Deck 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/9
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts
1
The number of standard deviations z that a particular value of r is from the mean 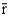 can be computed as
can be computed as 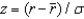 .Suppose that you work as a commission-only insurance agent earning $1,000 per week on average. Suppose that your standard deviation of weekly earnings is $500. What is the probability that you zero in a week? Use the following brief z-table to help with this problem.
.Suppose that you work as a commission-only insurance agent earning $1,000 per week on average. Suppose that your standard deviation of weekly earnings is $500. What is the probability that you zero in a week? Use the following brief z-table to help with this problem. 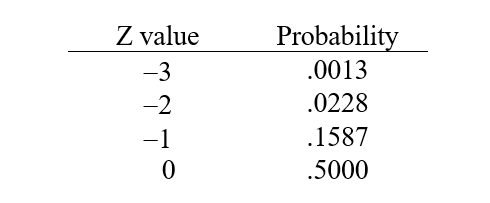
A) 1.3% chance of earning nothing in a week
B) 2.28% chance of earning nothing in a week
C) 15.87% chance of earning nothing in a week
D) 50% chance of earning nothing in a week
E) none of the above
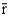 can be computed as
can be computed as 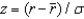 .Suppose that you work as a commission-only insurance agent earning $1,000 per week on average. Suppose that your standard deviation of weekly earnings is $500. What is the probability that you zero in a week? Use the following brief z-table to help with this problem.
.Suppose that you work as a commission-only insurance agent earning $1,000 per week on average. Suppose that your standard deviation of weekly earnings is $500. What is the probability that you zero in a week? Use the following brief z-table to help with this problem. 
A) 1.3% chance of earning nothing in a week
B) 2.28% chance of earning nothing in a week
C) 15.87% chance of earning nothing in a week
D) 50% chance of earning nothing in a week
E) none of the above
2.28% chance of earning nothing in a week
2
Consider an investment with the following payoffs and probabilities:  Determine the expected return for this investment.
Determine the expected return for this investment.
A) 1,300
B) 1,500
C) 1,700
D) 2,000
E) 3,000
 Determine the expected return for this investment.
Determine the expected return for this investment.A) 1,300
B) 1,500
C) 1,700
D) 2,000
E) 3,000
1,500
3
An investment advisor plans a portfolio your 85 year old risk-averse grandmother. Her portfolio currently consists of 60% bonds and 40% blue chip stocks. This portfolio is estimated to have an expected return of 6% and with a standard deviation 12%. What is the probability that she makes less than 0% in a year? [A portion of Appendix B1 is given below, where z = (x - , with as the mean and as the standard deviation.] ![<strong>An investment advisor plans a portfolio your 85 year old risk-averse grandmother. Her portfolio currently consists of 60% bonds and 40% blue chip stocks. This portfolio is estimated to have an expected return of 6% and with a standard deviation 12%. What is the probability that she makes less than 0% in a year? [A portion of Appendix B1 is given below, where z = (x - \mu , with \mu as the mean and \sigma as the standard deviation.] </strong> A) 2.28% B) 6.68% C) 15.87% D) 30.85% E) 50%](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9871/11ee6b54_f513_e349_9407_67478d0bfe2b_TB9871_00.jpg)
A) 2.28%
B) 6.68%
C) 15.87%
D) 30.85%
E) 50%
![<strong>An investment advisor plans a portfolio your 85 year old risk-averse grandmother. Her portfolio currently consists of 60% bonds and 40% blue chip stocks. This portfolio is estimated to have an expected return of 6% and with a standard deviation 12%. What is the probability that she makes less than 0% in a year? [A portion of Appendix B1 is given below, where z = (x - \mu , with \mu as the mean and \sigma as the standard deviation.] </strong> A) 2.28% B) 6.68% C) 15.87% D) 30.85% E) 50%](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB9871/11ee6b54_f513_e349_9407_67478d0bfe2b_TB9871_00.jpg)
A) 2.28%
B) 6.68%
C) 15.87%
D) 30.85%
E) 50%
30.85%
4
Complete the following table. 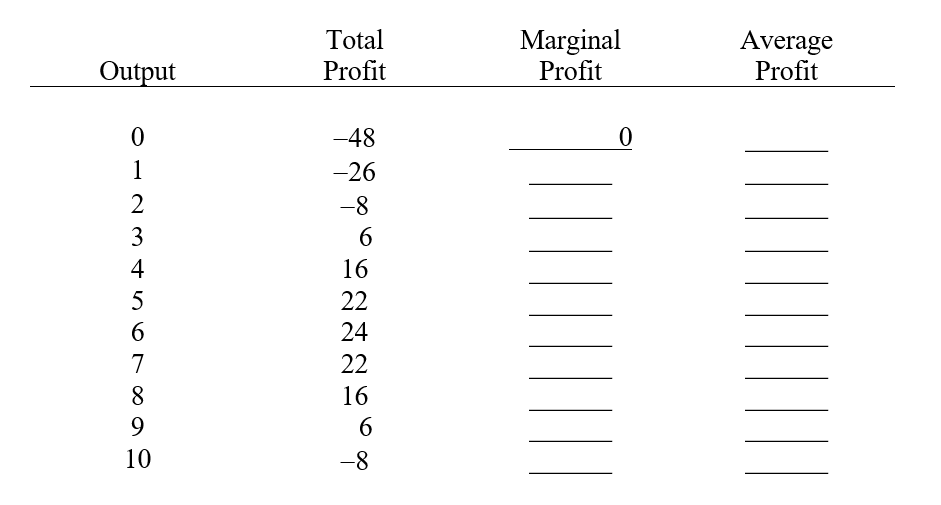


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A firm has decided to invest in a piece of land. Management has estimated that the land can be sold in 5 years for the following possible prices: 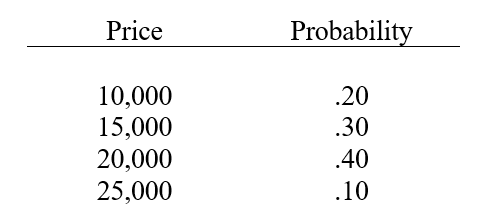 (a)Determine the expected selling price for the land.
(a)Determine the expected selling price for the land.
(b)Determine the standard deviation of the possible sales prices.
(c)Determine the coefficient of variation.
 (a)Determine the expected selling price for the land.
(a)Determine the expected selling price for the land.(b)Determine the standard deviation of the possible sales prices.
(c)Determine the coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A Real Option Value is:
A) An option that been deflated by the cost of living index makes it a "real" option.
B) An opportunity cost of capital.
C) An opportunity to implement a new cost savings or revenue expansion activity that arises from business plans that the managers adopt.
D) An objective function and a decision rule that comes from it.
E) Both a and b.
A) An option that been deflated by the cost of living index makes it a "real" option.
B) An opportunity cost of capital.
C) An opportunity to implement a new cost savings or revenue expansion activity that arises from business plans that the managers adopt.
D) An objective function and a decision rule that comes from it.
E) Both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following will increase (V0), the shareholder wealth maximization model of the firm:V0.(shares outstanding) = t = 1 ( t) / (1 + ke)t + Real Option Value.
A) Decrease the required rate of return (ke).
B) Decrease the stream of profits ( t).
C) Decrease the number of periods from to 10 periods.
D) Decrease the real option value.
E) All of the above.
A) Decrease the required rate of return (ke).
B) Decrease the stream of profits ( t).
C) Decrease the number of periods from to 10 periods.
D) Decrease the real option value.
E) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Recently, the American Medical Association changed its recommendations on the frequency of pap-smear exams for women. The new frequency recommendation was designed to address the family histories of the patients. The optimal frequency should be where the marginal benefit of an additional pap-test:
A) equals zero.
B) is greater than the marginal cost of the test
C) is lower than the marginal cost of an additional test
D) equals the marginal cost of the test
E) both a and b.
A) equals zero.
B) is greater than the marginal cost of the test
C) is lower than the marginal cost of an additional test
D) equals the marginal cost of the test
E) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What are the expected net profits to Johnson & Johnson in a pharmaceutical R&D joint venture with Amgen given the following joint profit payoffs. The joint profit payoffs are the difference between $180 and the sum of the cost realizations. Assume that the three columns are equally likely to occur, each row is equally likely to occur. Both Johnson and Johnson and Amgen can cancel the project and both will then earn $0 if the cost revelations give early warning of losses. 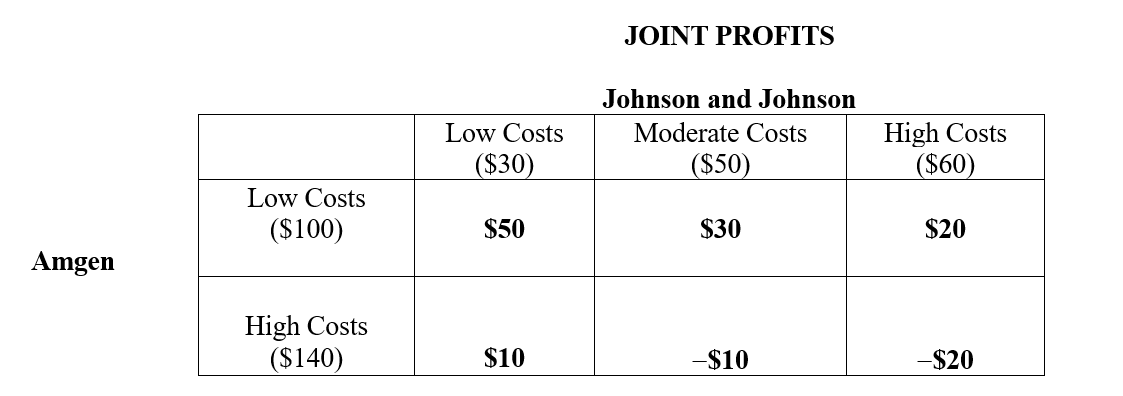 The figures in parentheses represent costs associated with the Low, Moderate and High cost realizations, and all figures are in millions.
The figures in parentheses represent costs associated with the Low, Moderate and High cost realizations, and all figures are in millions.
 The figures in parentheses represent costs associated with the Low, Moderate and High cost realizations, and all figures are in millions.
The figures in parentheses represent costs associated with the Low, Moderate and High cost realizations, and all figures are in millions.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 9 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



