Deck 3: Mechanical Objects, Part 1
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Mechanical Objects, Part 1
1
A popular playground toy is a flexible seat that has automobile springs attached to it for a little bounce. When a 200 N child sits on the toy, it compresses 5 mm downward. What is the ride's spring constant?
A) 1000 N
B) 5 mm
C) 40000 N/m
D) 1000 N/m
A) 1000 N
B) 5 mm
C) 40000 N/m
D) 1000 N/m
40000 N/m
2
You are playing with your younger cousins and find yourself on all fours, with your hands and feet on four bathroom scales on the level ground. You took a "Physics in Everyday Life" course so you can make a reasonable guess that the reading on each scale is obtained by
A) your mass.
B) dividing your mass by 4.
C) dividing your weight by 2.
D) dividing your weight by 4.
A) your mass.
B) dividing your mass by 4.
C) dividing your weight by 2.
D) dividing your weight by 4.
dividing your weight by 4.
3
Suppose you are standing on a bathroom scale when you are flying in a jet airplane. For a moment the scale reads less than your actual weight. During that moment, it's exerting an upward force on you that is
A) greater than your weight
B) equal to zero
C) equal to your weight.
D) less than your weight.
A) greater than your weight
B) equal to zero
C) equal to your weight.
D) less than your weight.
less than your weight.
4
Suppose you are standing on a bathroom scale when you are flying in a jet airplane. For a moment the scale reads more than your actual weight. During that moment, it's exerting an upward force on you that is greater than your weight and you are
A) accelerating upward.
B) accelerating downward.
C) not accelerating.
D) accelerating sideways.
A) accelerating upward.
B) accelerating downward.
C) not accelerating.
D) accelerating sideways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You have always wondered how much one of your friends weighs and devise a scheme to measure his weight secretly. You have him sit in a tubular steel chair. This popular style of chair consists of a single steel tube that is bent into a frame and that supports a seat bottom and a back. The empty chair weighs 10 pounds and is 30 inches tall. The frame acts as a spring and bends downward slightly when the chair is occupied. When you sit properly in the chair yourself, it bends downward 1 inch. When your friend sits properly in the chair, it bends downward 2 inches. From that observation, you know that your friend weighs about
A) 300 pounds.
B) twice as much as you do.
C) four times as much as you do.
D) 150 pounds.
A) 300 pounds.
B) twice as much as you do.
C) four times as much as you do.
D) 150 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
You are extremely bored during the long summer months when school is out of session, so you decide to attach a graphing calculator to a rubber band and repeatedly bounce it up and down vertically. When the rubber band is at its maximum stretch away from your hand
A) the calculator's velocity is downward but its acceleration is upward.
B) the calculator's velocity is zero but its acceleration is upward.
C) the calculator's velocity is upward but its acceleration is downward.
D) the calculator's velocity is zero but its acceleration is downward.
A) the calculator's velocity is downward but its acceleration is upward.
B) the calculator's velocity is zero but its acceleration is upward.
C) the calculator's velocity is upward but its acceleration is downward.
D) the calculator's velocity is zero but its acceleration is downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You have watched one too many old cartoons and decide to drive around town with a giant spring that is 4 m long and attached to the front of your car. You decide to help a semi truck that is stuck and try to push them with your car. You take a running start, and when you contact the truck the spring in your car compresses 3 m. During which portion of the compression did you do the least work on the spring?
A) During the second meter.
B) During the third meter.
C) During the first meter.
D) The work done is equal for all segments of the trip.
A) During the second meter.
B) During the third meter.
C) During the first meter.
D) The work done is equal for all segments of the trip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which system is in a state of stable equilibrium?
A) A marble in the bottom of a spherical bowl.
B) A Marble on top of a spherical bowl.
C) A marble on a flat, level surface.
D) A marble rolling down an inclined surface.
A) A marble in the bottom of a spherical bowl.
B) A Marble on top of a spherical bowl.
C) A marble on a flat, level surface.
D) A marble rolling down an inclined surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You are at a swimming pool and notice that different persons make the diving board bend by different amounts when they stand still on it. Assuming the board to behave like a spring (perfectly elastic) please discuss how you could secretly determine the weight of everybody that uses the board if you known the weight of one person that uses it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose your instructor staggers into class after an all-weekend pocket protector seminar and workshop. With the best of intentions, she tells you in going through an example for the class that an object in motion is clearly not in equilibrium. Please comment on the scientific validity of your instructor's statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A friend of your joins a weight loss group. Unfortunately, they try to control the readings on the scales by having you weigh yourself on either level ground or with the scale on a slight slope. How will the two weights obtained by these two different methods compare?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You thoughtfully set a 1 kg box on top of a loaf of bread and the loaf compresses by 15 cm. Thinking of the bread as a spring, its spring constant is
A) 1 N/m
B) 0.653 N/m
C) 65.3 N/m
D) 0.015 N/m
A) 1 N/m
B) 0.653 N/m
C) 65.3 N/m
D) 0.015 N/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Bolts work because they act like very strong springs and extend slightly when they are tightened. Suppose a steel bolt has spring constant 1.8x108 N/m. How far would it have to stretch in order to provide a force 2000N?
A) 1.8x10-3 m
B) 1.8x10-8 m
C) 1.11 m
D) 1.11x10-5 m
A) 1.8x10-3 m
B) 1.8x10-8 m
C) 1.11 m
D) 1.11x10-5 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You are watching a semi truck bounce up and down on a spring. (Yep it's a toy!) At the topmost point in the truck's path,
A) the truck's velocity is downward but its acceleration is upward.
B) the truck's velocity is zero but its acceleration is upward.
C) the truck's velocity is upward but its acceleration is downward.
D) the truck's velocity is zero but its acceleration is downward.
A) the truck's velocity is downward but its acceleration is upward.
B) the truck's velocity is zero but its acceleration is upward.
C) the truck's velocity is upward but its acceleration is downward.
D) the truck's velocity is zero but its acceleration is downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Imagine that you are able to go on a fishing trip that you have always wanted to. Your friend gets a bite that exerts a force of about 50N on the pole and it bends by a certain amount. Now you have a pole identical to your friends and you get a hit that bends the pole about twice as much. You can estimate that the force on your pole is about
A) Can't tell
B) 100 N
C) 200 N
D) 500 N
A) Can't tell
B) 100 N
C) 200 N
D) 500 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You are at a coffee shop with a close friend and the talk turns towards masses bouncing vertically on springs. Your friend makes the statement that "There is one unique point in time when the speed of the object is maximum, and that is when the acceleration is maximum too. Please comment on the scientific accuracy of your friend's statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Assuming there is nothing wrong with your bathroom scale, discuss two ways in which you could get a false reading when weighing yourself, with only you touching the top of the scale (and nothing else) and another surface touching its bottom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why do elastic balls bounce so well?
A) They store energy through compression, like a spring.
B) They permanently deform, storing energy.
C) They are all filled with a special energy-absorbent liquid.
D) They are always thrown well.
A) They store energy through compression, like a spring.
B) They permanently deform, storing energy.
C) They are all filled with a special energy-absorbent liquid.
D) They are always thrown well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Cars are designed so that their bodies buckle (permanently deform) when they are in an accident. How does the buckling make the car safer by not allowing it to recoil (bounce) so much?
A) The buckling stores energy.
B) The buckling dissipates the energy of the crash.
C) The buckling provides energy to the crashing objects.
D) The buckling gives the car a high coefficient of restitution.
A) The buckling stores energy.
B) The buckling dissipates the energy of the crash.
C) The buckling provides energy to the crashing objects.
D) The buckling gives the car a high coefficient of restitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When you drop a rubber ball on the floor and it bounces, the direction of its velocity reverses because
A) the ball can't stop moving and the floor blocks its path.
B) the ball's momentum is conserved.
C) the ball's energy is conserved.
D) the floor exerts an upward support force on the ball and this force stops the ball's descent and eventually propels it upward.
A) the ball can't stop moving and the floor blocks its path.
B) the ball's momentum is conserved.
C) the ball's energy is conserved.
D) the floor exerts an upward support force on the ball and this force stops the ball's descent and eventually propels it upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When you throw a tennis ball against the floor at an angle,
A) the direction of the vertical component of its velocity reverses.
B) the horizontal component of its velocity reverses.
C) the speed of the ball reverses.
D) the vertical component of its velocity doubles.
A) the direction of the vertical component of its velocity reverses.
B) the horizontal component of its velocity reverses.
C) the speed of the ball reverses.
D) the vertical component of its velocity doubles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The coefficient of restitution for a particular ball is 0.45. If he ball hits a surface traveling at 100 m/s its rebound speed will be
A) 100 m/s
B) 90 m/s
C) 45 m/s
D) 45 m/s2
A) 100 m/s
B) 90 m/s
C) 45 m/s
D) 45 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider an elastic ball that is falling downward toward the ground. The ball hits the ground and then begins traveling upward again. At what point in the trip does the ball have the most energy stored in it as elastic potential energy?
A) At the bottom of the path when it is not moving, right before it rebounds.
B) After it has rebounded and left the ground.
C) Right before it hits the ground
D) When it is moving the fastest.
A) At the bottom of the path when it is not moving, right before it rebounds.
B) After it has rebounded and left the ground.
C) Right before it hits the ground
D) When it is moving the fastest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A ball hits a wall going 10 m/s, and bounces off going 7 m/s. The coefficient of restitution is
A) 1.41
B) 0.70
C) 0.49
D) -17 m/s
A) 1.41
B) 0.70
C) 0.49
D) -17 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A bat moving at 90 km/h strikes an oncoming ball moving at 110 km/h. If the batter follows through so that the speed of the bat doesn't change during the hit and the coefficient of restitution of the ball is 0.6, what speed does the batted ball have after it has been struck?
A) 66 km/h
B) 200 km/h
C) 20 km/h
D) 210 km/h
A) 66 km/h
B) 200 km/h
C) 20 km/h
D) 210 km/h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When a baseball player hits a ball, the bat can respond by
A) rebounding.
B) rotating.
C) vibrating.
D) any combination of (A), (B) or (C).
A) rebounding.
B) rotating.
C) vibrating.
D) any combination of (A), (B) or (C).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a soccer game, someone has kicked the ball so that it is heading right toward your face. You want to slow the ball down with your arm. To execute your plan most effectively you should
A) move your arm rapidly toward the oncoming ball.
B) keep your arm still.
C) move your arm in the direction that the ball is moving.
D) move your arm slowly toward the oncoming ball.
A) move your arm rapidly toward the oncoming ball.
B) keep your arm still.
C) move your arm in the direction that the ball is moving.
D) move your arm slowly toward the oncoming ball.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You're riding on a pogo stick-a vertical stick with a spring at the bottom and foot pads on which you stand. You're holding the top of the stick tightly in your hands and you and the stick are bouncing up and down on its spring. As you land after one particularly high bounce, the spring becomes more and more tightly compressed. When the spring is at half its maximum compression, your velocity is
A) downward but your acceleration is upward.
B) upward and you acceleration is downward.
C) (A) or (B)
D) upward but your acceleration is upward.
A) downward but your acceleration is upward.
B) upward and you acceleration is downward.
C) (A) or (B)
D) upward but your acceleration is upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain why it is so difficult to ride a bicycle in tall grass or soft sand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You decide to go out to a baseball game Friday night and notice that the best hits are from the players that follow through with their swings. Why is it important to follow through when hitting or kicking a ball?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a baseball player hits a ball with the bat, the bat can undergo many different types of changes. Please discuss three different types of effects that contact with the ball has on the bat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why do balls that deform bounce poorly?
A) They store energy through compression, like a spring.
B) They dissipate energy in an unrecoverable form.
C) They are all filled with a special energy-absorbent liquid.
D) They are always thrown poorly.
A) They store energy through compression, like a spring.
B) They dissipate energy in an unrecoverable form.
C) They are all filled with a special energy-absorbent liquid.
D) They are always thrown poorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The coefficient of restitution for a particular ball is 0.7. If he ball rebounds from surface traveling at 60 m/s its collision speed was
A) 42 m/s
B) 53 m/s
C) 85.7 m/s
D) 85.7 m/s2
A) 42 m/s
B) 53 m/s
C) 85.7 m/s
D) 85.7 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Trace the energy transfer in an elastic ball that is dropped from rest, hits the floor and rebounds, being caught.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Trace the energy transfer in a perfectly inelastic ball that is dropped from rest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
From an energy point of view, explain why car collisions are much less dangerous when the bumpers lock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
You have heard the tried and true phrase "it is like running in to a brick wall". Now it is time to dig a little deeper and modify the phrase. Assume you are in a car driving and come in contact with this proverbial brick wall. Your car can do three things after the strike: it can go through, come to stop or bounce back. Assuming the car is in contact with the wall for the same amount of time for all three cases, select the option which will be the most dangerous to you from a force point of view and briefly discuss why the assumption of equal times has to be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
You have heard the tried and true phrase "it is like running in to a brick wall". Now it is time to dig a little deeper and modify the phrase. Assume you are in a car driving and come in contact with this proverbial brick wall. Your car can do three things after the strike: it can go through, come to stop or bounce back. Select the option which will be the most dangerous to you from an impulse point of view and briefly discuss why the assumption of equal times has to be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is present and the car comes to a stop at point E.
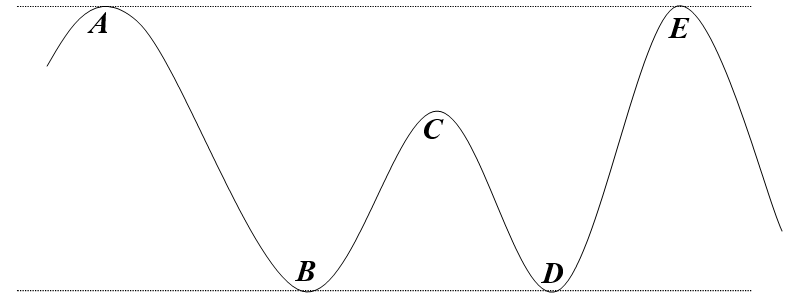
-What must be true of the car's motion at point A?

-What must be true of the car's motion at point A?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is present and the car comes to a stop at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum kinetic energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum kinetic energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is present and the car comes to a stop at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum potential energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum potential energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is present and the car comes to a stop at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum total energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum total energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Like a baseball bat, a tennis racket has a sweet spot at its center of percussion. If a tennis ball hits this center of percussion, the racket's handle does not accelerate. This is because
A) an impact at the center of percussion exerts no torque about the racket's center of mass and doesn't cause the racket to undergo angular acceleration.
B) the racket's center of mass accelerates backward while its handle rotates forward about its center of mass and the two motions cancel one another at the handle.
C) an impact at the center of percussion transfers no momentum to the racket and doesn't cause the racket to accelerate.
D) the racket's velocity doesn't change when the ball hits its center of percussion.
A) an impact at the center of percussion exerts no torque about the racket's center of mass and doesn't cause the racket to undergo angular acceleration.
B) the racket's center of mass accelerates backward while its handle rotates forward about its center of mass and the two motions cancel one another at the handle.
C) an impact at the center of percussion transfers no momentum to the racket and doesn't cause the racket to accelerate.
D) the racket's velocity doesn't change when the ball hits its center of percussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You go through a loop in a roller coaster at constant speed. Where is your apparent weight a minimum?
A) At the top
B) At the bottom
C) Halfway up, going down
D) Halfway up, going up
A) At the top
B) At the bottom
C) Halfway up, going down
D) Halfway up, going up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You are riding a very fast Ferris Wheel so that you actually notice a variation in your apparent weight. Where is your apparent weight maximum?
A) At the top
B) At the bottom
C) Halfway up, going down
D) Halfway up, going up
A) At the top
B) At the bottom
C) Halfway up, going down
D) Halfway up, going up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You are riding an amusement park ride where you are strapped to the inside of a giant metal wheel that is rotating quite rapidly. Your acceleration is
A) Zero
B) Straight down
C) Toward the center
D) Straight up
A) Zero
B) Straight down
C) Toward the center
D) Straight up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
You go to an amusement park and, being in a physics class, you have connections. The management lets you stand on a scale as you ride a Ferris Wheel that rotates fairly rapidly. You will notice the lowest reading on the scale
A) on top, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
B) on top, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight
C) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
D) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight.
A) on top, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
B) on top, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight
C) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
D) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
You go to an amusement park and, being in a physics class, you have connections. The management lets you stand on a scale as you ride a Ferris Wheel that rotates fairly rapidly. You will notice the highest reading on the scale
A) on top, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
B) on top, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight
C) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
D) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight.
A) on top, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
B) on top, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight
C) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is weaker than your weight.
D) on the bottom, because the normal force upwards is stronger than your weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You are on an airplane waiting to take off for a summer trip. Having just come from your physics final, you decide to measure the acceleration of the plane during takeoff by tying your graphing calculator to a string and suspending it. Your new device will do a great job of measuring the plane's constant acceleration during takeoff because, as the plane accelerates your calculator will
A) swing backward and stay there.
B) swing forward and stay there.
C) swing backward at a steady rate.
D) rotate around in a circle.
A) swing backward and stay there.
B) swing forward and stay there.
C) swing backward at a steady rate.
D) rotate around in a circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The curves on bicycle racetracks are steeply banked, so that the inner edge of each curve is much lower than its outer edge. This banking tips the support force that the track exerts on the bicycle wheel toward the center of each turn. That center-directed or centripetal force on the bicycle is important because it
A) helps the bicycle accelerate inward to complete each turn without skidding.
B) it does work on the bicycle during each turn and thus increases the bicycle's energy.
C) balances the outward centrifugal force that the bicycle experiences as it completes each turn, so that the bicycle experiences zero net force.
D) it does negative work on the bicycle during each turn and thus decreases the bicycle's energy.
A) helps the bicycle accelerate inward to complete each turn without skidding.
B) it does work on the bicycle during each turn and thus increases the bicycle's energy.
C) balances the outward centrifugal force that the bicycle experiences as it completes each turn, so that the bicycle experiences zero net force.
D) it does negative work on the bicycle during each turn and thus decreases the bicycle's energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You are flying on an airplane and you notice that a ball of aluminum foil from lunch starts to roll to the left. From the motion of the foil ball you can conclude that the plane is
A) moving at constant velocity toward the right.
B) turning toward the left.
C) moving at constant velocity toward the left.
D) turning toward the right.
A) moving at constant velocity toward the right.
B) turning toward the left.
C) moving at constant velocity toward the left.
D) turning toward the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Some engineers have suggested that we can simulate gravity in outer space by having a circular rotating space station where persons feel an outward - directed fictitious force due to the rotation of the station. The reason they feel such a force is because
A) their velocity is toward the center of the space station and their inertia tends to keep them moving outward.
B) the fictitious force is always in the direction of centripetal acceleration.
C) they are accelerating toward the center of the space station and inertia tends to keep them moving sideways.
D) their velocity is away from the center of the space station and their inertia tends to make them move in towards the center.
A) their velocity is toward the center of the space station and their inertia tends to keep them moving outward.
B) the fictitious force is always in the direction of centripetal acceleration.
C) they are accelerating toward the center of the space station and inertia tends to keep them moving sideways.
D) their velocity is away from the center of the space station and their inertia tends to make them move in towards the center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A classroom demo that is popular with students and unpopular with custodians is to fill a Styrofoam cup with water, poke a hole in the bottom and then drop the cup into a garbage can waiting below. On the way down, the leak will
A) stop because the cup doesn't experience gravity
B) stop because the cup and water are both in free fall and locally weightless.
C) increase because the cup is accelerating.
D) increase because gravity pulls on the water more than it does the cup.
A) stop because the cup doesn't experience gravity
B) stop because the cup and water are both in free fall and locally weightless.
C) increase because the cup is accelerating.
D) increase because gravity pulls on the water more than it does the cup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The spin cycle in your washing machine partially dries clothes by spinning them in a perforated metal basket. Such a process works because
A) the water leaves the basket moving tangent to the circular path
B) the water is forced directly outward from the basket
C) the water is drawn to the center of the basket
D) the water is drained by gravity out the bottom of the basket.
A) the water leaves the basket moving tangent to the circular path
B) the water is forced directly outward from the basket
C) the water is drawn to the center of the basket
D) the water is drained by gravity out the bottom of the basket.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You are swinging a tin can around your head in a perfectly horizontal circle of radius 4 m. (This is really not possible but we're saying it almost happens.) If the speed of the can is 4 m/s and its mass is 2 kg, what inward force is required to keep the can moving in the circle?
A) 1/16 N
B) 2 N
C) 16 N
D) 8 N
A) 1/16 N
B) 2 N
C) 16 N
D) 8 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You are swinging a tin can around your head in a perfectly horizontal circle of radius 4 m. (This is really not possible but we're saying it almost happens.) If the speed of the can is 4 m/s what is its acceleration?
A) 1/4 m/s2
B) 4 m/s2
C) 16 m/s2
D) 4 m/s
A) 1/4 m/s2
B) 4 m/s2
C) 16 m/s2
D) 4 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
You are swinging a tin can around your head in a perfectly horizontal circle of radius 4 m. (This is really not possible but we're saying it almost happens.) If you exert a force of 9 N and the mass of the can is 1 kg, with what speed is the can moving around the circle?
A) 6 m/s
B) 36 m/s
C) 36 m2/s2
D) 1/6 m/s
A) 6 m/s
B) 36 m/s
C) 36 m2/s2
D) 1/6 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A person is swinging a tin can around in a vertical circle at a constant speed. Please identify the points, if any, of
-maximum/ minimum kinetic energy
-maximum/ minimum kinetic energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A person is swinging a tin can around in a vertical circle at a constant speed. Please identify the points, if any, of
-maximum/ minimum potential energy
-maximum/ minimum potential energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A person is swinging a tin can around in a vertical circle at a constant speed. Please identify the points, if any, of
-maximum/ minimum total mechanical energy
-maximum/ minimum total mechanical energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A person is swinging a tin can around in a vertical circle at a constant speed. Please identify the points, if any, of
-maximum/ minimum value (magnitude) of centripetal acceleration
-maximum/ minimum value (magnitude) of centripetal acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose that you are riding a Ferris wheel which rotate at any constant speed you wish. The chairs swivel so you are always sitting upright. Please explain why it is possible for you to feel weightless at only one spot on the Ferris wheel. What spot is this? Here, "weightless" is defined to mean that the normal force of contact from the chair on you (the rider) is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose that a frantic weather reporter is covering a live tornado. It is in the mature stage just ripping right along and the reporter exclaims that "Wood, metal and all kinds of debris are being thrown directly outward from the edge the funnel." From a physics point of view (circular motion!) please comment on the accuracy of the reporter's statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Skateboarders often can skate on the inner surface of cylindrical or bowl - shaped tracks. As a result, the normal (support) force is able to point inwards towards the center of the circle wherever the person is. That center-directed or centripetal force on the skate wheels is important because it
A) helps the skater accelerate inward to complete each turn without skidding.
B) it does work on the skater during each turn and thus increases the skater's energy.
C) balances the outward centrifugal force that the skater experiences as it completes each turn, so that the skater experiences zero net force.
D) it does negative work on the skater during each turn and thus decreases the bicycle's energy.
A) helps the skater accelerate inward to complete each turn without skidding.
B) it does work on the skater during each turn and thus increases the skater's energy.
C) balances the outward centrifugal force that the skater experiences as it completes each turn, so that the skater experiences zero net force.
D) it does negative work on the skater during each turn and thus decreases the bicycle's energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You are swinging a tin can around your head in a perfectly horizontal circle and its acceleration is 32 m/s2. If its speed is 4 m/s what is the value of the radius of its circular path?
A) 4 m
B) 0.5 m
C) 0.5 m/s2
D) 2 m
A) 4 m
B) 0.5 m
C) 0.5 m/s2
D) 2 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Your apparent weight is equal to your weight
A) In an elevator accelerating upwards.
B) In an elevator accelerating downwards.
C) In an elevator in free fall.
D) In an elevator not accelerating.
A) In an elevator accelerating upwards.
B) In an elevator accelerating downwards.
C) In an elevator in free fall.
D) In an elevator not accelerating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is not present and the car is almost stopped, barely moving at point E.
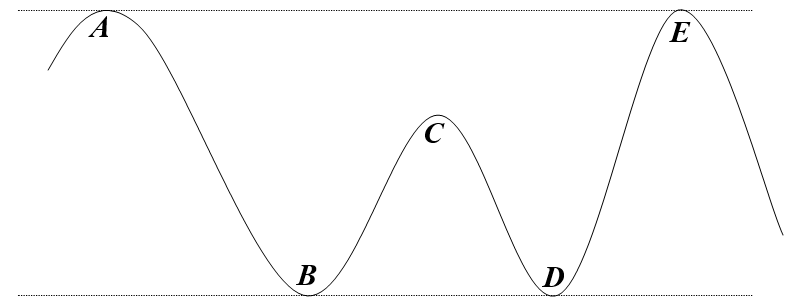
-What must be true of the car's motion at point A?

-What must be true of the car's motion at point A?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is not present and the car is almost stopped, barely moving at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum kinetic energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum kinetic energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is not present and the car is almost stopped, barely moving at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum potential energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum potential energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose a soap box car is coasting on a track (no motor; no brake), moving from left to right, and part of the track is shown below. Friction /air resistance is not present and the car is almost stopped, barely moving at point E.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum total energy, if any.

-Please identify points of maximum and minimum total energy, if any.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A bathroom scale reads
A) Your weight
B) Your apparent weight
C) The force with which the earth attracts you
D) Your mass in kg
A) Your weight
B) Your apparent weight
C) The force with which the earth attracts you
D) Your mass in kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that you are riding a Ferris wheel which rotate at any constant speed you wish. The chairs swivel so you are always sitting upright. Please explain why it is possible for you to feel heaviest at only one spot on the Ferris wheel. What spot is this? Here, "heaviness" is defined to mean that the normal force of contact from the chair on you (the rider) is maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
You are swinging a 2 kg tin can around your head in a perfectly horizontal circle of radius 1 m with a speed of 6 m/s. (This is really not possible but we're saying it almost happens.) If the string can safely exert a force of 30 N will it be able to swing the can?
A) No because the required force is 36 N.
B) No because the required acceleration is 36 m/s2.
C) Yes because only linear acceleration would break the string.
D) Yes because the weight of the can does not matter.
A) No because the required force is 36 N.
B) No because the required acceleration is 36 m/s2.
C) Yes because only linear acceleration would break the string.
D) Yes because the weight of the can does not matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



