Deck 12: Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Oligopoly
1
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 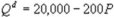 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's inverse residual demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's inverse residual demand function?
A)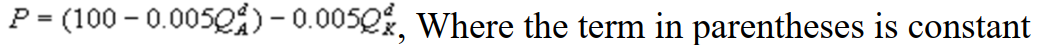
B)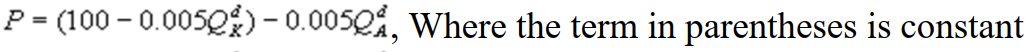
C)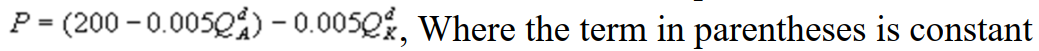
D)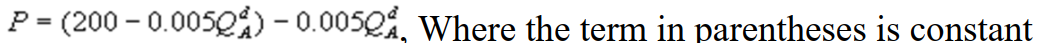
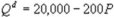 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's inverse residual demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's inverse residual demand function?A)
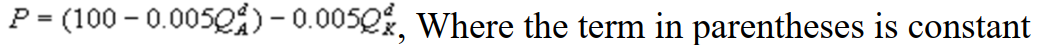
B)
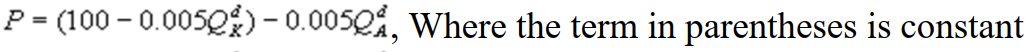
C)
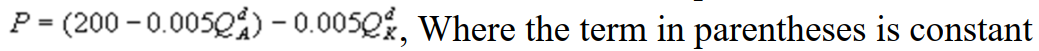
D)
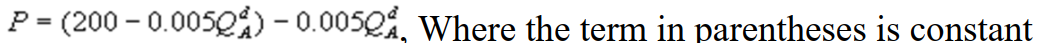
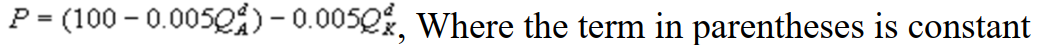
2
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 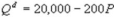 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's inverse residual demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's inverse residual demand function?
A)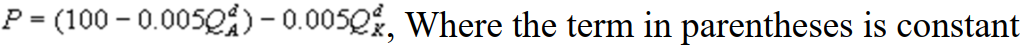
B)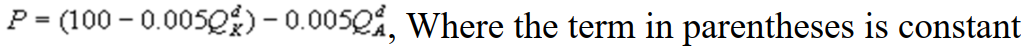
C)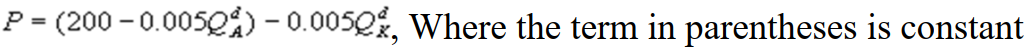
D)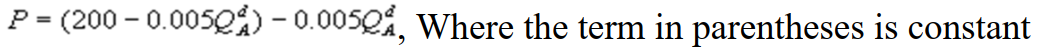
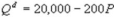 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's inverse residual demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's inverse residual demand function?A)
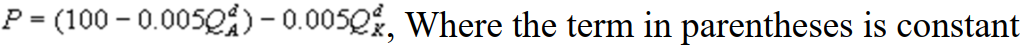
B)
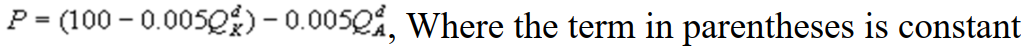
C)
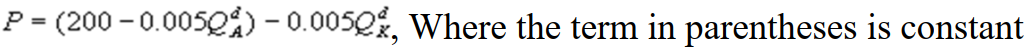
D)
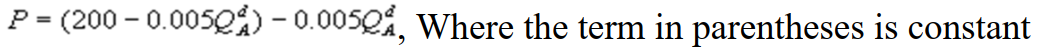
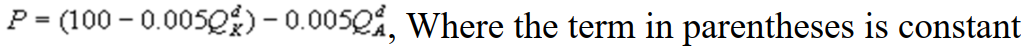
3
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 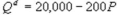 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Alice produces 5,000 cubic yards per year, what is Kate's inverse demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Alice produces 5,000 cubic yards per year, what is Kate's inverse demand function?
A)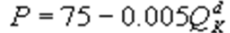
B)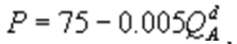
C)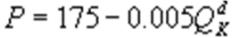
D)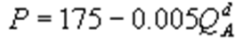
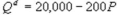 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Alice produces 5,000 cubic yards per year, what is Kate's inverse demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Alice produces 5,000 cubic yards per year, what is Kate's inverse demand function?A)
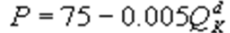
B)
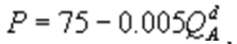
C)
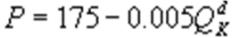
D)
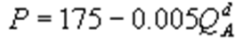
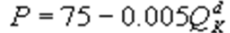
4
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 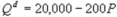 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Kate produces 10,000 cubic yards per year, what is Alice's inverse demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Kate produces 10,000 cubic yards per year, what is Alice's inverse demand function?
A)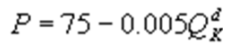
B)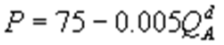
C)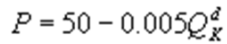
D)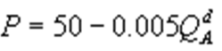
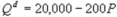 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Kate produces 10,000 cubic yards per year, what is Alice's inverse demand function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. If Kate produces 10,000 cubic yards per year, what is Alice's inverse demand function?A)
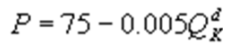
B)
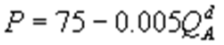
C)
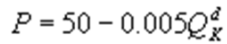
D)
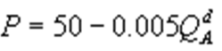

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 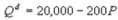 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's marginal revenue function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's marginal revenue function?
A)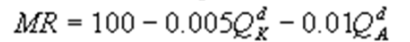
B)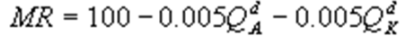
C)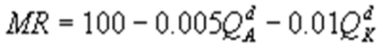
D)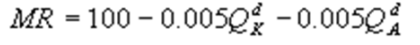
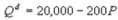 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's marginal revenue function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Alice's marginal revenue function?A)
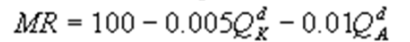
B)
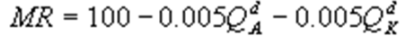
C)
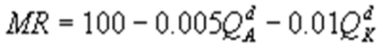
D)
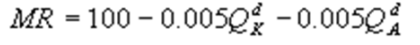

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 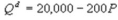 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's marginal revenue function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's marginal revenue function?
A)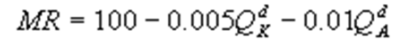
B)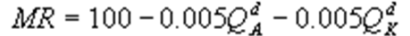
C)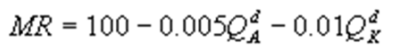
D)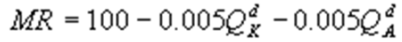
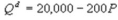 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's marginal revenue function?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is Kate's marginal revenue function?A)
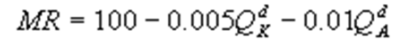
B)
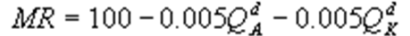
C)
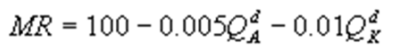
D)
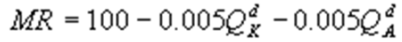

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 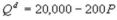 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Alice's best response function.
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Alice's best response function.
A)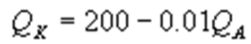
B)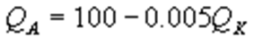
C)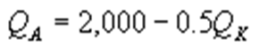
D)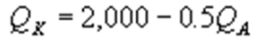
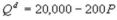 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Alice's best response function.
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Alice's best response function.A)
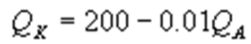
B)
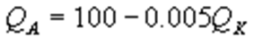
C)
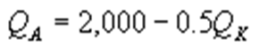
D)
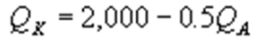

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 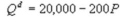 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Kate's best response function.
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Kate's best response function.
A)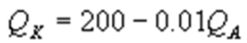
B)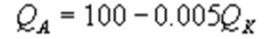
C)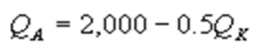
D)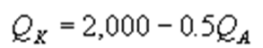
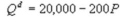 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Kate's best response function.
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. Find Kate's best response function.A)
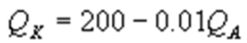
B)
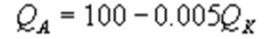
C)
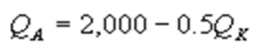
D)
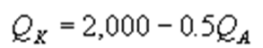

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 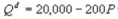 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Alice produce in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Alice produce in the Nash equilibrium?
A) 2,000
B) 1,333.33
C) 800
D) 4,000
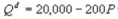 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Alice produce in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Alice produce in the Nash equilibrium?A) 2,000
B) 1,333.33
C) 800
D) 4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 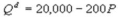 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Kate produce in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Kate produce in the Nash equilibrium?
A) 2,000
B) 1,333.33
C) 800
D) 4,000
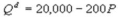 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Kate produce in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much does Kate produce in the Nash equilibrium?A) 2,000
B) 1,333.33
C) 800
D) 4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 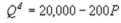 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is total output in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is total output in the Nash equilibrium?
A) 4,000
B) 2,666.66
C) 1,600
D) 8,000
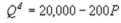 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is total output in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is total output in the Nash equilibrium?A) 4,000
B) 2,666.66
C) 1,600
D) 8,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 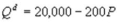 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the market price in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the market price in the Nash equilibrium?
A) $80
B) $86.67
C) $100
D) $93.34
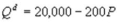 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the market price in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the market price in the Nash equilibrium?A) $80
B) $86.67
C) $100
D) $93.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 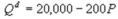 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much profit does each producer earn in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much profit does each producer earn in the Nash equilibrium?
A) $13,340
B) $0
C) $8893.31
D) $5,336
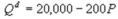 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much profit does each producer earn in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much profit does each producer earn in the Nash equilibrium?A) $13,340
B) $0
C) $8893.31
D) $5,336

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 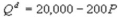 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much more profit does a monopolist earn compared to the joint profit each producer earns in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much more profit does a monopolist earn compared to the joint profit each producer earns in the Nash equilibrium?
A) $2,213.38
B) $0
C) $11,106.69
D) $2,000
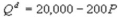 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much more profit does a monopolist earn compared to the joint profit each producer earns in the Nash equilibrium?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. How much more profit does a monopolist earn compared to the joint profit each producer earns in the Nash equilibrium?A) $2,213.38
B) $0
C) $11,106.69
D) $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 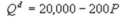 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the amount of the deadweight loss?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the amount of the deadweight loss?
A) $8,893.38
B) $6.67
C) $1,333,33
D) $4,446.69
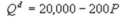 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the amount of the deadweight loss?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the amount of the deadweight loss?A) $8,893.38
B) $6.67
C) $1,333,33
D) $4,446.69

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 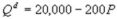 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the difference in the deadweight loss compared to a monopoly in this market?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the difference in the deadweight loss compared to a monopoly in this market?
A) $666.66
B) $2,000
C) $5,553.31
D) $10,000
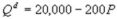 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the difference in the deadweight loss compared to a monopoly in this market?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. The Cournot model describes the competition in this market. What is the difference in the deadweight loss compared to a monopoly in this market?A) $666.66
B) $2,000
C) $5,553.31
D) $10,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 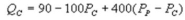 and
and 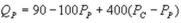 where QC and QP and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PP = $0.75, what is Coke's demand function?
where QC and QP and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PP = $0.75, what is Coke's demand function?
A)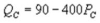
B)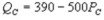
C)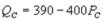
D)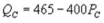
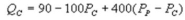 and
and 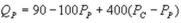 where QC and QP and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PP = $0.75, what is Coke's demand function?
where QC and QP and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PP = $0.75, what is Coke's demand function?A)
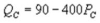
B)
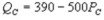
C)
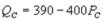
D)
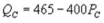

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 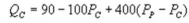 and
and 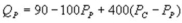 whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PC = $0.6, what is Pepsi's demand function?
whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PC = $0.6, what is Pepsi's demand function?
A)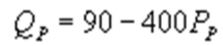
B)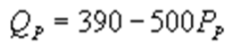
C)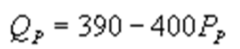
D)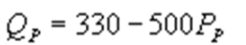
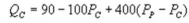 and
and 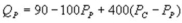 whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PC = $0.6, what is Pepsi's demand function?
whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. If PC = $0.6, what is Pepsi's demand function?A)
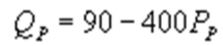
B)
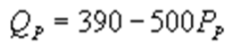
C)
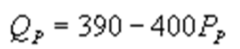
D)
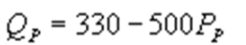

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 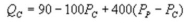 and
and 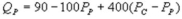 whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's inverse demand function?
whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's inverse demand function?
A)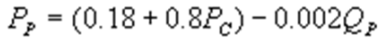
B)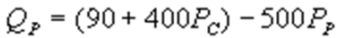
C)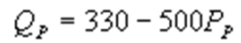
D)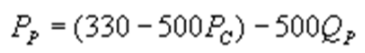
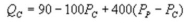 and
and 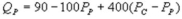 whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's inverse demand function?
whereQC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's inverse demand function?A)
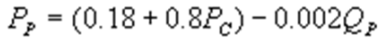
B)
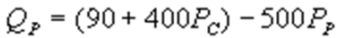
C)
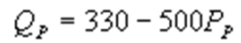
D)
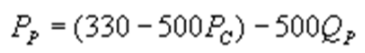

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 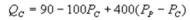 and
and 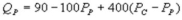 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's inverse demand function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's inverse demand function?
A)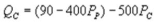
B)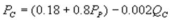
C)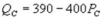
D)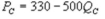
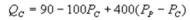 and
and 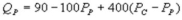 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's inverse demand function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's inverse demand function?A)
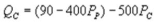
B)
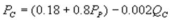
C)
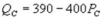
D)
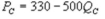

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 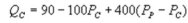 and
and 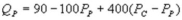 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's best response function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's best response function?
A)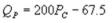
B)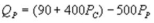
C)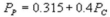
D)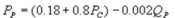
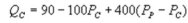 and
and 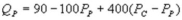 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's best response function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Pepsi's best response function?A)
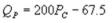
B)
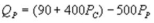
C)
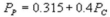
D)
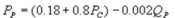

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 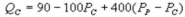 and
and 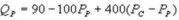 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day.PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's best response function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day.PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's best response function?
A)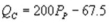
B)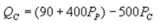
C)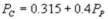
D)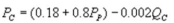
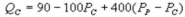 and
and 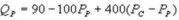 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day.PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's best response function?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day.PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is Coke's best response function?A)
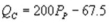
B)
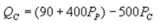
C)
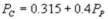
D)
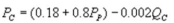

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 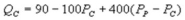 and
and 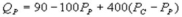 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Pepsi?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Pepsi?
A) $.016
B) $0.45
C) $0.53
D) $0.38
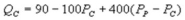 and
and 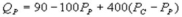 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Pepsi?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Pepsi?A) $.016
B) $0.45
C) $0.53
D) $0.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose the daily demand for Coke and Pepsi in a small city are given by 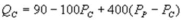 and
and 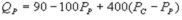 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Coke?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Coke?
A) $.016
B) $0.45
C) $0.53
D) $0.38
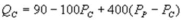 and
and 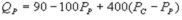 where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Coke?
where QC and QP are the number of cans Coke and Pepsi sell, respectively, in thousands per day. PC and PP are the prices of a can of Coke and Pepsi, respectively, measured in dollars. The marginal cost is $0.45 per can. What is the Nash equilibrium price for Coke?A) $.016
B) $0.45
C) $0.53
D) $0.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 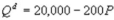 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit maximizing output?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit maximizing output?
A) 2,000
B) 1,333.34
C) 1,000
D) 4,000
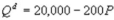 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit maximizing output?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit maximizing output?A) 2,000
B) 1,333.34
C) 1,000
D) 4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
45 Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 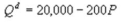 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit maximizing output?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit maximizing output?
A) 2,000
B) 1,333.34
C) 1,000
D) 4,000
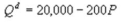 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit maximizing output?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit maximizing output?A) 2,000
B) 1,333.34
C) 1,000
D) 4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 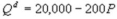 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. Given market demand, what is the market price per cubic yard?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. Given market demand, what is the market price per cubic yard?
A) $80
B) $85
C) $90
D) $95
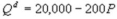 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. Given market demand, what is the market price per cubic yard?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. Given market demand, what is the market price per cubic yard?A) $80
B) $85
C) $90
D) $95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 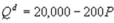 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit?
A) $10,000
B) $5,000
C) $20,000
D) $15,000
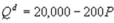 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qdis the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Kate's profit?A) $10,000
B) $5,000
C) $20,000
D) $15,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 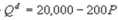 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit?
A) $10,000
B) $5,000
C) $20,000
D) $15,000
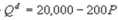 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is Alice's profit?A) $10,000
B) $5,000
C) $20,000
D) $15,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 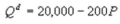 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Kate's profit when she enters the market first compared to when Kate and Alice choose their outputs simultaneously?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Kate's profit when she enters the market first compared to when Kate and Alice choose their outputs simultaneously?
A) $11,106.69
B) $5,000
C) $1106.69
D) -$3893.31
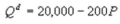 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Kate's profit when she enters the market first compared to when Kate and Alice choose their outputs simultaneously?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete andQd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Kate's profit when she enters the market first compared to when Kate and Alice choose their outputs simultaneously?A) $11,106.69
B) $5,000
C) $1106.69
D) -$3893.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Kate and Alice are small-town ready-mix concrete duopolists. The market demand function is 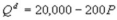 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Alice's profit when Kate enters the market first, compared to when they simultaneously select their outputs?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Alice's profit when Kate enters the market first, compared to when they simultaneously select their outputs?
A) $11,106.69
B) $5,000
C) $1106.69
D) -$3893.31
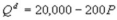 where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Alice's profit when Kate enters the market first, compared to when they simultaneously select their outputs?
where P is the price of a cubic yard of concrete and Qd is the number of cubic yards demanded per year. Marginal cost is $80 per cubic yard. Suppose Kate enters the market first and chooses her output before Alice. What is the difference in Alice's profit when Kate enters the market first, compared to when they simultaneously select their outputs?A) $11,106.69
B) $5,000
C) $1106.69
D) -$3893.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



