Deck 2: From Demand to Welfare, Constraints, Choices, and Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: From Demand to Welfare, Constraints, Choices, and Demand
1
Which of the following does NOT occur when the price of a good increases?
A) The good becomes more expensive relative to all other goods
B) The consumer's purchasing power increases
C) Consumers shift their purchases away from the more expensive good
D) The consumer is effectively poorer than before the increase in price
A) The good becomes more expensive relative to all other goods
B) The consumer's purchasing power increases
C) Consumers shift their purchases away from the more expensive good
D) The consumer is effectively poorer than before the increase in price
The consumer's purchasing power increases
2
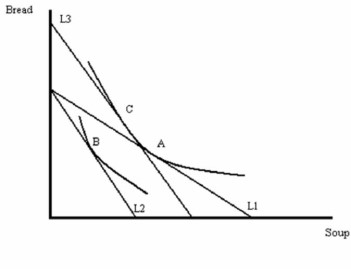
-Refer to Figure above. The substitution effect is shown by the movement
A) From bundle A to bundle C
B) From bundle A to bundle B
C) From bundle B to bundle C
D) From bundle C to bundle B
From bundle A to bundle C
3

-Refer to Figure above. The income effect is shown by the movement
A) From bundle A to bundle C
B) From bundle A to bundle B
C) From bundle B to bundle C
D) From bundle C to bundle B
From bundle C to bundle B
4
The effect of a compensated price change is known as:
A) The price effect of a price change
B) The income effect of a price change
C) The substitution effect of a price change
D) The replacement effect of a price change
A) The price effect of a price change
B) The income effect of a price change
C) The substitution effect of a price change
D) The replacement effect of a price change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following does NOT describe a compensating variation?
A) The amount of money that exactly compensates a consumer for a change in economic circumstances
B) The amount of money that produces an equivalent effect on a consumer's well-being
C) The most some one (someone) is willing to pay to experience something beneficial
D) The least someone is willing to pay to experience something harmful
A) The amount of money that exactly compensates a consumer for a change in economic circumstances
B) The amount of money that produces an equivalent effect on a consumer's well-being
C) The most some one (someone) is willing to pay to experience something beneficial
D) The least someone is willing to pay to experience something harmful

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
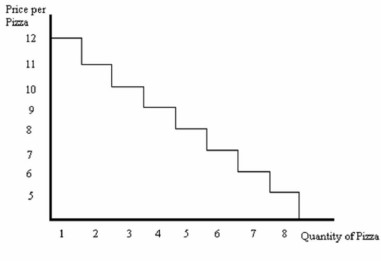
-Refer to Figure above. Suppose the price of pizza is $8.50. Then the consumer will purchase _____ pizzas and the net benefit is ______.
A) 5; $9.50
B) 4; $8.00
C) 5; $3.50
D) 4; $9.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

-Refer to Figure above. Suppose the price of pizza is $9.75. Then consumer surplus is ______.
A) $3.75
B) $3.50
C) $29.25
D) $33.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
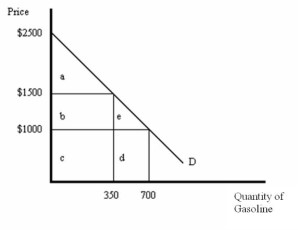
-Refer to Figure above. If the price is $1,500, then consumer surplus is equal to
A) $175,000
B) $535,000
C) $1,000
D) $262,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose a consumer's nominal income is $50,000 and the cost-of-living index is 1.3. The consumer's real income is
A) $50,000
B) $65,000
C) $53,000
D) $38, 462
A) $50,000
B) $65,000
C) $53,000
D) $38, 462

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For low wages, the leisure demand curve slopes ______; for higher wages it slopes ______.
A) Upward; downward
B) Downward; upward
C) Downward; downward
D) Upward; upward
A) Upward; downward
B) Downward; upward
C) Downward; downward
D) Upward; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A consumer's budget constraint is determined by
A) The consumer's income
B) The consumer's income and preferences
C) The consumer's income and the prices of the goods they buy
D) The consumer's preferences and the prices of the goods they buy
A) The consumer's income
B) The consumer's income and preferences
C) The consumer's income and the prices of the goods they buy
D) The consumer's preferences and the prices of the goods they buy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
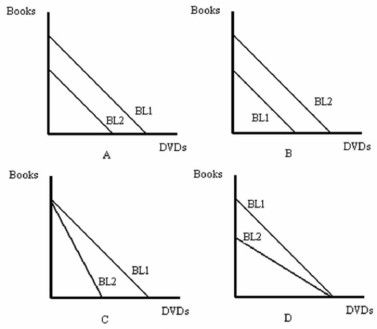
-Refer to Figure above. Which graph represents an increase in the consumer's income?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Whenever a consumer purchases good X but not good Y, then
A) MRSXY >= PX/PY at the chosen bundle
B) MRSXY <= PX/PY at the chosen bundle
C) MRSXY = PX/PY at the chosen bundle
D) MRSXY = -PX/PY at the chosen bundle
A) MRSXY >= PX/PY at the chosen bundle
B) MRSXY <= PX/PY at the chosen bundle
C) MRSXY = PX/PY at the chosen bundle
D) MRSXY = -PX/PY at the chosen bundle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Stewie spends all of his income on movie rentals (R) and noodles (N). His marginal rate of substitution for rentals with noodles is given by MRSRN = 20/√ R. Suppose that movies rent for $2 and noodles cost $1. Plot his income-consumption curve, his Engle curve for movie rentals and his Engel curve for noodles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



