Deck 21: Nuclear Chemistry and Radiochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Nuclear Chemistry and Radiochemistry
1
The nuclide with the formula 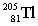 is best described as
is best described as
A) stable.
B) containing 81 neutrons and having a mass number of 205.
C) containing 205 protons and 81 neutrons.
D) containing 81 neutrons and 124 protons.
E) containing 124 neutrons and 81 protons.
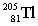 is best described as
is best described asA) stable.
B) containing 81 neutrons and having a mass number of 205.
C) containing 205 protons and 81 neutrons.
D) containing 81 neutrons and 124 protons.
E) containing 124 neutrons and 81 protons.
containing 124 neutrons and 81 protons.
2
Seborgium's most stable isotope contains one-hundred-six protons and one-hundred-fifty-seven neutrons. This nuclide's symbol is
A)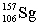 .S
.S
B)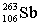
C)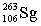
D)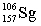
E)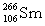
A)
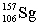 .S
.SB)
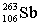
C)
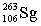
D)
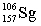
E)
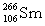
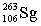
3
The nuclide with the formula 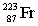 is best described as
is best described as
A) containing 136 neutrons and 87 protons.
B) containing 87 neutrons and having a mass number of 223.
C) containing 223 electrons and 87 protons.
D) containing 87 neutrons and 136 protons.
E) stable.
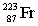 is best described as
is best described asA) containing 136 neutrons and 87 protons.
B) containing 87 neutrons and having a mass number of 223.
C) containing 223 electrons and 87 protons.
D) containing 87 neutrons and 136 protons.
E) stable.
containing 136 neutrons and 87 protons.
4
Which force is responsible for repulsions in the nucleus?
A) gravitational force
B) electrical force
C) magnetic force
D) strong nuclear force
E) the star wars force
A) gravitational force
B) electrical force
C) magnetic force
D) strong nuclear force
E) the star wars force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Calculate the binding energy per mole of nucleons for the boron isotope with mass of 12.0143 amu.(If needed, use the following equations: E = mc2 c = 3.0 x 108m/s E = m(8.988 x 1010 kJ/g)massproton = 1.007276 g/mol massneutron = 1.008665 g/mol masselectron = 0.0005486)
A) -1.537 x 109 kJ/mol
B) -6.404 x 108 kJ/mol
C) 6.404 x 108 kJ/mol
D) 1.736 x 1010 kJ/mol
E) -7.685 x 108 kJ/mol
A) -1.537 x 109 kJ/mol
B) -6.404 x 108 kJ/mol
C) 6.404 x 108 kJ/mol
D) 1.736 x 1010 kJ/mol
E) -7.685 x 108 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Nuclei that lie above the belt of stability generally decay by
A) emission.
B) emission.
C) electron capture.
D) positron emission.
E) emission.
A) emission.
B) emission.
C) electron capture.
D) positron emission.
E) emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Nuclei that lie below the belt of stability generally decay by
A) emission.
B) emission.
C) electron capture.
D) x-ray emission.
E) emission.
A) emission.
B) emission.
C) electron capture.
D) x-ray emission.
E) emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Nuclei that lie below the belt of stability are characterized by
A) high numbers of neutrons.
B) low neutron to proton ratio.
C) high neutron to proton ratio.
D) particle emission.
E) green colours.
A) high numbers of neutrons.
B) low neutron to proton ratio.
C) high neutron to proton ratio.
D) particle emission.
E) green colours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Strontium-90 decays by emission. Which of the following is the decay product?
A)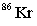
B)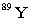
C)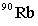
D)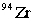
E)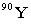
A)
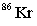
B)
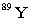
C)
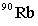
D)
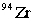
E)
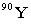

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
238U is an unstable nuclide that undergoes multiple decay events. One sequence is - - - - . The product nuclide is
A) 220Rn.
B) 222Rd.
C) 218Po.
D) 222Rn.
E) 220Rd.
A) 220Rn.
B) 222Rd.
C) 218Po.
D) 222Rn.
E) 220Rd.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
222Rn is an unstable nucleus that is hazardous. Several pathways are known for its decomposition. One is - - - - - . The product nuclide is
A) 210Tl.
B) 210Pb.
C) 210Po.
D) 214Po.
E) 206Tl.
A) 210Tl.
B) 210Pb.
C) 210Po.
D) 214Po.
E) 206Tl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which unstable species decays with the emission of an alpha and a gamma particle to form 222Rn?(If needed, use the following equation: 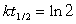
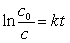 )
)
A) 226Po
B) 226Fr
C) 226Ra
D) 224Ra
E) 224Po
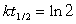
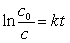 )
)A) 226Po
B) 226Fr
C) 226Ra
D) 224Ra
E) 224Po

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
64Ni and a positron are formed when which unstable species decays?(If needed, use the following equation: 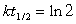
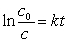 )
)
A) 64Co
B) 64Cu
C) 65Co
D) 65Cu
E) 63Co
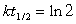
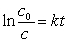 )
)A) 64Co
B) 64Cu
C) 65Co
D) 65Cu
E) 63Co

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Fission power produces unstable nuclides which have varying half-lives. One common product is cesium, with several different nuclides being produced. One nuclide that is problematic is 137Cs which decays by emission with a half-life of 30.2 years. How many years will it take for 1.5 kg of 137Cs to decompose to only 12 g of 137Cs?(If needed, use the following equation: 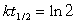
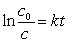 )
)
A) 60.4
B) 181.2
C) 210.4
D) 213.4
E) 240.6
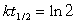
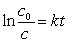 )
)A) 60.4
B) 181.2
C) 210.4
D) 213.4
E) 240.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Positron emission and electron capture cannot be directly observed, but are indirectly observed by the
A) emission of visible light.
B) capture of the particles.
C) observation of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
D) change in mass of the nuclide.
E) increase in half-life of the daughter nuclide.
A) emission of visible light.
B) capture of the particles.
C) observation of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
D) change in mass of the nuclide.
E) increase in half-life of the daughter nuclide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Radioactive waste nuclides with short half-lives are usually less of a problem for disposal because they are quite active but only for a short time. For example, 134 Cs has a half-life of 2.1 years. If initially there were 1.5 kg of 134Cs, how much of this nuclide would be present in 14.7 years?(If needed, use the following equation: 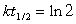
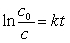 )
)
A) 1.2 kg
B) 120 g
C) 12 g
D) 10 g
E) 14.7 g
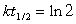
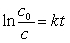 )
)A) 1.2 kg
B) 120 g
C) 12 g
D) 10 g
E) 14.7 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Neutron-capture reactions are
A) endothermic, and only occur at high temperature.
B) exothermic, as neutron is attracted by strong nuclear force.
C) exothermic, as they are spontaneous.
D) result in stable reaction products.
A) endothermic, and only occur at high temperature.
B) exothermic, as neutron is attracted by strong nuclear force.
C) exothermic, as they are spontaneous.
D) result in stable reaction products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which nuclei would undergo neutron capture and subsequent decay to produce 99Tc, two particles and one particle?
A) 106Ag
B) 107Ag
C) 99Mo
D) 98Mo
E) 98Ru
A) 106Ag
B) 107Ag
C) 99Mo
D) 98Mo
E) 98Ru

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Neutron bombardment of nuclei typically requires lower energies than proton bombardment of nuclei. The energy difference is because
A) the strong nuclear force has a stronger attraction for the neutron.
B) gravity acts more strongly on the neutron.
C) the proton is attracted to the electron cloud.
D) the proton is repelled by the nucleus.
E) the electron cloud gives the proton a spiraling approach.
A) the strong nuclear force has a stronger attraction for the neutron.
B) gravity acts more strongly on the neutron.
C) the proton is attracted to the electron cloud.
D) the proton is repelled by the nucleus.
E) the electron cloud gives the proton a spiraling approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When 60Ni is bombarded with a proton, the unstable product undergoes a further nuclear reaction, ejecting an particle to form a stable product. What is the identity of this stable product?
A) 56Co
B) 57Co
C) 57Fe
D) 55Fe
E) 65Ga
A) 56Co
B) 57Co
C) 57Fe
D) 55Fe
E) 65Ga

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Seaborgium (Z= 106) can be synthesized by the bombardment of 249Cf with 16O. If four (4) neutrons are produced in the reaction, what is the mass number of the Sg nuclide?
A) 259
B) 260
C) 261
D) 262
E) 264
A) 259
B) 260
C) 261
D) 262
E) 264

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A cyclotron could not be used to accelerate which of the following particles?
A) electron
B) proton
C) particle
D) neutron
E) 11B5+
A) electron
B) proton
C) particle
D) neutron
E) 11B5+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why do fission products tend to be radioactive?
A) They have excess electrons.
B) They have excess protons.
C) The neutron to proton ratio is high.
D) The neutron to proton ratio is low.
E) They emit gamma rays.
A) They have excess electrons.
B) They have excess protons.
C) The neutron to proton ratio is high.
D) The neutron to proton ratio is low.
E) They emit gamma rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not a characteristic of fission reactions?
A) Only a few nuclides undergo fission.
B) Fission produces large amounts of energy.
C) Fission gives only a few nuclides as products.
D) Fission products are often radioactive.
E) Fission products always include one or more neutrons.
A) Only a few nuclides undergo fission.
B) Fission produces large amounts of energy.
C) Fission gives only a few nuclides as products.
D) Fission products are often radioactive.
E) Fission products always include one or more neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the definition of critical mass?
A) mass needed to start a nuclear bomb
B) mass with a neutron recapture ratio of 1
C) mass with a neutron recapture ratio less than 1
D) mass needed to be detected by airport security
E) mass needed to start a nuclear reactor
A) mass needed to start a nuclear bomb
B) mass with a neutron recapture ratio of 1
C) mass with a neutron recapture ratio less than 1
D) mass needed to be detected by airport security
E) mass needed to start a nuclear reactor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following are differences between a nuclear reactor and a nuclear fission weapon?
A) The neutron recapture ratio.
B) The type of fuel.
C) The method of concentrating the fuel.
D) b and c
E) The kind of nuclear reaction occurring.
A) The neutron recapture ratio.
B) The type of fuel.
C) The method of concentrating the fuel.
D) b and c
E) The kind of nuclear reaction occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All waste from a nuclear fission reactor
A) are solid and composed of the daughter products of the fission reaction.
B) can be safely disposed of as they are composed of low grade radioactive materials.
C) include thermal waste in the form of warm water.
D) result from melt down of the reactor.
E) is radioactive and poses a potential threat to the environment.
A) are solid and composed of the daughter products of the fission reaction.
B) can be safely disposed of as they are composed of low grade radioactive materials.
C) include thermal waste in the form of warm water.
D) result from melt down of the reactor.
E) is radioactive and poses a potential threat to the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Successful operation of fission power plant requires
A) a fuel that will spontaneously decay via a radioactive process.
B) a moderator component to absorb neutrons and control the rate of the nuclear reactions.
C) a steam generator/turbine component that is fundamentally different than that found in coal driven power plants.
D) enriched grade uranium fuel.
E) a control component to limit the number neutrons available to trigger fission reactions.
A) a fuel that will spontaneously decay via a radioactive process.
B) a moderator component to absorb neutrons and control the rate of the nuclear reactions.
C) a steam generator/turbine component that is fundamentally different than that found in coal driven power plants.
D) enriched grade uranium fuel.
E) a control component to limit the number neutrons available to trigger fission reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How is electricity made from the energy released at a nuclear power plant?
A) via hot water
B) via steam
C) via heavy water
D) via refrigeration
E) via cooling towers
A) via hot water
B) via steam
C) via heavy water
D) via refrigeration
E) via cooling towers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The main impediment to fusion
A) is the fact that these are first-order reactions, so they are kinetically slow.
B) fusion occurs only for a few very rare nuclides.
C) reacting nuclei must have high kinetic energies to penetrate electron clouds.
D) the fusion products are often radioactive.
E) reacting nuclei must have high kinetic energies to overcome electrical repulsion between positive particles.
A) is the fact that these are first-order reactions, so they are kinetically slow.
B) fusion occurs only for a few very rare nuclides.
C) reacting nuclei must have high kinetic energies to penetrate electron clouds.
D) the fusion products are often radioactive.
E) reacting nuclei must have high kinetic energies to overcome electrical repulsion between positive particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Fusion is important
A) as a current method of producing electricity.
B) for understanding the formation of the elements.
C) for triggering fission bombs.
D) b and c.
E) as an energy source for space programs.
A) as a current method of producing electricity.
B) for understanding the formation of the elements.
C) for triggering fission bombs.
D) b and c.
E) as an energy source for space programs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a fusion reaction?
A) 1H + 1H 2He +
B) 1H + 12C 14N
C) 13C + 4He 16O + 1n
D) 235U + 1n 153Nd + 81Ge + 3 1n
E) 56Fe + 1n 57Co +
A) 1H + 1H 2He +
B) 1H + 12C 14N
C) 13C + 4He 16O + 1n
D) 235U + 1n 153Nd + 81Ge + 3 1n
E) 56Fe + 1n 57Co +

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following best explains why heavier elements don't form in first-generation stars?
A) The concentration of reactants is not high enough.
B) The heavier elements are only made in a supernova.
C) The spectrum of the star contains too much red.
D) Second generation stars are hotter.
E) There are free neutrons in a 1st generation star.
A) The concentration of reactants is not high enough.
B) The heavier elements are only made in a supernova.
C) The spectrum of the star contains too much red.
D) Second generation stars are hotter.
E) There are free neutrons in a 1st generation star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the primary cause of biological damage from radioactive emissions?
A) genetic mutation
B) loss of body fluids
C) sunburn from hair loss
D) ionization of molecules
E) opportunistic infection
A) genetic mutation
B) loss of body fluids
C) sunburn from hair loss
D) ionization of molecules
E) opportunistic infection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The REM unit
A) represents the total energy of radiation absorbed.
B) describes the effect of radiation on living humans.
C) is the amount of radiation necessary to treat food products.
D) accounts for the different properties of different types of radiation.
E) only applies to alpha emissions.
A) represents the total energy of radiation absorbed.
B) describes the effect of radiation on living humans.
C) is the amount of radiation necessary to treat food products.
D) accounts for the different properties of different types of radiation.
E) only applies to alpha emissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Shielding is an important aspect of working with radioactive materials. Which of the following is the order of radiation type in order of increasing penetration?
A) , ,
B) ,
C) , ,
D) , ,
E) , ,
A) , ,
B) ,
C) , ,
D) , ,
E) , ,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the order of radiation type as a function of increasing ionization potential?
A) , ,
B) , ,
C) , ,
D) , ,
E) , ,
A) , ,
B) , ,
C) , ,
D) , ,
E) , ,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Radiation treatment for cancer is effective because
A) cancer cells absorb more radiation than normal cells.
B) radioactive isotopes bind to tumours.
C) radiation has deleterious effects on rapidly dividing cells.
D) radiation can be precisely focused on cancerous cells.
E) it is less costly than other treatments.
A) cancer cells absorb more radiation than normal cells.
B) radioactive isotopes bind to tumours.
C) radiation has deleterious effects on rapidly dividing cells.
D) radiation can be precisely focused on cancerous cells.
E) it is less costly than other treatments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What radioactive particle do you need to be concerned about that can go through clothing but not through your body?
A) alpha
B) beta positive
C) beta negative
D) gamma
E) neutron
A) alpha
B) beta positive
C) beta negative
D) gamma
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Listed below are the mass numbers for several isotopes of cobalt, along with their mode(s) of decay and the half-lives. Which of them is best suited for use as a tracer?(If needed, use the following equations: 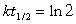
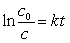 )
)
A) 53, + (1.46 min)
B) 55, + (17.5 hr)
C) 56, EC (77.7 day)
D) 58, + (70.9 dy)
E) 60, - (5.272 yr)
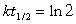
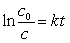 )
)A) 53, + (1.46 min)
B) 55, + (17.5 hr)
C) 56, EC (77.7 day)
D) 58, + (70.9 dy)
E) 60, - (5.272 yr)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following factors limit the radio-dating techniques?
A) The half-life of the isotope.
B) The amount of background radiation.
C) The quantity of sample.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The half-life of the isotope.
B) The amount of background radiation.
C) The quantity of sample.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Melvin Calvin received a Noble Prize for unravelling the reaction sequence of the production of sugar in plants. How was he able to do this?
A) using tritium to slow the reactions down
B) taking multiple x-rays as a plant is growing
C) using a radioactive tracer to follow the carbon throughout the plant
D) growing a plant by only using human breath
E) using Carbon-14 dating
A) using tritium to slow the reactions down
B) taking multiple x-rays as a plant is growing
C) using a radioactive tracer to follow the carbon throughout the plant
D) growing a plant by only using human breath
E) using Carbon-14 dating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Typically how old can an artifact found in an archeological dig be and still allow you to use Carbon-14 dating to analyze its age? (14C, t1/2 = 5730 years.)(If needed, use the following equations: 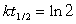
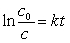 )
)
A) 1 half-life
B) 2 half-lives
C) 4 half-lives
D) 5 half-lives
E) can use it to determine the age of anything.
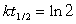
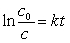 )
)A) 1 half-life
B) 2 half-lives
C) 4 half-lives
D) 5 half-lives
E) can use it to determine the age of anything.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Your lab is sent an ash sample from an archeological dig that you determine has a Carbon-14 activity of 1200 counts per minute. A piece of ash taken from your fireplace has a Carbon-14 activity of 3600 counts per minute. How old was the campsite where the ash was taken from? (14C has a half-life of 5730 years.)
A) 5700 years
B) 9100 years
C) 11,500 years
D) 17,200 years
E) 24,000 years
A) 5700 years
B) 9100 years
C) 11,500 years
D) 17,200 years
E) 24,000 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



