Deck 4: Estimating Evolutionary Trees
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Estimating Evolutionary Trees
1
Which of the following phylogeny inference tools is the best at reconstructing the most accurate phylogenetic trees?
A) parsimony
B) maximum likelihood
C) Bayesian inference
D) All of these methods have pros and cons.
A) parsimony
B) maximum likelihood
C) Bayesian inference
D) All of these methods have pros and cons.
D
2
A novel,derived character is also referred to as a(n)________.
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade
A
3
The illustration in the accompanying figure represents an early phylogenetic tree as depicted by ________. 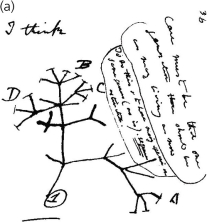
A) Dembski
B) Wallace
C) Lamark
D) Darwin

A) Dembski
B) Wallace
C) Lamark
D) Darwin
D
4
Estimating the uncertainty of phylogenetic trees using computer-generated replicates from an original data set is known as ________.
A) a heuristic search
B) the likelihood scenario
C) Bayesian inference
D) bootstrapping
A) a heuristic search
B) the likelihood scenario
C) Bayesian inference
D) bootstrapping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In determining the evolutionary relationships of current species,one needs to ________.
A) read along the tree tips: Species closer to each other are always more closely related
B) read along the tree tips: Species shown at the tips are arranged in patterns reflecting which groups evolved from others
C) read "back" to nodes connecting species to determine common ancestry
D) None of the above is an accurate way to read phylogenetic trees.
A) read along the tree tips: Species closer to each other are always more closely related
B) read along the tree tips: Species shown at the tips are arranged in patterns reflecting which groups evolved from others
C) read "back" to nodes connecting species to determine common ancestry
D) None of the above is an accurate way to read phylogenetic trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The label "1" in the accompanying figure represents ________. 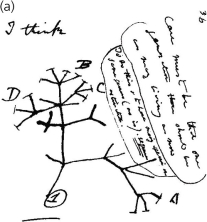
A) the "root" for the tree
B) the common ancestor for the hypothetical lineage
C) both A and B
D) None of the above.

A) the "root" for the tree
B) the common ancestor for the hypothetical lineage
C) both A and B
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A preexisting,ancestral character is also known as a(n)________.
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The use of phylogenetic trees in answering questions about the spatial distribution of living things is called ________.
A) biogeography
B) phylogeography
C) physiogeography
D) polyphyletogeography
A) biogeography
B) phylogeography
C) physiogeography
D) polyphyletogeography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Every node in a phylogenetic tree represents a(n)________.
A) common ancestor
B) extinction event
C) transitional form
D) sister species
A) common ancestor
B) extinction event
C) transitional form
D) sister species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Phylogenetic trees can always be regarded as ________ about evolutionary relationships.
A) facts
B) hypotheses
C) guesses
D) none of the above
A) facts
B) hypotheses
C) guesses
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An ancestor and all of its descendants are known as a monophyletic group or a(n)________.
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A derived character that is shared among two or more lineages is also called a(n)________.
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade
A) apomorphy
B) plesiomorphy
C) synapomorphy
D) clade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Two closely related species that share a recent common ancestor are called ________ species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the case study involving the phylogeny of whales,________.
A) molecular data and fossil data are in conflict with each other
B) molecular data confirmed what was already known from the fossil record: whales are cetaceans
C) fossil discoveries confirmed what molecular data already suggested: whales are cetaceans
D) both molecular and fossil data are inconclusive
A) molecular data and fossil data are in conflict with each other
B) molecular data confirmed what was already known from the fossil record: whales are cetaceans
C) fossil discoveries confirmed what molecular data already suggested: whales are cetaceans
D) both molecular and fossil data are inconclusive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A group consisting of a common ancestor and some,but not all,of its descendants is known as a ________ group.
A) monophyletic
B) paraphyletic
C) polyphyletic
D) polytomy
A) monophyletic
B) paraphyletic
C) polyphyletic
D) polytomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The wings of bats and birds and the streamlined body form of sharks and whales represent examples of ________.
A) convergence
B) reversal
C) outgroups
D) a clade
A) convergence
B) reversal
C) outgroups
D) a clade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A ________ [two words] is the evolutionary history of an ancestral lineage and its descendants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A phylogenetic tree grouping that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendants is known as a ________ group.
A) monophyletic
B) paraphyletic
C) polyphyletic
D) polytomy
A) monophyletic
B) paraphyletic
C) polyphyletic
D) polytomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In constructing phylogenetic trees,it is useful to think of monophyletic groups as being defined by ________.
A) apomorphies
B) plesiomorphies
C) synapomorphies
D) clades
A) apomorphies
B) plesiomorphies
C) synapomorphies
D) clades

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A(n)________ [two words] is a novel feature that evolved in a lineage and may be unique to a species or shared among species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Evaluate the merits and limits of parsimony,maximum likelihood,and Bayesian inference as tools for evaluating alternative phylogenies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
After correcting for the noted deletion in slots 62-64,it becomes clear that mutations in the ________ triplet have the most effects on changes in phenotype.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Complications in constructing phylogenetic trees due to reversals and convergent evolution are known collectively as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Analysis of neutral mutation rates to answer interesting questions such as "When did humans begin to wear clothes?" relies on the ________ [two words] hypothesis,which states that molecular traits change at a steady rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain what parsimony is,and why it is preferred in constructing phylogenetic trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Biogeographers study the spatial distribution of living things,and how they came to be where they are.Explain,using examples,how phylogeography can be used to answer the questions of biogeographers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Convergence and reversal are two complications that can interfere with accurate reconstruction of phylogenies.Describe each one,using examples,and explain the common strategies used to overcome them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the accompanying figure,the three "dashes" in the fourth row of nucleotides represent a(n)________ that was corrected for in this example of molecular data analysis.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
________ evolution is the independent evolution of similar derived characters in different lineages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Your textbook states that under optimal conditions,all of the methods discussed (parsimony,maximum likelihood,neighbor joining,and Bayesian inference reveal the true branching pattern of the phylogeny in question with accuracies approaching 100%.However,real phylogenies are rarely inferred under ideal circumstances.Explain,using examples,why this is so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



