Deck 5: Profit Planning and Decision-Making
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/186
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Profit Planning and Decision-Making
1
Which of the following is a fixed cost?
A) packing materials
B) insurance
C) direct labour
D) sales commission
A) packing materials
B) insurance
C) direct labour
D) sales commission
insurance
2
Which of the following is a variable cost?
A) finance costs
B) professional fees
C) depreciation
D) overtime
A) finance costs
B) professional fees
C) depreciation
D) overtime
overtime
3
How is the contribution margin calculated?
A) by subtracting fixed costs from revenue
B) by subtracting cost of sales from revenue
C) by subtracting variable costs from revenue
D) by subtracting operating income from revenue
A) by subtracting fixed costs from revenue
B) by subtracting cost of sales from revenue
C) by subtracting variable costs from revenue
D) by subtracting operating income from revenue
by subtracting variable costs from revenue
4
How is the PV ratio calculated?
A) by dividing the contribution margin by revenue
B) by dividing revenue by the contribution margin
C) by multiplying the contribution margin by the unit revenue
D) by multiplying revenue by the unit contribution margin
A) by dividing the contribution margin by revenue
B) by dividing revenue by the contribution margin
C) by multiplying the contribution margin by the unit revenue
D) by multiplying revenue by the unit contribution margin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When is the break-even point reached?
A) when revenue covers all fixed costs
B) when revenue covers all costs
C) when revenue covers fixed costs in excess of variable costs
D) when revenue covers all variable costs
A) when revenue covers all fixed costs
B) when revenue covers all costs
C) when revenue covers fixed costs in excess of variable costs
D) when revenue covers all variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the PV ratio divided into to calculate the revenue break-even point?
A) fixed costs
B) all operating costs
C) revenue
D) variable costs
A) fixed costs
B) all operating costs
C) revenue
D) variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is a non-cash expense?
A) prepaid expenses
B) electricity
C) fixed costs
D) depreciation
A) prepaid expenses
B) electricity
C) fixed costs
D) depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the unit contribution margin divided into to calculate the profit break-even point?
A) fixed costs
B) profit plus fixed costs
C) profit
D) profit plus variable costs
A) fixed costs
B) profit plus fixed costs
C) profit
D) profit plus variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A company wants to invest more money in its advertising budget. What is added to the additional advertising expense to calculate the new break-even point?
A) the existing fixed costs
B) the existing total costs
C) the existing variable costs
D) the existing profit objective
A) the existing fixed costs
B) the existing total costs
C) the existing variable costs
D) the existing profit objective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What are committed fixed costs?
A) costs that should be increased to generate more volume
B) costs that should be eliminated if a company experiences a loss
C) costs that can be changed with the volume of production
D) costs that CANNOT be controlled
A) costs that should be increased to generate more volume
B) costs that should be eliminated if a company experiences a loss
C) costs that can be changed with the volume of production
D) costs that CANNOT be controlled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the break-even calculation based on?
A) the profit before tax
B) the operating margin
C) the profit for the year before depreciation
D) the gross profit
A) the profit before tax
B) the operating margin
C) the profit for the year before depreciation
D) the gross profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What tool is used to analyze the relationships among volume, price, product mix, and product costs?
A) vertical analysis
B) horizontal analysis
C) cost of sales analysis
D) cost-volume-profit analysis
A) vertical analysis
B) horizontal analysis
C) cost of sales analysis
D) cost-volume-profit analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a semi-variable cost?
A) purchases
B) freight in
C) rent
D) electricity
A) purchases
B) freight in
C) rent
D) electricity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What variables are used to calculate the break-even point?
A) contribution margin, revenue, and fixed costs
B) revenue, fixed costs, and variable costs
C) revenue, variable costs, and gross profit
D) contribution margin, revenue, and variable costs
A) contribution margin, revenue, and fixed costs
B) revenue, fixed costs, and variable costs
C) revenue, variable costs, and gross profit
D) contribution margin, revenue, and variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What does PV ratio stand for?
A) profit-value ratio
B) performance-value ratio
C) profit-volume ratio
D) price-volume ratio
A) profit-value ratio
B) performance-value ratio
C) profit-volume ratio
D) price-volume ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does the relevant range refer to?
A) all costs that apply to a certain level of production
B) fixed costs that apply to a certain level of production
C) revenue that applies to a certain level of production
D) variable costs that apply to a certain level of production
A) all costs that apply to a certain level of production
B) fixed costs that apply to a certain level of production
C) revenue that applies to a certain level of production
D) variable costs that apply to a certain level of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are relevant costs?
A) variable cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
B) revenue alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
C) all cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
D) fixed cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
A) variable cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
B) revenue alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
C) all cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business
D) fixed cost alternatives that managers can choose from to operate a business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the break-even point formula?
A) SP×N=FC+VC×N
B) FC+VC=SP-N
C) N×FC=R
D) SP×FC=N×VC
A) SP×N=FC+VC×N
B) FC+VC=SP-N
C) N×FC=R
D) SP×FC=N×VC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When is the profit break-even point achieved?
A) when the revenue covers variable costs and the profit objective
B) when the revenue covers fixed costs and the profit objective
C) when the contribution margin covers fixed costs and the profit objective
D) when the contribution margin covers all costs and the profit objective
A) when the revenue covers variable costs and the profit objective
B) when the revenue covers fixed costs and the profit objective
C) when the contribution margin covers fixed costs and the profit objective
D) when the contribution margin covers all costs and the profit objective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What does the break-even wedge help managers to determine?
A) the most appropriate way of structuring revenue and variable costs
B) the most appropriate way of structuring revenue and fixed costs
C) the most appropriate way of structuring the contribution margin to achieve higher profit
D) the most appropriate way of structuring all fixed and variable costs
A) the most appropriate way of structuring revenue and variable costs
B) the most appropriate way of structuring revenue and fixed costs
C) the most appropriate way of structuring the contribution margin to achieve higher profit
D) the most appropriate way of structuring all fixed and variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What decisions are supported by break-even point analysis?
A) advertising effectiveness decisions
B) bookkeeping decisions
C) cost accounting decisions
D) pricing decisions
A) advertising effectiveness decisions
B) bookkeeping decisions
C) cost accounting decisions
D) pricing decisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Within the framework of the break-even point analysis, what do profit decisions help a company to achieve?
A) a certain level of profit before taxes
B) a certain level of gross profit
C) a certain level of operating profit
D) a certain level of contribution margin
A) a certain level of profit before taxes
B) a certain level of gross profit
C) a certain level of operating profit
D) a certain level of contribution margin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What costs remain constant at varying levels of production?
A) mixed costs
B) period costs
C) direct costs
D) variable costs
A) mixed costs
B) period costs
C) direct costs
D) variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What costs fluctuate directly with changes in volume of production?
A) period costs
B) product costs
C) out-of-pocket costs
D) sunk costs
A) period costs
B) product costs
C) out-of-pocket costs
D) sunk costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What costs change disproportionately with changes in output levels?
A) fixed costs
B) semi-variable costs
C) variable costs
D) output costs
A) fixed costs
B) semi-variable costs
C) variable costs
D) output costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A business can produce 1,000 units at a zero cost per unit with a total cost of $100,000. Production increases to 2,000 units at a zero cost per unit with a total cost of $100,000. What type of cost is the $100,000?
A) a semi-variable cost
B) a committed cost
C) a fixed cost
D) a variable cost
A) a semi-variable cost
B) a committed cost
C) a fixed cost
D) a variable cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Sales are at 2,000 units at a cost of $20,000, then increase to 4,000 units at a cost of $40,000, and finally reach 6,000 units at a cost of $60,000. What are these costs called?
A) committed costs
B) variable costs
C) semi-variable costs
D) fixed costs
A) committed costs
B) variable costs
C) semi-variable costs
D) fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A company sells 10,000 units at a cost of $10 per unit for a total of $200,000 in costs. The same company sells 20,000 units at the same cost of $10 per unit for a total of $300,000 in costs. What are these costs called?
A) total semi-variable costs
B) total fixed costs
C) total variable costs
D) total costs
A) total semi-variable costs
B) total fixed costs
C) total variable costs
D) total costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What costs are associated with fixed costs but are NOT related to inventory, such as distribution costs and administrative expenses?
A) calendar costs
B) non-inventory costs
C) accounting costs
D) period costs
A) calendar costs
B) non-inventory costs
C) accounting costs
D) period costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a period cost?
A) office salaries
B) direct labour
C) raw materials
D) purchases
A) office salaries
B) direct labour
C) raw materials
D) purchases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of following is an out-of-pocket cost for a retail store?
A) purchases
B) advertising
C) office salaries
D) depreciation
A) purchases
B) advertising
C) office salaries
D) depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Where does the break-even point occur on a break-even chart?
A) where the revenue line intersects the total fixed cost line
B) where the revenue line intersects the total cost line
C) where the revenue line intersects the total variable cost line
D) where the revenue line intersects the total semi-variable cost line
A) where the revenue line intersects the total fixed cost line
B) where the revenue line intersects the total cost line
C) where the revenue line intersects the total variable cost line
D) where the revenue line intersects the total semi-variable cost line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is divided by the contribution margin to calculate the revenue break-even point?
A) sales revenue
B) variable costs
C) total costs
D) fixed costs
A) sales revenue
B) variable costs
C) total costs
D) fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Given the following information, what is the contribution margin? Fixed costs $200 Sales revenue $1,000 Variable costs $750
A) $50
B) $250
C) $800
D) $1,950
A) $50
B) $250
C) $800
D) $1,950

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What formula is used to calculate the PV ratio?
A) revenue ÷ contribution margin
B) revenue × contribution margin
C) contribution margin ÷ revenue
D) revenue - contribution margin
A) revenue ÷ contribution margin
B) revenue × contribution margin
C) contribution margin ÷ revenue
D) revenue - contribution margin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given the following information, what is the PV ratio? 
A) 0.05
B) 0.25
C) 0.75
D) 25

A) 0.05
B) 0.25
C) 0.75
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the effect when a company decides to increase the unit selling price of its product, while keeping variable cost per unit, units sold, and fixed costs unchanged?
A) Total variable costs decrease.
B) Fixed costs increase.
C) Profit before tax increases.
D) Total variable costs increase.
A) Total variable costs decrease.
B) Fixed costs increase.
C) Profit before tax increases.
D) Total variable costs increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the effect when a company sells more units strictly on the basis of "image" improvement, and its variable costs per unit, selling price per unit, and fixed costs remain unchanged?
A) Profit for the year remains the same.
B) Revenue increases.
C) Variable costs decrease.
D) Fixed costs increase.
A) Profit for the year remains the same.
B) Revenue increases.
C) Variable costs decrease.
D) Fixed costs increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the effect when a company decreases its fixed costs while its variable cost per unit, units sold, and selling price per unit remain unchanged?
A) Fixed costs increase.
B) Variable costs increase.
C) Profit before tax increases.
D) Revenue decreases.
A) Fixed costs increase.
B) Variable costs increase.
C) Profit before tax increases.
D) Revenue decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A supplier has just informed a company about an increase in the cost per unit, although the number of units sold, the unit selling price, and the fixed costs remain unchanged. What will be the effect of these changes?
A) Profit before tax will decrease.
B) Contribution margin will increase.
C) Revenue will increase.
D) Fixed costs will decrease.
A) Profit before tax will decrease.
B) Contribution margin will increase.
C) Revenue will increase.
D) Fixed costs will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What does the following formula calculate? 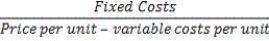
A) the unit break-even point
B) the profit break-even point
C) the contribution margin ratio
D) the revenue break-even point
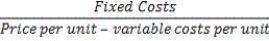
A) the unit break-even point
B) the profit break-even point
C) the contribution margin ratio
D) the revenue break-even point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What does the following formula calculate? 
A) the revenue break-even point
B) the profit break-even point
C) the contribution margin ratio
D) the unit break-even point

A) the revenue break-even point
B) the profit break-even point
C) the contribution margin ratio
D) the unit break-even point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Given the following information, what is the revenue break-even point? 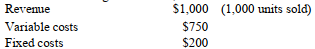
A) $ 250
B) $ 800
C) $ 1,000
D) $ 2,666
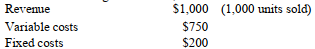
A) $ 250
B) $ 800
C) $ 1,000
D) $ 2,666

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Given the following information, what is the unit break-even point? 
A) 500 units
B) 800 units
C) 1,000 units
D) 2,000 units

A) 500 units
B) 800 units
C) 1,000 units
D) 2,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A company's break-even point is 5,000 units, and the president sets a profit objective. What will the company need to do to realize the objective?
A) increase its fixed costs
B) sell exactly 5,000 units
C) sell more than 5,000 units
D) sell less than 5,000 units
A) increase its fixed costs
B) sell exactly 5,000 units
C) sell more than 5,000 units
D) sell less than 5,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An entrepreneur is absolutely certain his new company will sell 10,000 units. He has already determined the break-even point is 3,000 units. Should he launch the company, and why or why not?
A) Do NOT start the company because the risk is too high.
B) Launch the company because the risk of NOT reaching the break-even point is high.
C) Launch the company because there is little risk since the break-even point is well below expected sales.
D) Do NOT start the company because according to the calculation, the break-even point will not be reached.
A) Do NOT start the company because the risk is too high.
B) Launch the company because the risk of NOT reaching the break-even point is high.
C) Launch the company because there is little risk since the break-even point is well below expected sales.
D) Do NOT start the company because according to the calculation, the break-even point will not be reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Product A has a contribution margin of $100 while product B has a contribution margin of $50., Which product should the company concentrate on selling, and why?
A) Changing the sales mix will not affect the profit level.
B) The company should concentrate on selling product B because it has a lower CM and will produce higher profit.
C) The company should concentrate on selling product A because it has a lower CM and will produce higher profit.
D) The company should concentrate on selling product A because it has a higher CM and will produce higher profit.
A) Changing the sales mix will not affect the profit level.
B) The company should concentrate on selling product B because it has a lower CM and will produce higher profit.
C) The company should concentrate on selling product A because it has a lower CM and will produce higher profit.
D) The company should concentrate on selling product A because it has a higher CM and will produce higher profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following are variable costs?
A) general expenses
B) direct labour
C) administrative expenses
D) depreciation
A) general expenses
B) direct labour
C) administrative expenses
D) depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following are period costs?
A) general expenses
B) purchases
C) contribution margin
D) electricity
A) general expenses
B) purchases
C) contribution margin
D) electricity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given the following information, what is the contribution margin? 
A) $50,000
B) $200,000
C) $250,000
D) $750,000

A) $50,000
B) $200,000
C) $250,000
D) $750,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the contribution margin?
A) the difference between revenue and fixed costs
B) the sum of revenue and variable costs
C) the revenue minus variable and direct costs
D) the difference between revenue and variable costs
A) the difference between revenue and fixed costs
B) the sum of revenue and variable costs
C) the revenue minus variable and direct costs
D) the difference between revenue and variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Given the following information, what is the PV ratio?

A) 0.50
B) 2.0
C) 0.50%
D) $20,000

A) 0.50
B) 2.0
C) 0.50%
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given the following information, what is the unit break-even point?

A) 1,000 units
B) 10,500 units
C) 20,000 units
D) 100,000 units

A) 1,000 units
B) 10,500 units
C) 20,000 units
D) 100,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given the following information, what is the revenue break-even point?

A) $ 100,000
B) $ 200,000
C) $ 250,000
D) $ 500,000

A) $ 100,000
B) $ 200,000
C) $ 250,000
D) $ 500,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Given the following information, what is the required number of units that must be sold? 
A) 55 units
B) 200 units
C) 550 units
D) 1,000 units

A) 55 units
B) 200 units
C) 550 units
D) 1,000 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A company wants to make a $10,000 profit by selling 500 units. By how much should the selling price per unit be increased?

A) $5
B) $20
C) $33
D) $50

A) $5
B) $20
C) $33
D) $50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A company wants to make a $10,000 profit by selling 500 units, without changing the selling price. By how much should the fixed costs be reduced?

A) $5,000
B) $10,000
C) $30,000
D) $100,000

A) $5,000
B) $10,000
C) $30,000
D) $100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Given the following information, what are the maximum fixed costs the company should incur if it wants to break even selling the three products? ? 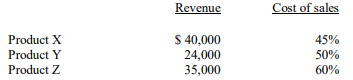
A) $ 48,000
B) $ 55,000
C) $ 58,000
D) $ 60,000
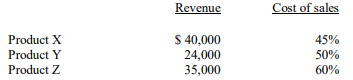
A) $ 48,000
B) $ 55,000
C) $ 58,000
D) $ 60,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is an example of fixed costs?
A) freight in
B) purchases
C) salaries (selling)
D) sales commission
A) freight in
B) purchases
C) salaries (selling)
D) sales commission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an example of variable costs?
A) office salaries
B) property taxes
C) purchases
D) telephone
A) office salaries
B) property taxes
C) purchases
D) telephone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A company provides the information below. If the company increases its selling price by 5% and increases its fixed costs by $100,000, how much more (or less) profit will the company realize?

A) Profit will decrease $ 25,000.
B) Profit will increase $ 25,000.
C) Profit will decrease $ 50,000.
D) Profit will increase $ 50,000.

A) Profit will decrease $ 25,000.
B) Profit will increase $ 25,000.
C) Profit will decrease $ 50,000.
D) Profit will increase $ 50,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A company provides the information below. If the company increases its advertising budget by $30,000, how much more revenue will need to be realized to maintain the same profit level?

A) $ 14,443
B) $ 20,833
C) $ 43,333
D) $ 93,750

A) $ 14,443
B) $ 20,833
C) $ 43,333
D) $ 93,750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A company provides the information below. If the company hires a new sales representative at an estimated cost of $60,000, what is the company's new revenue break-even point?

A) $ 2,187,500
B) $ 2,375,000
C) $ 2,575,000
D) $ 2,675,000

A) $ 2,187,500
B) $ 2,375,000
C) $ 2,575,000
D) $ 2,675,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Given the following information, what is the company's cash break-even point?
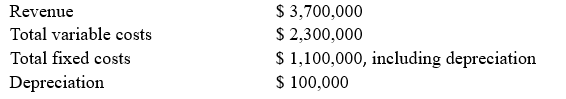
A) $ 1,500,553
B) $ 1,642,553
C) $ 2,220,245
D) $ 2,642,857
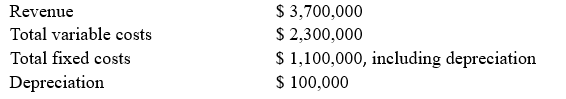
A) $ 1,500,553
B) $ 1,642,553
C) $ 2,220,245
D) $ 2,642,857

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Break-even analysis is a straightforward and very powerful financial analytical technique than can help managers make a wide range of important decisions related to cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Break-even analysis can help managers improve their decisions related to pricing and modernization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Pricing and automation decisions can be made more clearly with break-even analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Break-even analysis is an effective decision-making tool for market share analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Fixed costs remain constant at varying levels of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Costs that fluctuate directly with changes in volume of production are called semi-variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Cost of sales is considered a variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Packing materials is considered is a semi-variable cost because this type of cost varies almost automatically with volume of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Finance costs on a mortgage are considered fixed costs because they vary directly with sales volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The factors that affect profit levels are: market share, price | earnings ratio, fixed costs and variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Changes in product mix can have an impact on the level of the break-even point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Break-even point takes place when revenue equals fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When total costs meet revenue, it is the point where break-even is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
You can calculate the PV ratio by dividing the contribution margin by variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The higher the PV ratio the better it is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Changes in variables costs can alter the PV ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



