Deck 12: Epigenetic Mechanisms of Gene Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Epigenetic Mechanisms of Gene Regulation
1
As a general rule, cytosine DNA methylation marks genes for
A) activation.
B) silencing.
C) mutation.
D) programmed gene rearrangements.
A) activation.
B) silencing.
C) mutation.
D) programmed gene rearrangements.
silencing.
2
CpG islands have all of the following characteristics, except:
A) They are found near gene promoters.
B) They are protected from spontaneous deamination.
C) They are typically highly methylated.
D) They occur in clusters near the 5? end of genes.
A) They are found near gene promoters.
B) They are protected from spontaneous deamination.
C) They are typically highly methylated.
D) They occur in clusters near the 5? end of genes.
They are typically highly methylated.
3
The dinucleotide CG is underrepresented in the human genome because
A) it is highly deleterious in most genomic locations due to methylation.
B) methylcytosine is highly susceptible to spontaneous deamination, resulting in the TG dinucleotide.
C) methylcytosine is read as an thymine during replication, resulting in the CA dinucleotide.
D) methyltransferases cannot methylate cytosines when a guanine is the next nucleotide.
A) it is highly deleterious in most genomic locations due to methylation.
B) methylcytosine is highly susceptible to spontaneous deamination, resulting in the TG dinucleotide.
C) methylcytosine is read as an thymine during replication, resulting in the CA dinucleotide.
D) methyltransferases cannot methylate cytosines when a guanine is the next nucleotide.
methylcytosine is highly susceptible to spontaneous deamination, resulting in the TG dinucleotide.
4
During DNA replication, methylation is
A) maintained by a semiconservative process.
B) erased and then a maintenance methylase adds back methyl groups to both the templateand the newly synthesized strand.
C) erased and then a maintenance methylase adds back methyl groups to the templatestrand.
D) not maintained; replication results in hemimethylated progeny DNA.
A) maintained by a semiconservative process.
B) erased and then a maintenance methylase adds back methyl groups to both the templateand the newly synthesized strand.
C) erased and then a maintenance methylase adds back methyl groups to the templatestrand.
D) not maintained; replication results in hemimethylated progeny DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the allele choice is determined by its parent-of-origin, monoallelic gene expression is referred to
A) nutritional legacy.
B) transposition.
C) gene switching.
D) imprinting.
A) nutritional legacy.
B) transposition.
C) gene switching.
D) imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For imprinted genes, selection of the active allele
A) does not depend on the parent-of-origin
B) can either be random or nonrandom depending on the particular gene
C) is random
D) is nonrandom
A) does not depend on the parent-of-origin
B) can either be random or nonrandom depending on the particular gene
C) is random
D) is nonrandom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement is not true about imprinted genes?
A) Imprinting is maintained in the primordial germ cells.
B) Nearly all imprinted genes are organized in clusters in the genome.
C) Imprinting occurs in mammals, but no other vertebrates studied so far.
D) Imprinting affects a small subset of genes and results in the expression of those genesfrom only one of the two parental chromosomes.
A) Imprinting is maintained in the primordial germ cells.
B) Nearly all imprinted genes are organized in clusters in the genome.
C) Imprinting occurs in mammals, but no other vertebrates studied so far.
D) Imprinting affects a small subset of genes and results in the expression of those genesfrom only one of the two parental chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a proposed mechanism for monoallelic expression of imprinted genes?
A) Altered chromatin structure in the gene promoter.
B) Differential expression of an antisense RNA transcript.
C) Programmed gene rearrangements.
D) Blocking of an enhancer by an insulator.
A) Altered chromatin structure in the gene promoter.
B) Differential expression of an antisense RNA transcript.
C) Programmed gene rearrangements.
D) Blocking of an enhancer by an insulator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (Igf2r) gene is expressed exclusively from the maternal allele on chromosome 17 due to
A) differential methylation of an Igf2r intron.
B) differential expression of an antisense RNA transcript.
C) transposition of the maternal copy of Igf2r.
D) methylation of an imprinting control region.
A) differential methylation of an Igf2r intron.
B) differential expression of an antisense RNA transcript.
C) transposition of the maternal copy of Igf2r.
D) methylation of an imprinting control region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Imprinted genes are regulated by imprinting control regions (ICRs). Within these regions there are allele-specific differences in
A) DNA methylation
B) histone modification
C) the location of CpG islands
A) DNA methylation
B) histone modification
C) the location of CpG islands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
X chromosome inactivation in humans is
A) random
B) nonrandom
C) imprinted
D) preferential for the paternal X chromosome
A) random
B) nonrandom
C) imprinted
D) preferential for the paternal X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
XIST transcript levels are upregulated
A) on the active X chromosome
B) on the inactive X chromosome
C) on an autosome
D) by the expression of Tsix
A) on the active X chromosome
B) on the inactive X chromosome
C) on an autosome
D) by the expression of Tsix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
X chromosome inactivation is characterized by a series of epigenetic chromatin modifications, including all of the following except for:
A) DNA methylation
B) histone hyperacetylation
C) enrichment of variant histone macroH2A
D) coating with XIST RNA
A) DNA methylation
B) histone hyperacetylation
C) enrichment of variant histone macroH2A
D) coating with XIST RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Transposable elements
A) have the ability to move from one location to another in a genome.
B) occur very rarely in humans.
C) are small, extrachromosomal circles of DNA that have the ability to self-replicate.
D) are found only in bacteria and plants.
A) have the ability to move from one location to another in a genome.
B) occur very rarely in humans.
C) are small, extrachromosomal circles of DNA that have the ability to self-replicate.
D) are found only in bacteria and plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Transposable elements were first discovered while studying chromosomal breakage events in maize by
A) Mary Lyon
B) Gregor Johann Mendel
C) James Watson and Francis Crick
D) Barbara McClintock
A) Mary Lyon
B) Gregor Johann Mendel
C) James Watson and Francis Crick
D) Barbara McClintock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The wrinkled seed (rr) character of the garden pea described by Mendel is caused by
A) insertion of a transposable element
B) genomic imprinting
C) X chromosome inactivation
D) a nonsense mutation
A) insertion of a transposable element
B) genomic imprinting
C) X chromosome inactivation
D) a nonsense mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
DNA transposons move by a(n)
A) "copy and paste" mechanism.
B) "cut and paste" mechanism.
C) "Activator (Ac)-Dissociation (Ds)" mechanism.
D) "random walk" mechanism.
A) "copy and paste" mechanism.
B) "cut and paste" mechanism.
C) "Activator (Ac)-Dissociation (Ds)" mechanism.
D) "random walk" mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Retrotransposons move by a(n)
A) "copy and paste" mechanism.
B) "cut and paste" mechanism.
C) "Activator (Ac)-Dissociation (Ds)" mechanism.
D) "random walk" mechanism.
A) "copy and paste" mechanism.
B) "cut and paste" mechanism.
C) "Activator (Ac)-Dissociation (Ds)" mechanism.
D) "random walk" mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Alu elements are
A) active long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES) in the human genome
B) inactive long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES) in the human genome
C) active short interspersed nuclear elements (SINES) in the human genome
D) inactive short interspersed nuclear elements (SINES) in the human genome
A) active long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES) in the human genome
B) inactive long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES) in the human genome
C) active short interspersed nuclear elements (SINES) in the human genome
D) inactive short interspersed nuclear elements (SINES) in the human genome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
About 21% of the human genome is composed of members of the
A) Ac and Ds elements
B) L1 family of long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES)
C) Tc1/mariner superfamily elements
D) P elements
A) Ac and Ds elements
B) L1 family of long interspersed nuclear elements (LINES)
C) Tc1/mariner superfamily elements
D) P elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A nonautonomous transposon relies on other transposons for transposition because it
A) does not contain transposase recognition sequences.
B) does not encodes transposase.
C) does not undergo methylation.
D) all of the above.
A) does not contain transposase recognition sequences.
B) does not encodes transposase.
C) does not undergo methylation.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When a pregnant female of a particular strain of yellow agouti mice with the agouti viable yellow (Avy) allele was fed a diet rich in folic acid, the mouse give birth to offspring with mostly brown fur indicating that
A) an LTR retrotransposon was hypermethylated and moved from one chromosome to another, thereby turning on expression of the brown fur gene
B) an LTR retrotransposon was hypermethylated and moved from one chromosome to another, thereby shutting off expression of the agouti gene
C) the LTR retrotransposon promoter region was hypomethylated, thereby shutting off expression of the downstream agouti gene.
D) the retrotransposon promoter region was hypermethylated, thereby shutting off expression of the downstream agouti gene.
A) an LTR retrotransposon was hypermethylated and moved from one chromosome to another, thereby turning on expression of the brown fur gene
B) an LTR retrotransposon was hypermethylated and moved from one chromosome to another, thereby shutting off expression of the agouti gene
C) the LTR retrotransposon promoter region was hypomethylated, thereby shutting off expression of the downstream agouti gene.
D) the retrotransposon promoter region was hypermethylated, thereby shutting off expression of the downstream agouti gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A haploid yeast cell of mating-type that has budded and divided at least once
A) can switch to the opposite mating type.
B) must bud and divide again before switching to the opposite mating type.
C) will form a diploid / spore.
D) will stop budding and dividing.
A) can switch to the opposite mating type.
B) must bud and divide again before switching to the opposite mating type.
C) will form a diploid / spore.
D) will stop budding and dividing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that prior to mating-type switching in a haploid yeast cell, MAT is expressed in the active locus. During mating-type switching by homologous recombination
A) the MAT genes in the active locus switch places with HMRa genes at a silent, donorlocus
B) the MAT genes in the active locus are degraded and replaced with HMRa genes from asilent, donor locus.
C) the MAT genes in the active locus are returned to the HML silent locus; HMRa genesfrom a silent, donor locus are moved to the active MAT locus.
D) the MAT locus is inactivated and HMRa genes are activated by an epigeneticmechanism.
A) the MAT genes in the active locus switch places with HMRa genes at a silent, donorlocus
B) the MAT genes in the active locus are degraded and replaced with HMRa genes from asilent, donor locus.
C) the MAT genes in the active locus are returned to the HML silent locus; HMRa genesfrom a silent, donor locus are moved to the active MAT locus.
D) the MAT locus is inactivated and HMRa genes are activated by an epigeneticmechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
DNA methylation of transposable elements is thought to function
A) as a host defense mechanism.
B) as a mechanism to counteract silencing of the transposable element.
C) to promote excision of transposable element sequences.
D to promote insertion of new sequences into the transposable elements.
A) as a host defense mechanism.
B) as a mechanism to counteract silencing of the transposable element.
C) to promote excision of transposable element sequences.
D to promote insertion of new sequences into the transposable elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In plants, heterochromatinization of repeat sequences may be mediated by
A) histone hyperacetylation.
B) formation of nuclear pore-associated chromatin loops.
C) riboswitch-containing mRNAs.
D) RNA-directed DNA methylation.
A) histone hyperacetylation.
B) formation of nuclear pore-associated chromatin loops.
C) riboswitch-containing mRNAs.
D) RNA-directed DNA methylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During mating-type switching in haploid yeast cells, in the "off" state the recombination enhancer
A) represses all mating-type switching
B) represses mating-type switching in daughter cells
C) represses recombination between MAT and HML
D) represses recombination between MAT and HMRa
A) represses all mating-type switching
B) represses mating-type switching in daughter cells
C) represses recombination between MAT and HML
D) represses recombination between MAT and HMRa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Antigen switching in trypanosomes occurs by
A) gene conversion
B) reciprocal recombination
C) switching the active expression site
D) all of the above answers apply
A) gene conversion
B) reciprocal recombination
C) switching the active expression site
D) all of the above answers apply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is not true about variable surface glycoprotein (VSG) gene expression in the trypanosome, Trypanosoma brucei?
A) There are over 1000 different VSG genes, but only one is expressed at a time.
B) There is a single telomeric expression site.
C) VSG gene transcription is localized in the "expression site body."
D) VSG switching occurs predominantly by DNA homologous recombination.
A) There are over 1000 different VSG genes, but only one is expressed at a time.
B) There is a single telomeric expression site.
C) VSG gene transcription is localized in the "expression site body."
D) VSG switching occurs predominantly by DNA homologous recombination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
During development, millions of B cell types are produced. Each B cell has a unique antigen receptor generated from different V, D, and J gene segments by a series of
A) alternative splicing events during B-cell differentiation
B) multiple gene mutation events during B-cell differentiation
C) site-specific recombination events during B-cell differentiation
D) nucleotide excision repair events during B-cell differentiation
A) alternative splicing events during B-cell differentiation
B) multiple gene mutation events during B-cell differentiation
C) site-specific recombination events during B-cell differentiation
D) nucleotide excision repair events during B-cell differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During V(D)J recombination there is epigenetic control of the initial selection of the allele to be rearranged. This involves
A) progressive histone hyperacetylation of the heavy chain allele to be rearranged
B) differential methylation of the two light chain alleles
C) early replication of the light chain allele that undergoes rearrangement
D) all of the above answers apply
A) progressive histone hyperacetylation of the heavy chain allele to be rearranged
B) differential methylation of the two light chain alleles
C) early replication of the light chain allele that undergoes rearrangement
D) all of the above answers apply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following does not result from allelic exclusion?
A) transgenerational effects of diet
B) mating type switching in yeast
C) antigen switching in trypanosomes
D) unique immunoglobin gene expression in lymphocytes
A) transgenerational effects of diet
B) mating type switching in yeast
C) antigen switching in trypanosomes
D) unique immunoglobin gene expression in lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which does not constitute a major epigenetic mechanism involved in mammalian X inactivation?
A) cytosine methylation
B) histone methylation
C) association with Xist RNA
D) gene rearrangement
A) cytosine methylation
B) histone methylation
C) association with Xist RNA
D) gene rearrangement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Draw the structure of the normal base cytosine compared with 5-methyl-cytosine. Which base is more likely to undergo spontaneous deamination to thymine? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The CG dinucleotide is often denoted as "CpG." What does the "p" represent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You hypothesize that methylation of a gene of interest is correlated with decreased gene expression. Design an experiment to test your hypothesis and show sample positive results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
You prepare two samples of genomic DNA and digest one with HpaII and the other with MspI. After digestion you separate the DNA samples by agarose gel electrophoresis. Sketch the pattern of bands you would see and indicate the location of any CpG islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Discuss the connection between DNA methylation and fragile X mental retardation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Diagram how genomic imprinting is "reset" in the germline and then maintained throughout development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Compare and contrast three general mechanisms for ensuring monoallelic expression of maternally or paternally imprinted genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe how methylation analysis can be used for clinical diagnosis of Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) and Angelman syndrome (AS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A child shows symptoms of Angelman syndrome (AS), but their methylation pattern on chromosome 15 is normal. Explain how AS may have arisen in this case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
You have performed a bisulfite-PCR assay for distinguishing normal cytosine from 5-methyl cytosine. The starting sequence is: CGCGTAGCC. After sodium bisulfite treatment, PCR, and DNA sequencing, you obtain the following sequence: CGCGTAGTT. Which of the cytosines were methylated in the starting sequence? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
H19 is a maternally expressed imprinted gene. What evidence is suggestive that the H19 transcript is a protein-coding mRNA. What evidence favors its role as a regulatory RNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Diagram the mode of regulation of the insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2)-H19 locus.
Discuss some of the known consequences of loss of imprinting of Igf2.
Discuss some of the known consequences of loss of imprinting of Igf2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Discuss evidence for and against the "conflict hypothesis" for the origins of genomic imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Compare and contrast X-chromosome inactivation with imprinting of a paternal or maternal allele of a gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use a diagram to compare and contrast X chromosome inactivation in marsupials and placental mammals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Is XIST transcribed from the active or inactive X chromosome? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Discuss some of the implications of the findings that about 15% of genes on the inactive X chromosome escape inactivation and that in an additional 10% of genes the level of expression differs from woman to woman.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Describe changes in gene expression that are likely to occur upon transposition of the Ds mobile genetic element in maize to a site within a kernel color gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Diagram the mechanism by which DNA transposons move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Diagram the mechanism by which retrotransposons move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Describe a specific example of an active Alu element in humans and describe a diagnostic test for the presence of the Alu element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Define the terms "LINE" and "SINE". These elements are widespread in the human genome. Are any still active? Explain your answer, giving specific examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You have discovered a new species of plant with flowers that are either purple or white. Assume that you have enough sequence information for the purple pigment gene to design primers for PCR amplification of a specific region of the gene. You extract genomic DNA from purple flowers and white flowers and perform PCR. After gel electrophoresis of the PCR products, you find that you have amplified a 200 bp fragment from the purple flower. In contrast, using the same PCR primers, you amplify a 500 bp fragment from the white flower. Provide an explanation for these results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Discuss the connection between DNA methylation and the statement that "poor nutrition predisposes cells of an organism to cancer."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
DNA methylation may serve to defend the genome. Give an example of epigenetic control of an active LTR retrotransposon in mouse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
DNA methylation may serve to defend the genome from transposable elements. Other than methylation, what is another mechanism for epigenetic control of transposable elements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Diagram the process of gene conversion in yeast during switching from mating-type alpha to mating-type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the key characteristics of variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) gene expression in trypanosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What disease is caused by African trypanosomes and why is this disease so difficult to treat?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe an experiment to demonstrate that RNA polymerase I colocalizes with active expression site sequences in the expression site body (ESB) of Trypanosoma brucei .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Draw a sketch of an antibody showing the light and heavy chains and the antigen binding sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Diagram the rearrangement that occurs during B lymphocyte maturation at the immunoglobulin light-chain locus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Present a model for the cleavage and rejoining of DNA strands at immunoglobulin light-chain locus recombination signal sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Discuss evidence for the hypothesis that the V(D)J system evolved from a transposon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Compare and contrast the mechanisms for allelic exclusion (both initiation and maintenance) of (1) the Igf2 gene in embryonic cells and (2) antibody-encoding genes in developing B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes there is epigenetic control of the initial selection of the allele to be rearranged, as well as maintenance of allelic exclusion. You determine that both light chain alleles in pre-B cells have hyperacetylated histones, but one allele is methylated and late-replicating and the other allele is unmethylated and early replicating. Which allele is likely to be subject to rearrangement? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
You find that the maternal allele of the mouse MAMA gene is active, while the paternal allele is repressed. The gene encodes a growth factor.
(a) Predict the effect on allelic expression of treating adult mice with 5-aza-deoxycytidine.
(b) During the course of the experiment you find that mouse pups are born with completely yellow fur instead of the expected brown fur. Provide an explanation.
(a) Predict the effect on allelic expression of treating adult mice with 5-aza-deoxycytidine.
(b) During the course of the experiment you find that mouse pups are born with completely yellow fur instead of the expected brown fur. Provide an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The figure below shows the results of methylation analysis of DNA from a "normal" child, a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome, and two children with Angelman Syndrome.
Southern blot of genomic DNA digested with HindIII and HpaII, probed with PW71B, a chromosome 15-specific probe.
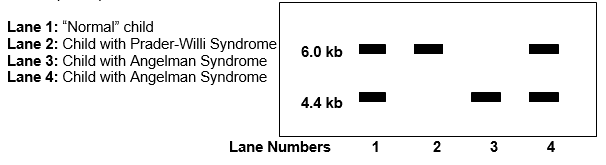 Interpret the results for each lane.
Interpret the results for each lane.
Southern blot of genomic DNA digested with HindIII and HpaII, probed with PW71B, a chromosome 15-specific probe.
 Interpret the results for each lane.
Interpret the results for each lane.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
On the inactive X chromosome many CpG islands are heavily methylated. Does this hold true for the CpG island upstream of the XIST gene? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Assume you have two cell-free transposition systems that have all the enzymes necessary for transposition of a yeast Ty element and a vertebrate Tc1/mariner element, respectively. What effect would the following inhibitors have on these two systems, and why?
(a) Inhibitors of translation
(b) Inhibitors of transcription
(c) Inhibitors of double-stranded DNA replication
(d) Inhibitors of reverse transcription
(a) Inhibitors of translation
(b) Inhibitors of transcription
(c) Inhibitors of double-stranded DNA replication
(d) Inhibitors of reverse transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Molecular biologists have demonstrated that there is preferential switching to the opposite mating type in budding yeast. Switching from a a (or ) with no change in mating type occurs rarely. Since the DNA sequence in the MATa locus would be the same as the donor HMRa, how would you show that a a had occurred or not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the most common mode of trypanosome antigen-switching, the VSG gene in the active expression site is degraded and replaced with the donor VSG gene. Why isn't there progressive loss of VSG genes over time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Is the genomic DNA in a bone marrow stem cell identical to the genomic DNA in a mature B cell? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



