Deck 7: Mendelian Genetics in Populations II: Migration, Drift, & Nonrandom Mating
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Mendelian Genetics in Populations II: Migration, Drift, & Nonrandom Mating
1
If genetic drift is not accompanied by natural selection,mutation,or migration,then the frequencies of alleles will "wander" between 0 and 1.Using the accompanying figure,which of the following is an accurate statement? 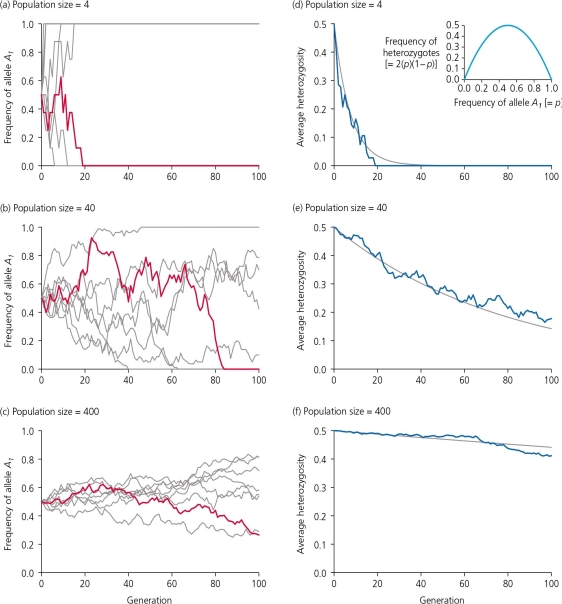
A) Random sampling error generates fluctuations in allelic frequencies over generations, so all populations-both simulated and real-have been found to follow the same evolutionary trajectory.
B) The effects of genetic drift are more immediate, and more pronounced, on small population sizes.
C) Genetic drift will have no long-term effect on allelic frequencies if the population numbers more than 40 individuals.
D) None of these is an accurate statement.

A) Random sampling error generates fluctuations in allelic frequencies over generations, so all populations-both simulated and real-have been found to follow the same evolutionary trajectory.
B) The effects of genetic drift are more immediate, and more pronounced, on small population sizes.
C) Genetic drift will have no long-term effect on allelic frequencies if the population numbers more than 40 individuals.
D) None of these is an accurate statement.
B
2
The accompanying figure details the possible outcomes in a scenario in which 10 zygotes are formed from a gene pool where frequency of the allele A1 is 0.6,and A2 is 0.4.This graph is shown here.According to this graph,the probability that the frequency of A1 will remain the same in the next generation is about ________. 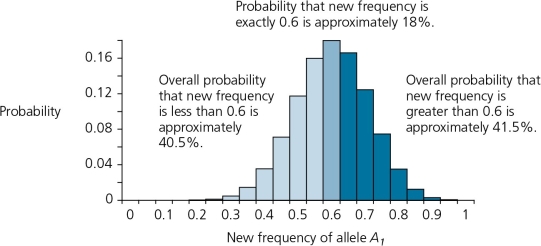
A) 8%
B) 12%
C) 16%
D) 18%
E) none of the above

A) 8%
B) 12%
C) 16%
D) 18%
E) none of the above
D
3
The accompanying figure details the possible outcomes in a scenario in which 10 zygotes are formed from a gene pool where the frequency of the allele A1 is 0.6,and A2 is 0.4.This graph is shown here.According to this graph,the probability that the frequency of A1 will increase to 0.7 in the next generation is about ________. 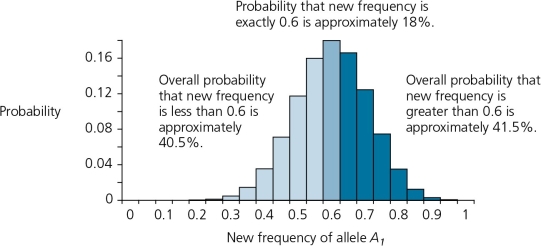
A) 8%.
B) 12%
C) 16%
D) 40%
E) 70%

A) 8%.
B) 12%
C) 16%
D) 40%
E) 70%
B
4
Gene flow through migration ________.
A) has no effect on allele frequencies of populations
B) can go only in one direction
C) may have the largest impact on small populations, such as those on islands
D) maintains the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
A) has no effect on allele frequencies of populations
B) can go only in one direction
C) may have the largest impact on small populations, such as those on islands
D) maintains the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle include all of the following except ________.
A) random mating
B) no migration
C) limited population size
D) All of these are assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg.
A) random mating
B) no migration
C) limited population size
D) All of these are assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The results of an experiment on genetic drift on Drosophila melanogaster are illustrated in the accompanying figure.These data show ________. 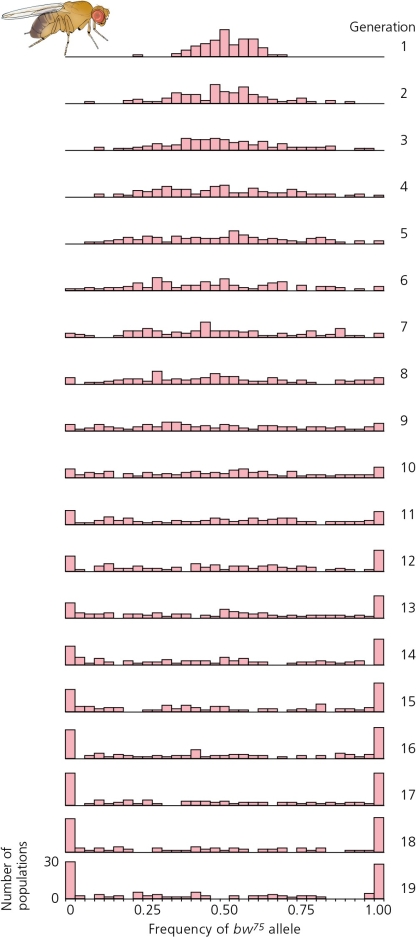
A) the loss of heterozygosity in the population over time
B) the fixation of alleles in the population over time
C) the permanent loss of alleles from the population over time
D) All of the above are accurate.
E) None of the above is accurate.

A) the loss of heterozygosity in the population over time
B) the fixation of alleles in the population over time
C) the permanent loss of alleles from the population over time
D) All of the above are accurate.
E) None of the above is accurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Unusually high rates of rare heritable traits,such as achromatopsia in the Pingelapese people,is often due to ________.
A) genetic drift
B) natural selection
C) hitchhiking
D) the founder effect
E) None of the above.
A) genetic drift
B) natural selection
C) hitchhiking
D) the founder effect
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Data in the accompanying figure shows the results of allelic frequency analysis of an insect-pollinated plant whose seeds are transported by wind and water,therefore making this plant one of the first colonizers of new islands.The data―particularly the lower variation of allele frequencies of intermediate-aged populations―supports the hypothesis that ________. 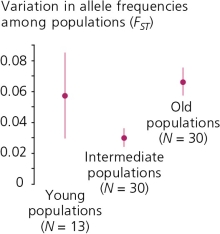
A) genetic drift tends to homogenize populations
B) migration tends to homogenize populations
C) gene flow tends to homogenize populations
D) A, B, and C are all accurate.
E) B and C are both accurate.

A) genetic drift tends to homogenize populations
B) migration tends to homogenize populations
C) gene flow tends to homogenize populations
D) A, B, and C are all accurate.
E) B and C are both accurate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In an evolutionary sense,________ is the transfer of alleles from one population to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The random discrepancy between theoretical predictions and actual outcomes is called ________.[two words]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
There are occasions when theoretical expectations do not match with actual outcomes,as you see in the case of zygote formation leading to genetic drift.This discrepancy is known as ________.
A) sampling bias
B) sampling error
C) nonrandom mating
D) random mutations
A) sampling bias
B) sampling error
C) nonrandom mating
D) random mutations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At present,the neutral theory of molecular evolution ________.
A) is strongly supported by significant amounts of empirical evidence
B) has been disproven, as neutral mutations have not been shown to have been fixed in populations
C) is inclusive, as enough data has not yet been evaluated
D) seems to work in some species but not others
A) is strongly supported by significant amounts of empirical evidence
B) has been disproven, as neutral mutations have not been shown to have been fixed in populations
C) is inclusive, as enough data has not yet been evaluated
D) seems to work in some species but not others

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Although most of the mechanisms of evolution are nonrandom,the one that is absolutely random is ________.
A) sexual selection
B) natural selection
C) artificial selection
D) genetic drift
A) sexual selection
B) natural selection
C) artificial selection
D) genetic drift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The fact that blind luck (more technically known as sampling error)can account for changes in allelic frequencies in populations is the evolutionary mechanism called ________.[two words]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The neutral theory of molecular evolution,as developed by Kimura,posits that ________.
A) functionally neutral mutations that become fixed in populations occur in much larger numbers than those that become fixed by natural selection
B) functionally neutral mutations never become fixed in populations without some element of selection also acting on them
C) functionally neutral mutations are not subject to genetic drift
D) functionally neutral mutations contribute very little to changes at the molecular level
A) functionally neutral mutations that become fixed in populations occur in much larger numbers than those that become fixed by natural selection
B) functionally neutral mutations never become fixed in populations without some element of selection also acting on them
C) functionally neutral mutations are not subject to genetic drift
D) functionally neutral mutations contribute very little to changes at the molecular level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a founding population carries an allelic frequency not typical of the original population.Which of the following effects would most likely lead to homogenization?
A) genetic drift within the founding population
B) random mating within the founding population
C) no mutations within either population
D) migration between the original and founding populations
E) None of the above.
A) genetic drift within the founding population
B) random mating within the founding population
C) no mutations within either population
D) migration between the original and founding populations
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The effects of inbreeding depression has been documented in ________.
A) plants only
B) animals only
C) both plants and animals
D) This is a hypothetical construct and has yet to be documented.
A) plants only
B) animals only
C) both plants and animals
D) This is a hypothetical construct and has yet to be documented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In terms of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,genetic drift results from a violation of ________.
A) the random mating assumption
B) the lack of natural selection assumption
C) the infinite population size assumption
D) the lack of mutation assumption
E) the lack of migration assumption
A) the random mating assumption
B) the lack of natural selection assumption
C) the infinite population size assumption
D) the lack of mutation assumption
E) the lack of migration assumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
With enough time and in the absence of other evolutionary mechanisms,genetic drift will ________.
A) reduce the genetic variation in a population
B) increase the genetic variation in a population
C) have no effect on the genetic variation of a population
D) None of the above.
A) reduce the genetic variation in a population
B) increase the genetic variation in a population
C) have no effect on the genetic variation of a population
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 7.6 from your text,shown below,is a set of histograms showing the frequency of different color patterns of water snakes of Lake Erie (Nerodia sipedon).Type A snakes are unbanded,Type B are strongly banded,and Types C and D are intermediates.Given that natural selection favors unbanded snakes on the islands,how can you account for the presence/perpetuation of banded snakes on the islands? 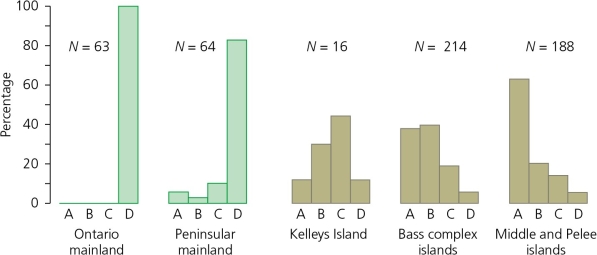
A) Mutation rates converting unbanded alleles to a banded form operate at high frequencies on islands.
B) Natural selection favors unbanded snakes on the mainland.
C) Snakes on the islands represent a case of the so-called founder effect.
D) Natural selection favors banded snakes on the mainland, which occasionally migrate to the islands.

A) Mutation rates converting unbanded alleles to a banded form operate at high frequencies on islands.
B) Natural selection favors unbanded snakes on the mainland.
C) Snakes on the islands represent a case of the so-called founder effect.
D) Natural selection favors banded snakes on the mainland, which occasionally migrate to the islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A phenomenon known as ________ [two words] occurs under conditions where a selection pressure works against deleterious mutations,resulting in the corresponding decrease in the frequency of a closely linked neutral mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A phenomenon known as ________ [one or two words] occurs under conditions where a strong selection pressure acts on a particular change in an amino acid,which results in the corresponding increase in frequency of a closely linked neutral (or even mildly deleterious)mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A locus at which different individuals in a population carry different alleles is known as a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Compare and contrast natural selection with genetic drift as mechanisms of evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The survival and fertility rates of the offspring of related individuals are commonly reduced.This is known as ________.[two words]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The most common form of nonrandom mating is inbreeding.Despite the fact that inbreeding will not change allelic frequencies,it can still have a significant impact on the evolution of a lineage.Explain,using examples,why this is so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When we track alleles from lineages backwards in time,we see them ultimately fuse into one lineage.The result is a gene tree,which is produced by a process called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A scenario in which 250 zygotes are formed from a gene pool in which the frequency of the allele A₁ is 0.6,and A₂ is 0.4,generates the accompanying figure.Explain,in general terms,what each of these graphs reveals.Is there a consistent pattern between all three graphs? If so,describe and provide an explanation for it.Are there inconsistencies among graphs? Describe and provide an explanation for these also.
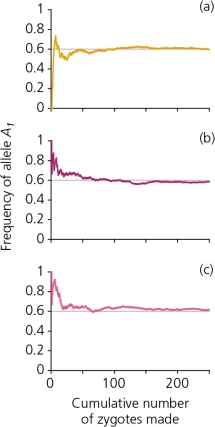


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
________,the most common type of nonrandom mating,will not change allelic frequencies,but it will change genotypic frequencies toward homozygosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose a large population exists on a continent,and a new population is formed by the migration of a few individuals to an island some distance away.The fact that the alleles being carried to this island are not going to be a complete and representative set,as compared to the continental population,is a case of genetic drift known as the ________.[two words]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



