiotin
D) oxalosuccinate
E) succinyl-phosphate
acetyl-CoA
4
______ is used in the first reaction of the citric acid cycle and regenerated upon completion of one turn of the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Aconitase catalyzes the _____ of citrate, followed by a _____ reaction.
A) oxidation; reduction
B) reduction; oxidation
C) hydration; dehydration
D) dehydration; hydration
E) isomerization; isomerization
A) oxidation; reduction
B) reduction; oxidation
C) hydration; dehydration
D) dehydration; hydration
E) isomerization; isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the following structure of isocitrate, the carbon labeled _____ is lost as CO2 by isocitrate dehydrogenase, and the carbon labeled _____ is lost as CO2 by -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. 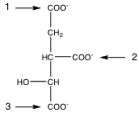
A) 1; 2
B) 2; 1
C) 1; 3
D) 3; 1
E) 2; 3

A) 1; 2
B) 2; 1
C) 1; 3
D) 3; 1
E) 2; 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Considering the reactions within the citric acid cycle, which of the following molecules will be produced from the intermediate pictured on the right? 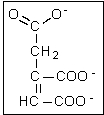
A) citrate
B) isocitrate
C) succinate
D) succinyl-CoA
E) -ketoglutarate

A) citrate
B) isocitrate
C) succinate
D) succinyl-CoA
E) -ketoglutarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
______ is the first compound that is oxidized in the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes a substrate-level phosphorylation?
A) malate synthase
B) succinate dehydrogenase
C) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
D) succinyl-CoA synthetase
E) fumarase
A) malate synthase
B) succinate dehydrogenase
C) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
D) succinyl-CoA synthetase
E) fumarase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
______ catalyzes a substrate-level phosphorylation reaction within the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following enzymes contains an FAD prosthetic group?
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) isocitrate dehydrogenase
C) succinate dehydrogenase
D) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
E) malate dehydrogenase
A) pyruvate dehydrogenase
B) isocitrate dehydrogenase
C) succinate dehydrogenase
D) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
E) malate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The oxidation of succinate to fumarate is best characterized as an oxidation of _____.
A) an alkane to an alkene
B) an alcohol to an aldehyde
C) an alcohol to a ketone
D) an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid
E) a -keto acid to CO2 and a carboxylic acid that is one carbon smaller
A) an alkane to an alkene
B) an alcohol to an aldehyde
C) an alcohol to a ketone
D) an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid
E) a -keto acid to CO2 and a carboxylic acid that is one carbon smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The reaction catalyzed by fumarase is _____.
A) an isomerization of an alcohol
B) a dehydration of an alcohol
C) a hydroxylation of an alkene
D) a hydration of an alkene
E) none of the above
A) an isomerization of an alcohol
B) a dehydration of an alcohol
C) a hydroxylation of an alkene
D) a hydration of an alkene
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How does the reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase proceed despite a G ' of 29.7 kJ/mol?
A) An elevated [H+] allows the reaction to proceed.
B) High levels of NAD+ allow the reaction to proceed.
C) Concentrations of oxaloacetate are kept very low by rapid use in the subsequent step.
D) The enzyme is unique in its ability to catalyze the reaction in only one direction.
E) The enzyme catalyzed reaction under cellular conditions has a much smaller energy of activation.
A) An elevated [H+] allows the reaction to proceed.
B) High levels of NAD+ allow the reaction to proceed.
C) Concentrations of oxaloacetate are kept very low by rapid use in the subsequent step.
D) The enzyme is unique in its ability to catalyze the reaction in only one direction.
E) The enzyme catalyzed reaction under cellular conditions has a much smaller energy of activation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is activated by ADP?
A) malate dehydrogenase
B) aconitase
C) isocitrate dehydrogenase
D) citrate synthase
E) succinyl-CoA synthetase
A) malate dehydrogenase
B) aconitase
C) isocitrate dehydrogenase
D) citrate synthase
E) succinyl-CoA synthetase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is inhibited by high levels of acetyl-CoA?
A) malate dehydrogenase
B) succinyl-CoA synthetase
C) pyruvate carboxylase
D) pyruvate dehydrogenase
E) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
A) malate dehydrogenase
B) succinyl-CoA synthetase
C) pyruvate carboxylase
D) pyruvate dehydrogenase
E) -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following can cause a large increase in the activity of the citric acid cycle?
A) activation of isocitrate dehydrogenase by ADP
B) activation of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase by Ca2+
C) increasing concentrations of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase
D) increasing concentrations of -ketoglutarate by transamination
E) all of the above
A) activation of isocitrate dehydrogenase by ADP
B) activation of -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase by Ca2+
C) increasing concentrations of oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase
D) increasing concentrations of -ketoglutarate by transamination
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following can be converted into glutamic acid in a single enzyme-catalyzed step?
A) isocitrate
B) oxaloacetate
C) malate
D) -ketoglutarate
E) succinyl-CoA
A) isocitrate
B) oxaloacetate
C) malate
D) -ketoglutarate
E) succinyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
_____ and pyruvate can be combined in an ATP-dependent reaction that regenerates one of the key intermediates in the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is an anaplerotic reaction that is often used in the cell?
A) conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
B) conversion of -ketoglutarate to glutamic acid
C) conversion of citrate to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA
D) conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate
E) conversion of succinyl-CoA to heme
A) conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
B) conversion of -ketoglutarate to glutamic acid
C) conversion of citrate to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA
D) conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate
E) conversion of succinyl-CoA to heme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the malate-aspartate shuttle, _____ is reduced to _____ in the cytosol.
A) aspartate; oxaloacetate
B) oxaloacetate; malate
C) aspartate; malate
D) malate; aspartate
E) malate; oxaloacetate
A) aspartate; oxaloacetate
B) oxaloacetate; malate
C) aspartate; malate
D) malate; aspartate
E) malate; oxaloacetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the malate aspartate shuttle, _____ is transferred into the mitochondria, and _____ is transferred to the cytosol.
A) NADH; NAD+
B) NAD+; NADH
C) malate; oxaloacetate
D) malate; aspartate
E) oxaloacetate; aspartate
A) NADH; NAD+
B) NAD+; NADH
C) malate; oxaloacetate
D) malate; aspartate
E) oxaloacetate; aspartate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Complexes I and II each transfer electrons to ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For eukaryotes, where are the complexes of electron transport located?
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) mitochondrial intermembrane space
D) inner mitochondrial membrane
E) mitochondrial matrix
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) mitochondrial intermembrane space
D) inner mitochondrial membrane
E) mitochondrial matrix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For every two electrons transferred from NADH to oxygen, _____ protons are pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The process of _____ allows electrons to be transferred between redox centers that are up to 1.4 nm apart.
A) reduction
B) swinging arm electron transfer
C) electron shuttling
D) electron teleporting
E) tunneling
A) reduction
B) swinging arm electron transfer
C) electron shuttling
D) electron teleporting
E) tunneling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What shuttle mechanism transfers cytosolic NADH into the mitochondria with a loss of reductive power, with the electrons entering the electron transport chain as ubiquinol instead of NADH?
A) glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle
B) alanine aminotransferase shuttle
C) malate-aspartate shuttle
D) adenine nucleotide shuttle
E) none of the above
A) glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle
B) alanine aminotransferase shuttle
C) malate-aspartate shuttle
D) adenine nucleotide shuttle
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The reduction potentials of all prosthetic groups of Complex I have reduction potentials between _____ and _____.
A) NAD+; ubiquinone
B) NADH; ubiquinol
C) FAD; ubiquinone
D) ubiquinone; oxygen
E) ubiquinone; cytochrome c
A) NAD+; ubiquinone
B) NADH; ubiquinol
C) FAD; ubiquinone
D) ubiquinone; oxygen
E) ubiquinone; cytochrome c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following represents the correct order of electron flow in Complex I?
A) NADH ubiquinone Fe-S clusters FMN
B) NADH Fe-S clusters FMN ubiquinone
C) NADH FMN ubiquinone Fe-S clusters
D) NADH FMN Fe-S clusters ubiquinone
E) NADH ubiquinone FMN Fe-S clusters
A) NADH ubiquinone Fe-S clusters FMN
B) NADH Fe-S clusters FMN ubiquinone
C) NADH FMN ubiquinone Fe-S clusters
D) NADH FMN Fe-S clusters ubiquinone
E) NADH ubiquinone FMN Fe-S clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How many protons are transported from the matrix to the intermembrane space by Complex I?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Ubiquinone is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane, and cytochrome c is found in the matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Complex III accepts electrons from _____ and transfers them to _____.
A) cytochrome c; cytochrome a
B) ubiquinol; cytochrome c
C) ubiquinone; cytochrome c
D) ubiquinol; cytochrome b
E) ubiquinone; cytochrome a
A) cytochrome c; cytochrome a
B) ubiquinol; cytochrome c
C) ubiquinone; cytochrome c
D) ubiquinol; cytochrome b
E) ubiquinone; cytochrome a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following results from the first round of the Q cycle?
A) two reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinone
B) one reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinone
C) one reduced cytochrome c, one reduced cytochrome B and one ubiquinone
D) two reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinol
E) one reduced cytochrome c and one semiquinone
A) two reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinone
B) one reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinone
C) one reduced cytochrome c, one reduced cytochrome B and one ubiquinone
D) two reduced cytochrome c and one ubiquinol
E) one reduced cytochrome c and one semiquinone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many cytochrome c molecules are oxidized by Complex IV for each molecule of oxygen that is reduced?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) It depends upon the efficiency of the electron transfer in Complex IV.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) It depends upon the efficiency of the electron transfer in Complex IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The cytochromes within Complex III all contain _____ groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic organisms?
A) NAD+
B) FAD
C) ubiquinone
D) varies from one organism to another
E) none of the above
A) NAD+
B) FAD
C) ubiquinone
D) varies from one organism to another
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Complex IV uses _____ and _____ ions to reduce oxygen to water.
A) manganese; iron
B) copper; iron
C) manganese; copper
D) zinc; copper
E) iron; zinc
A) manganese; iron
B) copper; iron
C) manganese; copper
D) zinc; copper
E) iron; zinc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following occurs when the catalytic subunit of ATP synthase is in the loose state?
A) ADP and Pi bind.
B) ADP and Pi are converted to ATP.
C) ATP is hydrolyzed.
D) ATP is released.
E) None of the above
A) ADP and Pi bind.
B) ADP and Pi are converted to ATP.
C) ATP is hydrolyzed.
D) ATP is released.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The imbalance of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane is referred to as _____.
A) the protonmotive force
B) the chemiosmotic force
C) the electron transport force
D) the ATP synthase force
E) the proton gradient force
A) the protonmotive force
B) the chemiosmotic force
C) the electron transport force
D) the ATP synthase force
E) the proton gradient force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the pH of the matrix is 7.7, what is the pH of the intermembrane space if the G for transport of H+ is 20 kJ/mol at 37 C with = 170 mV?
A) 2.6
B) 7.1
C) 8.3
D) 12.8
E) cannot be determined
A) 2.6
B) 7.1
C) 8.3
D) 12.8
E) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the G for the oxidation of NADH by oxygen is -220 kJ/mol and the G for transport of H+ across the inner membrane is 20 kJ/mol, what is the efficiency for energy captured in the proton gradient versus energy evolved from NADH oxidation?
A) 9.1%
B) 36%
C) 45%
D) 73%
E) 91%
A) 9.1%
B) 36%
C) 45%
D) 73%
E) 91%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



