Deck 11: Toddler and Preschooler Nutrition: Conditions and Interventions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Toddler and Preschooler Nutrition: Conditions and Interventions
1
The typical diet prescribed for children who are underweight with a chronic condition may be modified by _____.
A)increasing fat calories
B)changing texture
C)increasing portions
D)customizing to the individual child
E)All of the above
A)increasing fat calories
B)changing texture
C)increasing portions
D)customizing to the individual child
E)All of the above
E
2
Healthy toddlers are likely to develop diarrhea from _____.
A)introduction of vegetables into their diet
B)addition of too much fat into their diet
C)consumption of eggs
D)drinking too much fruit juice
E)drinking 2% milk versus whole milk
A)introduction of vegetables into their diet
B)addition of too much fat into their diet
C)consumption of eggs
D)drinking too much fruit juice
E)drinking 2% milk versus whole milk
D
3
Diplegia is a condition that is characterized by:
A)damage that occurs to underdeveloped lungs resulting in breathing that requires extra effort.
B)a genetic change on the X chromosome resulting in severe neurological delays.
C)damage to the part of the brain controlling movement of the legs,interfering with muscle control and ambulation.
D)damage to chromosome 7,interfering with all the exocrine functions in the body.
E)destruction of the infection-fighting abilities of the body by a virus.
A)damage that occurs to underdeveloped lungs resulting in breathing that requires extra effort.
B)a genetic change on the X chromosome resulting in severe neurological delays.
C)damage to the part of the brain controlling movement of the legs,interfering with muscle control and ambulation.
D)damage to chromosome 7,interfering with all the exocrine functions in the body.
E)destruction of the infection-fighting abilities of the body by a virus.
C
4
Characteristics of food choices by an autistic child might include all of the following EXCEPT:
A)preferring to eat solid foods rather than drink liquids.
B)refusing to eat when offered something he/she does not like.
C)having temper tantrums in which he/she can be injured.
D)preferring one type of drink above others.
E)All of the above ARE characteristics of food choices.
A)preferring to eat solid foods rather than drink liquids.
B)refusing to eat when offered something he/she does not like.
C)having temper tantrums in which he/she can be injured.
D)preferring one type of drink above others.
E)All of the above ARE characteristics of food choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Behavioral disorders that impact nutritional status include:
A)ASDs.
B)Prader-Willi syndrome.
C)attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
D)All of the above
E)a and c only
A)ASDs.
B)Prader-Willi syndrome.
C)attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
D)All of the above
E)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
It is estimated that up to _____ of children with disabilities have some type of nutritional problem.
A)25%
B)45%
C)55%
D)75%
E)90%
A)25%
B)45%
C)55%
D)75%
E)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Eligibility for early intervention services for a child with special health needs is based on all the following EXCEPT:
A)presence of developmental delays in cognitive,physical,language and speech,psychosocial,or self- helping skills.
B)presence of a physical or mental condition with a high probability of delay.
C)they are born preterm by at least 8 weeks.
D)they are at risk medically or environmentally for substantial developmental delay if services are not provided.
E)they have Down syndrome.
A)presence of developmental delays in cognitive,physical,language and speech,psychosocial,or self- helping skills.
B)presence of a physical or mental condition with a high probability of delay.
C)they are born preterm by at least 8 weeks.
D)they are at risk medically or environmentally for substantial developmental delay if services are not provided.
E)they have Down syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following conditions is associated with a lower calorie need?
A)Prader-Willi
B)Down syndrome
C)Spina bifida
D)Pediatric AIDS
E)a,b,and c
A)Prader-Willi
B)Down syndrome
C)Spina bifida
D)Pediatric AIDS
E)a,b,and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Generally,a diagnosis of FTT is suspected in children with chronic illnesses when their growth declines more than _____ percentiles and they are near or below the lowest percentiles.
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
John,a first-born,had a low birthweight.He grew steadily in length and continued to gain weight,remaining at the 10th percentile on the CDC growth charts,until age 3.Between ages 3 and 4,his weight declined without any presenting illnesses.Why would it be difficult to diagnose FTT?
A)Typical growth and development for a healthy child includes a decline in appetite and weight at this age.
B)There were no siblings to compare his growth rate to.
C)His growth pattern indicated that for the majority of his life he was developing appropriately.
D)His weight declined to the 7th percentile.
E)a and c
A)Typical growth and development for a healthy child includes a decline in appetite and weight at this age.
B)There were no siblings to compare his growth rate to.
C)His growth pattern indicated that for the majority of his life he was developing appropriately.
D)His weight declined to the 7th percentile.
E)a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Signs that indicate feeding problems in toddlers include:
A)low interest in eating.
B)long mealtimes (>30 minutes).
C)preferring liquids over solids.
D)refusing foods.
E)All of the above
A)low interest in eating.
B)long mealtimes (>30 minutes).
C)preferring liquids over solids.
D)refusing foods.
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Rett syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by:
A)damage that occurs to underdeveloped lungs resulting in breathing that requires extra effort.
B)a genetic change on the X chromosome resulting in severe neurological delays.
C)damage to the part of the brain controlling movement of the legs,interfering with muscle control and ambulation.
D)damage to chromosome 7 that interferes with all the exocrine functions in the body.
E)destruction of the infection-fighting abilities of the body by a virus.
A)damage that occurs to underdeveloped lungs resulting in breathing that requires extra effort.
B)a genetic change on the X chromosome resulting in severe neurological delays.
C)damage to the part of the brain controlling movement of the legs,interfering with muscle control and ambulation.
D)damage to chromosome 7 that interferes with all the exocrine functions in the body.
E)destruction of the infection-fighting abilities of the body by a virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Overweight and obesity are common in Down syndrome children because they have lower caloric needs due to:
A)low muscle mass.
B)lower mobility.
C)short stature.
D)All of the above
E)a and c only
A)low muscle mass.
B)lower mobility.
C)short stature.
D)All of the above
E)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A disorder where head growth is reduced starting in the toddler years is called _____.
A)Prader-Willi syndrome
B)Rett syndrome
C)cerebral palsy
D)autism
E)Down syndrome
A)Prader-Willi syndrome
B)Rett syndrome
C)cerebral palsy
D)autism
E)Down syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Failure to thrive (FTT)may result from a complex interplay of medical and environmental factors that include all of the following EXCEPT:
A)pediatric AIDS.
B)digestive problems such as gastrointestinal reflux.
C)post-term birth and high birth weight.
D)asthma.
E)neurological conditions such as seizures.
A)pediatric AIDS.
B)digestive problems such as gastrointestinal reflux.
C)post-term birth and high birth weight.
D)asthma.
E)neurological conditions such as seizures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Children that qualify for early intervention services include all of the following EXCEPT _____.
A)a two-year-old toddler with Down syndrome
B)a baby born with spina bifida
C)a four-year-old preschooler with autism
D)a preterm baby who is now three years old with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
A)a two-year-old toddler with Down syndrome
B)a baby born with spina bifida
C)a four-year-old preschooler with autism
D)a preterm baby who is now three years old with bronchopulmonary dysplasia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following conditions results in increased calorie needs?
A)Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
B)Down syndrome
C)Prader-Willi syndrome
D)Spina bifida
A)Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
B)Down syndrome
C)Prader-Willi syndrome
D)Spina bifida

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a program in which nutrition care may be accessed for children with special needs?
A)WIC
B)Head Start
C)Early intervention programs
D)a and b
E)All of the above
A)WIC
B)Head Start
C)Early intervention programs
D)a and b
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Cystic fibrosis is a condition in which _____.
A)chromosome 7 is genetically changed,causing pulmonary complications
B)cysts develop on the spinal cord and limit voluntary movement
C)there is difficulty with voluntary or involuntary muscle control
D)three copies of chromosome 21 occur
E)the lungs are underdeveloped
A)chromosome 7 is genetically changed,causing pulmonary complications
B)cysts develop on the spinal cord and limit voluntary movement
C)there is difficulty with voluntary or involuntary muscle control
D)three copies of chromosome 21 occur
E)the lungs are underdeveloped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A child who has Down syndrome would have a poorer health outcome associated with
A)skipping one meal.
B)offering meals in the school foodservice cafeteria on days when he is not attending.
C)reviewing his individualized education plan three weeks late.
D)mismatching his energy needs with food intake,thus leading to excessive weight gain.
A)skipping one meal.
B)offering meals in the school foodservice cafeteria on days when he is not attending.
C)reviewing his individualized education plan three weeks late.
D)mismatching his energy needs with food intake,thus leading to excessive weight gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At what age do early intervention programs occur?
A)0-12 months
B)0-16 months
C)6-18 months
D)6-24 months
E)0-36 months
A)0-12 months
B)0-16 months
C)6-18 months
D)6-24 months
E)0-36 months

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following treatments has been found to be effective in treating children with Down syndrome?
A)Herbal remedies that help with constipation
B)High-protein,low-fat diets
C)High levels of the antioxidant vitamins A and C
D)Low-glycemic index carbohydrate diets
E)None of the above
A)Herbal remedies that help with constipation
B)High-protein,low-fat diets
C)High levels of the antioxidant vitamins A and C
D)Low-glycemic index carbohydrate diets
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Treatment for an anaphylactic reaction to a food is:
A)mouth-to-mouth resuscitation.
B)injection with epinephrine.
C)application of an oxygen mask.
D)intravenous fluids.
E)a quick-acting source of glucose.
A)mouth-to-mouth resuscitation.
B)injection with epinephrine.
C)application of an oxygen mask.
D)intravenous fluids.
E)a quick-acting source of glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A child that is allergic to milk protein also may have a high risk of developing an allergy to:
A)soy.
B)oranges.
C)kiwi fruit.
D)bananas.
E)a and b
A)soy.
B)oranges.
C)kiwi fruit.
D)bananas.
E)a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Breathing problems in children:
A)increase nutritional needs.
B)lower interest in eating.
C)slow growth rate.
D)All of the above
E)a and c only
A)increase nutritional needs.
B)lower interest in eating.
C)slow growth rate.
D)All of the above
E)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the following diet record to answer questions 39-40.
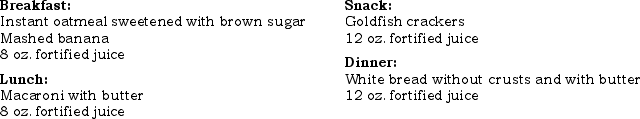
What would indicate that the 3-year-old girl following this diet has a potential feeding problem?
A)Lack of variety
B)Bland food choices
C)Excessive fluid intake
D)All of the above
E)a and c only
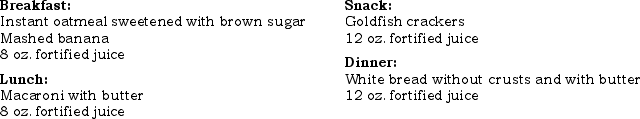
What would indicate that the 3-year-old girl following this diet has a potential feeding problem?
A)Lack of variety
B)Bland food choices
C)Excessive fluid intake
D)All of the above
E)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Typical food allergies do NOT include adverse reactions to _____.
A)eggs
B)soy
C)corn
D)peanuts
E)wheat
A)eggs
B)soy
C)corn
D)peanuts
E)wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following diet record to answer questions 39-40.
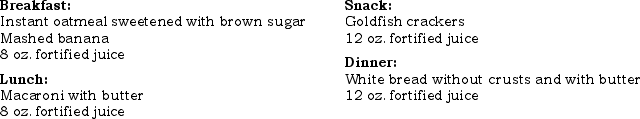
What foods could you suggest to increase variety and still make it easy for her to eat?
A)Pureed pears or peaches
B)Macaroni made with milk and cheese
C)Peanut butter sandwich crackers
D)Fortified juice smoothie
E)All of the above
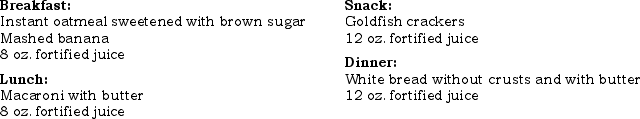
What foods could you suggest to increase variety and still make it easy for her to eat?
A)Pureed pears or peaches
B)Macaroni made with milk and cheese
C)Peanut butter sandwich crackers
D)Fortified juice smoothie
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following foods would be an inappropriate choice to feed a child with cerebral palsy who tires quickly at meal time?
A)Corn on the cob
B)Steamed or cooked carrots
C)Applesauce
D)Mashed potatoes
E)Cream of Wheat cereal
A)Corn on the cob
B)Steamed or cooked carrots
C)Applesauce
D)Mashed potatoes
E)Cream of Wheat cereal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are the dietary recommendations for toddlers with bronchopulmonary dysplasia?
A)Small,frequent meals
B)Concentrated sources of calories,such as commercially prepared supplements
C)Enteral (tube)feedings through the night
D)All of the above
E)a and b only
A)Small,frequent meals
B)Concentrated sources of calories,such as commercially prepared supplements
C)Enteral (tube)feedings through the night
D)All of the above
E)a and b only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Symptoms such as diarrhea and digestive problems associated with celiac disease usually develop by _____ years of age.
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Dietary management of celiac disease requires the elimination of:
A)wheat,rye,and barley.
B)wheat,rice,and soy.
C)wheat,rice,corn,and soy.
D)rice,corn,eggs,and bulgur.
E)fruits,vegetables,and nuts.
A)wheat,rye,and barley.
B)wheat,rice,and soy.
C)wheat,rice,corn,and soy.
D)rice,corn,eggs,and bulgur.
E)fruits,vegetables,and nuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following foods should be excluded from the diets of children with celiac disease?
A)Milk
B)Corn cereal
C)Pasta
D)Mashed potatoes
A)Milk
B)Corn cereal
C)Pasta
D)Mashed potatoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For a confirmation of celiac disease,a physician will
A)look for the appearance of extra chromosomes.
B)look for a missing chromosome.
C)test lung function.
D)test the blood for the antibodies to gluten.
E)take a stool sample.
A)look for the appearance of extra chromosomes.
B)look for a missing chromosome.
C)test lung function.
D)test the blood for the antibodies to gluten.
E)take a stool sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Toddlers with breathing problems need _____ calories than/as typical toddlers.
A)fewer
B)the same amount of
C)more
A)fewer
B)the same amount of
C)more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the growth chart below for question 36.
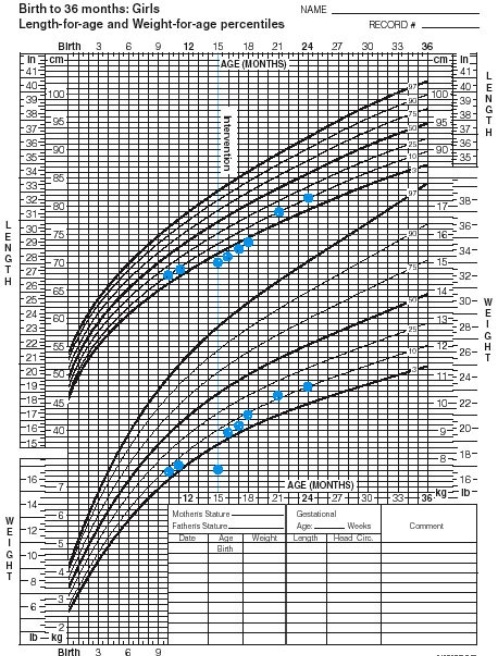
After looking ONLY at the growth chart,what condition might be suspected by a pediatrician?
A)Autism
B)Cerebral palsy
C)Failure-to-thrive (FTT)
D)Spastic quadriplegia
E)Cystic fibrosis

After looking ONLY at the growth chart,what condition might be suspected by a pediatrician?
A)Autism
B)Cerebral palsy
C)Failure-to-thrive (FTT)
D)Spastic quadriplegia
E)Cystic fibrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following foods would be least likely to invite bacterial contamination?
A)Canned peaches
B)Powdered infant formula mixed with water
C)Mashed banana
D)Blended soup
E)Uncovered infant formula
A)Canned peaches
B)Powdered infant formula mixed with water
C)Mashed banana
D)Blended soup
E)Uncovered infant formula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which food may not be appropriate to serve a child with sickle-cell disease also receiving a blood transfusion containing iron?
A)Cereal with milk
B)Hamburger with tomatoes
C)Green beans and butter
D)Hostess snack cake
E)Potato chips
A)Cereal with milk
B)Hamburger with tomatoes
C)Green beans and butter
D)Hostess snack cake
E)Potato chips

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Specific nutrition assessment for children with cerebral palsy begins with _____.
A)feeding ability
B)body composition indexes such as fat stores
C)swallowing evaluation
D)level of brain damage
E)All of the above
A)feeding ability
B)body composition indexes such as fat stores
C)swallowing evaluation
D)level of brain damage
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
True food allergies are estimated to occur in _____ of children.
A)<1%
B)2-8%
C)10-15%
D)20%
E)50%
A)<1%
B)2-8%
C)10-15%
D)20%
E)50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following foods would you need to have a closer look at to ensure its safety for consumption by someone with celiac disease?
A)Cherry pie filling
B)Chicken
C)Oat cereal
D)All of the above
E)a and c only
A)Cherry pie filling
B)Chicken
C)Oat cereal
D)All of the above
E)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Over-the-counter products can never be used in children with special health care needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A component of nutrition assessment in children with special health care needs is to assess the need for added vitamins and minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Genetic syndromes can affect growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Chronic condition and disability mean the same thing in referring to toddlers and preschoolers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The recommendation by the American Academy of Pediatrics to limit juice intake to 4 to 6 fluid ounces per day does NOT apply to children with special needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a child tires out easily while eating a piece of fruit and will not eat anything else,what can be done to increase her intake?
A)Change to pureed fruit or a fruit sauce
B)Soft-cook vegetables
C)Add protein to soups or noodles
D)Try a nutritional supplement like Pediasure
E)All of the above
A)Change to pureed fruit or a fruit sauce
B)Soft-cook vegetables
C)Add protein to soups or noodles
D)Try a nutritional supplement like Pediasure
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a child is allergic to eggs,it is not necessary to avoid a food that has eggs in it as long as it has been cooked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Some children have asthma as a result of food allergies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A gluten-free diet is recommended for autistic children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The consistent definition that must be met in order to qualify as having a disability in any state is whether a child has the ability to walk independently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A child with cerebral palsy in a wheelchair will likely require _____ energy than/as a child with cerebral palsy that is able to walk.
A)more
B)less
C)the same amount of
A)more
B)less
C)the same amount of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Food allergies are always a direct result of asthma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



