Deck 7: Theories of Chemical Bonding
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Theories of Chemical Bonding
1
Use the orbital overlap model to explain the bonding in simple molecules.
Bonding orbitals are constructed by combining atomic orbitals from adjacent atoms. Only the valence orbitals are needed to describe bonding.
2
Assign the correct hybrid orbitals used by each inner atom in a molecule and the molecular geometry that results.
The number of hybrid orbitals generated by the hybridization process equals the number of valence atomic orbitals participating in hybridization. The steric number of an inner atom can be used to infer the hybrid orbitals it is using. Elements beyond the second row of the periodic table can form bonds to more than four ligands and can be associated with more than an octet of electrons.
3
Describe the ? and bonding systems in multiple bonds.
A sigma (?) bond has high electron density distributed symmetrically along the bond axis. A pi ( ) bond has high electron density concentrated above and below the bond axis.
4
Use molecular orbital theory to calculate a bond order, predict magnetic properties of a molecule, and explain trends in bond length and energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Describe the bonding in three-atom systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Describe the bonding in extended systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Explain such properties as electrical conductivity and the colour of metals, non-metals, and metalloids in terms of band theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following molecules is NOT well described by the valence bond model?
A) SiH4
B) H2S
C) SbH3
D) H2Te
E) HF
A) SiH4
B) H2S
C) SbH3
D) H2Te
E) HF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the valence bond model, which of the following is NOT a requirement of bonding?
A) overlap of atomic orbitals
B) singly occupied atomic orbitals
C) no two electrons in a molecule have identical descriptions
D) atoms in molecule contain unpaired valence electrons
E) orbitals must have same azimuthal quantum number to overlap
A) overlap of atomic orbitals
B) singly occupied atomic orbitals
C) no two electrons in a molecule have identical descriptions
D) atoms in molecule contain unpaired valence electrons
E) orbitals must have same azimuthal quantum number to overlap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Valence bond theory based unhybrized orbitals fails to adequately describe the structure of methane
A) as carbon has only two unpaired electrons.
B) because p orbitals on carbon cannot overlap with s type orbitals on H to form bonds.
C) because it fails to adequately describe the shape of the methane molecule.
D) because the Aufbau principle is violated.
E) because methane is a square planar molecule.
A) as carbon has only two unpaired electrons.
B) because p orbitals on carbon cannot overlap with s type orbitals on H to form bonds.
C) because it fails to adequately describe the shape of the methane molecule.
D) because the Aufbau principle is violated.
E) because methane is a square planar molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The concept of hybridization of atomic orbitals was introduced
A) to predict shapes of molecules that cannot be described using traditional atomic orbitals.
B) to explain shapes of molecules that cannot be described using traditional atomic orbitals.
C) to account for the fact that carbon can form 4 bonds.
D) to explain bonding.
E) to explain delocalized bonding.
A) to predict shapes of molecules that cannot be described using traditional atomic orbitals.
B) to explain shapes of molecules that cannot be described using traditional atomic orbitals.
C) to account for the fact that carbon can form 4 bonds.
D) to explain bonding.
E) to explain delocalized bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the hybridization of the central atom in BeCl2?
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the hybridization of the central atom in ICl2-1?
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the hybridization of the central atom in SO2?
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp4
E) sp3d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify the steric number, shape, hybridization about the central atom and molecular polarity of sulphuryl chloride, SO2Cl2.
A) 4, square planar, sp3, non-polar
B) 4, tetrahedral, sp3, polar
C) 6, tetrahedral, sp3d2, polar
D) 4, square based pyramid, sp3, polar
E) 6, octahedral, sp3d2, non-polar
A) 4, square planar, sp3, non-polar
B) 4, tetrahedral, sp3, polar
C) 6, tetrahedral, sp3d2, polar
D) 4, square based pyramid, sp3, polar
E) 6, octahedral, sp3d2, non-polar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify the steric number, shape, hybridization about the central atom in XeF2Cl2.
A) 4, tetrahedral, sp3
B) 4, square planar, sp3
C) 6, octahedral, sp3d2
D) 6, tetrahedral, sp3d2
E) 6, square planar, sp3d2
A) 4, tetrahedral, sp3
B) 4, square planar, sp3
C) 6, octahedral, sp3d2
D) 6, tetrahedral, sp3d2
E) 6, square planar, sp3d2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the hybridization of Xe in the molecule XeF4?
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp3d2
D) sp3d
E) sp4
A) sp3
B) sp2
C) sp3d2
D) sp3d
E) sp4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The best description of the CO bond in acetaldehyde, CH3-(C=O)-H is
A) a sigma bond and two pi bonds.
B) two sigma bonds.
C) two pi bonds.
D) a sigma bond and a pi bond.
E) a delta bond and a pi bond.
A) a sigma bond and two pi bonds.
B) two sigma bonds.
C) two pi bonds.
D) a sigma bond and a pi bond.
E) a delta bond and a pi bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Carbon dioxide, CO2, exists as discrete molecular compounds, whereas SiO2 exists as a network covalent compound. Identify the hybridization and the number of sigma and pi bonds on each C and Si.
A) C(sp3, 2,2) S(sp3,2,2)
B) C(sp,2,2) S(sp3,0,4)
C) C(sp, 2,2) S(sp3,4,0)
D) C(sp, 2,2) S(sp,2,2)
E) C(sp3,4,0) S(sp3,4,0)
A) C(sp3, 2,2) S(sp3,2,2)
B) C(sp,2,2) S(sp3,0,4)
C) C(sp, 2,2) S(sp3,4,0)
D) C(sp, 2,2) S(sp,2,2)
E) C(sp3,4,0) S(sp3,4,0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Given that the bond energy of C-O single bond is 360 kJ/mol, a C-O double bond is 750 to 800 kJ/mol and Si-O single bond is 450 kJ/mol, what is the bond energy of a Si-O double bond?
A) 900 kJ/mol
B) significantly greater than 900 kJ/mol
C) significantly less than 900 kJ/mol
D) not possible to predict
E) slightly greater than 900 kJ/mol
A) 900 kJ/mol
B) significantly greater than 900 kJ/mol
C) significantly less than 900 kJ/mol
D) not possible to predict
E) slightly greater than 900 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Below is the line structure for the amino acid tryptophan. Determine the type of hybridization and number of each type for the starred atoms. 
A) 1 sp, 2 sp2, 2 sp3
B) 1 sp, 3 sp2, 1 sp3
C) 2 sp2, 3 sp3
D) 3 sp2, 2 sp3
E) 1 sp2, 4 sp3

A) 1 sp, 2 sp2, 2 sp3
B) 1 sp, 3 sp2, 1 sp3
C) 2 sp2, 3 sp3
D) 3 sp2, 2 sp3
E) 1 sp2, 4 sp3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many sigma and pi bonds are in acetic acid, CH3CO2H?
A) 4 , 3
B) 5 , 2
C) 6 , 2
D) 7 , 1
E) 7 , 2
A) 4 , 3
B) 5 , 2
C) 6 , 2
D) 7 , 1
E) 7 , 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following cations (O2+, C2+, N2+; F2+) would have a higher bond order than the neutral molecule?
A) all of them, removing electrons always increases bond order
B) none of them, removing electrons always decreases bond order
C) O2+, C2+
D) N2+; F2+
E) O2+, F2+
A) all of them, removing electrons always increases bond order
B) none of them, removing electrons always decreases bond order
C) O2+, C2+
D) N2+; F2+
E) O2+, F2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the bond order in Mg2?
A) 0
B) ½
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2
A) 0
B) ½
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What property of diatomic oxygen, O2, is explained by MO theory but not by Lewis, valence bond on VSEPR?
A) bond strength
B) paramagnetism
C) molecular shape
D) bond length
E) ability to form multiple bonds
A) bond strength
B) paramagnetism
C) molecular shape
D) bond length
E) ability to form multiple bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider HF, a heteronuclear diatomic molecule. Which of the following atomic orbitals will combine to form a molecular orbital?
A) H(1s) F(1s)
B) H(2px) F(2px)
C) H(1s) F(2s)
D) H(1s) F(2px)
E) H(1s) F(2px, 2py, 2pz)
A) H(1s) F(1s)
B) H(2px) F(2px)
C) H(1s) F(2s)
D) H(1s) F(2px)
E) H(1s) F(2px, 2py, 2pz)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following molecules/ions (O3, NO2-, NCO-, N2O, NO2) have the same bonding scheme as CO2?
A) NO2-, NO2
B) O3, N2O, NO2
C) NCO-, N2O, NO2
D) NCO-, N2O
E) O3, NO2-, NCO-, N2O, NO2
A) NO2-, NO2
B) O3, N2O, NO2
C) NCO-, N2O, NO2
D) NCO-, N2O
E) O3, NO2-, NCO-, N2O, NO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following best shows one of the bonds in H2C=C=CH2?
A)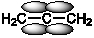
B)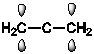
C)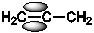
D)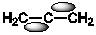
E)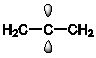
A)

B)
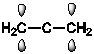
C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following does NOT have delocalized bonding?
A) NO2
B) SO2
C) F2O
D) NO2+
E) O3
A) NO2
B) SO2
C) F2O
D) NO2+
E) O3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the allene (H2C=C=CH2) molecule,
A) all the atoms lie in one plane.
B) the bonds are delocalized over all three C atoms.
C) the two H atoms on one C lie above and below the plane defined by the other CH2 group.
D) the non-bonding orbitals are full.
E) delocalized bonds are formed from overlap of hybridized orbitals.
A) all the atoms lie in one plane.
B) the bonds are delocalized over all three C atoms.
C) the two H atoms on one C lie above and below the plane defined by the other CH2 group.
D) the non-bonding orbitals are full.
E) delocalized bonds are formed from overlap of hybridized orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is needed to allow a orbital to be delocalized?
A) 4 or more atoms
B) more than 2 "p" orbitals with appropriate geometry
C) 6 electrons
D) an s and a p orbital in a molecular bond
E) carbon-carbon bonds
A) 4 or more atoms
B) more than 2 "p" orbitals with appropriate geometry
C) 6 electrons
D) an s and a p orbital in a molecular bond
E) carbon-carbon bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
P-O double bonds are stronger than P-S double bonds because
A) the O atom had greater electronegativity.
B) there is less polar character to the P-S bond.
C) the O atom has a smaller radius than the S atom.
D) the P atom is less electronegative than the O atom.
E) S has accessible d orbitals.
A) the O atom had greater electronegativity.
B) there is less polar character to the P-S bond.
C) the O atom has a smaller radius than the S atom.
D) the P atom is less electronegative than the O atom.
E) S has accessible d orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following sulphur species has the greatest delocalization as judged by the number of resonance structures?
A) H3SO4+
B) H2SO4
C) HSO4-
D) SO42-
E) SO3
A) H3SO4+
B) H2SO4
C) HSO4-
D) SO42-
E) SO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the perchlorate anion, ClO4-:
A) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having two double bonds and two single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.
B) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.
C) chlorine is not capable of forming multiple bonds.
D) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are not delocalized since the structure is not conjugated.
E) the steric number for this anion is 7, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.
A) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having two double bonds and two single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.
B) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.
C) chlorine is not capable of forming multiple bonds.
D) the steric number for this anion is 4, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are not delocalized since the structure is not conjugated.
E) the steric number for this anion is 7, the best description includes resonance structures having three double bonds and one single bonds, electrons are delocalized throughout the ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following compounds would be expected to absorb the longest wavelength light?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is true of a conjugate system?
A) The molecule is more reactive.
B) The molecule is more volatile.
C) The molecule is less reactive.
D) The molecule has the same reactivity.
E) The molecule reacts violently.
A) The molecule is more reactive.
B) The molecule is more volatile.
C) The molecule is less reactive.
D) The molecule has the same reactivity.
E) The molecule reacts violently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following compounds will absorb the most visible light, i.e,. be the most deeply coloured?
A)
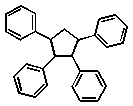
B)
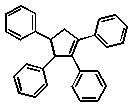
C)
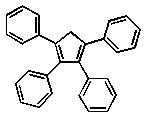
D)
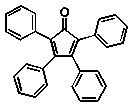
E)
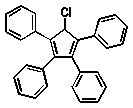
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many delocalized electrons are in the following molecule? 
A) 6
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
E) 14

A) 6
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
E) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following elements would be added to germanium to produce an n-type semiconductor?
A) gallium
B) silicon
C) aluminum
D) arsenic
E) tin
A) gallium
B) silicon
C) aluminum
D) arsenic
E) tin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In n-type seminconductor the
A) donor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the conduction band.
B) donor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the valence band.
C) acceptor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the conduction band.
D) the acceptor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the valence band.
A) donor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the conduction band.
B) donor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the valence band.
C) acceptor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the conduction band.
D) the acceptor level of the dopant lies close in energy to the valence band.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What will happen to a semiconductor made of GaP, if some of the P is replaced with As?
A) The band gap remains the same.
B) The band gap grows larger.
C) The band gap becomes smaller.
D) This cannot happen because As is not isoelectronic with P.
E) It will emit light of shorter wavelength.
A) The band gap remains the same.
B) The band gap grows larger.
C) The band gap becomes smaller.
D) This cannot happen because As is not isoelectronic with P.
E) It will emit light of shorter wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What would you dope a GaP semiconductor with to decrease the wavelength of light emitted?
A) In
B) As
C) N
D) Ge
E) The band gap cannot be changed.
A) In
B) As
C) N
D) Ge
E) The band gap cannot be changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Draw a picture showing the bonding between a hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom telling what orbitals from each are making the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the bonding between iodine atoms in molecular iodine, I2. Make sure to include a drawing to symbolize the overlap of orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
NH3 has bond angles of 107.3˚. Describe the bonding in NH3 only using unhybridized orbitals. Discuss why this type of bonding model is faulty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
H2O has a bond angle of 104.5˚. Describe the bonding in H2O only using unhybridized orbitals. Discuss why this type of bonding model is faulty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Methylene chloride, CH2Cl2, is a common industrial solvent. Sketch an orbital overlap picture of the bonds and describe the bonding present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Determine the hybridization of the central atoms of H2CCHCH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Determine the hybridization of the central atoms in H2NCHCH2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Draw the Lewis structure of the sulphite ion, SO3-2. Determine what the hybridization of the central atom is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Draw two sketches describing the bonding in propene, C3H6. The first should show any sigma bonding framework and the second sketch should illustrate the bonds that are formed, if any. Write a brief description of the bonding, naming the orbitals involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For the molecule ethene, C2H4, sketch a picture that shows the location of the bond as oriented with the plane of the hydrogen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain why carbon dioxide includes both pi and sigma bonds whereas SiO2 is formed from a network of sigma bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Draw a picture illustrating the atomic orbitals participating in the bonding in formaldehyde, H2C=O. List the orbitals used in bond formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Lewis structure of vinyl chloride is shown below; Draw orbital pictures of (a) the sigma bonding framework and (b) the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What orbitals overlap to make the bond(s) between C and O in acetone, CH3COCH3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In which chemical species would you expect the strongest bond: C2+; N2+; O2+? Write the electronic molecular orbital configuration and calculate the bond order for that species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Write the electron configuration and predict the bond order and number of unpaired electrons O2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Write the electron configuration and predict the bond order and number of unpaired electrons B-C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Determine the bond order for F2. How many electrons are in antibonding orbitals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Determine the bond order for O2+ and tell how many electrons are in antibonding orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Draw orbital pictures of the highest energy molecular orbital occupied in fluorine F2 and the atomic orbitals that form it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Predict the bond order and number of unpaired electrons in NO+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Predict using MO theory if NO- will be paramagnetic or diamagnetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What kind of bonds are obtained by the overlap of the dxy and the p orbitals shown below? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the text's problems, you were asked to find the Lewis structure of HNCO. Compare that Lewis structure with that of the isomer, NCOH and suggest why the HNCO isomer may be more stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Draw the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals for NO2-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain the difference between an isolated orbital and a delocalized orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What are non-bonding molecular orbitals of ozone, O3, and where do they originate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Determine the bonding for the nitrite ion, NO2-1. Determine what hybridization the central atom has and how many delocalized orbitals there are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Draw a combination of a 3d orbital on phosphorus and a 2p orbital on O that allows bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Describe the bonding in the polyatomic anion, nitrate (NO3-1) by drawing the resonance structures and the bonding molecular orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Draw the band diagram that is appropriate for a ZnS semiconductor that has been doped with copper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain how band theory can explain the electrical conductivity observed in Mg metal given that atomic Mg has valence electrons fully occupying the 2p atomic orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A new material is colourless, but is not an insulator. What can you deduce about the energy of the bandgap? Give an estimate of the bandgap in kJ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Draw a representation of a band gap for graphite and germanium and discuss any differences between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Semiconductors are used for solar energy conversion in devices called photovoltaic cells. For high efficiency, the cell should be able to utilize as much light as possible. What band gap (in kJ/mole) would be needed to utilize light of 550 nm (about the middle of the visible spectrum) and shorter wavelengths?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Describe what happens to an electron as it travels through an n p-type junction of a semiconductor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



