Deck 6: Carbohydrates I
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Carbohydrates I
1
The molecular formula for a monosaccharide is _____.
A) CnH2n+2On
B) CnH2nOn.
C) CnH2nOn
D) CnH2n+2On.
E) none of the above
A) CnH2n+2On
B) CnH2nOn.
C) CnH2nOn
D) CnH2n+2On.
E) none of the above
CnH2nOn.
2
Glucose and galactose are _____ of each other.
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) diastereomers
D) anomers
E) none of the above
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) diastereomers
D) anomers
E) none of the above
epimers
3
Which of the monosaccharides seen below are L sugars? 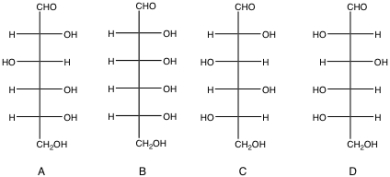
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) B and C
D) C and D
E) A, B and C

A) A and B
B) A and C
C) B and C
D) C and D
E) A, B and C
C and D
4
The structure below shows a Fischer projection of D-Idose.
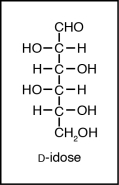 Which of the structures below represents -D-Idopyranose?
Which of the structures below represents -D-Idopyranose?
A)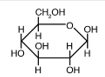
B)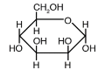
C)
D)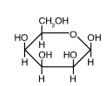
E)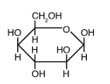
 Which of the structures below represents -D-Idopyranose?
Which of the structures below represents -D-Idopyranose?A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the following structure, which carbon is the anomeric carbon? 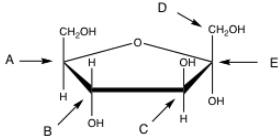
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The _____ sugars are monosaccharides in which a hydroxyl group is replaced with a hydrogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Any sugar that has a free aldehyde group is called a(n) _____.
A) reducing sugar
B) nonreducing sugar
C) ketose
D) aldohexose
E) alditol
A) reducing sugar
B) nonreducing sugar
C) ketose
D) aldohexose
E) alditol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Describe the properties, structures, and functions of the major categories of monosaccharides. 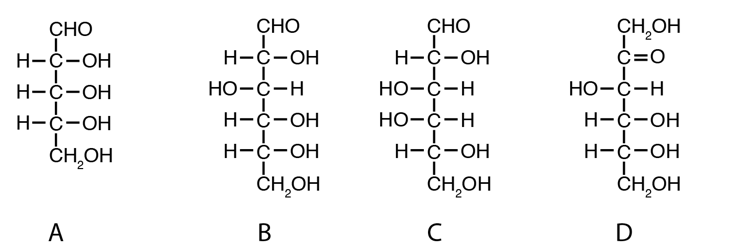
-Which structure(s) shown in the figure above represent reducing sugar(s)?
A) A
B) D
C) C and D
D) A, B, C, and D
E) A, B, and C

-Which structure(s) shown in the figure above represent reducing sugar(s)?
A) A
B) D
C) C and D
D) A, B, C, and D
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The disaccharide commonly found in dairy products is _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Amylopectin contains primarily _____ glycosidic bonds with _____ glycosidic bonds as branch points.
A) (1 4); (1 2)
B) (1 4); (1 6)
C) (1 4); (1 6)
D) (1 4); (1 4)
E) (1 4); (1 6)
A) (1 4); (1 2)
B) (1 4); (1 6)
C) (1 4); (1 6)
D) (1 4); (1 4)
E) (1 4); (1 6)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the major difference between glycogen and amylopectin?
A) Glycogen contains -glycosidic bonds; amylopectin contains -glycosidic bonds.
B) Glycogen is branched; amylopectin is linear.
C) Glycogen contains a reducing end; amylopectin does not.
D) Glycogen contains about twice the number of branch points as amylopectin.
E) Glycogen is found in plants; amylopectin is found in animals.
A) Glycogen contains -glycosidic bonds; amylopectin contains -glycosidic bonds.
B) Glycogen is branched; amylopectin is linear.
C) Glycogen contains a reducing end; amylopectin does not.
D) Glycogen contains about twice the number of branch points as amylopectin.
E) Glycogen is found in plants; amylopectin is found in animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following are characteristic of cellulose?
A) highly extended chains
B) (1 4) glycosidic bonds
C) extensive hydrogen bonding between individual molecules
D) unbranched polymer
E) all of the above
A) highly extended chains
B) (1 4) glycosidic bonds
C) extensive hydrogen bonding between individual molecules
D) unbranched polymer
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Unlike proteins and oligonucleotides, polysaccharides _____.
A) are readily metabolized in the absence of specialized enzymes
B) often have branched structures
C) are achiral
D) are always completely water soluble
E) are components of every known living organism
A) are readily metabolized in the absence of specialized enzymes
B) often have branched structures
C) are achiral
D) are always completely water soluble
E) are components of every known living organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
_____ is a homopolymer composed of (1-4)-linked N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine residues that is the principle structural component of the exoskeleton of various groups of invertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Both (1 4) and (1 6) bonds can be found in the plant product______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the catabolic pathway, major nutrients are _____ broken down mainly resulting in more _____ metabolites.
A) exergonically; reduced
B) endergonically; reduced
C) exergonically; oxidized
D) endergonically; oxidized
E) endergonically; phosphorylated
A) exergonically; reduced
B) endergonically; reduced
C) exergonically; oxidized
D) endergonically; oxidized
E) endergonically; phosphorylated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Energy is generated during _____, the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones, whereas energy is consumed during _____, the building of larger molecules from smaller ones.
A) reduction reactions; oxidation reactions
B) autotrophic reactions; heterotrophic reactions
C) catabolic reactions; anabolic reactions
D) hydrolysis reactions; condensation reactions
E) none of the above
A) reduction reactions; oxidation reactions
B) autotrophic reactions; heterotrophic reactions
C) catabolic reactions; anabolic reactions
D) hydrolysis reactions; condensation reactions
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The enzyme _____ is the major control point for glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The process of _____ converts glucose into _____.
A) electron transport; CO2
B) glycolysis; pyruvate
C) glycogenolysis; glycogen
D) gluconeogenesis; glycogen
E) glycogen synthesis; pyruvate
A) electron transport; CO2
B) glycolysis; pyruvate
C) glycogenolysis; glycogen
D) gluconeogenesis; glycogen
E) glycogen synthesis; pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following enzymes requires ATP as a substrate?
A) phosphofructokinase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) aldolase
D) triose phosphate isomerase
E) enolase
A) phosphofructokinase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) aldolase
D) triose phosphate isomerase
E) enolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which enzyme is responsible for splitting a hexose into two trioses?
A) enolase
B) phosphoglycerate mutase
C) phosphofructose isomerase
D) triose phosphate isomerase
E) aldolase
A) enolase
B) phosphoglycerate mutase
C) phosphofructose isomerase
D) triose phosphate isomerase
E) aldolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which enzyme catalyzes the major regulatory step of glycolysis?
A) hexokinase
B) aldolase
C) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
D) phosphofructokinase
E) phosphoglucose isomerase
A) hexokinase
B) aldolase
C) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
D) phosphofructokinase
E) phosphoglucose isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a potent activator of phosphofructokinase in mammals?
A) fructose-6-phosphate
B) glucose-6-phosphate
C) fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
D) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
E) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
A) fructose-6-phosphate
B) glucose-6-phosphate
C) fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
D) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
E) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The active site of aldolase contains a Lys residue that forms a(n) _____ and a(n) Asp residue that participates in _____ reactions.
A) amide; acid-base
B) Schiff base; acid-base
C) secondary amine; acid-base
D) amide; isomerization
E) Schiff base; isomerization
A) amide; acid-base
B) Schiff base; acid-base
C) secondary amine; acid-base
D) amide; isomerization
E) Schiff base; isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the reaction catalyzed by aldolase, the bond broken is between C-3 and C-4 of the substrate. Which functional groups are present on these two carbons (C-3 and C-4) in the products?
A) C-3 becomes an alcohol; C-4 becomes a carboxylic acid.
B) C-3 becomes an aldehyde; C-4 becomes a ketone.
C) C-3 becomes an aldehyde; C-4 becomes an alcohol.
D) C-3 becomes an alcohol; C-4 becomes an aldehyde.
E) C-3 becomes a ketone; C-4 becomes an alcohol.
A) C-3 becomes an alcohol; C-4 becomes a carboxylic acid.
B) C-3 becomes an aldehyde; C-4 becomes a ketone.
C) C-3 becomes an aldehyde; C-4 becomes an alcohol.
D) C-3 becomes an alcohol; C-4 becomes an aldehyde.
E) C-3 becomes a ketone; C-4 becomes an alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Triose phosphate isomerase catalyzes a reaction that is most like that of _____.
A) phosphoglycerate mutase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) hexokinase
D) aldolase
E) enolase
A) phosphoglycerate mutase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) hexokinase
D) aldolase
E) enolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the name for the process that produces ATP from ADP in glycolysis?
A) substrate-level phosphorylation
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) autophosphorylation
D) glycolytic phosphorylation
E) cytosolic phosphorylation
A) substrate-level phosphorylation
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) autophosphorylation
D) glycolytic phosphorylation
E) cytosolic phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 is oxidized to _____, which can transfer a phosphate to _____.
A) phosphoenolpyruvate; ADP
B) phosphoenolpyruvate; AMP
C) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; ADP
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; AMP
E) 3-phosphoglycerate; ADP
A) phosphoenolpyruvate; ADP
B) phosphoenolpyruvate; AMP
C) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; ADP
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; AMP
E) 3-phosphoglycerate; ADP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is phosphoglycerate kinase still considered a kinase even though ADP is converted to ATP?
A) The enzyme is freely reversible.
B) ATP is the ultimate source of the phosphate that is transferred to ADP.
C) The phosphate is transferred in conjunction with an oxidation reaction.
D) The reaction is metabolically irreversible.
E) None of the above
A) The enzyme is freely reversible.
B) ATP is the ultimate source of the phosphate that is transferred to ADP.
C) The phosphate is transferred in conjunction with an oxidation reaction.
D) The reaction is metabolically irreversible.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following compounds is used to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis?
A)
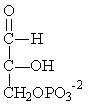
B)
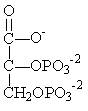
C)

D)
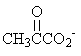
E)

A)
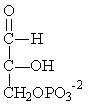
B)
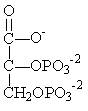
C)

D)
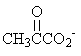
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What type of enzyme is enolase, which catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate and water?
A) transferase
B) hydrolase
C) ligase
D) lyase
E) oxidoreductase
A) transferase
B) hydrolase
C) ligase
D) lyase
E) oxidoreductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What sort of activity does fructose-1,6-bisphosphate have on pyruvate kinase?
A) no effect
B) competitive inhibitor
C) noncompetitive inhibitor
D) allosteric inhibitor
E) activator
A) no effect
B) competitive inhibitor
C) noncompetitive inhibitor
D) allosteric inhibitor
E) activator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following contains a bond that is used for a substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis?
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
B) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
C) acetyl phosphate
D) 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
E) 1-phosphoglycerate
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
B) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
C) acetyl phosphate
D) 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
E) 1-phosphoglycerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What regulatory enzyme of glycolysis is skipped during fructose metabolism?
A) hexokinase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) phosphofructokinase
D) pyruvate kinase
E) fructose metabolism does not skip any steps of glycolysis
A) hexokinase
B) phosphoglucose isomerase
C) phosphofructokinase
D) pyruvate kinase
E) fructose metabolism does not skip any steps of glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a cell were given glucose labeled at C-3 with 14C, which carbon(s) of pyruvate would contain the label?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What pathway is used to make glucose from other metabolites such as pyruvate or lactate?
A) glycogen synthesis
B) glycogen degradation
C) glycolysis
D) pentose phosphate pathway
E) gluconeogenesis
A) glycogen synthesis
B) glycogen degradation
C) glycolysis
D) pentose phosphate pathway
E) gluconeogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors by______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is true concerning the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase?
A) It is an oxidative decarboxylation.
B) It is activated by high concentrations of ATP.
C) The enzyme contains a pyridoxal phosphate prosthetic group.
D) The reaction is an anaplerotic reaction because it can replace citric acid intermediates that are removed for other pathways.
E) The enzyme contains two different types of subunits.
A) It is an oxidative decarboxylation.
B) It is activated by high concentrations of ATP.
C) The enzyme contains a pyridoxal phosphate prosthetic group.
D) The reaction is an anaplerotic reaction because it can replace citric acid intermediates that are removed for other pathways.
E) The enzyme contains two different types of subunits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following pyruvate dehydrogenase enzymes is correctly paired with the coenzyme that is associated with it?
A) E1: coenzyme A
B) E2: thiamine pyrophosphate
C) E3: FAD
D) E2: NAD+
E) E3: lipoamide
A) E1: coenzyme A
B) E2: thiamine pyrophosphate
C) E3: FAD
D) E2: NAD+
E) E3: lipoamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following coenzymes is directly responsible for the oxidation of the hydroxyethyl group to the acetyl group?
A) coenzyme A
B) thiamine pyrophosphate
C) FAD
D) NAD+
E) lipoamide
A) coenzyme A
B) thiamine pyrophosphate
C) FAD
D) NAD+
E) lipoamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What type of bond forms when the hydroxyethyl group is transferred to lipoamide?
A) ester
B) amide
C) thioester
D) anhydride
E) none of the above
A) ester
B) amide
C) thioester
D) anhydride
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
A) CoA
B) pyruvate
C) FADH2
D) NADH
E) CO2
A) CoA
B) pyruvate
C) FADH2
D) NADH
E) CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to _____ by pyruvate dehydrogenase.
A) oxaloacetate
B) ethanol
C) lactate
D) glucose
E) acetyl-CoA
A) oxaloacetate
B) ethanol
C) lactate
D) glucose
E) acetyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What cellular location contains pyruvate dehydrogenase and most of the citric acid cycle enzymes?
A) cytosol
B) mitochondrial matrix
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) outer mitochondrial membrane
A) cytosol
B) mitochondrial matrix
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) outer mitochondrial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Glycolysis forms _____ under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which enzyme has an intermediate of the form presented below? 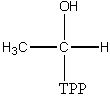
A) phosphofructokinase
B) aldolase
C) pyruvate dehydrogenase
D) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate decarboxylase
E) triose phosphate isomerase

A) phosphofructokinase
B) aldolase
C) pyruvate dehydrogenase
D) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate decarboxylase
E) triose phosphate isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



