Deck 8: Lipids and Membranes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Lipids and Membranes
1
Which of the following is considered an omega-3 fatty acid?
A) 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid
B) 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid
C) 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid
D) 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid
E) 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid
A) 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid
B) 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid
C) 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid
D) 8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acid
E) 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid
9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid
2
Which of the following alcohols is esterified to the phosphate group of glycerophospholipids?
A) choline
B) ethanolamine
C) glycerol
D) serine
E) all of the above
A) choline
B) ethanolamine
C) glycerol
D) serine
E) all of the above
all of the above
3
Which of the following explains why free fatty acids do not form bilayers?
A) the width of the polar head is greater than the nonpolar tail
B) the width of the polar head is less than the nonpolar tail
C) the width of the polar head is equal to the nonpolar tail
D) the width of the nonpolar head is greater than the polar tail
E) the width of the nonpolar head is less than the polar tail
A) the width of the polar head is greater than the nonpolar tail
B) the width of the polar head is less than the nonpolar tail
C) the width of the polar head is equal to the nonpolar tail
D) the width of the nonpolar head is greater than the polar tail
E) the width of the nonpolar head is less than the polar tail
the width of the polar head is greater than the nonpolar tail
4
As temperatures grow colder with the onset of winter, animals will adapt by changing the fatty acid composition of cell membranes. What characteristics of fatty acids will be seen?
A) longer chains with greater unsaturation
B) longer chains with greater saturation
C) shorter chains with greater unsaturation
D) shorter chains with greater saturation
E) chain length and saturation do not change in a cell membrane
A) longer chains with greater unsaturation
B) longer chains with greater saturation
C) shorter chains with greater unsaturation
D) shorter chains with greater saturation
E) chain length and saturation do not change in a cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a transmembrane domain of protein contains -sheet structure, the overall structure of the transmembrane portion is likely a ____________.
A) -barrel
B) -tube
C) -turn
D) -helix
E) none of the above
A) -barrel
B) -tube
C) -turn
D) -helix
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which fatty acid is commonly attached to proteins to allow membrane localization?
A) eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
B) arachidonic acid
C) linoleic acid
D) myristic acid
E) farnesylic acid
A) eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
B) arachidonic acid
C) linoleic acid
D) myristic acid
E) farnesylic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If polar amino acids are found in a membrane spanning -helical region, they are most likely _____.
A) mutations
B) modified with nonpolar groups by prenylation, methylation and/or acylation
C) hydrogen-bonded to other polar amino acids to prevent interaction with the membrane lipids
D) hydrogen-bonded with hydroxyl groups of the membrane fatty acids
E) none of the above
A) mutations
B) modified with nonpolar groups by prenylation, methylation and/or acylation
C) hydrogen-bonded to other polar amino acids to prevent interaction with the membrane lipids
D) hydrogen-bonded with hydroxyl groups of the membrane fatty acids
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a characteristic of integral membrane proteins?
A) most of their movement is by lateral diffusion
B) transverse diffusion occurs often but rather slowly
C) interactions between proteins makes the membrane highly rigid
D) all have carbohydrates attached to the extracellular domain
E) none of the above
A) most of their movement is by lateral diffusion
B) transverse diffusion occurs often but rather slowly
C) interactions between proteins makes the membrane highly rigid
D) all have carbohydrates attached to the extracellular domain
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The carbohydrate portion of a membrane spanning glycoprotein is found _____.
A) spanning the membrane
B) on both the cytoplasmic and extracellular sides of the membrane
C) only on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane
D) only on the extracellular side of the membrane
E) carbohydrates are not found on membrane spanning glycoproteins
A) spanning the membrane
B) on both the cytoplasmic and extracellular sides of the membrane
C) only on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane
D) only on the extracellular side of the membrane
E) carbohydrates are not found on membrane spanning glycoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following aspects of membrane protein movement is explained by the fluid mosaic model?
A) proteins that are immobile are often esterified to cholesterol via an Asp residue
B) proteins that are mobile only in a small area are sequestered by proteins attached to the cytoskeleton
C) proteins that freely diffuse through the membrane often undergo flip-flopping
D) proteins confined to a lipid raft are linked to phosphatidylserine via and amide bond
E) none of the above
A) proteins that are immobile are often esterified to cholesterol via an Asp residue
B) proteins that are mobile only in a small area are sequestered by proteins attached to the cytoskeleton
C) proteins that freely diffuse through the membrane often undergo flip-flopping
D) proteins confined to a lipid raft are linked to phosphatidylserine via and amide bond
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
___ and ___ have the appropriate geometry to form lipid bilayers while ___ tends to form micelles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For a saturated fatty acid, melting point _____ with increasing chain length due to a greater number of _____ interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a mixed bilayer, longer acyl chains tend to be ___ than shorter acyl chains and unsaturated acyl chains are ___ than saturated chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a mixed bilayer, cholesterol restricts the movement of nearby acyl chains, thus preventing the membrane from becoming too ___. Cholesterol inserts between membrane lipids, preventing close packing, thus preventing the membrane from becoming too ___.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Transverse diffusion occurs ___ lateral diffusion occurs ___.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A membrane protein in a lipid raft will ___ a membrane protein attached to the cytoskeleton will ___.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Considering the characteristics of common fatty acids found in animals described in the text, which of the structures shown below would you consider the rarest fatty acid if found in animals?
A)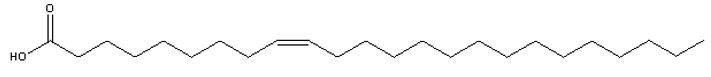
B)
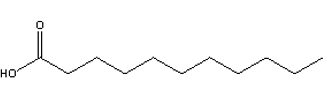
C)
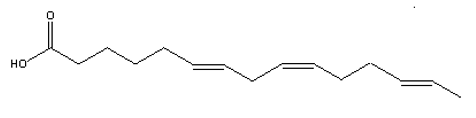
D)
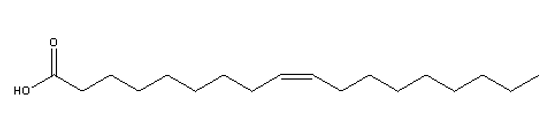
E) All structures would be equally rare.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All structures would be equally rare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the structures below is an example of an -3 polyunsaturated fatty acid?
A)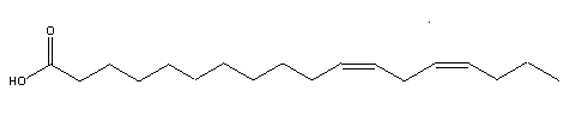
B)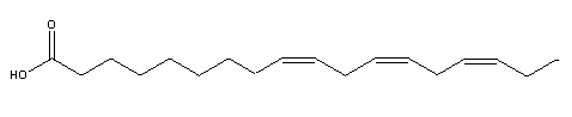
C)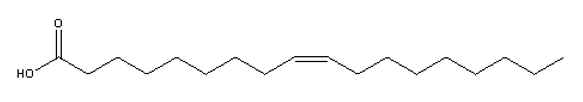
D)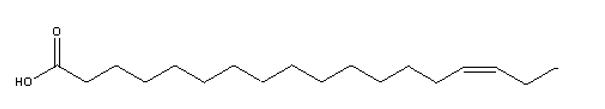
E) none of the above
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following structures correctly represents a glycerophospholipid?
A)
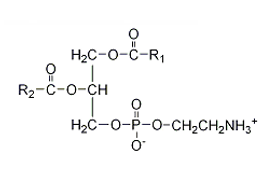
B)
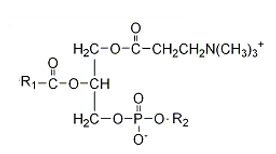
C)
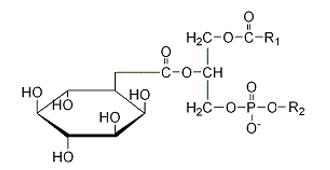
D)
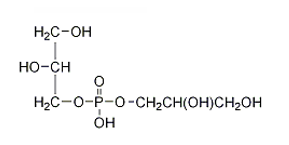
E) none of the above
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



