Deck 19: Aerobic Gram-Positive Rods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Aerobic Gram-Positive Rods
1
The two genera, Bacillus and Clostridium, are similar in that both are
A) catalase positive.
B) strict anaerobes.
C) spore formers.
D) strict pathogens.
A) catalase positive.
B) strict anaerobes.
C) spore formers.
D) strict pathogens.
spore formers.
2
A physician suspects her patient has erysipeloid. She calls the laboratory for help with specimen selection and collection. You recommend she collect a
A) swab of infected skin surface.
B) nasopharyngeal swab.
C) swab of sinus tract drainage.
D) full thickness biopsy.
A) swab of infected skin surface.
B) nasopharyngeal swab.
C) swab of sinus tract drainage.
D) full thickness biopsy.
full thickness biopsy.
3
To diagnose diphtheria, the appropriate specimen for collection is a
A) pharyngeal swab.
B) portion of the membrane.
C) portion of the black scab.
D) swab of the contaminated medical device.
A) pharyngeal swab.
B) portion of the membrane.
C) portion of the black scab.
D) swab of the contaminated medical device.
pharyngeal swab.
4
Loeffler's medium is useful in making a presumptive identification of Corynebacterium diphtheriae from a pharyngeal culture because it
A) inhibits the growth of normal upper respiratory flora.
B) detects hydrogen sulfide production.
C) enhances metachromatic granule formation.
D) detects toxin-producing strains.
A) inhibits the growth of normal upper respiratory flora.
B) detects hydrogen sulfide production.
C) enhances metachromatic granule formation.
D) detects toxin-producing strains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Overlaying an agar plate with sterile olive oil ensures adequate growth of
A) Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae.
B) Arcanobacterium haemolyticum.
C) Lactobacillus spp.
D) Corynebacterium urealyticum.
A) Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae.
B) Arcanobacterium haemolyticum.
C) Lactobacillus spp.
D) Corynebacterium urealyticum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The breakdown of casein, tyrosine, and xanthine is used in differentiating ____________ spp.
A) Nocardia
B) Streptomyces
C) Actinomyces
D) Corynebacterium
A) Nocardia
B) Streptomyces
C) Actinomyces
D) Corynebacterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A positive reaction for the inverse CAMP test appears as an arrowhead of
A) non-hemolysis for Arcanobacterium haemolyticum when tested against Group B Streptococcus.
B) non-hemolysis for Corynebacterium ulcerans when tested against Staphylococcus aureus.
C) enhanced hemolysis for Arcanobacterium haemolyticum when tested against Group B Streptococcus.
D) enhanced hemolysis for Corynebacterium ulcerans when tested against Staphylococcus aureus
A) non-hemolysis for Arcanobacterium haemolyticum when tested against Group B Streptococcus.
B) non-hemolysis for Corynebacterium ulcerans when tested against Staphylococcus aureus.
C) enhanced hemolysis for Arcanobacterium haemolyticum when tested against Group B Streptococcus.
D) enhanced hemolysis for Corynebacterium ulcerans when tested against Staphylococcus aureus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Nocardia, Actinomyces, and Streptomyces spp. microscopically appear as
A) palisading, clubbed, gram-positive rods.
B) gram-variable rods.
C) branching gram-positive rods.
D) long, thin, gram-positive rods.
A) palisading, clubbed, gram-positive rods.
B) gram-variable rods.
C) branching gram-positive rods.
D) long, thin, gram-positive rods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Lactobacillus spp. typically produce colonies that are
A) white and chalky.
B) large, dry, and beta-hemolytic.
C) gray-white, translucent. with subtle beta-hemolysis.
D) pinpoint and alpha-hemolytic.
A) white and chalky.
B) large, dry, and beta-hemolytic.
C) gray-white, translucent. with subtle beta-hemolysis.
D) pinpoint and alpha-hemolytic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following tests can be used to identify Gardnerella vaginalis?
1) Catalase negative
2) Oxidase positive
3) Beta hemolysis on human blood agar
4) Beta hemolysis on sheep blood agar
5) Starch fermentation
A) 1, 2, 3, and 5
B) 2, 4, and 5
C) 1 and 3
D) 1, 3, and 5
1) Catalase negative
2) Oxidase positive
3) Beta hemolysis on human blood agar
4) Beta hemolysis on sheep blood agar
5) Starch fermentation
A) 1, 2, 3, and 5
B) 2, 4, and 5
C) 1 and 3
D) 1, 3, and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The only catalase-negative, gram-positive rod capable of producing hydrogen sulfide is also
A) intrinsically vancomycin resistant.
B) esculin positive.
C) motile.
D) gelatinase positive.
A) intrinsically vancomycin resistant.
B) esculin positive.
C) motile.
D) gelatinase positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A pinpoint, gray-white colony is isolated as >100,000 colonies/mL from the urine of an 89-year-old leukemic patient. The colony stains as palisading gram-positive rods. The organism should be
A) catalase negative and urea positive.
B) catalase positive and urea positive.
C) catalase negative and urea negative.
D) catalase positive and urea negative.
A) catalase negative and urea positive.
B) catalase positive and urea positive.
C) catalase negative and urea negative.
D) catalase positive and urea negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The gram-positive rod that produces an umbrella motility pattern in semisolid medium is also
A) catalase positive.
B) esculin negative.
C) non-hemolytic.
D) sodium hippurate negative.
A) catalase positive.
B) esculin negative.
C) non-hemolytic.
D) sodium hippurate negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The colonies of Streptococcus agalactiae and Listeria monocytogenes are nearly identical. The two organisms can be differentiated by the
A) sodium hippurate hydrolysis test.
B) CAMP factor test.
C) catalase test.
D) diseases they cause.
A) sodium hippurate hydrolysis test.
B) CAMP factor test.
C) catalase test.
D) diseases they cause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 20-year-old female presents with pharyngitis. The rapid group A Streptococcus screen is negative, and a blood agar plate is inoculated. After 24 hours incubation, a tiny gray colony with a narrow zone of beta-hemolysis is observed. The microbiologist performs a streptococcal serotype for group A and the result is negative. She should
A) perform a Gram stain and catalase test.
B) finalize the culture as "No Group A Streptococcus isolated."
C) repeat the streptococcal serotype after boiling the organism suspension.
D) perform an ELEK test.
A) perform a Gram stain and catalase test.
B) finalize the culture as "No Group A Streptococcus isolated."
C) repeat the streptococcal serotype after boiling the organism suspension.
D) perform an ELEK test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A large gram-positive rod was isolated from a hand wound of a farmer. Review the image provided to observe its colony. You would expect this organism to be
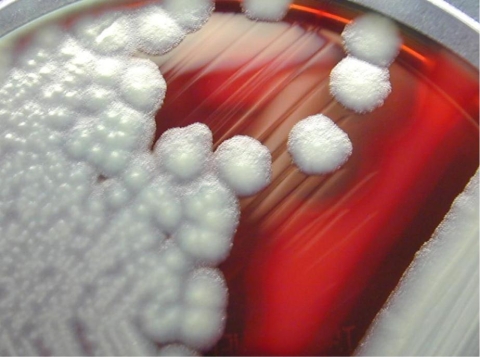 Source: CDC and Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory
Source: CDC and Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory
1) unable to grow on PEA.
2) motile.
3) susceptible to penicillin.
4) lecithinase positive.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1, 2, and 3
C) 2 and 4
D) 2, 3, and 4
 Source: CDC and Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory
Source: CDC and Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory1) unable to grow on PEA.
2) motile.
3) susceptible to penicillin.
4) lecithinase positive.
A) 1 and 4
B) 1, 2, and 3
C) 2 and 4
D) 2, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following organisms is not considered pathogenic until it has been infected by a bacteriophage?
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
C) C. diphtheriae
D) Actinomyces israelii
A) Bacillus anthracis
B) Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
C) C. diphtheriae
D) Actinomyces israelii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A blood culture reveals the Gram stain results observed in the image provided.
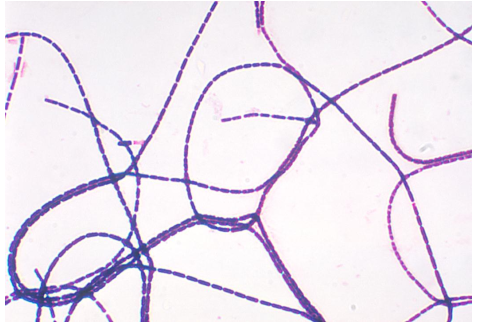 The microbiologist should
The microbiologist should
A) ignore this organism as a contaminant.
B) call the physician and report it as presumptive Bacillus anthracis.
C) suspect Clostridium spp. and plate to anaerobic media.
D) follow the CDC recommendations for the workup of a potential Bacillus anthracis.
 The microbiologist should
The microbiologist shouldA) ignore this organism as a contaminant.
B) call the physician and report it as presumptive Bacillus anthracis.
C) suspect Clostridium spp. and plate to anaerobic media.
D) follow the CDC recommendations for the workup of a potential Bacillus anthracis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The modified ELEK test is used to
A) detect the metachromatic granules of Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
B) identify C. diphtheriae.
C) detect toxin-producing strains of C. diphtheriae.
D) differentiate C. jeikeium and C. urealyticum.
A) detect the metachromatic granules of Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
B) identify C. diphtheriae.
C) detect toxin-producing strains of C. diphtheriae.
D) differentiate C. jeikeium and C. urealyticum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A leg wound from a 15-year-old male football player yields: Heavy growth of Staphylococcus aureus
Light growth of Staphylococcus not S. aureus
Light growth of Diphtheroids
Light growth of viridians Streptococcus
A) report the Staphylococcus aureus and call the other organisms normal skin flora.
B) report each of the organisms isolated individually.
C) perform further testing on the diphtheroids.
D) report all four organisms as normal skin flora.
Light growth of Staphylococcus not S. aureus
Light growth of Diphtheroids
Light growth of viridians Streptococcus
A) report the Staphylococcus aureus and call the other organisms normal skin flora.
B) report each of the organisms isolated individually.
C) perform further testing on the diphtheroids.
D) report all four organisms as normal skin flora.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Individuals infected with toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae must be treated with
A) penicillin.
B) DPT vaccine.
C) antitoxin.
D) a and c.
E) b and c.
A) penicillin.
B) DPT vaccine.
C) antitoxin.
D) a and c.
E) b and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A gray-white colony displaying subtle beta-hemolysis is isolated from a cerebrospinal fluid. The organism is a gram-positive rod that is catalase positive, motile at room temperature, and esculin positive. Which patient history is most likely associated with this culture?
A) 45-year-old female weaver
B) 2-day-old infant male delivered at 32 weeks gestation
C) 33-year-old female with recent dental surgery
D) 58-year-old cattle farmer
A) 45-year-old female weaver
B) 2-day-old infant male delivered at 32 weeks gestation
C) 33-year-old female with recent dental surgery
D) 58-year-old cattle farmer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



