Deck 10: Ordinary Annuities: Future Value and Present Value
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/137
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Ordinary Annuities: Future Value and Present Value
1
If you pay automobile insurance premiums by monthly pre-authorized chequing, do the payments form an ordinary annuity?
No. Insurance premiums are paid at the beginning of the period of coverage. In the present case, the monthly payments will be made at the beginning of each month of coverage. To qualify as an ordinary annuity, the monthly payments would have to occur at the end of each month of coverage.
2
If an ordinary annuity with quarterly payments and a 5½ -year term began June 1, 2005, what are the dates of the first and last payments?
The payment interval is 3 months. In an ordinary annuity, the payments are made at the end of each payment interval. Therefore, the first payment was on August 31, 2000 (the end of the first 3-month interval) and the final payment will be on November 30 2005 (the end of the final 3-month interval).
3
This problem demonstrates the dependence of an annuity's future value on the size of the periodic payment. Suppose a fixed amount will be invested at the end of each year and that the invested funds will earn 8% compounded annually. What will be the future value of the investments after 25 years if the periodic investment is:
a. $1000 per year?
b. $2000 per year?
c. $3000 per year?
(Note that the future value of an annuity is proportional to the size of the periodic payment.)
a. $1000 per year?
b. $2000 per year?
c. $3000 per year?
(Note that the future value of an annuity is proportional to the size of the periodic payment.)
a) $73,105.94
b) $146,211.88
c) $219,317.82
b) $146,211.88
c) $219,317.82
4
This problem demonstrates the dependence of the future value of an annuity on the number of payments. Suppose $1000 is invested at the end of each year. Assume the investments earn 10% compounded annually. Calculate the future value of the investments after each of the following numbers of payments:
a) 5
b) 10
c) 15
d) 20
e) 25
f) 30
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than n as n is increased.
a) 5
b) 10
c) 15
d) 20
e) 25
f) 30
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than n as n is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This problem demonstrates the dependence of the future value of an annuity on the interest rate. Suppose $1000 is invested at the end of each year for 20 years. Calculate the future value if the investments earn an annually compounded rate of return of:
a) 9%
b) 10%
c) 11%
d) 12%
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than the interest rate.
a) 9%
b) 10%
c) 11%
d) 12%
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Calculate the future value after 25 years in each of the following scenarios:
a. $6000 invested at end of each year earning 9% compounded annually.
b. $3000 invested at end of each half-year earning 9% compounded semiannually.
c. $1500 invested at end of each quarter earning 9% compounded quarterly?
d. $500 invested at end of each month earning 9% compounded monthly?
[Note that the same total amount ($6000) is invested every year at nominally equal rates of return (7.5%). The combined beneficial effects of (i) smaller but earlier and more frequent payments, and (ii) more frequent compounding are quite significant.]
a. $6000 invested at end of each year earning 9% compounded annually.
b. $3000 invested at end of each half-year earning 9% compounded semiannually.
c. $1500 invested at end of each quarter earning 9% compounded quarterly?
d. $500 invested at end of each month earning 9% compounded monthly?
[Note that the same total amount ($6000) is invested every year at nominally equal rates of return (7.5%). The combined beneficial effects of (i) smaller but earlier and more frequent payments, and (ii) more frequent compounding are quite significant.]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the future value after 5½ years of $100 invested at the end of every quarter if the funds earn 10% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
$75 was invested at the end of every month for 2½ years. Calculate the future value if the funds earned 8% compounded monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Aaron contributed $2000 to his RRSP at the end of every half-year. What was the value of his RRSP after 12½ years if the RRSP grew at 7.5% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Elga plans to invest $175 every month by purchasing units of a diversified equity mutual fund. If the fund generates an overall rate of return of 6% compounded monthly, what will her holdings be worth after 8¼ years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Danica has purchased $700 worth of units in a Global Equity Fund every calendar quarter for the past 7 years and 9 months. On average, the fund has earned 9% compounded quarterly. What were Danica's holdings worth immediately after her last purchase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What will be the future value after 6 years and 7 months of regular month-end investments of $435 earning 8.5% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Markus spends $60 per month on cigarettes. Suppose he quits smoking and invests the same amount at the end of each month for 20 years. If the invested money earns 7.5% compounded monthly, how much will Markus accumulate after 20 years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Herb has made contributions of $2000 to his RRSP at the end of every six months for the past eight years. The plan has earned 9.5% compounded semiannually. He has just moved the funds to another plan, paying 8% compounded quarterly. He will now contribute $1500 at the end of every three months. What total amount will he have in the plan seven years from now?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Using the Future Value Chart The NET @ssets feature describes how to access and use the Future Value Chart available in this textbook's Online Learning centre (OLC). Use this chart to answer the following problems (rounded to the nearest dollar).
a. This problem demonstrates the dependence of the future value of an annuity on the number of payments. Suppose $1000 is invested at the end of each year. Assume the investments earn 10% compounded annually. Calculate the future value of the investments after each of the following numbers of payments:
a) 5
b) 10
c) 15
d) 20
e) 25
f) 30
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than n as n is increased.
a. This problem demonstrates the dependence of the future value of an annuity on the number of payments. Suppose $1000 is invested at the end of each year. Assume the investments earn 10% compounded annually. Calculate the future value of the investments after each of the following numbers of payments:
a) 5
b) 10
c) 15
d) 20
e) 25
f) 30
Note that the future value increases proportionately more than n as n is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Stop Smoking and Save Calculator Go to the Student Edition on this student textbook's OLC. In the navigation bar, select "Chapter 10" in the drop-down box. In the list of resources for Chapter 10, select "Links in Student textbook" and then click on the link named "Stop Smoking and Save." This calculator allows you to estimate how much you will accumulate over several years if you stop smoking and invest the savings. The calculator assumes that the compounding frequency equals in investing frequency. Based on a half-pack per day consumption and the price of cigarettes where you live, how much would you accumulate after 30 years if your savings earn 9%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
This problem demonstrates the dependence of an annuity's future value on the size of the periodic payment. Calculate the present value of 25 end-of-year payments of:
a. $1000.
b. $2000.
c. $3000.
Use a discount rate of 8% compounded annually. After completing the calculations, note that the present value is proportional to the size of the periodic payment
a. $1000.
b. $2000.
c. $3000.
Use a discount rate of 8% compounded annually. After completing the calculations, note that the present value is proportional to the size of the periodic payment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An ordinary annuity consists of quarterly payments of $100 for 5½ years. What is the annuity's present value, discounting at 10% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Determine the present value of end-of-month payments of $75 continuing for 2½ years. Use 8% compounded monthly as the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How much will it cost to purchase an ordinary annuity delivering semiannual payments of $2000 for 12½ years if the money used to purchase the annuity can earn 7.5% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A contract requires end-of-month payments of $175 for another 8¼ years. What would an investor pay to purchase this contract if she requires a rate of return of 6% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A new loan at 9% compounded quarterly requires quarterly payments of $727.88 for seven years. Rounded to the nearest dollar, what amount was borrowed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Semiannual payments of $1240 will pay off the balance owed on a loan in 9½ years. If the interest rate on the loan is 9.9% compounded semiannually, what is the current balance on the loan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The original lender wishes to sell a loan contract delivering month-end payments of $350 for another 11 years and 5 months. At what price would an investor be prepared to buy the contract in order to "build in" a rate of return of 8.75% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The rate of return offered by Reliance Insurance Co. on its 20-year annuities is 4.8% compounded monthly. What amount is required to purchase a 20-year annuity with month-end payments of $1000?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Mr. and Mrs. Dafoe are doing some estimates of the amount of funds they will need in their RRSP to purchase an annuity paying $5000 at the end of each month. For each combination of term and monthly compounded interest rate in the following table, calculate the initial amount required to purchase the annuity.
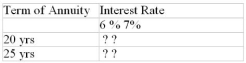


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Isaac wishes to purchase a 25-year annuity providing monthly payments of $1000 for the first 15 years and $1500 for the remaining 10 years. An insurance company has quoted him a rate of return of 4.8% compounded monthly for such an annuity. How much will he pay for the annuity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the maximum price you should pay for a contract guaranteeing month-end payments of $500 for the next 12 years if you require a rate of return of at least 8% compounded monthly for the first five years and at least 9% compounded monthly for the next seven years?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Ottawa Senators fired their coach two years into his five-year contract, which paid him $30,000 at the end of each month. If the team owners buy out the remaining term of the coach's contract for its economic value at the time of firing, what will be the settlement amount? Use 7.5% compounded monthly as the time value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You have received two offers on the used car you wish to sell. Mr. Lindberg is offering $9500 cash, and Mrs. Martel's offer is five semiannual payments of $2000 including one on the purchase date. Which offer has the greater economic value using a discount rate of 6% compounded semiannually? What is the economic advantage in current dollars of the preferred alternative?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Current Amounts Needed to Purchase an Annuity Go to the Student Edition of the student textbook's OLC. In the navigation bar, select "Chapter 10" in the drop-down box. In the list of resources for Chapter 10, select "Links in Student textbook" and then click on the link named "RRIF Annuities." Obtain high, low, and mid-range interest rate quotes from three financial institutions for a 20-year RRIF annuity. Assuming the interest rates are compounded monthly, calculate the amount required in each case to purchase a 20- year annuity paying $3000 at the end of each month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Influence of Annuity Variables Go to the Student Edition of the student textbook's OLC. In the navigation bar, select "Chapter 10" in the drop-down box. In the list of resources for Chapter 10, select "Links in Student textbook" and then click on the link named "Influence of Annuity Variables." This interactive chart enables you to observe and compare the effects of changes in the variables PMT, n, and i on both the future value and present value of an annuity.
a )Enter PMT _ $100 and i _ 8% for both Annuity A and Annuity B. Set n _ 20 for Annuity A and n _ 40 for Annuity B. This means that B contains twice as many payments as A. In percentage terms.
(i) How much larger is the present value of B than the present value of A?
(ii) How much larger is the future value of B than the future value of A?
b) Enter PMT _ $100 and n _ 30 for both annuities. Set i _ 8% for Annuity A and i _ 9% for Annuity B. In relative terms, the interest rate for B is _ 12.5% larger than the rate for A. In percentage terms.
(i) How much smaller is the present value of B than the present value of A?
(ii) How much larger is the future value of B than the future value of A?
a )Enter PMT _ $100 and i _ 8% for both Annuity A and Annuity B. Set n _ 20 for Annuity A and n _ 40 for Annuity B. This means that B contains twice as many payments as A. In percentage terms.
(i) How much larger is the present value of B than the present value of A?
(ii) How much larger is the future value of B than the future value of A?
b) Enter PMT _ $100 and n _ 30 for both annuities. Set i _ 8% for Annuity A and i _ 9% for Annuity B. In relative terms, the interest rate for B is _ 12.5% larger than the rate for A. In percentage terms.
(i) How much smaller is the present value of B than the present value of A?
(ii) How much larger is the future value of B than the future value of A?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Determine the unknown value for the following deferred annuity. The annuity is understood to be an ordinary annuity after the period of deferral.
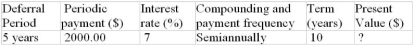


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The first of ten semiannual payments of $2000 will be made 5½ years from today. What is the present value of this deferred annuity using a discount rate of 7% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A life insurance company can invest funds to earn (after expenses) 8% compounded quarterly. A client wishes to purchase a five-year ordinary annuity that will commence 3½ years from now. What will the insurance company charge for the annuity if the quarterly payments are $750?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What minimum initial amount of money, invested to earn 9% compounded monthly, will support a monthly payout of $500 for 3½ years if the first payment occurs 2 years and 10 months from now?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What amount of money invested now will provide monthly payments of $200 for five years, if the ordinary annuity is deferred for 3½ years and the money earns 7.5% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A deferred annuity is comprised of eight annual payments of $1500. What is the period of deferral if the present value of the payments, discounted at 7.9% compounded annually, is $6383.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For $30,000, Manny purchased a deferred annuity from an insurance company that will pay him quarterly payments of $1076.71 for 12½ years. The payments are based upon the purchase amount earning 7% compounded quarterly. When will Manny receive the first payment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Ronelda has accumulated $33,173.03 in her RRSP. If she makes no further contributions and her RRSP continues to earn 9.75% compounded monthly, for how long a period of deferral must she wait before her RRSP can sustain month-end withdrawals of $400 for 15 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Using an inheritance he recently received, Sam wants to purchase a deferred annuity that will pay $5000 every three months between age 60 (when he plans to retire) and age 65 (when his permanent pension will begin). The first payment is to be three months after he reaches 60, and the last is to be on his 65th birthday. If Sam's current age is 50 years and 6 months, and the invested funds will earn 6% compounded quarterly, what amount must he invest in the deferred annuity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A conditional sale contract requires the debtor to make six quarterly payments of $569, with the first payment due in six months. What amount will a finance company pay to purchase the contract on the date of sale if the finance company requires a rate of return of 16% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A $10,000 investment will be allowed to grow at 8.5% compounded semiannually until it can support semiannual withdrawals of $1000 for 20 years. Rounded to the nearest month, how long before the first withdrawal must the investment be allowed to grow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mrs. Corriveau has just retired at age 58 with $160,360 in her RRSP. She plans to live off other savings for a few years and allow her RRSP to continue to grow on a tax-deferred basis until there is a sufficient amount to purchase a 25-year annuity paying $2000 at the end of each month. If her RRSP and the annuity each earn 7.5% compounded monthly, how much longer must she let her RRSP grow (before she buys the annuity)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The nominal interest rate associated with an ordinary general annuity is 7% compounded annually. Rounded to the nearest 0.001%, what is the corresponding periodic rate of interest that matches the payment interval for:
a. Semiannual payments?
b. Quarterly payments?
c. Monthly payments?
a. Semiannual payments?
b. Quarterly payments?
c. Monthly payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The nominal interest rate associated with an ordinary general annuity is 7% compounded semiannually. Rounded to the nearest 0.001%, what is the corresponding periodic rate of interest that matches the
payment interval for:
payment interval for:
a. Annual payments?
b. Quarterly payments?
c. Monthly payments?
payment interval for:
payment interval for:
a. Annual payments?
b. Quarterly payments?
c. Monthly payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The nominal interest rate associated with an ordinary general annuity is 8% compounded quarterly. Rounded to the nearest 0.001%, what is the corresponding periodic rate of interest that matches the payment interval for:
a. Annual payments?
b. Semiannual payments?
c. Monthly payments?
a. Annual payments?
b. Semiannual payments?
c. Monthly payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The nominal interest rate associated with an ordinary general annuity is 8% compounded monthly. Rounded to the nearest 0.001%, what is the corresponding periodic rate of interest that matches the payment interval for:
a. Annual payments?
b. Semiannual payments?
c. Quarterly payments?
a. Annual payments?
b. Semiannual payments?
c. Quarterly payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
This problem demonstrates the dependence of an annuity's future value on the compounding frequency. Suppose $1000 is invested at the end of each year for 25 years. Calculate the future value if the invested funds earn:
a. 6% compounded annually.
b. 6% compounded semiannually.
c. 6% compounded quarterly.
d. 6% compounded monthly.
a. 6% compounded annually.
b. 6% compounded semiannually.
c. 6% compounded quarterly.
d. 6% compounded monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
This problem demonstrates the dependence of an annuity's present value on the compounding frequency. What minimum initial amount will sustain a 25-year annuity paying $1000 at the end of each year if the initial amount can be invested to earn:
a. 6% compounded annually?
b. 6% compounded semiannually?
c. 6% compounded quarterly?
d. 6% compounded monthly?
a. 6% compounded annually?
b. 6% compounded semiannually?
c. 6% compounded quarterly?
d. 6% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An ordinary annuity consists of quarterly payments of $400 for 11 years. Based on a nominal rate of 6.5% compounded annually, calculate the annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An annuity consists of end-of-month payments of $150 continuing for 6½ years. Based on a nominal rate of 10% compounded quarterly, calculate the annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An ordinary annuity consists of semiannual payments of $2750 for a 3½ -year term. Using a nominal rate of 8% compounded monthly, calculate the annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Payments of $1500 will be made at the end of every quarter for 13½ years. Using a nominal rate of 7.5% compounded semiannually, calculate the annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Payments of $3500 will be made at the end of every year for 17 years. Using a nominal rate of 5.25% compounded monthly, calculate the annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An annuity consists of semiannual payments of $950 for a term of 8½ years. Using a nominal rate of 9% compounded quarterly, calculate the ordinary annuity's:
a. Present value.
b. Future value.
a. Present value.
b. Future value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A deferred annuity consists of an ordinary annuity paying $2000 semiannually for a 10-year term after a 5-year period of deferral. Calculate the deferred annuity's present value using a discount rate of 7% compounded quarterly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The first quarterly payment of $750 in a five-year annuity will be paid 3¾ years from now. Based on a discount rate of 8.25% compounded monthly, what is present value of the payments today?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A loan granted today will be repaid by payments of $500 per month running for 3½ years. The first payment is due 2 years and 10 months from today. What amount was borrowed if the interest rate on the loan is 9% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the future value eight years from now of each of the following cash-flow streams if money can earn 9% compounded semiannually?
a) A single payment of $5000 today.
b) An ordinary annuity starting today with eight annual payments of $900.
c) An ordinary annuity starting in three years with 20 quarterly payments of $400.
a) A single payment of $5000 today.
b) An ordinary annuity starting today with eight annual payments of $900.
c) An ordinary annuity starting in three years with 20 quarterly payments of $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Kent sold his car to Carolynn for $2000 down and monthly payments of $259.50 for 3½ years, including interest at 7.5% compounded annually. What was the selling price of the car?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
LeVero's monthly payments of $567.89 will pay off his mortgage loan in 4 years and 7 months. The interest rate on his mortgage is 6.6% compounded semiannully. What is the current balance on the loan?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Advantage of Early Investing Go to the Student Edition on this student textbook's OLC. In the navigation bar, select "Chapter 10" in the drop-down box. In the list of resources for Chapter 10, select "Links in Student textbook" and then click on the link named "Early Investing." When the Web page loads, scroll down the screen to find the link named "Advantage of Early Investing." Click on it. The window that opens allows you to enter data to compare three investment plans. For each plan, enter your regular end-of period investment contribution, the frequency of contribution, the age range over which you will contribute, any initial amount already accumulated, and the projected rate of return. Compare the outcomes at age 65 for the following three alternatives:
(i) Plan A: Invest $100/month starting at age 25.
(ii) Plan B: Invest $200/month starting at age 35.
(iii) Plan C: Invest $400/month starting at age 45.
Enter 9% for the growth rate. The calculations will assume annual compounding. After completing the data entry, click on "Submit." A new window opens presenting a table of future values at various ages for each investment plan. Scroll down the window to view an attractive graphic comparing the growth of the three plans.
a) Calculate the total of the nominal contributions under each plan. Compare them using a ratio A:B:C with terms reduced to small integers.
b) Compare the future values at age 65 in a ratio A:B:C. Reduce the ratio so that the smallest term is "1."
(i) Plan A: Invest $100/month starting at age 25.
(ii) Plan B: Invest $200/month starting at age 35.
(iii) Plan C: Invest $400/month starting at age 45.
Enter 9% for the growth rate. The calculations will assume annual compounding. After completing the data entry, click on "Submit." A new window opens presenting a table of future values at various ages for each investment plan. Scroll down the window to view an attractive graphic comparing the growth of the three plans.
a) Calculate the total of the nominal contributions under each plan. Compare them using a ratio A:B:C with terms reduced to small integers.
b) Compare the future values at age 65 in a ratio A:B:C. Reduce the ratio so that the smallest term is "1."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How much larger will the value of an RRSP be at the end of 25 years if the contributor makes month-end contributions of $300 instead of year-end contributions of $3600? In both cases the RRSP earns 8.5% compounded semiannually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Year-end contributions of $1000 will be made to a TFSA for 25 years. What will be the future value of the account if it earns 7½ % compounded monthly for the first 10 years and 8% compounded semiannually thereafter?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Gloria has just made her ninth annual $2000 contribution to her TFSA. She now plans to make semiannual contributions of $2000. The first contribution will be made six months from now. How much will she have in her TFSA 15 years from now if the plan has earned and will continue to earn 8% compounded quarterly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Toronto Raptors announce the signing of their top draft pick to a "7-year deal worth $43.2 million." The player will earn $200,000 at the end of each month for the first three years, and $600,000 at the end of each month for the subsequent four years. How do the Raptors get the $43.2 million figure? To the nearest $1000, what is the current economic value of the deal if money can earn 7% compounded annually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the current economic value of an inheritance that will pay $2000 to the beneficiary at the beginning of every three months for 20 years, starting when the beneficiary reaches 20 years of age, 4½ years from now? Assume that money is worth 6% compounded monthly. (Round to the nearest dollar.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Sabrina borrowed $30,000 at an interest rate of 7% compounded quarterly. Monthly payments of $356.83 will commence after a period of deferral and will pay off the loan over the subsequent 12½ years. What is the length of the period of deferral?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An investor purchased a deferred annuity contract for $4608.07, a price calculated to provide a rate of return on investment of 9.75% compounded monthly. The semiannual payments of $400, once started, continue for a term of 15 years. How long is the period of deferral?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What amount of money invested now will provide payments of $500 at the end of every month for five years following a four-year period of deferral? The money will earn 7.2% compounded monthly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Calculate the future value of an ordinary annuity consisting of monthly payments of $300 for five years. The rate of interest was 9% compounded monthly for the first two years and will be 7.5% compounded monthly for the last three years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How much larger will the value of an RRSP be at the end of 20 years if the contributor makes month-end contributions of $500 instead of year-end contributions of $6000? In both cases the RRSP earns 7.5% compounded semiannually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A Province of Ontario bond has 14½ years remaining until it matures. The bond pays $231.25 interest at the end of every six months. At maturity, the bond repays its $5000 face value in addition to the final interest payment. What is the fair market value of the bond if similar provincial bonds are currently providing investors with a return of 7.8% compounded semiannually?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Calculate the future value of investments consisting of payments of $800 at the end of each calendar quarter for seven years. The rate of interest earned will be 10% compounded quarterly for the first 30 months and 9% compounded semiannually for the remainder of the annuity's term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A mortgage broker offers to sell you a mortgage loan contract that will pay $900 per month for the next 2¾ years. At that point, the principal balance of $37,886 is due and payable. What should you pay for the contract if you require a return of 7.2% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose Evan contributes $2000 to his RRSP at the end of every quarter for the next 15 years and then contributes $1000 at each month's end for the subsequent 10 years. How much will he have in his RRSP at the end of the 25 years? Assume that the RRSP earns 8% compounded semiannually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Surinder is saving $50 per month. How much will she have in her account in five years if her account is earning 3.5% compounded monthly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Sam invests $5000 per year in an RRSP. What will be the value of the plan after 30 years if interest is 4.5% compounded annually. How much interest did Sam's investment earn?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Saminder quit smoking and saves $80 per month previously spent on cigarettes. He invests the money at 5% compounded monthly. How much will he have in 10 years?
A) $7542.51
B) $17,919.63
C) $12,422.58
D) $11,898.88
E) $12,474.34
A) $7542.51
B) $17,919.63
C) $12,422.58
D) $11,898.88
E) $12,474.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 137 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



