Deck 3: Technology and Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Technology and Production
1
A firm's _______ shows the amount of output a firm can produce from given amounts of inputs using efficient production methods.
A) Production possibilities set
B) Efficient production frontier
C) Production function
D) Production possibilities curve
A) Production possibilities set
B) Efficient production frontier
C) Production function
D) Production possibilities curve
Production function
2
Suppose that a firm uses both labour (L) and capital (K) as inputs. The firm's long-run production function is Q = F(L,K) = 5?L?K. If the firm has 100 units of capital, what is its short-run production function?
A) Q=F(K)=50?K
B) Q = F(L) = 500?L
C) Q = F(L,K) = 50?L?K
D) Q=F(L)=50?L
A) Q=F(K)=50?K
B) Q = F(L) = 500?L
C) Q = F(L,K) = 50?L?K
D) Q=F(L)=50?L
Q=F(L)=50?L
3
Which of the following is the formula for the average product of labour?
A) F(L) - F(L - ?L)
B) F(L)/L
C) F(L)/?L
D) (F(L) - F(L - ?L))/?L
A) F(L) - F(L - ?L)
B) F(L)/L
C) F(L)/?L
D) (F(L) - F(L - ?L))/?L
F(L)/L
4
When labour inputs are finely divisible, the average product of labour curve is ______ sloping at L if the marginal product is ______ the average product.
A) Downward; above
B) Upward; above
C) Upward; below
D) Vertical; equal to
A) Downward; above
B) Upward; above
C) Upward; below
D) Vertical; equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is NOT a property of isoquants?
A) Isoquants curves are thin
B) Isoquants may slope upward or downward
C) Isoquants for the same technology never cross
D) Higher-level isoquants lie farther from the origin
A) Isoquants curves are thin
B) Isoquants may slope upward or downward
C) Isoquants for the same technology never cross
D) Higher-level isoquants lie farther from the origin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that the marginal product of a firm's labour is 10 units of output per hour. Also assume that the marginal product of the firm's capital is 30 units of output per hour. In this case, the marginal rate of technical substitution for labour with capital is
A) 3
B) 300
C) 40
D) 1/3
A) 3
B) 300
C) 40
D) 1/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
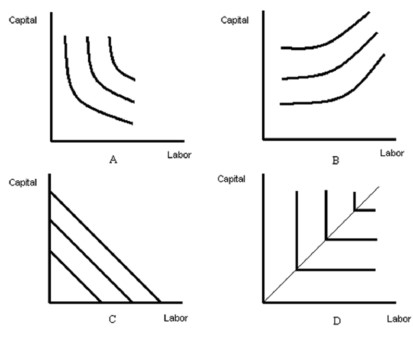
-Refer to Figure above. Which diagram represents isoquants for fixed-proportions technology?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Two inputs ______ when they must be combined in a fixed ratio.
A) Are perfect substitutes
B) Are perfect complements
C) Represent Cobb-Douglas technology
D) Are fixed inputs
A) Are perfect substitutes
B) Are perfect complements
C) Represent Cobb-Douglas technology
D) Are fixed inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
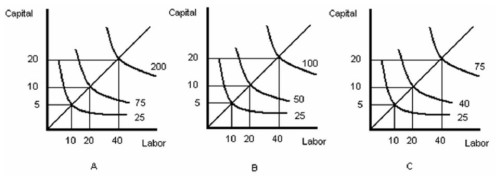
-Refer to Figure above. Which graph represents decreasing returns to scale?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Both graph A and graph C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements regarding comparisons of productivity across two firms is true?
A) The firm with the higher APL is the more productive firm
B) The firm with the higher MPL is the more productive firm
C) The firm with the lower MPL is the more productive firm
D) The average product of labour can vary with the choice of inputs and the level of outputs, so the firm with the higher APL may not be the most productive
A) The firm with the higher APL is the more productive firm
B) The firm with the higher MPL is the more productive firm
C) The firm with the lower MPL is the more productive firm
D) The average product of labour can vary with the choice of inputs and the level of outputs, so the firm with the higher APL may not be the most productive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The productivity changes resulting from research and development would be best represented by
A) An upward shift of a firm's production function
B) A downward shift of a firm's production function
C) The firm's isoquants shifting away from the origin
D) A movement to the northeast along the firm's production function
A) An upward shift of a firm's production function
B) A downward shift of a firm's production function
C) The firm's isoquants shifting away from the origin
D) A movement to the northeast along the firm's production function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose a firm uses both labour (L) and capital (K) and its long-run production function is given by the expression Q = F(L,K) = L2√(L + 2K). The firm currently uses 100 units of capital. Assuming labour is finely divisible, graph the firm's short-run production function for the first five workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose a firm uses both labour (L) and capital (K) and its long-run production function is given by the expression Q = F(L,K) = 2L√(L + K). The firm currently uses 10 units of capital. Complete the following table: 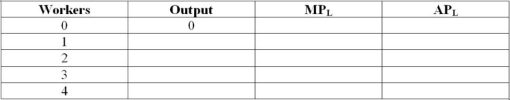


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



