Deck 21: Nuclear Reactions and Their Role in Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Nuclear Reactions and Their Role in Chemistry
1
The conversion of mass to energy is measurable only in
A)chemiluminescent transformations.
B)exothermic reactions.
C)explosive chemical reactions.
D)spontaneous processes.
E)nuclear reactions.
A)chemiluminescent transformations.
B)exothermic reactions.
C)explosive chemical reactions.
D)spontaneous processes.
E)nuclear reactions.
nuclear reactions.
2
The conversion of energy to mass is only in
A)chemiluminescent transformations.
B)exothermic reactions.
C)explosive chemical reactions.
D)spontaneous processes.
E)nuclear reactions.
A)chemiluminescent transformations.
B)exothermic reactions.
C)explosive chemical reactions.
D)spontaneous processes.
E)nuclear reactions.
nuclear reactions.
3
If you add energy to an electron, you can get it to move faster. This can be done using electromagnetic fields. If an electron is given energy in the amount of 220,000 eV (an electron volt unit of energy)it can reach speeds of 2.70 × 108 m/s. At this speed what would the mass of an electron be? An electron has a rest mass of 9.109 × 10-28 g.
A)2.10 × 10-30 g
B)2.46 × 10-19 g
C)3.37 × 10-36 g
D)2.10 × 10-27 g
E)9.109 × 10-28 g
A)2.10 × 10-30 g
B)2.46 × 10-19 g
C)3.37 × 10-36 g
D)2.10 × 10-27 g
E)9.109 × 10-28 g
2.10 × 10-27 g
4
During a nuclear fusion reaction, it is possible to produces neutrons with 14.1 MeV (mega-electron volts). This results in neutrons with a speed approaching 52,000 km/s. At this speed what is the mass of a neutron. The rest mass of a neutron is 1.675 × 10-24 g.
A)1.68 × 10-24 g
B)1.70 × 10-24 g
C)3.22 × 10-32 g
D)8.71 × 10-20 g
E)8.71 × 10-17 g
A)1.68 × 10-24 g
B)1.70 × 10-24 g
C)3.22 × 10-32 g
D)8.71 × 10-20 g
E)8.71 × 10-17 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A certain chemical reaction results in the release of 4295 kJ of energy. The loss of mass from this type of reaction would be equal to
A)1.29 × 1012 kg.
B)1.40 × 10-5 kg.
C)4.78 × 10-11 kg.
D)1.40 × 10-2 kg.
E)4.78 × 10-14 kg.
A)1.29 × 1012 kg.
B)1.40 × 10-5 kg.
C)4.78 × 10-11 kg.
D)1.40 × 10-2 kg.
E)4.78 × 10-14 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A certain chemical reaction results in the release of 365 kJ of energy. The loss of mass from this type of reaction would be equal to
A)1.22 × 10-6 kg.
B)4.06 × 10-12 kg.
C)1.22 × 10-3 kg.
D)1.09 × 1011 kg.
E)4.06 × 10-15 kg.
A)1.22 × 10-6 kg.
B)4.06 × 10-12 kg.
C)1.22 × 10-3 kg.
D)1.09 × 1011 kg.
E)4.06 × 10-15 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 4He nucleus weighs 4.002602 u. Calculate the mass defect of the nucleus in amu.
A)0.029281 u
B)1.98666 u
C)2.6316 u
D)0.001388 u
E)0.058562 u
A)0.029281 u
B)1.98666 u
C)2.6316 u
D)0.001388 u
E)0.058562 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 4He nucleus weighs 4.002602 u. Calculate the total binding energy of the nucleus.
A)1.66 × 10-7 joule
B)2.27 × 10-12 joule
C)3.86 × 10-11 joule
D)4.38 × 10-12 joule
E)4.38 × 10-10 joule
A)1.66 × 10-7 joule
B)2.27 × 10-12 joule
C)3.86 × 10-11 joule
D)4.38 × 10-12 joule
E)4.38 × 10-10 joule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which isotope has the maximum binding energy per nucleon, that is, it lies at the maximum in the binding energy per nucleon curve?
A)251Cf
B)197Au
C)56Fe
D)1H
E)4He
A)251Cf
B)197Au
C)56Fe
D)1H
E)4He

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 19F nucleus weighs 18.9984032 u. Calculate the mass defect of the nucleus in amu.
A)16.9825 u
B)0.16623 u
C)0.13985 u
D)0.15373 u
E)0.15235 u
A)16.9825 u
B)0.16623 u
C)0.13985 u
D)0.15373 u
E)0.15235 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 19F nucleus weighs 18.9984032 u. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon for this nucleus.
A)1.208 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
B)2.368 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
C)4.735 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
D)6.230 × 10-13 joule/nucleon
E)8.307 × 10-13 joule/nucleon
A)1.208 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
B)2.368 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
C)4.735 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
D)6.230 × 10-13 joule/nucleon
E)8.307 × 10-13 joule/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 75As nucleus weighs 74.92160 u. Calculate the mass defect of the nucleus in amu.
A)0.682450 u
B)0.078400 u
C)0.728269 u
D)0.624135 u
E)0.669954 u
A)0.682450 u
B)0.078400 u
C)0.728269 u
D)0.624135 u
E)0.669954 u

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 75As nucleus weighs 74.92160 u. Calculate the total binding energy of the nucleus.
A)1.464 × 10-7 joule
B)1.019 × 10-9 joule
C)2.090 × 10-9 joule
D)6.235 × 10-12 joule
E)1.255 × 10-7 joule
A)1.464 × 10-7 joule
B)1.019 × 10-9 joule
C)2.090 × 10-9 joule
D)6.235 × 10-12 joule
E)1.255 × 10-7 joule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 103Rh nucleus weighs 102.90550 u. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon for this nucleus.
A)2.442 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
B)1.340 × 10-12 joule /nucleon
C)2.0239 × 10-9 joule/nucleon
D)2.442 × 10-9 joule/nucleon
E)2.0239 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
A)2.442 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
B)1.340 × 10-12 joule /nucleon
C)2.0239 × 10-9 joule/nucleon
D)2.442 × 10-9 joule/nucleon
E)2.0239 × 10-11 joule/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 31P nucleus weighs 30.973761 u. Calculate the total binding energy of the nucleus.
A)2.662 × 10-11 joule
B)2.801 × 10-12 joule
C)1.0978 × 10-10 joule
D)4.090 × 10-11 joule
E)4.212 × 10-8 joule
A)2.662 × 10-11 joule
B)2.801 × 10-12 joule
C)1.0978 × 10-10 joule
D)4.090 × 10-11 joule
E)4.212 × 10-8 joule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 197Au nucleus weighs 196.96655 u. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (nuclear particle)for this nucleus.
A)2.498 × 10-10 joule/nucleon
B)1.236 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
C)3.567 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
D)2.117 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
E)3.162 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
A)2.498 × 10-10 joule/nucleon
B)1.236 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
C)3.567 × 10-11 joule/nucleon
D)2.117 × 10-12 joule/nucleon
E)3.162 × 10-12 joule/nucleon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following best describes the source of energy from nuclear reactions?
A)The energy comes from the breaking of chemical bonds to form different molecules.
B)The energy comes from movements of electrons between orbitals.
C)The energy comes from the fact that nuclides are more stable in a nucleus than as individual atomic particles, thus resulting in lower energy and mass than individual particles.
D)The energy comes from the absorption of gamma radiation produced by neutrinos.
E)There is no energy change in nuclear reactions.
A)The energy comes from the breaking of chemical bonds to form different molecules.
B)The energy comes from movements of electrons between orbitals.
C)The energy comes from the fact that nuclides are more stable in a nucleus than as individual atomic particles, thus resulting in lower energy and mass than individual particles.
D)The energy comes from the absorption of gamma radiation produced by neutrinos.
E)There is no energy change in nuclear reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The nuclear particle that is described by the symbol, 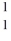 H, is a(n)
H, is a(n)
A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.
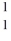 H, is a(n)
H, is a(n)A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The nuclear particle that is described by the symbol, 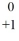 e, is a(n)
e, is a(n)
A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.
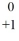 e, is a(n)
e, is a(n)A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The nuclear particle that is described by the symbol, 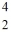 He, is a(n)
He, is a(n)
A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.
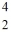 He, is a(n)
He, is a(n)A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The nuclear particle that is described by the symbol, 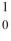 n, is a(n)
n, is a(n)
A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.
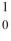 n, is a(n)
n, is a(n)A)alpha particle.
B)electron.
C)neutron.
D)positron.
E)proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The nuclear radiation having particles with the greatest charge is
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The nuclear radiation with the least penetrating ability is
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The nuclear radiation having particles with the greatest mass is
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.
A)alpha radiation.
B)beta radiation.
C)gamma radiation.
D)neutrons.
E)X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify the isotope that is the product in the nuclear equation 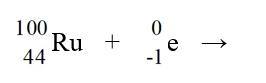
A)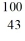 Ru
Ru
B)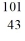 Ru
Ru
C)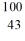 Tc
Tc
D)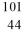 Tc
Tc
E)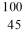 Tc
Tc
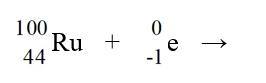
A)
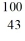 Ru
RuB)
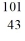 Ru
RuC)
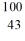 Tc
TcD)
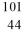 Tc
TcE)
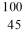 Tc
Tc
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify the isotope that is the missing product in the nuclear equation 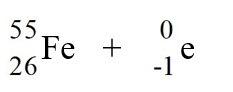
A)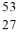 Fe
Fe
B)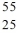 Mn
Mn
C)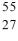 Co
Co
D)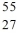 Fe
Fe
E)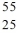 Fe
Fe
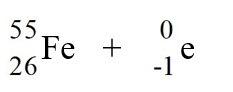
A)
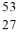 Fe
FeB)
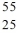 Mn
MnC)
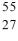 Co
CoD)
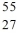 Fe
FeE)
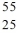 Fe
Fe
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 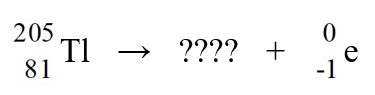
A)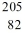 Tl
Tl
B)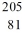 Pb
Pb
C)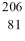 Pb
Pb
D)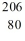 Pb
Pb
E)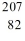 Pb
Pb
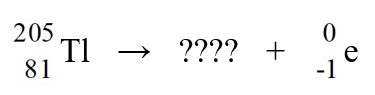
A)
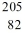 Tl
TlB)
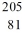 Pb
PbC)
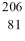 Pb
PbD)
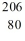 Pb
PbE)
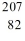 Pb
Pb
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 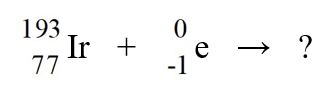
A)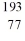 Os
Os
B)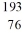 Ir
Ir
C)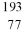 Ir
Ir
D)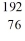 Os
Os
E)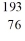 Os
Os
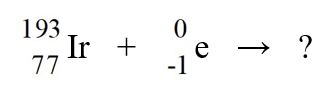
A)
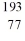 Os
OsB)
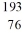 Ir
IrC)
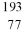 Ir
IrD)
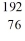 Os
OsE)
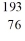 Os
Os
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 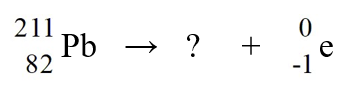
A)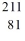 Tl
Tl
B)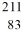 Bi
Bi
C)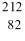 Pb
Pb
D)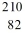 Pb
Pb
E)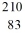 Bi
Bi
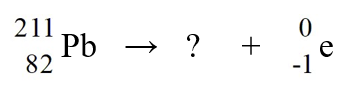
A)
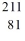 Tl
TlB)
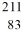 Bi
BiC)
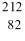 Pb
PbD)
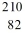 Pb
PbE)
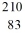 Bi
Bi
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the nucleus of an isotope captures a beta particle, the atomic number of the nucleus produced
A)is the same as that of the original nuclide.
B)increases by one unit.
C)decreases by one unit.
D)increases by two units.
E)decreases by two units.
A)is the same as that of the original nuclide.
B)increases by one unit.
C)decreases by one unit.
D)increases by two units.
E)decreases by two units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the nucleus of an isotope emits a beta particle, the atomic number of the nucleus produced
A)is the same as that of the original nuclide.
B)increases by one unit.
C)decreases by one unit.
D)increases by two units.
E)decreases by two units.
A)is the same as that of the original nuclide.
B)increases by one unit.
C)decreases by one unit.
D)increases by two units.
E)decreases by two units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When 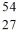 Co decays an isotope of iron is formed. What other products are formed?
Co decays an isotope of iron is formed. What other products are formed?
A)a positron and neutrino
B)a positron only
C)beta rays and gamma rays
D)alpha particles and gamma rays
E)gamma rays only
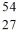 Co decays an isotope of iron is formed. What other products are formed?
Co decays an isotope of iron is formed. What other products are formed?A)a positron and neutrino
B)a positron only
C)beta rays and gamma rays
D)alpha particles and gamma rays
E)gamma rays only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 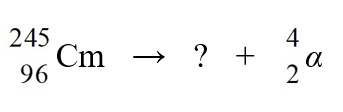
A)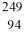 Pu
Pu
B)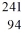 Pu
Pu
C)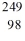 Cf
Cf
D)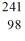 Cf
Cf
E)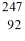 U
U
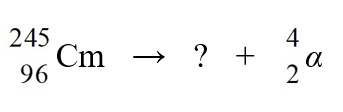
A)
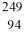 Pu
PuB)
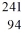 Pu
PuC)
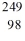 Cf
CfD)
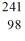 Cf
CfE)
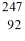 U
U
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 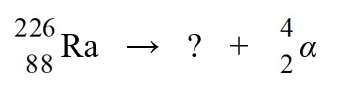
A)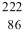 Rn
Rn
B)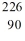 Th
Th
C)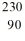 Th
Th
D)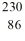 Rn
Rn
E)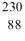 Ra
Ra
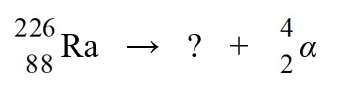
A)
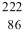 Rn
RnB)
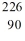 Th
ThC)
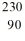 Th
ThD)
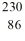 Rn
RnE)
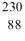 Ra
Ra
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 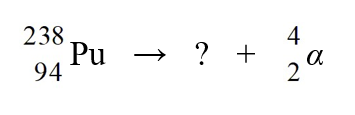
A)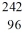 Pu
Pu
B)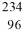 Pu
Pu
C)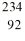 Pu
Pu
D)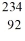 U
U
E)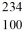 U
U
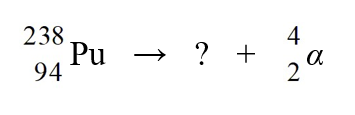
A)
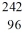 Pu
PuB)
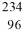 Pu
PuC)
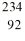 Pu
PuD)
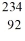 U
UE)
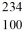 U
U
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 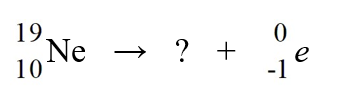
A)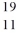 F
F
B)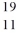 Na
Na
C)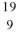 F
F
D)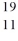 Ne
Ne
E)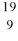 Ne
Ne
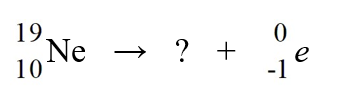
A)
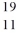 F
FB)
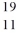 Na
NaC)
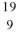 F
FD)
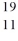 Ne
NeE)
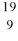 Ne
Ne
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify the missing species in the nuclear equation 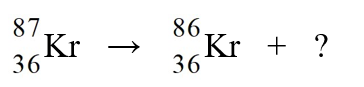
A)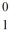 n
n
B)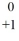 e
e
C)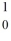 n
n
D)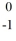 e
e
E)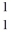 p
p
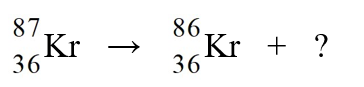
A)
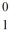 n
nB)
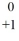 e
eC)
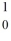 n
nD)
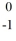 e
eE)
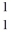 p
p
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which nuclear process does not cause a change in the atomic number of the isotope undergoing the process?
A)emission of -particle
B)emission of -particle
C)emission of a -ray
D)emission of a positron
E)capture of an electron
A)emission of -particle
B)emission of -particle
C)emission of a -ray
D)emission of a positron
E)capture of an electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The nuclear reaction depicted below is an example of 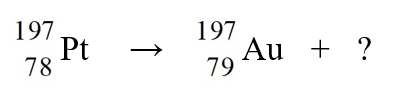
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.
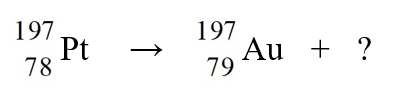
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The nuclear reaction depicted below is an example of 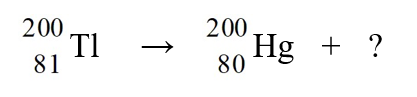
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.
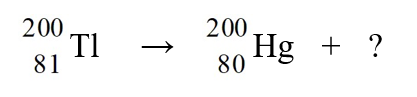
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Carbon-14 is generated in the atmosphere by the nuclear reaction 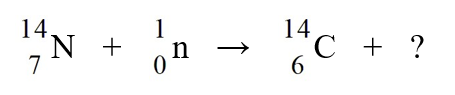
A)an -particle.
B)a -particle.
C)a -ray.
D)a positron.
E)a proton.
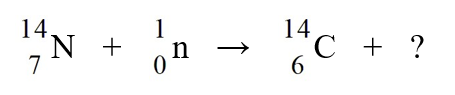
A)an -particle.
B)a -particle.
C)a -ray.
D)a positron.
E)a proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The two steps in the reaction that takes place in breeder reactors are 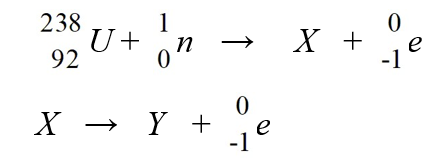
A)239Np and 239Am
B)239Np and 241Pu
C)239Np and 239Pu
D)239U and 239Np
E)237Np and 237Pu
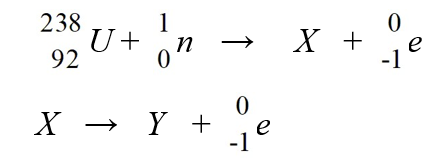
A)239Np and 239Am
B)239Np and 241Pu
C)239Np and 239Pu
D)239U and 239Np
E)237Np and 237Pu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The nuclear process, 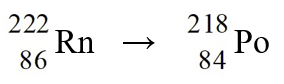 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)tritium emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)tritium emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The nuclear process, 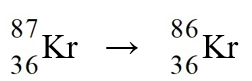 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The nuclear process, 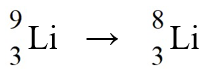 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The nuclear process, 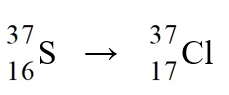 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
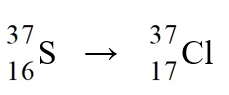 could be caused by
could be caused byA)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The nuclear process, 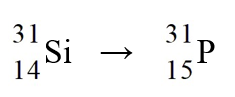 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The nuclear process, 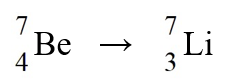 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The nuclear process, 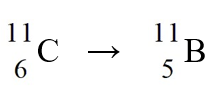 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The nuclear process, 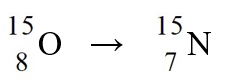 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
 could be caused by
could be caused byA)positron emission from the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The nuclear process, 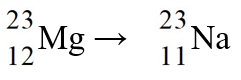 could be caused by
could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
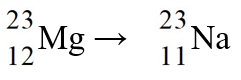 could be caused by
could be caused byA)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The nuclear process in which aluminum-27 is transmutated into magnesium-24 could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)tritium emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)tritium emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The nuclear process in which polonium-214 is transmutated into lead-210 could be caused by
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.
A)electron capture by the reactant nucleus.
B)beta-emission from the reactant nucleus.
C)alpha-emission from the reactant nucleus.
D)proton emission from the reactant nucleus.
E)neutron emission from the reactant nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When radium-226 is transmutated by a nuclear decay to radon-222, the process involved is
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.
A)emission of -particle.
B)emission of -particle.
C)emission of a -ray.
D)emission of a positron.
E)capture of an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
One becquerel equals
A)one disintegration per second.
B)3.7 × 1010 disintegrations per second.
C)a mole of disintegrations per second.
D)100 rads.
E)one rem.
A)one disintegration per second.
B)3.7 × 1010 disintegrations per second.
C)a mole of disintegrations per second.
D)100 rads.
E)one rem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The intensity of X-rays, gamma rays, or any other radiation is
A)directly proportional to the distance from the source.
B)directly proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
C)inversely proportional to the distance from the source.
D)inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
E)inversely proportional to the cube of the distance from the source.
A)directly proportional to the distance from the source.
B)directly proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
C)inversely proportional to the distance from the source.
D)inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
E)inversely proportional to the cube of the distance from the source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the halflife of a radioactive element is 30.0 years, how long will it take for a sample to decay to the point where its activity is 70.0% of the original value?
A)5.0 years
B)12.2 years
C)15.4 years
D)30.8 years
E)86.1 years
A)5.0 years
B)12.2 years
C)15.4 years
D)30.8 years
E)86.1 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which unit measures the rate of radioactive decay?
A)the curie
B)the rad
C)the gray
D)the sievert
E)the rem
A)the curie
B)the rad
C)the gray
D)the sievert
E)the rem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which unit of radiation dose considers the biological effects of the particular kind of radiation absorbed?
A)the curie
B)the becquerel
C)the rem
D)the rad
E)the gray
A)the curie
B)the becquerel
C)the rem
D)the rad
E)the gray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Rhenium186 is a -emitter with a half-life of 90.0 hours. How long would it take for the activity in a sample of this isotope to decay to exactly one-third of its original value?
A)121 hours
B)143 hours
C)158 hours
D)180 hours
E)189 hours
A)121 hours
B)143 hours
C)158 hours
D)180 hours
E)189 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Ytterbium-175 is a -emitter with a half-life of 101 hours. How long would it take for the activity in a sample of this isotope to decay to exactly one-fifth of its original value?
A)215 hours
B)225 hours
C)235 hours
D)250 hours
E)275 hours
A)215 hours
B)225 hours
C)235 hours
D)250 hours
E)275 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The specific activity of a carbon sample from the bones of a mummy in a secret tomb recently discovered in Egypt is found to be 60.0% of that of living plants. Calculate the age of the artifact. 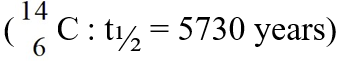
A)3440 years
B)2870 years
C)4220 years
D)2110 years
E)8440 years
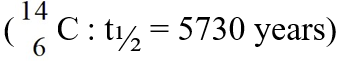
A)3440 years
B)2870 years
C)4220 years
D)2110 years
E)8440 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which one of the following is not a device for determining radiation?
A)Geiger counter
B)ionometer
C)scintillation counter
D)film dosimeter
A)Geiger counter
B)ionometer
C)scintillation counter
D)film dosimeter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The carbon-14 dating method can be used to determine the age of
A)carbonate rocks.
B)silicate rocks.
C)ancient bones.
D)bronze beakers.
E)Roman coins.
A)carbonate rocks.
B)silicate rocks.
C)ancient bones.
D)bronze beakers.
E)Roman coins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The carbon-14 dating method cannot be used to determine the age of
A)wooden remains of an historic house.
B)the cork in a very old bottle of wine.
C)ancient bones.
D)a canvas used in a historic painting.
E)Roman coins.
A)wooden remains of an historic house.
B)the cork in a very old bottle of wine.
C)ancient bones.
D)a canvas used in a historic painting.
E)Roman coins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The following are all applications of radioactivity except one. Which one?
A)tracer analysis
B)neutron activation
C)carbon-14 dating
D)potassium-14 dating
E)electron impact activation
A)tracer analysis
B)neutron activation
C)carbon-14 dating
D)potassium-14 dating
E)electron impact activation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How many nucleons (protons and neutrons)are in the most common isotope of uranium?
A)234
B)235
C)236
D)238
E)239
A)234
B)235
C)236
D)238
E)239

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How many total nucleons are there in the natural fissile isotope of uranium?
A)234
B)235
C)236
D)238
E)239
A)234
B)235
C)236
D)238
E)239

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Fission reactors are restrained from going supercritical through
A)use of liquid metal coolants.
B)use of organic coolant.
C)use of control rods that absorb neutrons.
D)use of liquid nitrogen to maintain correct reaction rate.
E)proper reactor design.
A)use of liquid metal coolants.
B)use of organic coolant.
C)use of control rods that absorb neutrons.
D)use of liquid nitrogen to maintain correct reaction rate.
E)proper reactor design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Many nuclear reactions emit more neutrons than what is used to initiate the reaction leading to what is called a
A)fissile isotope.
B)transmutation reaction.
C)critical mass.
D)nuclear chain reaction.
E)tracer element.
A)fissile isotope.
B)transmutation reaction.
C)critical mass.
D)nuclear chain reaction.
E)tracer element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Reactor "meltdowns"like the one at Chernobyl in the Ukraine were caused by
A)supercritical masses of fissile nuclides accumulating near the bottom of the reactor.
B)failure of the cooling system that distributes the heat generated in the reactor core.
C)decomposition of heavy water coolant D2O into H2O and neutrons that have very large thermal energies.
D)slow accumulation of critical masses of impurities at particular sites in the fuel rods, caused by improper design.
E)inhomogeneities in the containment magnetic fields caused by small temperature fluctuations in the field winding coils.
A)supercritical masses of fissile nuclides accumulating near the bottom of the reactor.
B)failure of the cooling system that distributes the heat generated in the reactor core.
C)decomposition of heavy water coolant D2O into H2O and neutrons that have very large thermal energies.
D)slow accumulation of critical masses of impurities at particular sites in the fuel rods, caused by improper design.
E)inhomogeneities in the containment magnetic fields caused by small temperature fluctuations in the field winding coils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A certain chemical reaction results in the release of 9287 kJ of energy. The loss of mass from this type of reaction would be ________ kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The average energy holding the nucleons in the nucleus together is called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The formation of multiple nuclei of smaller mass from a high mass nuclei is best classified as a ________ reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The isotope 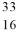 S has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
S has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
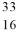 S has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
S has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The isotope 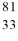 Br has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
Br has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
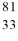 Br has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
Br has ________ neutrons and protons. (nucleons)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The energy that an electron receives when accelerated through a potential difference of one volt is one ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 127I nucleus weighs 126.904477 u. Calculate the mass defect of the nucleus in amu.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 127I nucleus weighs 126.904477 u. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon for this nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The rest mass of a proton is 1.0072764666 u and that of a neutron is 1.0086649158 u. The 37Cl nucleus weighs 36.965903 u. The mass defect of the nucleus is ________ u.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



