Deck 11: Organic Chemistryreactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Organic Chemistryreactions
1
Recognize nucleophiles and electrophiles. Show electron movement in a reaction using curved arrows.
All chemical reactions happen as a result of the movement of electrons. Substitution as well as elimination and addition reactions involve the attraction of an electrophile to a nucleophile.
2
Predict the products from SN2 and SN1 reactions. Write and explain the mechanisms of SN2 and SN1 reactions.
SN2 reactions occur in a single step. SN1 reactions occur via the formation of a carbocation, followed by its reaction with a nucleophile. Rates of substitution reactions are sensitive to the type of substrate, nucleophile, and leaving group.
3
Predict the products from E2 and E1 reactions. Write and explain the mechanisms of E2 and E1 reactions.
Elimination reactions convert a single bond into a double bond. E2 reactions occur in a single step. E1 reactions occur via the formation of a carbocation, followed by its reaction with a nucleophile.
4
Predict the products of addition reactions. Write the mechanisms of electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides, water, or halogens to alkenes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following does not contain a nucleophile?
A) propanol
B) propane
C) n-propylamide
D) propene
E) propoxide ion
A) propanol
B) propane
C) n-propylamide
D) propene
E) propoxide ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is an electrophile?
A) H2O
B) CH3O-
C) NH3
D) NH4+
E) All are nucleophiles.
A) H2O
B) CH3O-
C) NH3
D) NH4+
E) All are nucleophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
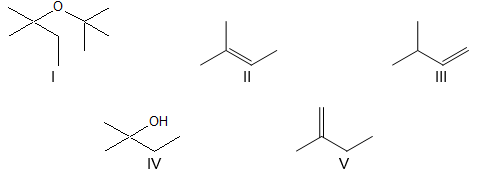
Ambident nucleophiles are ones which can react with a substrate at either of two nucleophilic sites. Which of the following is NOT an ambident nucleophile? 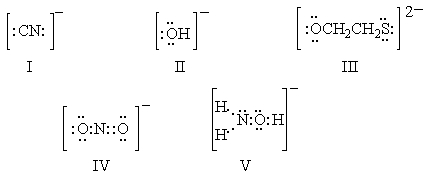
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the nucleophile in the following reaction:
2 H2O + RX ROH + H3O+ + X-
A) X-
B) H3O+
C) ROH
D) H2O
E) RX
2 H2O + RX ROH + H3O+ + X-
A) X-
B) H3O+
C) ROH
D) H2O
E) RX

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a nucleophile?
A) hexane
B) cyclohexane
C) 1-chlorohexane
D) cyclohexene
E) none of the above
A) hexane
B) cyclohexane
C) 1-chlorohexane
D) cyclohexene
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the SN2 reaction of butyl bromide with OH- ion.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + OH- CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + Br-
A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + OH- CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + Br-
A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the SN2 reaction of 2-iodopentane with CH3CO2- ion. 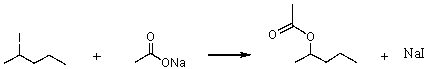 Assuming no other changes, what effect on the rate would result from simultaneously doubling the concentrations of both 2-iodopentane and CH3CO2- ion?
Assuming no other changes, what effect on the rate would result from simultaneously doubling the concentrations of both 2-iodopentane and CH3CO2- ion?
A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times
 Assuming no other changes, what effect on the rate would result from simultaneously doubling the concentrations of both 2-iodopentane and CH3CO2- ion?
Assuming no other changes, what effect on the rate would result from simultaneously doubling the concentrations of both 2-iodopentane and CH3CO2- ion?A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Select the rate law for the following reaction, e.g.,
CH3CH2CH2CHBrCH3 + OH- CH3CH2CH2CHOHCH3 + X-(RBr)
A) Rate = k [RBr]
B) Rate = k [RBr] [OH-]
C) Rate = k [RBr]2 [OH-]
D) Rate = k [RBr] [OH-]2
E) Rate = k [RBr]2 [OH-]2
CH3CH2CH2CHBrCH3 + OH- CH3CH2CH2CHOHCH3 + X-(RBr)
A) Rate = k [RBr]
B) Rate = k [RBr] [OH-]
C) Rate = k [RBr]2 [OH-]
D) Rate = k [RBr] [OH-]2
E) Rate = k [RBr]2 [OH-]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The rate equation for a nucleophilic substitution reaction of a tertiary alkyl bromide (R-Br) with I- ion would be
A) Rate = k [RBr]
B) Rate = k [I-]
C) Rate = k [RBr][I-]
D) k [RBr]2[I-]
E) Rate = k [RBr][I-]2
A) Rate = k [RBr]
B) Rate = k [I-]
C) Rate = k [RBr][I-]
D) k [RBr]2[I-]
E) Rate = k [RBr][I-]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The rate equation for a nucleophilic substitution reaction of a secondary alkyl chloride (R-Cl) with I- ion would be
A) Rate = k [RCl]
B) Rate = k [I-]
C) Rate = k [RCl][I-]
D) Rate = k [RCl]2[I-]
E) Rate = k [RCl][I-]2
A) Rate = k [RCl]
B) Rate = k [I-]
C) Rate = k [RCl][I-]
D) Rate = k [RCl]2[I-]
E) Rate = k [RCl][I-]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane with sodium iodide: 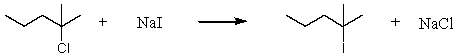 Assuming no other changes, how would it affect the rate if one simultaneously doubled the concentration of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide?
Assuming no other changes, how would it affect the rate if one simultaneously doubled the concentration of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide?
A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times
 Assuming no other changes, how would it affect the rate if one simultaneously doubled the concentration of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide?
Assuming no other changes, how would it affect the rate if one simultaneously doubled the concentration of 2-chloro-2-methylpentane and sodium iodide?A) no effect
B) double the rate
C) triple the rate
D) rate would increase by four times
E) rate would increase by six times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What product(s) would you expect to obtain from the following SN2 reaction? 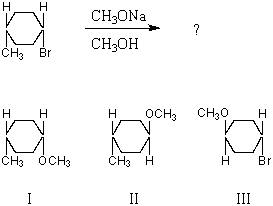
A) I
B) II
C) equimolar mixture of I and II
D) III
E) mixture of II and III

A) I
B) II
C) equimolar mixture of I and II
D) III
E) mixture of II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The major product of the following reaction would be 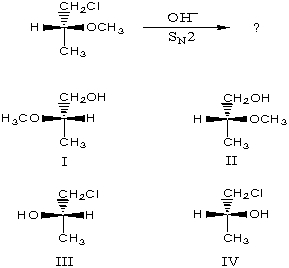
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar mixture of I and II

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar mixture of I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The major product(s) of the following reaction is (are) 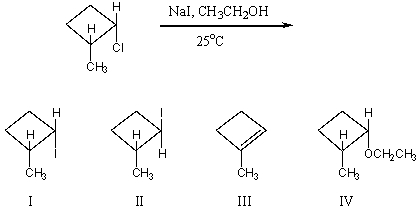
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar mixture of I and II

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar mixture of I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What would be the major product of the following reaction? 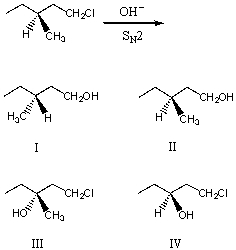
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What would be the major product of the following reaction? 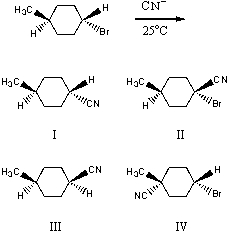
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar amounts of I and III

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) equimolar amounts of I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is (are) true of SN1 reactions of alkyl halides in general?
A) The rate of an SN1 reaction depends on the concentration of the alkyl halide.
B) The rate of an SN1 reaction depends on the concentration of the nucleophile.
C) SN1 reactions of alkyl halides are favoured by polar solvents.
D) Answers a) and c) only are true.
E) Answers a, b, and c are true.
A) The rate of an SN1 reaction depends on the concentration of the alkyl halide.
B) The rate of an SN1 reaction depends on the concentration of the nucleophile.
C) SN1 reactions of alkyl halides are favoured by polar solvents.
D) Answers a) and c) only are true.
E) Answers a, b, and c are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
SN2 reactions of the type, Nu- + RL Nu-R + L-, are favoured
A) when tertiary substrates are used.
B) by using a high concentration of the nucleophile.
C) by using a solvent of high polarity.
D) by the use of weak nucleophiles.
E) answers b and c
A) when tertiary substrates are used.
B) by using a high concentration of the nucleophile.
C) by using a solvent of high polarity.
D) by the use of weak nucleophiles.
E) answers b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which would be the major product of the following reaction? 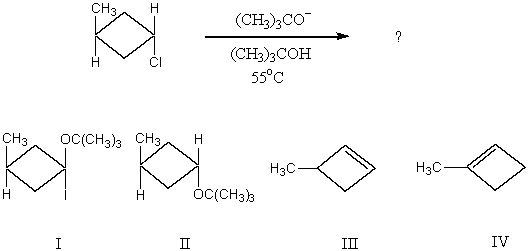
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) II and III

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What would be the major product(s) of the following reaction? 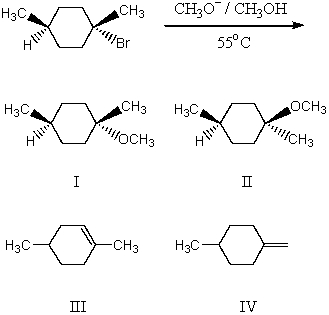
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) I and II
E) III

A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) I and II
E) III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which product (or products) would be formed in appreciable amount(s) when trans-1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane undergoes dehydrohalogenation upon treatment with sodium ethoxide in ethanol? 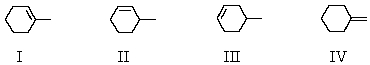
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I and II
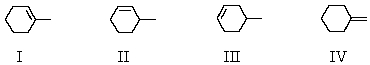
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the major product of this reaction? 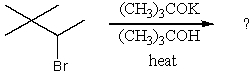
A) (CH3)2C=C(CH3)2
B) (CH3)3C-CH=CH2
C) (CH3)2C=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2C=CHCH2CH3
E) (CH3)2C=C(CH3)2 and (CH3)3C-CH=CH2
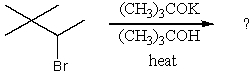
A) (CH3)2C=C(CH3)2
B) (CH3)3C-CH=CH2
C) (CH3)2C=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2C=CHCH2CH3
E) (CH3)2C=C(CH3)2 and (CH3)3C-CH=CH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which compound would be the major product? 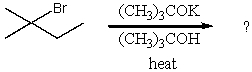
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
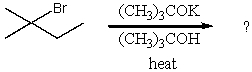

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A correct IUPAC name for the following compound is 
A) 3,3,5-trimethyl-2-hexene.
B) 3-isobutyl-3-isopropyl-2-propene.
C) 3-isobutyl-4-methyl-2-pentene.
D) 3-(1-methylethyl)-5-methyl-2-hexene.
E) 3-ethene-2,5-methylhexane.

A) 3,3,5-trimethyl-2-hexene.
B) 3-isobutyl-3-isopropyl-2-propene.
C) 3-isobutyl-4-methyl-2-pentene.
D) 3-(1-methylethyl)-5-methyl-2-hexene.
E) 3-ethene-2,5-methylhexane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which compound listed below would you expect to be the major product when 2-bromo-2-methylbutane is refluxed with KOH/ethanol?
I
II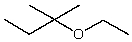
III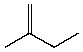
IV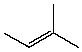
V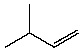
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
I

II

III

IV

V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Elimination reactions
A) require an attacking group that is a Lewis acid.
B) require and attacking group that is a Lewis base.
C) always involve the formation of a carbocation.
D) do not involve the formation of a carboncation.
E) occur via a single step.
A) require an attacking group that is a Lewis acid.
B) require and attacking group that is a Lewis base.
C) always involve the formation of a carbocation.
D) do not involve the formation of a carboncation.
E) occur via a single step.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
E2 reactions
A) require a Lewis acid as a reactant.
B) occur via the formation of a carbocation.
C) occur in a single step.
D) occur via a two step process.
E) eliminate only the leaving group from the molecule.
A) require a Lewis acid as a reactant.
B) occur via the formation of a carbocation.
C) occur in a single step.
D) occur via a two step process.
E) eliminate only the leaving group from the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
E1 reactions
A) require a Lewis acid as a reactant.
B) occur via the formation of a carbocation.
C) occur in a single step.
D) rate is determined by the removal of a proton from the carbocation.
E) eliminate only the leaving group from the molecule.
A) require a Lewis acid as a reactant.
B) occur via the formation of a carbocation.
C) occur in a single step.
D) rate is determined by the removal of a proton from the carbocation.
E) eliminate only the leaving group from the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What would be the major product of the following reaction? 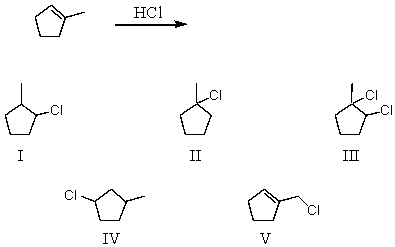
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Treating 1-methylcyclohexene with HCl would yield primarily which of these? 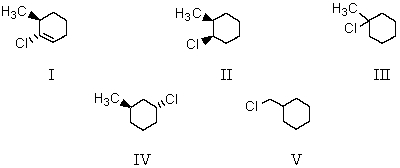
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Acid-catalyzed hydration of 2-methyl-1-butene would yield which of the following?
A) (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH3
B) CH2OHCH(CH3)CH2CH3
C) (CH3)2CHCHOHCH3
D) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH
A) (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH3
B) CH2OHCH(CH3)CH2CH3
C) (CH3)2CHCHOHCH3
D) (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH
E) CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of these is NOT formed when cyclopentene reacts with an aqueous solution of bromine? 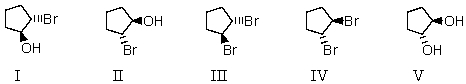
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
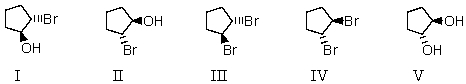
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Addition of hydrogen chloride to the following molecule would produce 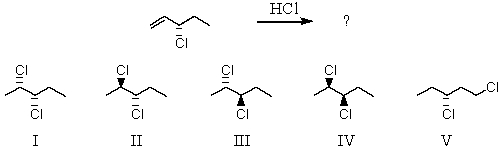
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I and IV
D) V
E) II

A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I and IV
D) V
E) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Reaction of trans-2-hexene with a solution of Br2 in CCl4 produces 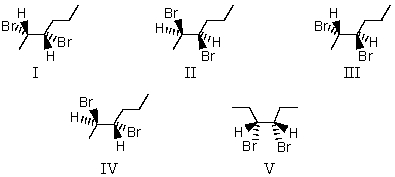
A) I and II
B) I and V
C) III and IV
D) IV and V
E) V

A) I and II
B) I and V
C) III and IV
D) IV and V
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Reagents that seek to react with a proton or some other electron-deficient centre are called ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
bonds often react with electron-seeking reagents, also referred to as ______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



