Deck 4: Nutrition During Pregnancy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Nutrition During Pregnancy
1
The first half of pregnancy is considered the "maternal _____," while the second half of pregnancy is considered the "maternal _____."
A)anatomic phase/catatonic phase
B)catatonic phase/anatomic phase
C)catabolic phase/anabolic phase
D)anabolic phase/catabolic phase
E)hyperplastic phase/hypertrophic phase
A)anatomic phase/catatonic phase
B)catatonic phase/anatomic phase
C)catabolic phase/anabolic phase
D)anabolic phase/catabolic phase
E)hyperplastic phase/hypertrophic phase
D
2
According to the text,infants weighing _____ at birth are least likely to die within the first year of life.
A)~3000-4000 g
B)~3500-4500 g
C)~4000-5000 g
D)~4500-5500 g
A)~3000-4000 g
B)~3500-4500 g
C)~4000-5000 g
D)~4500-5500 g
B
3
Improvements in _____ have corresponded to greater reductions in infant mortality,while small improvements in infant mortality in the past few decades are largely due to _____.
A)technical advances in medical care;infectious disease control and sanitation
B)infectious disease control and sanitation;the industrial revolution
C)infectious disease control and sanitation;technical advances in medical care
D)vaccination rates: infectious disease control and sanitation
A)technical advances in medical care;infectious disease control and sanitation
B)infectious disease control and sanitation;the industrial revolution
C)infectious disease control and sanitation;technical advances in medical care
D)vaccination rates: infectious disease control and sanitation
C
4
The preferred source of fuel for the fetus is _____.
A)glucose
B)fatty acids
C)proteins
D)cholesterol
E)fiber
A)glucose
B)fatty acids
C)proteins
D)cholesterol
E)fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The changes in maternal physiology affect all parts of the body.Which of the following would NOT be a normal change in a woman's gastrointestinal tract during pregnancy?
A)Decreased gastric and intestinal transit time
B)Relaxed gastrointestinal tract muscle tone
C)Heartburn
D)Constipation
E)Nausea
A)Decreased gastric and intestinal transit time
B)Relaxed gastrointestinal tract muscle tone
C)Heartburn
D)Constipation
E)Nausea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Research is emerging that suggests pregnant women should increase their food sources of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).Which of the following foods would provide the most DHA to pregnant women?
A) 1 / 2 tuna salad sandwich
B)1/4 cup granola containing 1 tsp sunflower seed
C)8-oz glass whole milk
D)1 cup broccoli
A) 1 / 2 tuna salad sandwich
B)1/4 cup granola containing 1 tsp sunflower seed
C)8-oz glass whole milk
D)1 cup broccoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How can the change in lipid blood levels that occurs during pregnancy best be described?
A)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels decrease due to the increased water volume in the blood
B)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels remain the same as pre-pregnancy levels
C)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels increase dramatically from pre-pregnancy levels
D)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels fluctuate daily depending on when the fetus is building nerve cells
A)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels decrease due to the increased water volume in the blood
B)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels remain the same as pre-pregnancy levels
C)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels increase dramatically from pre-pregnancy levels
D)Cholesterol and triglyceride levels fluctuate daily depending on when the fetus is building nerve cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Hemodilution of nutrients occurs during pregnancy because:
A)women are eating less.
B)blood volume increases so much.
C)amniotic fluid displaces many nutrients.
D)glomerular filtration decreases.
E)maternal organs and tissues grow.
A)women are eating less.
B)blood volume increases so much.
C)amniotic fluid displaces many nutrients.
D)glomerular filtration decreases.
E)maternal organs and tissues grow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A critical period of spinal cord development following conception is:
A)1-2 weeks after conception.
B)3-4 weeks after conception.
C)5-6 weeks after conception.
D)7-8 weeks after conception.
E)9-10 weeks after conception.
A)1-2 weeks after conception.
B)3-4 weeks after conception.
C)5-6 weeks after conception.
D)7-8 weeks after conception.
E)9-10 weeks after conception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A pregnant woman in the anabolic phase of pregnancy
A)has increased appetite.
B)notices a significant (>1 lb/ week)weight gain.
C)is not hungry and eats less because nutrients aren't needed until the catabolic phase.
D)has decreased exercise tolerance.
E)both a and d
A)has increased appetite.
B)notices a significant (>1 lb/ week)weight gain.
C)is not hungry and eats less because nutrients aren't needed until the catabolic phase.
D)has decreased exercise tolerance.
E)both a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Infants weighing _____ are least likely to die within the first year of life.
A)5 lbs 11 oz to 6 lbs 5 oz
B)6 lbs 10 oz to 7 pounds 2 oz
C)7 lbs 12 oz to 10 lbs
D)8 lbs 8 oz to 10 lbs 2 oz
A)5 lbs 11 oz to 6 lbs 5 oz
B)6 lbs 10 oz to 7 pounds 2 oz
C)7 lbs 12 oz to 10 lbs
D)8 lbs 8 oz to 10 lbs 2 oz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Pre-term birth rate is defined as
A)births <30 weeks gestation/100 live births.
B)births <34 weeks gestation/100 live births.
C)births <37 weeks gestation/100 live births.
D)births <40 weeks gestation/100 live births.
A)births <30 weeks gestation/100 live births.
B)births <34 weeks gestation/100 live births.
C)births <37 weeks gestation/100 live births.
D)births <40 weeks gestation/100 live births.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The reduction in the U.S.infant mortality rate over the past 20 years has been:
A)increasing at a RAPID rate.
B)increasing at a SLOWER rate than the historical infant mortality rate reductions.
C)due to technological advancements.
D)LARGELY due to high levels of medical care.
E)both b and c
A)increasing at a RAPID rate.
B)increasing at a SLOWER rate than the historical infant mortality rate reductions.
C)due to technological advancements.
D)LARGELY due to high levels of medical care.
E)both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Pregnant women of _____ ethnicity are more likely than those of other ethnicities to have an eating disorder known as pica.
A)African American
B)White Caucasian
C)Hispanic
D)Hmong
E)Chinese
A)African American
B)White Caucasian
C)Hispanic
D)Hmong
E)Chinese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When cell size increases due to an accumulation of protein and lipids,the increase is characterized as _____.
A)hyperplasia
B)hypertrophy
C)differentiation
D)maturation
E)development
A)hyperplasia
B)hypertrophy
C)differentiation
D)maturation
E)development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
_____ do(es)NOT pose any foodborne bacterial risks in pregnant women.
A)Brie cheese
B)Ready-to-eat deli meats
C)Raw oysters
D)Unpasteurized milk
E)Organic bananas
A)Brie cheese
B)Ready-to-eat deli meats
C)Raw oysters
D)Unpasteurized milk
E)Organic bananas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Approximately what proportion of infants who die within the first year of life die within the first month after birth?
A)1/3
B)2/3
C)1/2
D)3/4
E)5/8
A)1/3
B)2/3
C)1/2
D)3/4
E)5/8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All of the following substances are transported through the placenta easily,with the exception of _____,which is not transferred at all.
A)water
B)cholesterol
C)oxygen
D)ketones
E)insulin
A)water
B)cholesterol
C)oxygen
D)ketones
E)insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The recommended daily protein (g)intake for pregnant women is _____.
A)30 g
B)71 g
C)90 g
D)120 g
A)30 g
B)71 g
C)90 g
D)120 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement is NOT correct about hormones and carbohydrate metabolism during pregnancy?
A)During the second maternal phase,rising levels of hCS and prolactin from the pituitary gland inhibit the conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat for storage.
B)Insulin resistance builds and increases the reliance on fats for energy during the second half of pregnancy.
C)Estrogen and progesterone levels increase and stimulate insulin production during the first half of pregnancy.
D)hCG levels increase to a greater extent in the second phase than in the first phase and stimulate conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat stores.
A)During the second maternal phase,rising levels of hCS and prolactin from the pituitary gland inhibit the conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat for storage.
B)Insulin resistance builds and increases the reliance on fats for energy during the second half of pregnancy.
C)Estrogen and progesterone levels increase and stimulate insulin production during the first half of pregnancy.
D)hCG levels increase to a greater extent in the second phase than in the first phase and stimulate conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat stores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
It is recommended that woman consume at least _____ of carbohydrate during pregnancy to meet fetal needs for glucose.
A)125 grams per day
B)150 grams per day
C)175 grams per day
D)225 grams per day
E)250 grams per day
A)125 grams per day
B)150 grams per day
C)175 grams per day
D)225 grams per day
E)250 grams per day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A baby born to a single mom who lost her job and experienced a severe food shortage at the end of her pregnancy will most likely be classified as
A)very small for gestational age (vSGA).
B)disproportionately small for gestational age (dSGA).
C)proportionately small for gestational age (pSGA).
D)appropriate for gestational age (AGA).
A)very small for gestational age (vSGA).
B)disproportionately small for gestational age (dSGA).
C)proportionately small for gestational age (pSGA).
D)appropriate for gestational age (AGA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When the nutrient concentration in the fetal blood is greater than the nutrient concentration in the maternal blood,nutrients will likely be transferred against the concentration gradient via:
A)passive diffusion.
B)facilitated diffusion.
C)active transport.
D)pinocytosis.
E)exocytosis.
A)passive diffusion.
B)facilitated diffusion.
C)active transport.
D)pinocytosis.
E)exocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why must volume expansion occur BEFORE maternal nutrient stores accumulate?
A)In order to support large gains in fetal weight
B)In order to provide the fetus with sufficient energy,nutrients,and oxygen
C)In order to provide the mother with plenty of fluids
D)In order to dilute the high concentration of nutrients in pregnant women
E)In order to make room for growing organs
A)In order to support large gains in fetal weight
B)In order to provide the fetus with sufficient energy,nutrients,and oxygen
C)In order to provide the mother with plenty of fluids
D)In order to dilute the high concentration of nutrients in pregnant women
E)In order to make room for growing organs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During pregnancy,as the dose of iron _____ the amount of iron absorbed from supplements _____.
A)decreases/ increases
B)increases/ decreases
C)doubles/ triples
D)triples/ doubles
A)decreases/ increases
B)increases/ decreases
C)doubles/ triples
D)triples/ doubles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Factors associated with reduced fetal growth include all of the following EXCEPT:
A)pre-pregnancy underweight and shortness.
B)high-carbohydrate diets.
C)low weight gain during pregnancy.
D)smoking.
E)poor dietary intake.
A)pre-pregnancy underweight and shortness.
B)high-carbohydrate diets.
C)low weight gain during pregnancy.
D)smoking.
E)poor dietary intake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Factors related to the birth of infants who are large for gestational age (LGA)include:
A)pre-pregnancy obesity.
B)excessive weight gain during pregnancy.
C)poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy.
D)all of the above
E)a and b only
A)pre-pregnancy obesity.
B)excessive weight gain during pregnancy.
C)poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy.
D)all of the above
E)a and b only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
It is recommended that overweight women gain approximately _____ during pregnancy.
A)5-10 pounds
B)15-25 pounds
C)25-35 pounds
D)28-40 pounds
E)35-45 pounds
A)5-10 pounds
B)15-25 pounds
C)25-35 pounds
D)28-40 pounds
E)35-45 pounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If taken on an EMPTY stomach,folic acid supplements are nearly _____ bioavailable.
A)45%
B)60%
C)75%
D)85%
E)100%
A)45%
B)60%
C)75%
D)85%
E)100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The recommended weight gain range for normal-weight women is:
A)5-10 pounds.
B)15-25 pounds.
C)25-35 pounds.
D)28-40 pounds.
E)35-45 pounds.
A)5-10 pounds.
B)15-25 pounds.
C)25-35 pounds.
D)28-40 pounds.
E)35-45 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is a major function of the placenta?
A)Hormone and enzyme production
B)Nutrient and gas exchange between mother and fetus
C)Removal of waste products from the fetus
D)Barrier to drugs and alcohol
E)a,b,and c
F)all of the above
A)Hormone and enzyme production
B)Nutrient and gas exchange between mother and fetus
C)Removal of waste products from the fetus
D)Barrier to drugs and alcohol
E)a,b,and c
F)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Decreased conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat,lowered maternal utilization of glucose,and increased liver production of glucose help:
A)ensure the mother does not gain excessive weight during the second half of pregnancy.
B)ensure a constant supply of fat for maternal energy needs.
C)ensure a constant supply of glucose for fetal growth and development.
D)ensure that women do not expend too much energy on metabolism and have plenty of energy to support fetal growth.
E)promote healthy weight gain for pregnant women.
A)ensure the mother does not gain excessive weight during the second half of pregnancy.
B)ensure a constant supply of fat for maternal energy needs.
C)ensure a constant supply of glucose for fetal growth and development.
D)ensure that women do not expend too much energy on metabolism and have plenty of energy to support fetal growth.
E)promote healthy weight gain for pregnant women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Iron is absorbed best when:
A)you take a separate iron supplement (not in a multi-vitamin).
B)you have a higher need for iron.
C)you eat meat,poultry,or fish.
D)all of the above
E)b and c only
A)you take a separate iron supplement (not in a multi-vitamin).
B)you have a higher need for iron.
C)you eat meat,poultry,or fish.
D)all of the above
E)b and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Approximately what proportion of women in the U.S.gain within the recommended weight ranges during pregnancy?
A)20%
B)31%
C)40%
D)52%
E)none of the above
A)20%
B)31%
C)40%
D)52%
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Small for gestational age (SGA)is different than low birthweight because:
A)low birth weight is <2500 g (5 lb 8 oz),while SGA is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
B)SGA is <2500 g (5 lb 8 oz),while low birth weight is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
C)SGA is <1500 g (3 lb 5 oz),while low birth weight is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
D)SGA is ≤10th %tile for gestational age,while low birth weight is <1500 g (3 lb 4 oz).
A)low birth weight is <2500 g (5 lb 8 oz),while SGA is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
B)SGA is <2500 g (5 lb 8 oz),while low birth weight is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
C)SGA is <1500 g (3 lb 5 oz),while low birth weight is ≤10th %tile for gestational age.
D)SGA is ≤10th %tile for gestational age,while low birth weight is <1500 g (3 lb 4 oz).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements is NOT a national health objective for pregnant women or newborns?
A)Reduce the rate of fetal and infant deaths
B)Increase abstinence from alcohol during pregnancy
C)Increase the proportion of women who gain weight appropriately during pregnancy
D)Reduce post-term births
E)All of the above ARE national health objectives for pregnant women and newborns
A)Reduce the rate of fetal and infant deaths
B)Increase abstinence from alcohol during pregnancy
C)Increase the proportion of women who gain weight appropriately during pregnancy
D)Reduce post-term births
E)All of the above ARE national health objectives for pregnant women and newborns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Jane Smith (and her husband)sought medical care for persistent nausea and vomiting throughout the day.Following a pregnancy test and medical examination,the doctor determined that she was in the 5th week of pregnancy.Following this report,Jane's husband remarked,"You will have to stop eating potato chips and eat more healthy foods." What is the best response the doctor could make?
A)"I agree-it is important to eat high-fiber foods."
B)"I agree-drink lots of water with meals."
C)"I recommend that you continue to eat foods that you can tolerate and that will help you gain weight."
D)"I suggest you eat a very small amount of chips to reduce your salt intake and prevent high blood pressure problems."
A)"I agree-it is important to eat high-fiber foods."
B)"I agree-drink lots of water with meals."
C)"I recommend that you continue to eat foods that you can tolerate and that will help you gain weight."
D)"I suggest you eat a very small amount of chips to reduce your salt intake and prevent high blood pressure problems."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The best weight gain advice for normal-weight women is that:
A)women should gain approximately 0.5 lb/week throughout the pregnancy.
B)women should not gain in the first trimester but gain approximately 1 lb/week in the other two trimesters.
C)women of different races gain weight at different rates throughout pregnancy.
D)approximately 3-5 lbs should be gained in the first trimester and gradual,consistent gains thereafter.
A)women should gain approximately 0.5 lb/week throughout the pregnancy.
B)women should not gain in the first trimester but gain approximately 1 lb/week in the other two trimesters.
C)women of different races gain weight at different rates throughout pregnancy.
D)approximately 3-5 lbs should be gained in the first trimester and gradual,consistent gains thereafter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following fruits and vegetables would supply a large amount of antioxidants?
A)Bananas and green grapes
B)Pumpkin and Swiss chard
C)Blueberries and cranberries
D)a and b
E)b and c
A)Bananas and green grapes
B)Pumpkin and Swiss chard
C)Blueberries and cranberries
D)a and b
E)b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Natality statistics are data that summarize information about:
A)the occurrence of pregnancy complications.
B)infant morbidity.
C)infant mortality.
D)harmful behaviors during pregnancy.
E)all of the above
A)the occurrence of pregnancy complications.
B)infant morbidity.
C)infant mortality.
D)harmful behaviors during pregnancy.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the following information to answer questions 43-45:
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
What is Jane's body mass index?
A)19.7
B)25.1
C)31.4
D)43
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
What is Jane's body mass index?
A)19.7
B)25.1
C)31.4
D)43

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following information and the growth chart provided to answer questions 49 and 50.
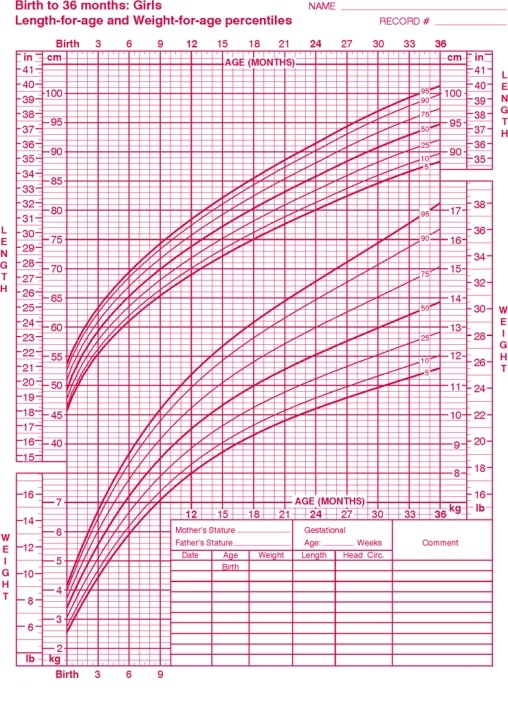
Your best friend just had a full-term baby girl that weighed 7 pounds.
Based on your above answer,this baby is:
A)small for gestational age (SGA).
B)large for gestational age (LGA).
C)appropriate for gestational age (AGA).

Your best friend just had a full-term baby girl that weighed 7 pounds.
Based on your above answer,this baby is:
A)small for gestational age (SGA).
B)large for gestational age (LGA).
C)appropriate for gestational age (AGA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The highest rate of weight gain occurs mid-pregnancy,prior to the time the fetus gains most of its weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Within the 40 weeks' duration of pregnancy,50% of fetal growth is accomplished in the first 20 weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following information and the growth chart provided to answer questions 49 and 50.

Your best friend just had a full-term baby girl that weighed 7 pounds.
Plot this infant's weight at birth on the growth chart and indicate which of the following percentiles she falls in.
A)10th
B)25th
C)50th
D)75th
E)90th

Your best friend just had a full-term baby girl that weighed 7 pounds.
Plot this infant's weight at birth on the growth chart and indicate which of the following percentiles she falls in.
A)10th
B)25th
C)50th
D)75th
E)90th

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Low weight gain increases the risk of:
A)spina bifida.
B)intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR).
C)a macrosomic baby.
D)cleft palate.
E)rickets.
A)spina bifida.
B)intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR).
C)a macrosomic baby.
D)cleft palate.
E)rickets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following information to answer questions 43-45:
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
Jane becomes pregnant.How many pounds should Jane gain during her pregnancy,based on her BMI?
A)11 to 20
B)15 to 25
C)25 to 35
D)28 to 40
E)35 to 45
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
Jane becomes pregnant.How many pounds should Jane gain during her pregnancy,based on her BMI?
A)11 to 20
B)15 to 25
C)25 to 35
D)28 to 40
E)35 to 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
On average,women who gain within the recommended ranges for weight gain are 2.0 pounds heavier one year after delivery than they were before pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Restricting weight gain in pregnancy does NOT increase the risk of infant death and low birth weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Maternal and fetal needs for protein are fulfilled by maternal protein and muscle stores entering pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following information to answer questions 43-45:
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
Based on her BMI,Jane would be considered:
A)underweight.
B)normal weight.
C)overweight.
D)obese.
E)morbidly obese.
Jane is 5'7" (1.70 m)and weighs 160 pounds (72.7 kg).
Based on her BMI,Jane would be considered:
A)underweight.
B)normal weight.
C)overweight.
D)obese.
E)morbidly obese.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The mother stores protein in the maternal anabolic phase of pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If not accompanied by hypertension,edema in pregnancy generally reflects a healthy expansion of plasma volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The fetus accounts for approximately 70% of the increased energy needs of pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Changes in blood lipids during pregnancy are related to maternal dietary intake and should be monitored on a regular basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Pregnancy increases the absorption of _____ and _____.
A)iron
B)calcium
C)zinc
D)a and b
E)b and c
A)iron
B)calcium
C)zinc
D)a and b
E)b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about the fetal origins hypothesis is NOT true?
A)Research shows that lower birthweight is associated with higher risk of adult diseases such as cardiovascular disease,type 2 diabetes,and hypertension.
B)Both low birthweights (less than 5.5 lb)and high birthweights (more than 10 lb)in humans are strongly associated with later risk of disease in adulthood .
C)Evidence from animal studies shows the expression of genes that produce insulin receptors on muscle membranes may be suppressed in response to a low availability of glucose.
D)The effects of fetal programming on adult disease may be strongly modified by infant and childhood diets.
A)Research shows that lower birthweight is associated with higher risk of adult diseases such as cardiovascular disease,type 2 diabetes,and hypertension.
B)Both low birthweights (less than 5.5 lb)and high birthweights (more than 10 lb)in humans are strongly associated with later risk of disease in adulthood .
C)Evidence from animal studies shows the expression of genes that produce insulin receptors on muscle membranes may be suppressed in response to a low availability of glucose.
D)The effects of fetal programming on adult disease may be strongly modified by infant and childhood diets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The recommended daily dietary intake of folate during pregnancy is:
A)200 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
B)400 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
C)600 mcg total with 400 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
D)800 mcg total with 600 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
E)4000 mcg total in any form.
A)200 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
B)400 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
C)600 mcg total with 400 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
D)800 mcg total with 600 mcg from fortified food or supplements.
E)4000 mcg total in any form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Neural tube defects are among the most preventable types of congenital abnormalities that exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Infants born to African American mothers are more likely to have a low birthweight than infants born to Caucasian mothers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Women with small increases in plasma volume are more likely to have complications such as low-birth weight infants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



