Deck 4: The REA Enterprise Ontology: Business Process Modeling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The REA Enterprise Ontology: Business Process Modeling
1
The REA pattern can only be portrayed using entity-relationship modeling notation.
False
2
Conceptual modeling constructs include entities, relationships, attributes, and participation cardinalities.
True
3
Driver's license number would serve as a good primary key for the entity set Student.
False
4
A simple attribute is an attribute that cannot be further decomposed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The value of a volatile derivable attribute will not change if additional transaction data are entered into the database.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Typification is an abstraction relationship used to relate an entity set (A) in which the members are instances to an entity set (B) in which the members are categories into which the instances of set (A) belong. For example, typification relates the entity set Employee to the entity set Employee Category.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A minimum participation cardinality of zero for an entity set in a relationship indicates that an instance of that entity set cannot exist without a related instance of the related entity set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The REA core pattern completely describes the business processes of most enterprises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
To take advantage of script pattern thinking we need to sift away the details that make scripts different from each other and discover conceptual commonalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Claims in the REA ontology are timing differences between economic increment and economic decrement events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Preparation of a value chain level REA model accomplishes the first four steps of business process level REA modeling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assignment of attributes to entities in a business process level REA effectively communicates enterprise business rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a model that includes the entities Course and Student, in which many students enroll in the same course and in which a student can take several courses, the attribute grade earned by a student in a course should be assigned to the Student entity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Instances of a Cash entity in a business process level REA model typically are specific physical currency and coins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The heuristic for participation cardinalities of stockflow relationships assumes enterprises want to be able to enter data about resource types before they actually acquire them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
No heuristic has been identified for the participation cardinalities of duality relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For most enterprises, good business practice recommends a vendor selection policy that results in supplier information being entered into its system before allowing entry of any commitment or economic events involving the supplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A contract or mutual commitment event is one that commits two enterprises to engage in future economic events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Resource-agent and agent-agent relationships should be included in a business process level REA model only when those entities have associations that are independent of the events in which they mutually participate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Development of a five year business plan, deciding whether or not to design a new product, and deciding whether or not to change vendors are all examples of information process events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An "Inventory Type" entity has the following attributes: part name, supplier number, part number, purchase date, quantity on hand, and cost. Which attribute is the best primary key for the Inventory Type entity?
A) Cost
B) Quantity on hand
C) Supplier ID
D) Part number
E) Purchase date
A) Cost
B) Quantity on hand
C) Supplier ID
D) Part number
E) Purchase date

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Composite attributes
A) Must be stored in separate relations
B) Can have more than one instance
C) Should be combined into one aggregated attribute
D) Can and should be decomposed into separate attributes
E) Describe more than one entity instance
A) Must be stored in separate relations
B) Can have more than one instance
C) Should be combined into one aggregated attribute
D) Can and should be decomposed into separate attributes
E) Describe more than one entity instance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which term best describes relationship "A" below?

A) Stockflow
B) Generalization
C) Typification
D) Fulfillment
E) Duality

A) Stockflow
B) Generalization
C) Typification
D) Fulfillment
E) Duality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following conceptual representation 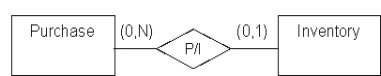
A) Says a purchase can consist of more than one of the same inventory item ID
B) Says one inventory item ID can be used for many specific units of the same type of inventory
C) Requires specific identification of each separate inventory item purchased
D) Says an inventory item ID can not be recorded in this database until it has been purchased
E) Says multiple units of one inventory item ID can be included on the same purchase

A) Says a purchase can consist of more than one of the same inventory item ID
B) Says one inventory item ID can be used for many specific units of the same type of inventory
C) Requires specific identification of each separate inventory item purchased
D) Says an inventory item ID can not be recorded in this database until it has been purchased
E) Says multiple units of one inventory item ID can be included on the same purchase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the corresponding conceptual model for Bumpkin's Manufacturing, indicate the one best answer from the choices below: 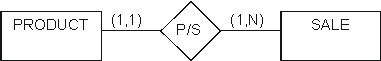
A) Bumpkin's builds custom products for each sale
B) Bumpkin's Manufacturing holds (stocks) product inventory
C) Bumpkin's sometimes re-acquires products it previously sold and then sells them again
D) Bumpkin's sales are for only one product
E) Bumpkin's records and tracks products only at the type level

A) Bumpkin's builds custom products for each sale
B) Bumpkin's Manufacturing holds (stocks) product inventory
C) Bumpkin's sometimes re-acquires products it previously sold and then sells them again
D) Bumpkin's sales are for only one product
E) Bumpkin's records and tracks products only at the type level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following conceptual representation in ER grammar format
Relationship: Leads-to
Connected Entities: (0,N) Sale
(0,1) Cash Receipt
Attributes: Amount Applied
A) Allows for accounts receivable
B) Indicates a sale will always be "paid in full" when a payment for that sale is made
C) Allows for installment payments
D) Both A and B above
E) Both A and C above
Relationship: Leads-to
Connected Entities: (0,N) Sale
(0,1) Cash Receipt
Attributes: Amount Applied
A) Allows for accounts receivable
B) Indicates a sale will always be "paid in full" when a payment for that sale is made
C) Allows for installment payments
D) Both A and B above
E) Both A and C above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the statements listed below is an accurate interpretation of one or more of the participation cardinalities as depicted between the "Sale Order" and "Shipment" events in the following conceptual model? 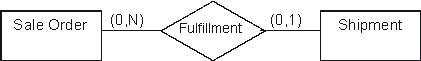
A) Each shipment can be associated with multiple sale orders
B) No shipment can be made without a valid sale order
C) No sale order can be taken without a prior shipment to the customer
D) A sale order can be fulfilled in multiple shipment events
E) Both A and B above are accurate interpretations of the depicted cardinalities

A) Each shipment can be associated with multiple sale orders
B) No shipment can be made without a valid sale order
C) No sale order can be taken without a prior shipment to the customer
D) A sale order can be fulfilled in multiple shipment events
E) Both A and B above are accurate interpretations of the depicted cardinalities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why are diamonds sometimes used to represent relationships in an REA diagram?
A) Because there is only one way to draw REA diagrams and that requires diamonds.
B) Because diamonds provide a place to label the relationships.
C) There is no reason to use diamonds.
D) Although people may want to use diamonds, they should not use diamonds because there is only one way to draw REA diagrams and that is without diamonds
E) Although people might want to use diamonds to represent relationships, they should in fact be using rectangles to represent the relationships - diamonds are supposed to be used to represent the resources, events, agents, and locations in REA modeling.
A) Because there is only one way to draw REA diagrams and that requires diamonds.
B) Because diamonds provide a place to label the relationships.
C) There is no reason to use diamonds.
D) Although people may want to use diamonds, they should not use diamonds because there is only one way to draw REA diagrams and that is without diamonds
E) Although people might want to use diamonds to represent relationships, they should in fact be using rectangles to represent the relationships - diamonds are supposed to be used to represent the resources, events, agents, and locations in REA modeling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When an event participates in a stock-flow relationship, which of the following is true?
A) The other participant in the relationship must be an event-type.
B) The other participant in the relationship must be an external agent.
C) The other participant in the relationship must be another event.
D) The other participant in the relationship must be an internal agent.
E) The other participant in the relationship must be a resource or resource-type.
A) The other participant in the relationship must be an event-type.
B) The other participant in the relationship must be an external agent.
C) The other participant in the relationship must be another event.
D) The other participant in the relationship must be an internal agent.
E) The other participant in the relationship must be a resource or resource-type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identifying external agents is associated with which essential characteristic of business events?
A) What happened?
B) When did it occur?
C) Who was involved and what roles did they play?
D) What resources were involved and how much?
E) Where did the event occur?
A) What happened?
B) When did it occur?
C) Who was involved and what roles did they play?
D) What resources were involved and how much?
E) Where did the event occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A retail store customer takes her merchandise to the counter. The clerk scans the item's control tag to enter the price. The customer pays cash for the merchandise. The customer then exits the store with her package. The internal agent involved in these business events is:
A) The customer
B) The clerk
C) The retail store manager
D) The shipping agent
E) Both A and B above are internal agents involved in these events.
A) The customer
B) The clerk
C) The retail store manager
D) The shipping agent
E) Both A and B above are internal agents involved in these events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the five "Journalism 101" questions does the Duality relationship typically answer in a business process level REA model?
A) What resources were involved in an event and how much of each resource were involved?
B) When did an event occur?
C) Who was involved in an event and what roles did they play?
D) Why did an event occur?
E) Where did an event occur?
A) What resources were involved in an event and how much of each resource were involved?
B) When did an event occur?
C) Who was involved in an event and what roles did they play?
D) Why did an event occur?
E) Where did an event occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Heuristic cardinalities for stockflow relationships are typically
A) (1,1) Resource Type - (0,N) Economic Event
B) (0,N) Resource Type - (1,1) Economic Event
C) (0,1) Resource Type - (1,1) Economic Event
D) (0,N) Resource Type - (1,N) Economic Event
E) (1,N) Resource Type - (0,1) Economic Event
A) (1,1) Resource Type - (0,N) Economic Event
B) (0,N) Resource Type - (1,1) Economic Event
C) (0,1) Resource Type - (1,1) Economic Event
D) (0,N) Resource Type - (1,N) Economic Event
E) (1,N) Resource Type - (0,1) Economic Event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a sale must involve either an inventory type or a service, the minimum participation cardinality on the Sale entity in its relationship with the Inventory Type entity should be
A) 1
B) 0
C) N
D) M
E) Q
A) 1
B) 0
C) N
D) M
E) Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The participation cardinalities of a relationship between an external agent and a noncash economic event (such as a sale) are most often: 
A) External Agent (0,N) - participation - (1,1) Economic Event
B) External Agent (1,1) - participation - (0,N) Economic Event
C) External Agent (0,1) - participation - (1,1) Economic Event
D) External Agent (0,N) - participation - (1,N) Economic Event
E) External Agent (1,N) - participation - (0,1) Economic Event

A) External Agent (0,N) - participation - (1,1) Economic Event
B) External Agent (1,1) - participation - (0,N) Economic Event
C) External Agent (0,1) - participation - (1,1) Economic Event
D) External Agent (0,N) - participation - (1,N) Economic Event
E) External Agent (1,N) - participation - (0,1) Economic Event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following describes a common exception to the heuristic of 1 as the minimum participation cardinality on the acquisition economic event in a stockflow relationship?
A) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are combined into one entity set, whereas the resources are separated into two entity sets.
B) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are combined into one entity set and the two kinds of resources are also combined into one entity set.
C) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are separated into two entity sets and the two kinds of resources are also separated into two entity sets
D) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are separated into two entity sets; whereas the resources are combined into one entity set
E) There is never an exception to the heuristic of 1 as the minimum participation cardinality on the acquisition economic event in a stockflow relationship.
A) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are combined into one entity set, whereas the resources are separated into two entity sets.
B) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are combined into one entity set and the two kinds of resources are also combined into one entity set.
C) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are separated into two entity sets and the two kinds of resources are also separated into two entity sets
D) Acquisitions of two kinds of resources are separated into two entity sets; whereas the resources are combined into one entity set
E) There is never an exception to the heuristic of 1 as the minimum participation cardinality on the acquisition economic event in a stockflow relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a REA model, a relationship between two events
A) Sometimes reflects the fact that one of the events fulfills the other event
B) Is always a stock-flow relationship
C) Is always a duality relationship
D) Is always a control relationship
E) Requires that both events are also related to the same internal agent
A) Sometimes reflects the fact that one of the events fulfills the other event
B) Is always a stock-flow relationship
C) Is always a duality relationship
D) Is always a control relationship
E) Requires that both events are also related to the same internal agent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Management activities can be broadly categorized into
A) Planning, controlling, and evaluating
B) Identifying, measuring, and accumulating
C) Controlling, measuring, and identifying
D) Executing, controlling, and measuring
E) Preparing, analyzing, and maintaining
A) Planning, controlling, and evaluating
B) Identifying, measuring, and accumulating
C) Controlling, measuring, and identifying
D) Executing, controlling, and measuring
E) Preparing, analyzing, and maintaining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Information process events include
A) Providing goods and services to customers
B) Recording and maintaining data about an organization and its business activities
C) Reporting useful information to those who plan, control, and evaluate the business processes
D) Acquiring and paying for input resources, converting inputs into finished goods and services, and selling and collecting payment from customers for goods and services provided
E) Both B and C above
A) Providing goods and services to customers
B) Recording and maintaining data about an organization and its business activities
C) Reporting useful information to those who plan, control, and evaluate the business processes
D) Acquiring and paying for input resources, converting inputs into finished goods and services, and selling and collecting payment from customers for goods and services provided
E) Both B and C above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Operating events include
A) Capturing, storing, combining, summarizing, and organizing data into information that is meaningful to management in a decision-making activity
B) Recording and maintaining data about an organization and its business activities
C) Reporting useful information to those who execute, control, and evaluate the business processes
D) Acquiring and paying for input resources, converting inputs into finished goods and services, and selling and collecting payment from customers for goods and services provided
E) Both B and C above
A) Capturing, storing, combining, summarizing, and organizing data into information that is meaningful to management in a decision-making activity
B) Recording and maintaining data about an organization and its business activities
C) Reporting useful information to those who execute, control, and evaluate the business processes
D) Acquiring and paying for input resources, converting inputs into finished goods and services, and selling and collecting payment from customers for goods and services provided
E) Both B and C above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What general conceptual modeling constructs are included in a business process level REA model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What characteristics must a primary key attribute have?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Draw an entity-relationship segment with minimum and maximum cardinalities to represent the following. A purchase order may be placed by any one of Noname Company's five buyers. Buyers are added to the database as soon as they are hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Draw an entity-relationship segment with minimum and maximum cardinalities to represent the relationship between purchase order and purchase based on the following narrative description. Purchases result only from purchase orders. Partial shipments are accepted (e.g. if some of the goods ordered are out of stock and will be shipped as soon as they are in). If goods ordered are unavailable from one vendor, a new purchase order will be placed with a different vendor. If two different purchase orders are placed with the same vendor, that vendor may fill them with a single shipment and invoice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain the information provided by the minimum and maximum cardinalities in the following conceptual model segment
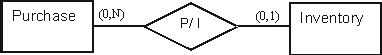


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is a claim in the REA enterprise ontology? Provide two examples of claims.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the heuristic cardinalities for stockflow relationships involving specifically identified resources?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The heuristic cardinalities on participation relationships are (1,1) Economic event - (0,N) Agent. What is a common exception that changes the mandatory participation to optional if the relationship involves external agents?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What are the three main types of activities that make up information process events?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe the seven steps needed to create a core pattern business level REA model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the five Journalism 101 questions about events, and how are they answered in a business process level REA model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
China U-Town is a very successful restaurant that delivers Chinese food to customers in a medium-sized city that has a large public university. China U-Town has four locations, one on each side of town (north, south, east, and west) in order to provide quick delivery (30 minutes or less, or the customer gets $5 off) and delicious food to the majority of the city. China U-Town's owner, Laura, frequently generates and analyzes reports that give her information about her company's competitors and customers. Using these reports, Laura decides whether to change the menu items and prices, delivery areas, etc. She is able to gauge relative performance of the four store locations. China U-Town has approximately sixty employees. Order clerks take customer orders over the telephone and instruct the cooks as to what they need prepared. The cooks prepare the requested food and give it to the order clerks who package it for delivery. Delivery people take the final packaged orders to the customers' residences using company owned delivery vehicles. Customers pay the delivery people either by check or with cash. Delivery people return a copy of the delivery ticket along with the customer's remittance to the company's order clerk who records the cash receipt using the company's electronic cash register. Each days' receipts are totaled and Laura decides into which of China U-Town's bank accounts those receipts should be deposited.
Required: List the operating events and the decision/management events discussed in this example.
Required: List the operating events and the decision/management events discussed in this example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Bill's Bells is a company that sells several kinds of bells to customers. Offered are cow bells, sleigh bells, dinner bells, bicycle bells, etc. Each bell style comes in various sizes. Bill is the chief purchasing agent for Bill's Bells, but there are several other purchasing agents as well. Bill prefers certain vendors for different bells; for instance he likes to buy cow bells from Bessie's Wholesale Bells. However, he sometimes purchases cow bells from Farm-time Follies. He has one preferred vendor and at least one back-up vendor for each type of bell. A vendor can be the preferred vendor for more than one kind of bell. Bill pays for all purchases made from a vendor during a given month on the last day of that month. Bill has several salespeople who are paid on commission. If a customer's assigned salesperson is not working when the customer comes in, another salesperson may assist that customer. The resulting commission would be split between the two salespeople. No sale is allowed without the customer paying at least 25% down at the time of the sale. Most customers pay the 25%, then make 3 more equal monthly installments. Some customers pay in full at the time of the sale. Cashiers process all cash receipts and cash disbursements. Bill's Bells has several different types of cash accounts into which cash receipts are deposited.
Required: Prepare business process level REA models with entities and relationships only to represent Bill's Bells acquisition/payment and sales/collection processes.
Required: Prepare business process level REA models with entities and relationships only to represent Bill's Bells acquisition/payment and sales/collection processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hamster Essentials Corporation (HEC) sells hamster furniture and accessories (which also can be used for gerbils). Its customers are retail stores who often purchase a number of different furniture and accessory items at the same time. The products are not unique, and they are identified by type (e.g., hamster chairs, hamster desks, hamster collars, etc.). Each retail store is assigned a salesperson based on geographic location. Salespeople receive a commission for each sale made to an assigned store. A store is assigned to only one salesperson, and the average salesperson works with 35 different stores. HEC bills customers for each sale, and the customers are required to pay the amount in full within 10 days. Customers must pay for each sale with a separate check; checks are processed by cashiers. All employees and customers are added to the database before any transactions involving them are entered. HEC has cash receipts from activities that are not included in this process (e.g. loans) but that will be entered into the company's enterprise-wide database.
Required: Prepare a business process level REA model for this process, with entities, relationships, and participation cardinalities. You need not assign any attributes.
Required: Prepare a business process level REA model for this process, with entities, relationships, and participation cardinalities. You need not assign any attributes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Charlie's Computer Repair Services, LLC (CCRS) is a limited liability company that provides computer repair services to customers. These repair services may involve just labor (e.g. resolving a hardware device conflict) or may involve replacing parts. CCRS stocks a supply of spare parts to use in its repairs. CCRS offers many different types of repair services, and a customer's repair service engagement may reflect more than one type. For example, a customer may request to have a monitor repaired and a hard disk replaced at the same time. However, if the customer has more than one computer to be repaired, repairs on the separate computers must be written up on different invoices. For example, if a customer brought in a desktop computer and a laptop computer, all repairs made to the desktop computer would be reflected on one invoice, and all repairs made to the laptop computer would be reflected on a second invoice. CCRS's repair people specialize in different types of service, therefore more than one employee may need to participate in a repair service engagement. For example, employees Jim and Sarah both specialize in video/monitor problems. Jamie, Emily, or Dale can handle problems with disk drives (hard or floppy). CCRS has several sales clerks who are responsible for bringing in repair service engagements, and for processing the resulting cash receipts. These sales clerks are not assigned to particular customers, and they never work together to accomplish a transaction. Customers are required to make a deposit of 50% of the estimated charges before the repair services are begun. The customers are required to pay the balance of the bill before they can retrieve their computer(s). All cash receipts for a particular day are deposited into one of several bank accounts owned by CCRS; which account they are deposited into rotates from day to day. NOTE: CCRS has specifically requested to keep repair people and sales clerks in separate tables (i.e., do NOT make one combined employee table).
Required: Prepare a business process level REA model with entities, relationships, cardinalities, and attributes. Use all the attributes in the following list in your model; do not add or subtract any attributes. If any of the attributes are derivable, describe how they can be derived and note whether they are static or volatile derivable attributes.

Required: Prepare a business process level REA model with entities, relationships, cardinalities, and attributes. Use all the attributes in the following list in your model; do not add or subtract any attributes. If any of the attributes are derivable, describe how they can be derived and note whether they are static or volatile derivable attributes.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



